Abstract
Background
Lignin is a complex aromatic heteropolymer comprising 15–30% dry weight of the lignocellulose. The complex structural characteristic of lignin renders it difficult for value-added utilization. Exploring efficient lignin-degrading microorganisms and investigating their lignin-degradation mechanisms would be beneficial for promoting lignin valorization. In this study, a newly isolated white-rot basidiomycete, Trametes hirsuta X-13, with capacity to utilize alkaline lignin as the sole substrate was investigated.
Results
The analysis of the fermentation properties of T. hirsuta X-13 using alkaline lignin as the sole substrate, including the mycelial growth, activities of ligninolytic enzymes and the rates of lignin degradation and decolorization confirmed its great ligninolysis capacity. The maximum lignin degradation rate reached 39.8% after 11 days of T. hirsuta X-13 treatment, which was higher than that of reported fungi under the same condition. Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) scanning electron micrographs (SEM), two-dimensional heteronuclear single quantum coherence NMR analysis (2D-HSQC NMR) collaborated with pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (py-GC/MS) analyses proved that lignin structure was severely deconstructed along with amounts of monomer aromatics generated. Furthermore, according to those chemical analysis, in addition to canonical Cα–Cβ breakage, the cleavage of lignin interunit linkages of β–β might also occur by T. hirsuta X-13.
Conclusions
This study characterized a newly isolated white-rot basidiomycete T. hirsuta X-13 with impressive alkaline lignin degradation ability and provided mechanistic insight into its ligninolysis mechanism, which will be valuable for the development of lignin valorization strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Lignin is a complex aromatic and optically inactive amorphous heteropolymer accounting for 15–30% dry weight of the lignocellulosic biomass, which is the most abundant source of renewable aromatic carbon on earth. It contains three different phenyl propane units (p-hydroxyphenyl, guaiacyl and syringyl units) connected by a multiplicity of C–O and C–C bonds, such as β-O-4, β–β, 4-O-5, β-5 [1]. The heterogeneous and complex structural characteristics of lignin render it difficult for degradation. In lignocellulosic biomass structure, lignin is embedded between cellulose and hemicellulose structures, forming a complex heterogeneous network that limits the accessibility of enzymes or chemicals [2]. Hence, depolymerization of lignin structure of lignocellulosic biomass is a crucial step in the biorefinery industry aiming at increasing the accessibility of relevant enzymes to polysaccharides [3]. In addition, lignin consist of phenyl propane units also representing a potentially intriguing valuable source of renewable aromatic chemicals [4, 5]. The valorization of lignin by microorganisms which converted it into valuable chemicals such as vanillin, eugenol and other phenolics has attracted much attention [6,7,8].
To date, a number of microorganisms including fungi and bacteria were found with capacity to depolymerize lignin [1, 9]. In fungi, as the extensively studied lignin degraders, white-rot basidiomycetes were demonstrated as the exclusive species that can degrade lignin completely [10, 11]. White-rot basidiomycete fungi produce several types of highly efficient and unique extracellular oxidative enzymes including laccase, and lignin-degrading peroxidases that are involved in lignin degradation. Instead of degrading lignin, brown-rot fungi were found to modify the lignin structure through hydroxyl radical oxidants produced via Fenton chemistry pathway [12, 13]. Although some bacteria, such as Pseudomonas putida, Cupriavidus basilensis, and Rhodococcus jostii have been reported with lignin degradation ability, their lignin depolymerization activities were significantly weaker than those of fungi [14,15,16]. Hence, ligninolytic fungi especially white-rot basidiomycete fungi represent promising microorganisms for lignin biological treatment.
Although ligninolytic enzymes have been extensively identified and characterized in white-rot fungi, the degradation pathways of lignin largely remain unknown. The only demonstrated ligninolysis routes in white-rot fungi were Cα–Cβ and β-O-4 cleavages based on the detection of the corresponding benzoic acid derivatives during the lignocellulosic biomass degradation [17,18,19,20]. Furthermore, knowledge of the degradation routes of lignin by white-rot basidiomycete fungi when used as the sole carbon source were less studied. With the global availability and chemical versatility, lignin is regarded as an intriguing renewable aromatic complex and has a promising potential in the production of commercially valuable chemicals [21]. Yet so far the use of enzymatic technology for commercial lignin conversion remains challenging. Exploring efficient lignin-degrading fungi and investigating their degradation mechanisms for lignin substrate would be available for promoting lignin valorization.
