Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive cognitive decline, accompanied by amyloid-β (Aβ) overload and hyperphosphorylated tau accumulation in the brain. Synaptic dysfunction, an important pathological hallmark in AD, is recognized as the main cause of the cognitive impairments. Accumulating evidence suggests that synaptic dysfunction could be an early pathological event in AD. Pathological tau, which is detached from axonal microtubules and mislocalized into pre- and postsynaptic neuronal compartments, is suggested to induce synaptic dysfunction in several ways, including reducing mobility and release of presynaptic vesicles, decreasing glutamatergic receptors, impairing the maturation of dendritic spines at postsynaptic terminals, disrupting mitochondrial transport and function in synapses, and promoting the phagocytosis of synapses by microglia. Here, we review the current understanding of how pathological tau mediates synaptic dysfunction and contributes to cognitive decline in AD. We propose that elucidating the mechanism by which pathological tau impairs synaptic function is essential for exploring novel therapeutic strategies for AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder, which potentially affects 50 million individuals worldwide and represents 60%–80% of dementia cases [1]. The pathological hallmarks of AD include extracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in the brain, as well as loss of neurons and synapses, resulting in cognitive impairment and eventually dementia [2]. The pathophysiology of AD follows a stereotypical spatiotemporal pattern: Aβ plaques first appear in the frontal lobes, even before any clinical symptoms, followed by the appearance of NFTs in the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus, triggering a series of toxic events and ultimately leading to cognitive decline [3]. It is becoming clear that synaptic loss and synaptic dysfunction are two key components of the neurodegenerative process of AD, especially in early AD [4,5,6]. Although Aβ plaques precede NFTs in patients with AD, epidemiological studies suggest that the regional distribution of NFTs is highly correlated with the severity of cognitive deficits [2, 7]. As the main component of NFTs, tau is a microtubule-associated protein that has been identified as a key molecule in AD and a series of neurodegenerative diseases collectively referred to as tauopathies [8]. The pathogenic role of tau in neurodegenerative disease has been confirmed by the identification of MAPT mutations and polymorphisms in patients with frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism-17 [9].
Synaptic dysfunction is considered to be an early pathological manifestation and key component of the neurodegenerative process of AD. Epidemiological studies have shown that synaptic loss is closely correlated with cognitive decline in patients with AD, suggesting that synaptic integrity plays a causal role in the etiology of AD [2, 10]. Importantly, studies in mouse models support that the accumulation of pathological tau triggers synaptic loss and deregulation without widespread neuron loss [11, 12]. In addition, growing evidence suggests that soluble forms of tau species, especially oligomers, rather than NFTs, are toxic to synapses [13,14,15].
Tau is predominantly present in the axonal compartments of neurons and its main function is to regulate microtubule assembly and stabilization, and axonal transport [13]. Some studies have shown that tau can also be detected in the dendrites and the pre- and postsynaptic terminals of normal healthy neurons, and participates in important physiological functions related to synapses [14, 16, 17]. Under pathological conditions, mutations or post-translational modifications of tau are able to lower its affinity to microtubules [13], leading to its detachment from axonal microtubules, and subsequent aberrant aggregation, missorting to subcellular compartments, and propagation to other brain regions [5, 14]. Pathological tau is produced from aberrant post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination and truncation, leading to conformational changes, aggregation, NFT formation and synaptic dysfunction in AD [18]. The pathological tau induces synaptic dysfunction in several ways, including reducing the mobility and release of presynaptic vesicles, decreasing glutamatergic receptors, impairing the maturation of dendritic spines at postsynaptic terminals, disrupting mitochondrial transport and function in synapses, and promoting the phagocytosis of synapses by microglia. Reducing endogenous pathological tau can protect against excitotoxicity and neuronal dysfunction, and ameliorate cognitive deficits in mouse models of familial AD and related conditions [19]. Elucidating potential pre- and postsynaptic pathways of pathological tau will help reveal the pathogenesis of synaptic dysfunction. Therefore, it is essential to better understand the relationship between pathological tau and synaptic dysfunction in AD, which will help to clarify the molecular mechanisms of tau-mediated cognitive dysfunction and provide constructive strategies for protecting synapses. Here, we review the recent research advances on the role of pathological tau in synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline in AD.
Overview of tau protein
Tau, a major microtubule-assembly protein, is encoded by the MAPT gene which comprises 16 exons, located on chromosome 17q21. In the adult brain, tau is mainly present in neurons, and at low levels in oligodendrocytes and astrocytes [20, 21]. The functions of tau in oligodendrocytes and astrocytes include transporting glutamate and maintaining the integrity of the myelin sheath and the blood–brain barrier [22,23,24]. Tau has long been considered as an axon-associated protein, as it binds to axonal microtubules and participates in microtubule stabilization and axonal transport [25]. The primary sequence of tau consists of four functional regions: the N-terminal region, a proline-rich domain, microtubule-binding repeats (MTRs), and the C-terminal projection domain [26]. There are six isoforms of tau in the mature human brain, including those having four microtubule-binding repeats (4R) with no amino-terminal inserts (0N), 4R1N, 4R2N, 3R0N, 3R1N and 3R2N, which are derived from alternative splicing at exons 2, 3 and 10 of the pre-mRNA [27, 28]. The different isoforms are present in distinct subcellular localization patterns in wild-type mice: the 0N isoform is highly expressed in cell bodies and axons, the 1N isoform is strongly localized to the neuronal nucleus, detectable in cell bodies and dendrites, but absent from axons; the 2N isoform is strongly localized in axons and cell bodies, and detectable in dendrites [29]. The different distributions of tau isoforms may reflect distinct physiological functions. Additionally, the 3R and 4R isoforms have a ratio of about 1:1 in the healthy human brain, and this ratio varies in neurodegenerative diseases [30]. As a substrate of a large number of kinases, tau potentially has 80 serine/threonine and 5 tyrosine phosphorylation sites which mainly cluster in the proline-rich region and the tail domain adjacent to the MTRs [27, 31]. The ability of tau to assemble microtubules is inversely related to its degree of phosphorylation [32]. Changes in the local microenvironment and insufficiency or degradation of molecular chaperones make tau prone to form paired helical filaments and ultimately lead to NFTs [33]. Although tau was initially described as an axonal protein, it can be mislocalized into dendrites and pre- and postsynaptic compartments in certain pathological contexts, and is involved in the blockade of neuronal signaling and impairment of synaptic plasticity [34,35,36].
