Abstract
Background
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a myeloid neoplasm classified in the myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm (MDS/MPN) category. Molecular abnormalities are reported in about 90 % of patients with CMML. ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations, but not TET2 or SFRS2 mutations are reported to be associated with prognosis.
Methods
We studied frequency of TET2, SRSF2, ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations in 145 patients with CMML using Sanger sequencing, and determined the prognostic factors for OS. We also identified the predictive value of ASXL1 mutations (frameshift and nonsense mutations) through comparing the Mayo Prognostic Model with the Mayo Molecular Model.
Results
Forty-seven (32 %) had a mutation in TET2, 42 (29 %), a mutation in SRSF2, 65 (45 %), a mutation (nonsense and frame-shift) in ASXL1 and 26 (18 %), a mutation in SETBP1. Significant variables in multivariable analysis of survival included ASXL1 (HR = 1.99 [1.20–3.28]; P = 0.007), hemoglobin <100 g/L (HR = 2.42 [1.40–4.19]; P = 0.002) and blood immature myeloid cells (IMCs) (HR = 2.08 [1.25–3.46]; P = 0.005). When our patients were analyzed using the Mayo Prognostic Model median OS were not reached, 26 months and 15 months (P = 0.014). An analysis using the Mayo Molecular Model identified 4 cohorts with median OS of not reached, 70 months, 26 months and 11 months (P < 0.001). Data fitting using our patients suggest the Molecular Mayo Model has significantly higher survival predictive power compared with Mayo Prognostic Model (P < 0.001, −2 log-likelihood ratios of 538.070 and 552.260).
Conclusions
There were high frequencies of mutations in TET2, SRSF2, ASXL1 and SETBP1 in patients with CMML. With the addition of ASXL1 frameshift and nonsense mutations, the Mayo Molecular Model fitted better than Mayo Prognostic Model of our patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is in the overlap category of myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasms (MDS/MPN) in the World Health Organization (WHO) classification. CMML is uncommon with an estimated incidence of 0.4/100,000 patients/year. In the WHO classification it is defined as persistent blood monocytes >1 × 109/L, no BCR-ABL1 or PDGFRA/B mutation, <20 % myeloblasts or promonocytes in the blood or bone marrow and dysplasia in one or more myeloid lineages [1].
Molecular abnormalities are detected in about 90 % of patients with CMML [2, 3] including TET2 in 50–60 %, SRFS2 in 40–50 %, ASXL1 in 40–50 % and SETBP1 in 5–10 % [2, 4]. ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations, but not TET2 or SFRS2 mutations are reported to be associated with prognosis [4–7].
Several models are used to predict survival of patients with CMML including: (1) the MD Anderson prognostic scoring system (MDAPS) in 213 patients [8]; (2) the CMML-specific prognostic scoring system (CPSS) in a large series of 558 patients [9]; (3) the Mayo Prognostic Model (MPM) in 226 patients [10]; (4) Groupe Francais des Myelodysplasies (GFM) in 312 patients [4]; (5) the Mayo Molecular Model (MMM) [11], and etc. A study from the Mayo Clinic reported no significant association between ASXL1 mutations (missense, nonsense and frameshift) and leukemia free survival (LFS) or overall survival (OS) [10]. In contrast a study of GFM reported a significant association between ASXL1 mutations (nonsense and frameshift) and OS [4]. A second report from the Mayo Clinic and cooperators in 466 patients using the MMM reported a significant association between ASXL1 mutation (nonsense, frameshift) and LFS and OS [11]. We studied the frequency of TET2, SRSF2, ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations in 145 patients with CMML and compared their outcomes with those predicted in the two Mayo Clinic prognostic models.
Results
Patients
Baseline variable are listed in Table 1. Median age was 63 years (range, 18–85 years) and 98 (68 %) were male. Applying the WHO classification 84 (58 %) of patients were identified as CMML-1 and 61 (42 %), as CMML-2. Applying the FAB classification 51 patients (35 %) patients were classified as having CMML-MD and 94 (65 %), CMML-MP. Median WBC was 21.88 × 109/L (range, 3.01–117.57 × 109/L). Median platelets were 78 × 109/L (4–1001 × 109/L). Median hemoglobin concentration was 88.0 g/L (43.0–166.0 g/L). Three patients received a transplant, 13, decitabine and the remainder hydroxyurea and supportive treatment.