In this study, we characterized a newly isolated ligninolytic white-rot basidiomycete Trametes hirsuta X-13. To assess the lignin degradation ability, the fermentation properties of T. hirsuta X-13 using alkaline lignin as the sole carbon source including the mycelial growth, activities of lignin-degrading enzymes and rates of lignin degradation and decolorization were investigated. Furthermore, Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS), scanning electron micrographs (SEM), two-dimensional heteronuclear single quantum coherence NMR analysis (2D-HSQC NMR) and pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (py-GC/MS) were employed for exploration of the structure variations of lignin residues, the corresponding metabolic compounds and the ligninolysis route by the strain.
Results and discussion
Isolation, screening and identification of ligninolytic fungus strain
During the isolation process, 13 strains in total were isolated from collected rotten wood samples. Of these isolates, the strain X-13 produced the largest colorization zone and decolorization zone on guaiacol-containing and Azure B-containing PDA medium, respectively, in the screening procedure (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Guaiacol and Azure B are commonly used as indicators for determining the lignolytic potential [22]. This indicated the potentially strong ligninolytic activity of strain X-13. The morphological analysis of strain showed that the colony of strain X-13 was milky white with the dense hyphae, and it revealed a thread-like septate mycelium without any reproductive structures (Additional file 2: Figure S2), which were similar to those of reported Trametes hirsuta genus strains [23, 24]. Moreover, the ITS region sequence of strain X-13 (GenBank: MT995079) showed 99% similarity with that of white-rot basidiomycete Trametes hirsuta JL-22-2 according to NCBI BLAST algorithm analysis. As shown in Fig. 1, phylogenetic tree analysis revealed that strain X-13 belongs to species of Trametes hirsuta. Therefore, the strain X-13 was identified as Trametes hirsuta strain, which has since been deposited in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection (CGMCC No. 18567).
Characterization of lignin degradation by T. hirsuta X-13
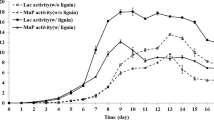
To evaluate the lignin degradation property of T. hirsuta X-13, the growth of mycelial biomass, the rates of lignin degradation and decolorization, and the ligninolytic enzymes activity were investigated during the incubation with alkaline lignin as sole carbon source. As shown in Fig. 2a, the dry weight of mycelial biomass increased with the time and achieved a maximum on day 7 and then started to decline gradually. This suggested that T. hirsuta X-13 could utilize alkaline lignin as the sole carbon and energy source for growth. Although numerous microorganisms including fungi and bacteria have been found with lignin degradation ability, less was reported with sole lignin substrate for growth [10, 11]. As the complete oxidation of lignin is highly exothermic, lignin degradation is too slow to function as a source of metabolic energy [25]. Hence, during the lignin degradation process of the most ligninolytic microorganisms, additional carbon or nitrogen source was needed to be supplemented to initiate lignin depolymerization [25,26,27]. Despite that the presence of polysaccharides impurities in the alkaline lignin might also contribute to the growth of T. hirsuta X-13, the small amount of these (1.52%) (Additional file 3: Table S1) limited their effects on the strain growth. The rapid growth of T. hirsuta X-13 in the medium containing alkaline lignin as the sole carbon source suggested the dramatic capacity of lignin depolymerization and metabolism for this fungus strain. The decline of fungal growth after 7 days of incubation in lignin-containing medium might be due to the accumulation of toxic metabolic compounds including lignin-derived aromatic compounds and the reduction of nutrient essential for strain growth.
The rates of lignin degradation and decolorization showed the same trends during whole incubation time (Fig. 2a). The rates of both lignin degradation and decolorization increased rapidly in the initial 7 days, which then almost remained unchanged. This was directly correlated with the mycelial biomass growth of the strain. The maximum rates of both lignin degradation and decolorization were obtained at 11th day, with the values of 39.8% and 52.4%, respectively. The maximum lignin degradation rate by T. hirsuta X-13 was higher than that of reported fungi under the same condition [11]. These results further indicated the strong ability of lignin degradation by T. hirsuta X-13.