Physiological roles of tau in synaptic plasticity: lessons from tau knockout mice
Synaptic plasticity refers to the activity-dependent enhancing or weakening of the existing synapses, including changes in the number of synapses, morphological structures, and function. Synaptic plasticity is crucial to cognitive functions, including learning and memory [37]. Impairments in synaptic plasticity cause defects in synaptic function, ultimately leading to neurodegeneration and loss of neuronal connectivity [38]. The translocation of endogenous tau from dendrites to excitatory postsynaptic compartments induced by pharmacological stimuli implicates that tau may be involved in the regulation of synaptic plasticity [39]. Some studies have reported that tau depletion does not impair cognition [19, 40], while others have observed synaptic plasticity and memory deficits in tau knockout (KO) mice. Chen et al. [41] have revealed that tau is involved in the regulation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced morphological synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Tau plays a critical role in certain cognitive functions and tau KO mice demonstrate impairment of long-term potentiation (LTP), which is a form of synaptic plasticity that is regarded as the primary cellular substrate for learning and memory [42]. On the other hand, Kimura et al. [43] have found a selective defect of long-term depression (LTD) in tau KO mice, and this effect can be replicated through knocking down tau by RNA interference in hippocampal slices of the CA1 region. As a weakening of synaptic strength following a stimulus, LTD is thought to be fundamental for clearing old memory traces [44]. Phosphorylated tau, mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3β), is required for N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR)-dependent LTD and has a critical physiological function in promoting LTD [43]. Regan et al. [45] have also observed impaired internalization of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) in the hippocampus of tau KO mice, and that tau phosphorylated specifically at serine 396 and 404 residues can promote LTD. Additionally, tau KO mice show reductions of the insulin-induced LTD, which is caused by altered activities of the tumor suppressor PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue on chromosome 10) [46]. A recent study has shown that Mapt−/−mice with a distinct genetic background display synaptic plasticity defects, hyperactivity and aging-dependent short-term memory impairments, while partial deletion of tau (Mapt+/−) only shows a mild short memory deficit [47]. The results on cognitive impairments may depend on the genetic background of mice, the use of different Mapt−/− models, the type and conditions of memory tests performed, and variations in housing and diet conditions. Therefore, it is important to further explore the role of tau in synaptic plasticity in the context of aging, which could further shed light on why certain forms of tau cause neurotoxicity in mature and/or aging brains.
Synaptic dysfunction in AD
In the central nervous system (CNS), synapses are considered to be the fundamental units for transmitting electrical or chemical signals among neurons, and are subject to strict spatiotemporal regulation [10]. Synapses are composed of three specialized compartments: the presynaptic terminal which is dedicated to the coordinated release of vesicles containing neurotransmitters [48]; the postsynaptic compartment which transduces the incoming signals through neurotransmitter receptors such as AMPARs and NMDARs [49]; and the synaptic cleft which is located between the pre- and postsynapse. Postsynaptic density (PSD) is an assembly in the postsynaptic compartment, and refers to the postsynaptic receptor-rich portion that harbors a series of scaffolding proteins and metabotropic receptors [50]. Moreover, other neural cell types such as microglia can contribute to synaptic maintenance and function [51].
Synaptic dysfunction may lead to some forms of neurodegeneration and dementia, highlighting the importance of synapses for healthy brain functions [52]. Patients with AD have fewer synapses than healthy controls [53]. Synaptic loss is described as an early indicator of neuronal dysfunction and the best biologically relevant factor for disease progression of AD [2, 54, 55] and other tauopathies [56,57,58] such as frontotemporal dementia, progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration and Pick’s disease. Synaptic dysfunction includes changes in the morphology and function of presynapses, dendrites, postsynapses, and synaptic clefts. Mitochondrial energy supply disorder and phagocytosis of synapses by microglia may also contribute to synaptic dysfunction.
Pathological tau and synaptic dysfunction
It is generally considered that tau is absent in dendrites, except for developing neurons or when under pathological conditions. However, extensive emerging evidence suggests that tau can also be detected in dendrites and pre- and postsynaptic compartments of normal healthy neurons, and is involved in the regulation of synaptic function [11, 14, 28]. In healthy human brains, tau is detected in 55% of presynaptic compartments and 70% of postsynaptic compartments [9]. The presence of tau in dendritic and synaptic compartments opens up a new and convincing chapter on the function of tau. However, its physiological and pathological effects are still not well-understood, especially in terms of learning, memory, and cognition.
Synaptic dysfunction is an early pathological feature associated with pathological tau in AD. During the pathogenesis of AD, the mechanisms involved in synaptic plasticity are dysregulated, leading to synaptic dysfunction and collapse [5, 59]. Pathological tau in sporadic AD has reduced microtubule-binding affinity, resulting in its detachment from axonal microtubules and subsequent mislocalization into somatodendritic compartments, impairing the integrity of microtubules and inducing synaptic dysfunction [5, 11, 31]. In fresh post-mortem tissues of patients with AD, phosphorylated tau has a higher level in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex than in the neocortical regions, and accumulates at synaptic terminals [17]. The accumulation of pathological tau in the synapses can promote synaptic loss and synaptic plasticity impairment [5, 60,61,62]. The density of NFTs is strongly correlated with synaptic loss and cognitive decline, suggesting that the pathological tau may be a pathogenic factor [63]. Reducing the levels of endogenous tau can prevent synaptic dysfunction in a mouse model of AD, which is mediated by changes in postsynaptic molecules [34, 64]. Additionally, synaptic defects are also associated with the soluble form of tau preceding the NFT formation, which implies that the soluble tau is sufficient to drive synaptic dysfunction [65, 66]. AD patients with relatively high levels of pathological tau have more severely impaired synaptic plasticity and faster cognitive decline [67]. However, the effect of pathological tau on synaptic dysfunction is still not fully understood.