Spectrum and correlation of gene mutations
TET2 mutations were detected in 47 (32 %) patients, of them, 22 were frameshift mutations, 6 nonsense mutations and 19 missense mutations. SRSF2 mutations were detected in 42 (29 %) patients including 39 missense and 3 frameshift mutations. 74 patients (51 %) had an ASXL1 mutation including 59 with frameshift mutations (31 with c.1934dupG; p.G646WfsX12), 6 a nonsense mutation and 9 missense and synonymous mutations (the following analysis of ASXL1 mutations only include the frameshift and nonsense mutations due to the prognostic value of only frameshift and nonsense mutations). Missense mutations focused on a hotspot area from D868 to I871 in SETBP1 were detected 26 (18 %) patients. No mutation in these 4 genes was detected in 38 patients (26 %). Mutations in SRSF2 were more frequent in CMML-MP than CMML-MD (38 % vs. 12 %; P = 0.001). Similarly, SETBP1 mutations were more common in patients with CMML-MP compared with patients with CMML-MD (23 % vs. 8 %, P = 0.023, respectively) (Fig. 1a). There were no significant differences in mutation frequencies of these four genes between patients with CMML-1 vs. those with CMML-2 (Fig. 1b). Combinations of mutations according ASXL1 mutational state are shown in Fig. 2. TET2 and SRSF2 mutations were frequently concordant (P = 0.035). Similarly, ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations were frequently concordant (P < 0.001; Table 2).
Mutational spectrum of TET2, SRSF2, ASXL1 and SETBP1 stratified by FAB and WHO subtypes. (a) Mutations in SRSF2 and SETBP1 were more frequent in CMML-MP than CMML-MD. (b) There were no significant differences in mutation frequencies of these four genes between patients with CMML-1 vs. those with CMML-2
Associations between baseline variables and mutations
Associations between baseline variables and mutations are summarized in Table 3. TET2 mutation was associated with older age (P = 0.005) and a greater proportion of patients with <10 % bone marrow blasts (P = 0.008). SRSF2 mutations was also associated with older age (P = 0.000), higher WBC levels (P = 0.027), higher absolute neutrophil levels (P = 0.008), higher blood monocyte levels (P = 0.004) and higher hemoglobin concentration (P < 0.001). There was no significant difference in baseline variables in patients with and without ASXL1 or SETBP1 mutations.
Prognostic impact of mutations
Follow-up data were available for 127 patients (88 %) with a median follow-up interval of 13 months (range, 1–95 months), 18 patients (14 %) transformed to acute leukemia and 71 (56 %) died (including 15 cases died after acute leukemia transformation).
Variables significantly associated with survival in multivariable analysis included ASXL1 (HR = 1.99 [1.20–3.28]; P = 0.007) (Fig. 3), hemoglobin <100 g/L (HR = 2.42 [1.40–4.19]; P = 0.002) and blood immature myeloid cells (IMCs) (HR = 2.08 [1.25–3.46]; P = 0.005) (Table 4).
To clarify the prognostic impact of ASXL1 mutations on survival we evaluated survival of subgroups based on the Mayo Prognostic Model and Molecular Mayo Model. Median survivals using the Mayo Prognostic Model were not reached, 26 months (95 % CI, 19–34 months) and 15 months (95 % CI, 11–19 months) (P = 0.014) (Fig. 4a). Median survivals using the Molecular Mayo Model were not reached, 70 months (95 % CI not available), 26 months (95 % CI, 20–32 months) and 11 months (95 % CI, 7–15 months) (P < 0.001) (Fig. 4b). Data fitting using our patients suggest the Molecular Mayo Model has significantly higher survival predictive power compared with Mayo Prognostic Model (P < 0.001, −2 log-likelihood ratios of 538.070 and 552.260).
Survival data for 127 patients with CMML stratified by the Mayo prognostic model and the Molecular Mayo model. (a) Median survivals using the Mayo Prognostic Model were not reached, 26 months, and 15 months. (b) Median survivals using the Molecular Mayo Model were not reached, 70 months, 26 months and 11 months
Discussion
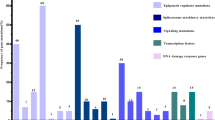
Mutations in patients with CMML typically involve epigenetic regulator genes, spliceosome component pathway genes, genes controlling transcription factors and signaling regulator genes [12, 13]. Itzykson R et al. [3] have recently demonstrated that patients with increased variant allelic frequency of TET2 are more likely to demonstrate granulomonocytic hematopoietic skewing on the basic of early clonal dominance. The diverse combinations of mutations detected in CMML suggest multi-step pathogenesis of the disease in some cases. For example, although TET2 and ASXL1 mutations may be independent drivers of CMML in some patients [3], combined mutations of TET2 and SRSF2 and of ASXL1 with SETBP1 are consistent with a two-step ‘linear’ model of CMML development [14]. The complex and diverse mutation spectrum detected by us and others in patients with CMML suggest complexity from driver mutation to clonal evolution to clonal dominance and finally to the disease. This complex pattern may account for the considerable clinical diversity of CMML.
Recurrent mutations of SETBP1 gene are detected in about 80 % of patients with chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) [15] and in about 25 % of patients with atypical chronic myeloid leukemia [16]. Mutations in SETBP1 decrease PP2A activity resulting in increased proliferation [16, 17]. This increase could explain why patients with SETBP1 mutations in our study were more likely to be in the CMML-MP subtype vs. the CMML-MD subtype.
Patients with SRSF2 mutation were also more likely to be in the CMML-MP. SRSF2 mutation was also associated with increased age and a higher hemoglobin concentration as reported previously [7]. Interestingly, Yoshida K et al. [18] reported splice-gene mutations introduced into normal hematopoietic cells cause a proliferation defect in vitro and a competitive disadvantage in vivo.
ASXL1 regulates epigenetic functions (histone and chromatin modification) and transcription. ASXL1 mutations are detected in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), primary myelofibrosis, CMML and acute myeloid leukemia. Most ASXL1 mutations are frameshift mutations [4, 10]. We also found a predominance of frameshift mutations (31 of c.1934dupG; p.G646WfsX12), 59 vs. only 6 nonsense mutations. There is controversy whether c.1934dupG; p.G646WfsX12 is real or is a PCR artifact [19]. However, recent data indicate patients with c.1934dupG; p.G646WfsX12 have a similar clinical phenotype to patients with other ASXL1 mutations [4, 20]. Based on these data we consider c.1934dupG; p.G646WfsX12 bona fide mutations. In Mayo Clinic study nonsense/frame-shift ASXL1 mutations were associated with worse survival whereas they were not together with missense mutations [10, 11]. We found nonsense/frame-shift ASXL1 mutations were significantly associated with survival in the final Cox model along with hemoglobin concentration <100 g/L and presence of blood IMCs.
There were several prognostic systems for CMML based either on the FAB classification of CMML or using systems designed for other diseases including a cytogenetics-based risk-stratification [21]. Other prognostic models were developed specifically for patients with CMML. For example, the MDAPS model uses data on hemoglobin concentration, blood IMCs, absolute lymphocyte counts (ALC) and percent bone marrow blasts [22] to define risk categories. The G-MDAPS, developed for patients with de novo and secondary MDS, and CMML, uses age, performance score, platelet level, hemoglobin concentration, bone marrow blasts, cytogenetics data and RBC-transfusion state to define risk cohorts [23]. The Mayo Prognostic Model used WBC count, platelet count, hemoglobin concentration, and blood IMCs to define risk cohorts. We tested our survival data against to Mayo Prognostic Model and Mayo Molecular Model to determine the best fit. We found the Mayo Molecular Model, with the addition of ASXL1 mutations (nonsense and frameshift mutations) based on Mayo Prognostic Model, had better predictive power compared with the Mayo Prognostic Model.
Conclusions
In summary, we found a high frequency of mutations in TET2, SRSF2, ASXL1 and SETBP1 in patients with CMML. Often there were several mutations in a person and we found some significant association between mutation spectrum and clinical and laboratory variables. We also found the Mayo Molecular Model best fitted the survival experience of our patients.
Patients and methods
Patients
A hundred and forty five consecutive patients ≥16 years of age diagnosed with CMML at 3 centers in China from January, 2007 to December, 2014 were enrolled. None received prior therapy or exposed to environmental carcinogens. Baseline variables at diagnosis or referral were analyzed and patients classified into CMML-1 or CMML-2 according to the 2008 WHO criteria [1]. Myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative subtypes (CMML-MD and CMML-MP, respectively) were defined according to FAB criteria [24]. The study was approved by the Ethical Committees of the Institute of Hematology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) and Peking Union Medical College (PUMC) following principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and all patients gave written informed consent.