Pathological tau induces presynaptic dysfunction
The presence of pathological tau in the presynaptic compartment is linked to the decreased mobility and release rate of synaptic vesicles [35] and the pathogenesis of AD [68]. Tau interacts with a subset of presynaptic proteins, including synaptophysin, synapsin-1, synaptotagmin, synaptogyrin-3, syntaxin-1B, α-synuclein and β-synuclein [69]. Microinjection of recombinant human tau into the presynaptic terminals results in transient neurotransmitter release mediated by calcium, persistent synaptic depression failure, and disruption of synaptic transmission, when using a squid giant synapse model [70]. McInnes et al. [71] have found that tau with N-terminal sequence can bind to synaptogyrin-3, a presynaptic vesicle-associated protein, causing excessive aggregation of synaptic vesicles and restricting presynaptic vesicle mobility, thereby attenuating neurotransmission in fly and mouse models of tauopathy. On the other hand, reducing synaptogyrin-3 expression prevents tau from binding to vesicles, attenuates the vesicle mobility defects, and restores neurotransmitter release, thereby alleviating early synaptic dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases [71] (Fig. 1). Moreover, Largo-Barrientos et al. [72] have shown that tau binds to synaptogyrin-3 on synaptic vesicles and excessively aggregates at presynaptic terminals, driving synaptic dysfunction in PS19 mice. The presynaptic pathological tau directly induces working memory defects, which are dependent on the presence of synaptogyrin-3. Synaptic loss and memory decline can be alleviated by lowering synaptogrin-3 expression [72]. The pathological tau also causes neuroinflammation, which is involved in axonal trafficking impairment, membrane disruption, and reactive oxygen species production [73, 74]. The presence of pro-aggregated tau at presynapses contributes to the terminal enlargement and synaptic vesicle pool exhaustion, along with impaired synaptic plasticity [75]. The pathological tau impairs presynaptic function in the entorhinal cortex in models of early AD [66]. It also impairs neuronal endocytosis through the miR-132–methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2)–dynamin 1 pathway, which represents a possible mechanism underlying the role of tau in presynaptic dysfunction [76] (Fig. 1). Further studies are needed to address whether direct regulation of this pathway in vivo can ameliorate the presynaptic disorder caused by pathological tau in AD. In conclusion, these data suggest an essential role for pathological tau in presynaptic dysfunction. However, the precise mechanisms through which pathological tau in presynaptic compartments induces synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline remain to be investigated.
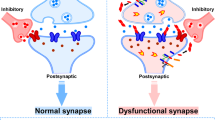
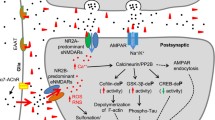
Pathological tau induces synaptic dysfunction. At presynaptic terminals, the interaction of pathological tau with synaptogyrin-3 on synaptic vesicles hampers vesicle mobility and impairs presynaptic vesicle cycling. Pathological tau impairs neuronal endocytosis through the miR-132–meCP2–dynamin 1 pathway. Pathological tau induces tagging of synapses by complement initiation factor (C1q) and activates synapse phagocytosis by microglia. The infiltration of pathological tau into postsynapses recruits Fyn to NMDAR/PSD-95 complexes and causes excitotoxicity mediated by amyloid-β and excessive glutamate. Accumulation of acetylated tau contributes to KIBRA deficiency, which blocks the activity-dependent F-actin polymerization and disrupts AMPA receptor membrane anchoring at postsynapses
Pathological tau induces postsynaptic dysfunction
Growing evidence implicates that the infiltration of pathological tau to the postsynapses contributes to the postsynaptic excitotoxicity and memory deficits by impairing the trafficking of NMDARs and AMPARs and synaptic anchoring in dendritic spines and postsynapses [11, 77,78,79]. Tau at postsynaptic terminals can promote the interaction between GluA2 subunit of AMPAR and PICK1 (protein interacting with C kinase 1), supporting the critical role of tau in regulating AMPAR endocytosis and hippocampal LTD in vitro [80]. In postsynaptic compartments in vivo, tau interacts with the PSD-95/NMDAR complexes through binding with the Src tyrosine kinase Fyn, a substrate of which is NMDAR [34, 81]. Under pathological conditions, missorted tau acts as a scaffold protein to deliver more Fyn to postsynaptic compartments and promotes phosphorylation of the NR2B subunit of NMDARs [34]. This induces the excessive activation of NMDARs, Ca2+ influx, and neuronal excitotoxicity [16, 34] (Fig. 1). Saracatinib (AZD0530), a Fyn inhibitor, was able to rescue the synaptic density loss and synaptic dysfunction in a mouse model of AD [82]. In a Phase Ib clinical trial (NCT01864655) in patients with mild-to-moderate AD, AZD0530 could achieve substantial CNS penetration through oral dosing at 100–125 mg [83], and later in a multicenter Phase IIa randomized clinical trial (NCT02167256), it showed a trend for slowing the reduction of hippocampal volume and entorhinal thickness [84]. Furthermore, expression of truncated tau or tau deficiency prevents Fyn from trafficking into postsynaptic terminals, thus improving the survival rate of the APP23 AD mouse model [34, 85]. Tau is a substrate of GSK3β and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) which exist in postsynaptic compartments and participate in the regulation of synaptic function, especially LTP [2, 86, 87]. Tan et al. [88] revealed that isoorientin, a GSK-3β inhibitor, attenuates phosphorylation of tau and rescues synaptic dysfunction in APP/PS1 model mice. Tideglusib, another competitive GSK-3β inhibitor, showed good tolerance and safety, and improved the cognitive function of patients with mild-to-moderate AD at a specific concentration in a Phase II clinical trial, but did not produce clinical efficacy [89]. Tau phosphorylation and acetylation play an essential role in tau mislocalization and postsynaptic dysfunction. Abnormally phosphorylated tau reduces the trafficking of glutamate receptor subunits GluA1 and GluA2/3 to PSD-95 [11, 90]. In addition, a mimic of phosphorylated tau impairs postsynaptic function through global disruption of synaptic trafficking or anchoring of AMPARs and NMDARs in cultured mouse neurons [11]. Tau is also required for the formation of dendritic spines and PSD, and tau deficiency or mutation impairs the sensitivity of newborn granule neurons to modulation of hippocampal neurogenesis and synapse maturation [91, 92]. Elimination of tau-specific phosphorylation at KxGS motifs by AMP-activated kinase counteracts the loss of dendritic spines and restores the synaptic function of hippocampal neurons both in vitro and in APP mouse models [93]. On the other hand, p38γ-mediated phosphorylation of tau inhibits the Aβ-induced excitotoxicity in both cellular and APP23 AD mouse models, suggesting a protective role of phosphorylated tau in postsynaptic terminals [94]. In addition, accumulation of K281- and K274-acetylated tau causes hippocampal LTP impairment and memory deficits, which are attributed to the reduction of memory-associated postsynaptic Kidney/BRAin (KIBRA) protein, as well as postsynaptic F-actin remodeling and disruption of AMPAR membrane anchoring, in both AD patient brains and transgenic mice expressing human tau that mimics K281 and K274 acetylation [12] (Fig. 1). Min et al. have demonstrated that salsalate, a drug that inhibits the activity of p300 to deacetylate tau, can potentially be used to improve synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline [95]. Enhancing KIBRA levels or restoring the downstream signal transmission at postsynapses may be another strategy for AD therapeutic intervention [96]. In addition, miR-135a-5p, which is reduced in excitatory hippocampal neurons in a tau-dependent manner in AD mice, mediates the cytoskeleton re-organization disorder and synaptic impairments in these excitatory hippocampal neurons [97]. miRNAs are the most important post-transcriptional regulators, acting as fine-tuners for synaptic plasticity, and how they interact with pathological tau to induce postsynaptic dysfunction needs to be further investigated.