PCR and Sanger sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted using the AxyPrep blood genomic DNA Miniprep kit (Axygen Biosciences, AP-MN-BL-GDNA-250 Union City, CA, USA) from bone marrow cells. Oligonucleotide primers for TET2 (exon 3 to 17), SRSF2 (exon 1, covering amino acid Pro95), ASXL1 (exon 12) and SETBP1 (amino acid 800 to 935) were used described previously [25, 26]. All PCR products were confirmed by 1 % agarose gel, purified using QIAquick Spin Kit (Qiagen, Santa Clarita, CA, USA) and sequenced using two ABI PRISM 3730xl DNA Analyzers (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Sequencing was bi-directional.
Statistical analyses
Numerical variables are presented as medians and ranges. Categorical variables are described as counts and relative frequencies (%). Comparisons between categorical variables were performed using χ 2 tests. Comparisons between continuous variables were performed using the Mann–Whitney U-test. Survival was analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. A Cox model was used to identify the prognostic variables. The above analyses were conducted with SPSS version 17.0. The likelihood ratio test was used to compare the Mayo Prognostic Model [10] and MMM [11] conducted with SAS 9.3. All P-values are two-tailed, and statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Abbreviations
- CMML:
-
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
- MDS/MPN:
-
Myelodysplastic syndrome/ myeloproliferative neoplasms
- MDAPS:
-
MD Anderson prognostic scoring system
- CPSS:
-
CMML-specific prognostic scoring system
- MPM:
-
Mayo prognostic mode
- GFM model:
-
Groupe Francais des myelodysplasies model
- MMM:
-
Mayo molecular model
- LFS:
-
Leukemia free survival
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- WBC:
-
White blood cell count
- ANC:
-
Absolute neutrophil count
- AMC:
-
Absolute monocyte count
- SRSF2:
-
Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 2. ASXL1, additional sex combs 1 gene
- SETBP1:
-
SET binding protein 1
- Hb:
-
Hemoglobin
- PLT:
-
Platelet count
- IMCs:
-
Blood immature myeloid cells
References
Swederlow S, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC: Lyon; 2008.
Patnaik MM, Parikh SA, Hanson CA, Tefferi A. Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a concise clinical and pathophysiological review. Br J Hematol. 2014;165:273–86.
Itzykson R, Kosmider O, Renneville A, Morabito M, Preudhomme C, Berthon C, et al. Clonal architecture of chronic myelomonocytic leukemias. Blood. 2013;121:2186–98.
Itzykson R, Kosmider O, Renneville A, Gelsi-Boyer V, Meggendorfer M, Morabito M, et al. Prognostic score including gene mutations in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2428–36.
Gelsi-Boyer V, Trouplin V, Adelaide J, Bonansea J, Cervera N, Carbuccia N, et al. Mutations of polycomb-associated gene ASXL1 in myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Br J Hematol. 2009;145:788–800.
Laborde RR, Patnaik MM, Lasho TL, Finke CM, Hanson CA, Knudson RA, et al. SETBP1 mutations in 415 patients with primary myelofibrosis or chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: independent prognostic impact in CMML. Leukemia. 2013;27:2100–2.
Meggendorfer M, Roller A, Haferlach T, Eder C, Dicker F, Grossmann V, et al. SRSF2 mutations in 275 cases with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). Blood. 2012;120:3080–8.
Onida F, Kantarjian HM, Smith TL, Ball G, Keating MJ, Estey EH, et al. Prognostic factors and scoring systems in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a retrospective analysis of 213 patients. Blood. 2002;99:840–9.
Such E, Germing U, Malcovati L, Cervera J, Kuendgen A, Della PM, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic scoring system for patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Blood. 2013;121:3005–15.
Patnaik MM, Padron E, LaBorde RR, Lasho TL, Finke CM, Hanson CA, et al. Mayo prognostic model for WHO-defined chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: ASXL1 and spliceosome component mutations and outcomes. Leukemia. 2013;27:1504–10.