Extracellular pathological tau contributes to synaptic dysfunction
In addition to regulating intracellular synaptic transmission, tau also has extracellular functions. Four different manners of tau release have been proposed, including direct translocation from the cytoplasm across the plasma membrane, lysosomal release, release via secretory exosomes, and micro-vesicle shedding [13]. The direct translocation across the membrane to extracellular space is an unconventional pathway of tau secretion. The secretion of tau increases with the degree of its phosphorylation, and sulfated proteoglycans on the plasma membrane facilitate its export [98]. Potassium-induced depolarization demonstrates increased release of tau and tau fragments from the presynaptic terminals in AD postmortem samples compared to control samples [99]. The extracellular tau regulates the signal transduction of synaptic receptors, such as muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) [2, 100]. The binding affinity of extracellular recombinant tau to mAChRs is much higher than that of acetylcholine, thus affecting the interneuronal signal transmission [101, 102]. It has been reported that extracellular oligomeric tau impairs LTP memory in mice [103, 104]. Neuron treatment with oligomeric tau impairs the morphology and density of dendritic spines, along with an increase in the concentration of intracellular reactive oxygen species and calcium [105]. In addition, extracellular oligomeric tau absorbed by neurons triggers abnormal tau accumulation, impairs the rapid transport of axons, and disrupts normal neuronal homeostasis [106]. Injection of N-terminal fragments of tau induces alterations of synaptic activity independently of overt neurodegeneration [107]. Furthermore, extracellular tau leads to synaptic dysfunction when secretomes from the human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuronal AD models are injected into the rat brain [108]. Application of a monoclonal antibody that recognizes and blocks extracellular tau aggregates can reduce the activation of microglia and improve cognitive deficits in P301S transgenic mice [109]. Another monoclonal antibody, DC8E8, can inhibit extracellular tau–tau interactions, discriminate between healthy and pathological tau, reduce tau pathology in mouse tauopathy models, and inhibit internalization of extracellular pathogenic tau in AD neurons in vitro [110]. Nevertheless, the underlying mechanisms of synaptic dysfunction caused by extracellular pathological tau need to be further investigated. Identifying and characterizing elements that promote or participate in the restriction and degradation of extracellular pathological tau will help to develop novel therapeutic approaches for AD treatment.
Pathological tau and mitochondrial dysfunction at synapses
The synaptic terminal is an energy high-demanding place, and the process of synaptic transmission requires high levels of ATP for exocytosis and release of neurotransmitters [111]. Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a key role in the occurrence and development of AD [112]. When mitochondria cannot be efficiently transported into synapses, ATP production and calcium buffering would be diminished, and the trafficking of glutamate receptor subunits to the postsynaptic membrane is impaired, ultimately resulting in synaptic dysfunction [113]. Pathological tau plays a vital role in impairing mitochondrial transport, thereby reducing the number of presynaptic mitochondria and hampering the release of synaptic vesicles [35, 114, 115]. In cultured neurons from P301L tau knock-in mice, the number of mitochondria is significantly decreased in axons and the volume of individual motile mitochondria increased, indicating that tau regulates mitochondrial functions [116]. In addition, the interaction between phosphorylated tau and dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1), a mitochondrial fission protein, enhances excessive mitochondrial fragmentation, causing mitochondrial and synaptic degeneration, ultimately leading to neuronal damage and cognitive decline in AD [117]. Furthermore, tau and GSK-3β double-transgenic mice exhibit elevated Drp1 expression and mitochondrial fragmentation [118]. Treatment designed to reduce Drp1 expression can decrease the interaction between Drp1 and phosphorylated tau, thereby blocking the mitochondrial abnormalities and synaptic damage in AD [119]. The synaptic protein α1-takusan directly or indirectly interacts with tau and PSD-95 to prevent the Aβ-induced tau hyper-phosphorylation and mitochondrial fragmentation at postsynaptic terminals, thereby protecting the synapse [120]. Mitochondria in AD animal models and brains of AD patients are enriched in N-terminal tau fragment (tau26-230), which is associated with mitochondrial and synaptic dysfunction [121]. A recent study reported that the presence of truncated tau at Asp421 impairs mitochondrial dynamics by reducing the level of optic atrophy protein 1 (Opa1) in AD [122]. The relationship between pathological tau and Opa1 expression, and the relationship between downregulation of Opa1 and mitochondrial integrity in AD need further clarification. In addition, approaches to reducing abnormal interactions between pathological tau and mitochondrial proteins to increase the number and quality of mitochondria in synapses are worthy of investigation.
Effects of microglia in tau-induced synaptic dysfunction
AD is accompanied by neuroinflammation, manifested by microgliosis, astrogliosis, and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokine levels. Microglia are macrophages residing in the brain, which originate from erythromyeloid progenitor cells derived from the yolk sac [123]. Microglia can respond to inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters, and interact with neuronal synapses in an activity-dependent manner [124]. They can also engulf the tau-positive synaptic compartments of neurons with aberrant pathology via a complement-dependent mechanism, leading to synaptic dysfunction [125]. In particular, the classical complement initiator C1q is upregulated in patients with AD and tauopathy and has been detected to be present with hyperphosphorylated tau in synapses of AD patients and PS19 mice, which is associated with microglial phagocytosis of synapses and synaptic density decline [125, 126]. The tau-affected and C1q-tagged synapses are further tagged with the central complement component C3, and engulfed and phagocytosed by microglia [126, 127]. Moreover, the inactivation of complement C3a receptor which predominantly originates from microglia, can attenuate tau pathology and rescue synaptic deficits and neurodegeneration in the PS19 mouse model of tauopathy [128]. C1q and C3 are located at synapses and trigger microglia to engulf the synapses. Antibodies against C1q have been shown to reduce the pathological tau-mediated synaptic engulfment by microglia [126]. Gratuze et al. [129] have hypothesized that synaptogyrin-3 on synaptic vesicles clusters at the presynaptic terminal through interaction with phosphorylated tau, leading to synaptic tagging with C1q and downstream synaptic deposition of C3, and finally synapses are engulfed by microglia [129] (Fig. 1). More studies are needed to uncover the association between pathological tau and C1q-mediated tagging of synapses to protect synapses from microglial phagocytosis. In addition, fractalkine, a unique chemokine that suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory genes, can reduce tau hyper-phosphorylation and neurodegeneration, and improves cognitive deficits by inhibiting the activation of microglia in a tauopathy mouse model [130].
Conclusions and perspectives
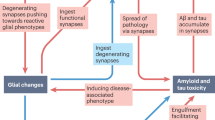
Synaptic dysfunction occurs in early AD and is closely associated with cognitive decline. Tau plays an important role in altering synaptic function during the pathogenesis of AD. Recent advances reviewed here shape our understanding of how pathological tau contributes to synaptic dysfunction. The pathological tau clearly promotes synaptic dysfunction through multiple mechanisms, including affecting the regulation of dendritic spine density, the presynaptic vesicle dynamics, the engulfment of synapses, the synaptic mitochondrial transport, and the synaptic plasticity (Fig. 2). It is crucial to determine the impact of pathological tau on synaptic loss and cognitive impairment, especially since there is no effective treatment for AD. Targeting synapses may also be an attractive therapeutic strategy. Therefore, the relationship between pathological tau and synaptic dysfunction should be further studied to understand its toxic effects, and to provide insights into new therapeutic targets for maintaining synaptic number, structure and function and slowing cognitive decline in AD.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid-beta
- NFTs:
-
Neurofibrillary tangles
- MTR:
-
Microtubule-binding repeat
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- LTD:
-
Long-term depression
- GSK-3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3
- AMPAR:
-
α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor
- NMDAR:
-
N-methyl-D- aspartic acid receptor
- PSD:
-
Postsynaptic density
- mAChRs:
-
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
- KIBRA:
-
Memory-associated postsynaptic Kidney/BRAin
- Drp1:
-
Dynamin-related protein 1
References
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M, Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10284):1577–90.
Forner S, Baglietto-Vargas D, Martini AC, Trujillo-Estrada L, LaFerla FM. Synaptic impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: a dysregulated symphony. Trends Neurosci. 2017;40(6):347–57.
Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):239–59.
Crimins JL, Pooler A, Polydoro M, Luebke JI, Spires-Jones TL. The intersection of amyloid β and tau in glutamatergic synaptic dysfunction and collapse in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12(3):757–63.
Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT. The intersection of amyloid beta and tau at synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2014;82(4):756–71.
Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002;298(5594):789–91.
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Hyman BT. Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2011;1(1):006189.
Goedert M, Wischik CM, Crowther RA, Walker JE, Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(11):4051–5.
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, et al. Association of missense and 5’-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature. 1998;393(6686):702–5.
Chen Y, Fu AKY, Ip NY. Synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;195:186–98.
Hoover BR, Reed MN, Su J, Penrod RD, Kotilinek LA, Grant MK, et al. Tau mislocalization to dendritic spines mediates synaptic dysfunction independently of neurodegeneration. Neuron. 2010;68(6):1067–81.
Tracy TE, Sohn PD, Minami SS, Wang C, Min SW, Li Y, et al. Acetylated tau obstructs KIBRA-mediated signaling in synaptic plasticity and promotes tauopathy-related memory loss. Neuron. 2016;90(2):245–60.
Wang Y, Mandelkow E. Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016;17(1):5–21.
Tai HC, Serrano-Pozo A, Hashimoto T, Frosch MP, Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT. The synaptic accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau oligomers in Alzheimer disease is associated with dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(4):1426–35.
Guerrero-Muñoz MJ, Gerson J, Castillo-Carranza DL. Tau oligomers: the toxic player at synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:464.
Regan P, Whitcomb DJ, Cho K. Physiological and pathophysiological implications of synaptic tau. Neuroscientist. 2017;23(2):137–51.
Fein JA, Sokolow S, Miller CA, Vinters HV, Yang F, Cole GM, et al. Co-localization of amyloid beta and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease synaptosomes. Am J Pathol. 2008;172(6):1683–92.
Guo T, Noble W, Hanger DP. Roles of tau protein in health and disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133(5):665–704.
Roberson ED, Scearce-Levie K, Palop JJ, Yan F, Cheng IH, Wu T, et al. Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid beta-induced deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Science. 2007;316(5825):750–4.
LoPresti P, Szuchet S, Papasozomenos SC, Zinkowski RP, Binder LI. Functional implications for the microtubule-associated protein tau: localization in oligodendrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(22):10369–73.
Gorath M, Stahnke T, Mronga T, Goldbaum O, Richter-Landsberg C. Developmental changes of tau protein and mRNA in cultured rat brain oligodendrocytes. Glia. 2001;36(1):89–101.
Dabir DV, Robinson MB, Swanson E, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, et al. Impaired glutamate transport in a mouse model of tau pathology in astrocytes. J Neurosci. 2006;26(2):644–54.
Seiberlich V, Bauer NG, Schwarz L, Ffrench-Constant C, Goldbaum O, Richter-Landsberg C. Downregulation of the microtubule associated protein tau impairs process outgrowth and myelin basic protein mRNA transport in oligodendrocytes. Glia. 2015;63(9):1621–35.
Kahlson MA, Colodner KJ. Glial tau pathology in tauopathies: functional consequences. J Exp Neurosci. 2015;9(Suppl 2):43–50.
Drubin DG, Kirschner MW. Tau protein function in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1986;103(6 Pt 2):2739–46.
Morris M, Maeda S, Vossel K, Mucke L. The many faces of tau. Neuron. 2011;70(3):410–26.
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Jakes R, Rutherford D, Crowther RA. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 1989;3(4):519–26.
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Potier MC, Ulrich J, Crowther RA. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989;8(2):393–9.
Liu C, Götz J. Profiling murine tau with 0N, 1N and 2N isoform-specific antibodies in brain and peripheral organs reveals distinct subcellular localization, with the 1N isoform being enriched in the nucleus. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):84849.
Gao YL, Wang N, Sun FR, Cao XP, Zhang W, Yu JT. Tau in neurodegenerative disease. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(10):175.
Noble W, Hanger DP, Miller CC, Lovestone S. The importance of tau phosphorylation for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurol. 2013;4:83.
Alonso AC, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Role of abnormally phosphorylated tau in the breakdown of microtubules in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(12):5562–6.
Spires-Jones TL, Stoothoff WH, de Calignon A, Jones PB, Hyman BT. Tau pathophysiology in neurodegeneration: a tangled issue. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32(3):150–9.
Ittner LM, Ke YD, Delerue F, Bi M, Gladbach A, van Eersel J, et al. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-beta toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Cell. 2010;142(3):387–97.
Zhou L, McInnes J, Wierda K, Holt M, Herrmann AG, Jackson RJ, et al. Tau association with synaptic vesicles causes presynaptic dysfunction. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15295.