Patnaik MM, Itzykson R, Lasho TL, Kosmider O, Finke CM, Hanson CA, et al. ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations and their prognostic contribution in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a two-center study of 466 patients. Leukemia. 2014;28:2206–12.
Savona MR, Malcovati L, Komrokji R, Tiu RV, Mughal TI, Orazi A, et al. An international consortium proposal of uniform response criteria for myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms (MDS/MPN) in adults. Blood. 2015;125:1857–65.
Li B, Gale RP, Xiao Z. Molecular genetics of chronic neutrophilic leukemia, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:93.
Itzykson R, Solary E. An evolutionary perspective on chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2013;27:1441–50.
Cui Y, Li B, Gale RP, Jiang Q, Xu Z, Qin T, et al. CSF3R, SETBP1 and CALR mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:77.
Piazza R, Valletta S, Winkelmann N, Redaelli S, Spinelli R, Pirola A, et al. Recurrent SETBP1 mutations in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2013;45:18–24.
Minakuchi M, Kakazu N, Gorrin-Rivas MJ, Abe T, Copeland TD, Ueda K, et al. Identification and characterization of SEB, a novel protein that binds to the acute undifferentiated leukemia-associated protein SET. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:1340–51.
Yoshida K, Sanada M, Shiraishi Y, Nowak D, Nagata Y, Yamamoto R, et al. Frequent pathway mutations of splicing machinery in myelodysplasia. Nature. 2011;478:64–9.
Abdel-Wahab O, Kilpivaara O, Patel J, Busque L, Levine RL. The most commonly reported variant in ASXL1 (c.1934dupG;p.Gly646TrpfsX12) is not a somatic alteration. Leukemia. 2010;24:1656–7.
Gelsi-Boyer V, Brecqueville M, Devillier R, Murati A, Mozziconacci MJ, Birnbaum D. Mutations in ASXL1 are associated with poor prognosis across the spectrum of malignant myeloid diseases. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:12.
Such E, Cervera J, Costa D, Sole F, Vallespi T, Luno E, et al. Cytogenetic risk stratification in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Hematologica. 2011;96:375–83.
Abdel-Wahab O, Pardanani A, Patel J, Wadleigh M, Lasho T, Heguy A, et al. Concomitant analysis of EZH2 and ASXL1 mutations in myelofibrosis, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and blast-phase myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia. 2011;25:1200–2.
Kantarjian H, O'Brien S, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Shan J, Bennett JM, et al. Proposal for a new risk model in myelodysplastic syndrome that accounts for events not considered in the original International Prognostic Scoring System. Cancer. 2008;113:1351–61.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Hematol. 1982;51:189–99.
Wang J, Ai X, Gale RP, Xu Z, Qin T, Fang L, et al. TET2, ASXL1 and EZH2 mutations in Chinese with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 2013;37:305–11.
Meggendorfer M, Haferlach T, Alpermann T, Jeromin S, Haferlach C, Kern W, et al. Specific molecular mutation patterns delineate chronic neutrophilic leukemia, atypical chronic myeloid leukemia, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Hematologica. 2014;99:e244–6.
Acknowledgments
Contract grant sponsor: National Natural Science Funds; Contract grant numbers: 81470297, 81270585, 81370611, 81470295.
Contract grant sponsor: Tianjin Key Natural Science Funds; Contract grant number: 12JCZDJC23900.
Contract grant sponsor: National Public Health Grand Research Foundation; Contract grant number: 201202017.
Contract grant sponsor: SRFDP; Contract grant number: 20121106130005.
Contract grant sponsor: NIHR Biomedical Research Center fund.
Contract grant sponsor: National Key Technology R&D Program; Contract grant number: 2014BAI09B13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
Robert Peter Gale is a part-time employee of Celgene Corp., Summit, NJ. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Authors’ contributions
ZJX, conception, design, analysis, and drafting of the manuscript; YJC, data acquisition, analysis, interpretation, and drafting of the manuscript; HYT, XD, BL, TJQ, JQL, ZFX, YZ, GH, JJ, LWF, HLZ, LJP, NBH, SQQ, data acquisition; RPG, drafting of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Yajuan Cui, Hongyan Tong and Xin Du contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Y., Tong, H., Du, X. et al. Impact of TET2, SRSF2, ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations on survival of patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Exp Hematol Oncol 4, 14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40164-015-0009-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40164-015-0009-y