Pooler AM, Noble W, Hanger DP. A role for tau at the synapse in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neuropharmacology. 2014;76(Pt A):1–8.
Kandel ER, Dudai Y, Mayford MR. The molecular and systems biology of memory. Cell. 2014;157(1):163–86.
Hanger DP, Goniotaki D, Noble W. Synaptic localisation of tau. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1184:105–12.
Frandemiche ML, De Seranno S, Rush T, Borel E, Elie A, Arnal I, et al. Activity-dependent tau protein translocation to excitatory synapse is disrupted by exposure to amyloid-beta oligomers. J Neurosci. 2014;34(17):6084–97.
Morris M, Hamto P, Adame A, Devidze N, Masliah E, Mucke L. Age-appropriate cognition and subtle dopamine-independent motor deficits in aged tau knockout mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2013;34(6):1523–9.
Chen Q, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhang YW, Zhong M, et al. Tau protein is involved in morphological plasticity in hippocampal neurons in response to BDNF. Neurochem Int. 2012;60(3):233–42.
Ahmed T, Van der Jeugd A, Blum D, Galas MC, D’Hooge R, Buee L, et al. Cognition and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in mice with a homozygous tau deletion. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35(11):2474–8.
Kimura T, Whitcomb DJ, Jo J, Regan P, Piers T, Heo S, et al. Microtubule-associated protein tau is essential for long-term depression in the hippocampus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014;369(1633):20130144.
Collingridge GL, Peineau S, Howland JG, Wang YT. Long-term depression in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11(7):459–73.
Regan P, Piers T, Yi JH, Kim DH, Huh S, Park SJ, et al. Tau phosphorylation at serine 396 residue is required for hippocampal LTD. J Neurosci. 2015;35(12):4804–12.
Marciniak E, Leboucher A, Caron E, Ahmed T, Tailleux A, Dumont J, et al. Tau deletion promotes brain insulin resistance. J Exp Med. 2017;214(8):2257–69.
Biundo F, Del Prete D, Zhang H, Arancio O, D’Adamio L. A role for tau in learning, memory and synaptic plasticity. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3184.
Südhof TC. Neurotransmitter release: the last millisecond in the life of a synaptic vesicle. Neuron. 2013;80(3):675–90.
Waites CL, Craig AM, Garner CC. Mechanisms of vertebrate synaptogenesis. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:251–74.
Sheng M, Kim E. The postsynaptic organization of synapses. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011;3(12):005678.
Kettenmann H, Kirchhoff F, Verkhratsky A. Microglia: new roles for the synaptic stripper. Neuron. 2013;77(1):10–8.
Sheng M, Sabatini BL, Südhof TC. Synapses and Alzheimer’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4(5):005777.
de Wilde MC, Overk CR, Sijben JW, Masliah E. Meta-analysis of synaptic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease reveals selective molecular vesicular machinery vulnerability. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12(6):633–44.
Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 1991;30(4):572–80.
Scheff SW, Price DA, Schmitt FA, Mufson EJ. Hippocampal synaptic loss in early Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27(10):1372–84.
Krishnamurthy K, Pasinelli P. Synaptic dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal dementia: Therapeutic strategies and novel biomarkers. J Neurosci Res. 2021;99(6):1499–503.
Bigio EH, Vono MB, Satumtira S, Adamson J, Sontag E, Hynan LS, et al. Cortical synapse loss in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2001;60(5):403–10.
Yoshida M. Astrocytic inclusions in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Neuropathology. 2014;34(6):555–70.
Koffie RM, Meyer-Luehmann M, Hashimoto T, Adams KW, Mielke ML, Garcia-Alloza M, et al. Oligomeric amyloid beta associates with postsynaptic densities and correlates with excitatory synapse loss near senile plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(10):4012–7.
Yoshiyama Y, Higuchi M, Zhang B, Huang SM, Iwata N, Saido TC, et al. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron. 2007;53(3):337–51.
Busche MA, Wegmann S, Dujardin S, Commins C, Schiantarelli J, Klickstein N, et al. Tau impairs neural circuits, dominating amyloid-β effects, in Alzheimer Models in vivo. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(1):57–64.
Chabrier MA, Cheng D, Castello NA, Green KN, LaFerla FM. Synergistic effects of amyloid-beta and wild-type human tau on dendritic spine loss in a floxed double transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;64:107–17.
Nelson PT, Alafuzoff I, Bigio EH, Bouras C, Braak H, Cairns NJ, et al. Correlation of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic changes with cognitive status: a review of the literature. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2012;71(5):362–81.
Mucke L, Selkoe DJ. Neurotoxicity of amyloid β-protein: synaptic and network dysfunction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2(7):a006338.
Koss DJ, Jones G, Cranston A, Gardner H, Kanaan NM, Platt B. Soluble pre-fibrillar tau and β-amyloid species emerge in early human Alzheimer’s disease and track disease progression and cognitive decline. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;132(6):875–95.
Polydoro M, Dzhala VI, Pooler AM, Nicholls SB, McKinney AP, Sanchez L, et al. Soluble pathological tau in the entorhinal cortex leads to presynaptic deficits in an early Alzheimer’s disease model. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;127(2):257–70.
Koch G, Di Lorenzo F, Del Olmo MF, Bonní S, Ponzo V, Caltagirone C, et al. Reversal of LTP-like cortical plasticity in Alzheimer’s disease patients with tau-related faster clinical progression. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;50(2):605–16.
Tai HC, Wang BY, Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT. Frequent and symmetric deposition of misfolded tau oligomers within presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2014;2:146.
Liu C, Song X, Nisbet R, Götz J. Co-immunoprecipitation with tau isoform-specific antibodies reveals distinct protein interactions and highlights a putative role for 2N tau in disease. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(15):8173–88.
Moreno H, Morfini G, Buitrago L, Ujlaki G, Choi S, Yu E, et al. Tau pathology-mediated presynaptic dysfunction. Neuroscience. 2016;325:30–8.
McInnes J, Wierda K, Snellinx A, Bounti L, Wang YC, Stancu IC, et al. Synaptogyrin-3 mediates presynaptic dysfunction induced by tau. Neuron. 2018;97(4):823-35.e8.
Largo-Barrientos P, Apóstolo N, Creemers E, Callaerts-Vegh Z, Swerts J, Davies C, et al. Lowering Synaptogyrin-3 expression rescues Tau-induced memory defects and synaptic loss in the presence of microglial activation. Neuron. 2021;109(5):767-77.e5.
López-González I, Aso E, Carmona M, Armand-Ugon M, Blanco R, Naudí A, et al. Neuroinflammatory gene regulation, mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and brain lipid modifications with disease progression in tau P301S transgenic mice as a model of frontotemporal lobar degeneration-tau. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015;74(10):975–99.
Dixit R, Ross JL, Goldman YE, Holzbaur EL. Differential regulation of dynein and kinesin motor proteins by tau. Science. 2008;319(5866):1086–9.
Decker JM, Krüger L, Sydow A, Zhao S, Frotscher M, Mandelkow E, et al. Pro-aggregant tau impairs mossy fiber plasticity due to structural changes and Ca(++) dysregulation. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2015;3:23.
Xie AJ, Hou TY, Xiong W, Huang HZ, Zheng J, Li K, et al. Tau overexpression impairs neuronal endocytosis by decreasing the GTPase dynamin 1 through the miR-132/MeCP2 pathway. Aging Cell. 2019;18(3):e12929.
Kim Y, Choi H, Lee W, Park H, Kam TI, Hong SH, et al. Caspase-cleaved tau exhibits rapid memory impairment associated with tau oligomers in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;87:19–28.
Yin Y, Gao D, Wang Y, Wang ZH, Wang X, Ye J, et al. Tau accumulation induces synaptic impairment and memory deficit by calcineurin-mediated inactivation of nuclear CaMKIV/CREB signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(26):E3773–81.
Zhao X, Kotilinek LA, Smith B, Hlynialuk C, Zahs K, Ramsden M, et al. Caspase-2 cleavage of tau reversibly impairs memory. Nat Med. 2016;22(11):1268–76.
Yagishita S, Murayama M, Ebihara T, Maruyama K, Takashima A. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β-mediated phosphorylation in the most c-terminal region of protein interacting with C Kinase 1 (PICK1) regulates the binding of PICK1 to glutamate receptor subunit GluA2. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(49):29438–48.
Mondragón-Rodríguez S, Trillaud-Doppia E, Dudilot A, Bourgeois C, Lauzon M, Leclerc N, et al. Interaction of endogenous tau protein with synaptic proteins is regulated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent tau phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(38):32040–53.
Kaufman AC, Salazar SV, Haas LT, Yang J, Kostylev MA, Jeng AT, et al. Fyn inhibition rescues established memory and synapse loss in Alzheimer mice. Ann Neurol. 2015;77(6):953–71.
Nygaard HB, Wagner AF, Bowen GS, Good SP, MacAvoy MG, Strittmatter KA, et al. A phase Ib multiple ascending dose study of the safety, tolerability, and central nervous system availability of AZD0530 (saracatinib) in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015;7(1):35.
van Dyck CH, Nygaard HB, Chen K, Donohue MC, Raman R, Rissman RA, et al. Effect of AZD0530 on cerebral metabolic decline in Alzheimer disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76(10):1219–29.
Ittner A, Ittner LM. Dendritic tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2018;99(1):13–27.
Llorens-Martín M, Fuster-Matanzo A, Teixeira CM, Jurado-Arjona J, Ulloa F, Defelipe J, et al. GSK-3β overexpression causes reversible alterations on postsynaptic densities and dendritic morphology of hippocampal granule neurons in vivo. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(4):451–60.
Bolshakov VY, Carboni L, Cobb MH, Siegelbaum SA, Belardetti F. Dual MAP kinase pathways mediate opposing forms of long-term plasticity at CA3-CA1 synapses. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3(11):1107–12.
Tan X, Liang Z, Li Y, Zhi Y, Yi L, Bai S, et al. Isoorientin, a GSK-3β inhibitor, rescues synaptic dysfunction, spatial memory deficits and attenuates pathological progression in APP/PS1 model mice. Behav Brain Res. 2021;398:112968.
Lovestone S, Boada M, Dubois B, Hüll M, Rinne JO, Huppertz HJ, et al. A phase II trial of tideglusib in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(1):75–88.
Jurado S. AMPA receptor trafficking in natural and pathological aging. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:446.
Pallas-Bazarra N, Jurado-Arjona J, Navarrete M, Esteban JA, Hernández F, Ávila J, et al. Novel function of tau in regulating the effects of external stimuli on adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Embo J. 2016;35(13):1417–36.
Hoffmann NA, Dorostkar MM, Blumenstock S, Goedert M, Herms J. Impaired plasticity of cortical dendritic spines in P301S tau transgenic mice. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2013;1:82.
Mairet-Coello G, Courchet J, Pieraut S, Courchet V, Maximov A, Polleux F. The CAMKK2-AMPK kinase pathway mediates the synaptotoxic effects of Aβ oligomers through tau phosphorylation. Neuron. 2013;78(1):94–108.
Ittner A, Chua SW, Bertz J, Volkerling A, van der Hoven J, Gladbach A, et al. Site-specific phosphorylation of tau inhibits amyloid-β toxicity in Alzheimer’s mice. Science. 2016;354(6314):904–8.
Min SW, Chen X, Tracy TE, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang C, et al. Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits. Nat Med. 2015;21(10):1154–62.
Tracy TE, Gan L. Acetylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease: An instigator of synaptic dysfunction underlying memory loss: Increased levels of acetylated tau blocks the postsynaptic signaling required for plasticity and promotes memory deficits associated with tauopathy. Bioessays. 2017;39(4):1600224.
Zheng K, Hu F, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Zheng J, Lai C, et al. miR-135a-5p mediates memory and synaptic impairments via the Rock2/Adducin1 signaling pathway in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1903.
Katsinelos T, Zeitler M, Dimou E, Karakatsani A, Müller HM, Nachman E, et al. Unconventional secretion mediates the trans-cellular spreading of tau. Cell Rep. 2018;23(7):2039–55.
Sokolow S, Henkins KM, Bilousova T, Gonzalez B, Vinters HV, Miller CA, et al. Pre-synaptic C-terminal truncated tau is released from cortical synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2015;133(3):368–79.
Morozova V, Cohen LS, Makki AE, Shur A, Pilar G, El Idrissi A, et al. Normal and pathological tau uptake mediated by M1/M3 muscarinic receptors promotes opposite neuronal changes. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:403.
Gómez-Ramos A, Díaz-Hernández M, Rubio A, Miras-Portugal MT, Avila J. Extracellular tau promotes intracellular calcium increase through M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors in neuronal cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;37(4):673–81.
Gómez-Ramos A, Díaz-Hernández M, Rubio A, Díaz-Hernández JI, Miras-Portugal MT, Avila J. Characteristics and consequences of muscarinic receptor activation by tau protein. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009;19(10):708–17.
Fá M, Puzzo D, Piacentini R, Staniszewski A, Zhang H, Baltrons MA, et al. Extracellular tau oligomers produce an immediate impairment of LTP and memory. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19393.
Puzzo D, Piacentini R, Fá M, Gulisano W, Li Puma DD, Staniszewski A, et al. LTP and memory impairment caused by extracellular Aβ and Tau oligomers is APP-dependent. Elife. 2017;6:26991.
Kaniyappan S, Chandupatla RR, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E. Extracellular low-n oligomers of tau cause selective synaptotoxicity without affecting cell viability. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13(11):1270–91.
Swanson E, Breckenridge L, McMahon L, Som S, McConnell I, Bloom GS. Extracellular tau oligomers induce invasion of endogenous tau into the somatodendritic compartment and axonal transport dysfunction. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;58(3):803–20.
Florenzano F, Veronica C, Ciasca G, Ciotti MT, Pittaluga A, Olivero G, et al. Extracellular truncated tau causes early presynaptic dysfunction associated with Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Oncotarget. 2017;8(39):64745–78.
Hu NW, Corbett GT, Moore S, Klyubin I, O’Malley TT, Walsh DM, et al. Extracellular forms of Aβ and tau from iPSC models of Alzheimer’s disease disrupt synaptic plasticity. Cell Rep. 2018;23(7):1932–8.
Yanamandra K, Kfoury N, Jiang H, Mahan TE, Ma S, Maloney SE, et al. Anti-tau antibodies that block tau aggregate seeding in vitro markedly decrease pathology and improve cognition in vivo. Neuron. 2013;80(2):402–14.
Weisová P, Cehlár O, Škrabana R, Žilková M, Filipčík P, Kováčech B, et al. Therapeutic antibody targeting microtubule-binding domain prevents neuronal internalization of extracellular tau via masking neuron surface proteoglycans. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7(1):129.
Reddy PH, Beal MF. Amyloid beta, mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage: implications for cognitive decline in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14(2):45–53.
Yao J, Irwin RW, Zhao L, Nilsen J, Hamilton RT, Brinton RD. Mitochondrial bioenergetic deficit precedes Alzheimer’s pathology in female mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(34):14670–5.
Ivannikov MV, Sugimori M, Llinás RR. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis in hippocampal synaptosomes correlates directly with total mitochondrial volume. J Mol Neurosci. 2013;49(1):223–30.
Kopeikina KJ, Carlson GA, Pitstick R, Ludvigson AE, Peters A, Luebke JI, et al. Tau accumulation causes mitochondrial distribution deficits in neurons in a mouse model of tauopathy and in human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(4):2071–82.
Quntanilla RA, Tapia-Monsalves C. The Role of Mitochondrial impairment in Alzheimer´s disease neurodegeneration: the tau connection. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(11):1076–91.
Rodríguez-Martín T, Pooler AM, Lau DHW, Mórotz GM, De Vos KJ, Gilley J, et al. Reduced number of axonal mitochondria and tau hypophosphorylation in mouse P301L tau knockin neurons. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;85:1–10.
Manczak M, Reddy PH. Abnormal interaction between the mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 and hyperphosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease neurons: implications for mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal damage. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(11):2538–47.
Rockenstein E, Ubhi K, Trejo M, Mante M, Patrick C, Adame A, et al. CerebrolysinTM efficacy in a transgenic model of tauopathy: role in regulation of mitochondrial structure. BMC Neurosci. 2014;15:90.
Kandimalla R, Reddy PH. Multiple faces of dynamin-related protein 1 and its role in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(4):814–28.
Nakanishi N, Ryan SD, Zhang X, Khan A, Holland T, Cho EG, et al. Synaptic protein α1-takusan mitigates amyloid-β-induced synaptic loss via interaction with tau and postsynaptic density-95 at postsynaptic sites. J Neurosci. 2013;33(35):14170–83.
Amadoro G, Corsetti V, Ciotti MT, Florenzano F, Capsoni S, Amato G, et al. Endogenous Aβ causes cell death via early tau hyperphosphorylation. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32(6):969–90.
Pérez MJ, Vergara-Pulgar K, Jara C, Cabezas-Opazo F, Quintanilla RA. Caspase-cleaved tau impairs mitochondrial dynamics in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(2):1004–18.
Gomez Perdiguero E, Klapproth K, Schulz C, Busch K, Azzoni E, Crozet L, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature. 2015;518(7540):547–51.
Tremblay M, Lowery RL, Majewska AK. Microglial interactions with synapses are modulated by visual experience. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(11):e1000527.
Vogels T, Murgoci AN, Hromádka T. Intersection of pathological tau and microglia at the synapse. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7(1):109.
Dejanovic B, Huntley MA, De Mazière A, Meilandt WJ, Wu T, Srinivasan K, et al. Changes in the synaptic proteome in tauopathy and rescue of tau-induced synapse loss by C1q antibodies. Neuron. 2018;100(6):1322.e7-1336.e7.
Wu T, Dejanovic B, Gandham VD, Gogineni A, Edmonds R, Schauer S, et al. Complement C3 is activated in human AD brain and is required for neurodegeneration in mouse models of amyloidosis and tauopathy. Cell Rep. 2019;28(8):2111-23.e6.
Litvinchuk A, Wan YW, Swartzlander DB, Chen F, Cole A, Propson NE, et al. Complement C3aR inactivation attenuates tau pathology and reverses an immune network deregulated in tauopathy models and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2018;100(6):1337-53.e5.
Gratuze M, Holtzman DM. Targeting pre-synaptic tau accumulation: a new strategy to counteract tau-mediated synaptic loss and memory deficits. Neuron. 2021;109(5):741–3.
Finneran DJ, Morgan D, Gordon MN, Nash KR. CNS-wide over expression of Fractalkine improves cognitive functioning in a tauopathy model. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019;14(2):312–25.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported partially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82030032, 32070960, 81871108 to DL, 81760221 and 81960221 to XPY, and 81660209 to ZYC); the National Science & Technology Fundamental Resource Investigation Program of China (2018FY100903 to XPY); and Science and Technology Project Founded by the Education Department of Jiangxi Province (GJJ201834 to MXW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The initial idea for this review was from DL and ZYC; MXW and MQZ wrote and revised the manuscript; XPY, KC and ZJH contributed to illustration preparation; QZ and XMC edited the manuscript; DL and MXW read, reviewed, and approved the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Zhang, M., Yin, X. et al. The role of pathological tau in synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s diseases. Transl Neurodegener 10, 45 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-021-00270-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-021-00270-1