The degradation of lignin by white-rot fungi mainly depends on the action of a series of ligninolytic enzymes including laccase, lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase [28]. As shown in Fig. 2b, the activities of laccase (Lac) and manganese peroxidase (MnP) showed approximate increase trend during the initial 7 days. After that, they started to decline. The lignin peroxidase (LiP) activity was undetected across the whole incubation time. Furthermore, secretomic analysis was carried out to provide insight into the ligninolytic system of T. hirsuta X-13. There were in total 792 proteins identified in lignin cultures of T. hirsuta X-13 (Additional file 4), which were divided into six categories according to their biological function (Additional file 5 and Additional file 6: Figure S3). Among these, 42 proteins that functioned as ligninolytic enzymes are listed in Additional file 7: Table S2, which include six laccases, eight manganese peroxidases, four lignin peroxidases, two dye-decolorizing peroxidases and one GMC oxidoreductase. Most of those identified ligninolytic enzymes were predicted as the extracellular proteins. The existence of the abundance of those ligninolytic enzymes cocktail in the secretory proteins of T. hirsuta X-13 indicated its strong ability towards lignin degradation. Although four lignin peroxidases were found, the corresponding activity was undetectable during the lignin degradation by T. hirsuta X-13, which might be due to that the protein level of lignin peroxidase was too low to be detected for enzyme activity. It should be noted that considerable amount of proteins (71) belonging to CAZy (glycoside hydrolase, carbohydrate esterase and carbohydrate-binding module) were found in the secretory proteins. As lignin was used as the sole carbon with less impurity, those identified CAZy enzymes might be derived from the constitutive expression by the strain with low level [29, 30]. Quantitative secretomic analysis is needed in further study to clarify this speculation. In addition, the variation of detected ligninolytic enzymes activity was in line with that of strain growth and lignin degradation. These results suggested that laccase and manganese peroxidase were the main enzymes responsible for lignin degradation by T. hirsuta X-13. A number of Trametes genus strains have been found with lignin-degrading activity, and they could secrete abundance of lignin-degrading enzymes including laccase, lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase [31, 32]. However, the lignin degradation studies with these strains were conducted under the co-existence of a large amount of glucose substrate [33, 34]. The utilization of alkaline lignin as the sole carbon resource by Trametes hirsuta strain was rarely reported.
FTIR analysis
To investigate the changes of functional groups and chemical structures of alkaline lignin after treatment with T. hirsuta X-13, FTIR analysis was performed. As shown in Fig. 3, the FTIR spectra of raw and treated lignin by T. hirsuta X-13 displayed distinct changes, especially on the lignin fingerprint region (1700–1000 cm−1). The major peaks of samples were assigned as listed in Table 1 based on the previous literature reports [35,36,37].
FTIR spectra of the control and treated lignin samples with T. hirsuta X-13 for 7 and 13 days. The labeled peaks with number assigned to the corresponding functional groups and structures are listed in Table 1
The intensities of bands at 2860 cm−1 and 1420 cm−1 which were assigned to C–H stretching in aromatic methoxyl groups and aromatic skeletal vibrations combined with O–CH3 in plane deform, respectively, were reduced with the increase in the treatment time of T. hirsuta X-13, suggesting the demethoxylation reaction of lignin by the strain. The decline of the intensities of the bands at 1275 cm−1 and 1041 cm−1 ascribed to C–O in guaiacyl group, and 1511 cm−1 belongs to aromatic skeletal vibrations (G > S) in T. hirsuta X-13-treated samples implied the removal of guaiacyl unit in lignin. Meanwhile, the weakened intensities of bands at 1600 cm−1 and 1317 cm−1, relating to aromatic skeletal vibrations and C=O stretch (S > G) and C–O in syringyl group, respectively, suggested the decline of syringyl unit content in lignin after T. hirsuta X-13 treatment. The decreased intensities of the bands at 1090 cm−1 corresponding to C–O vibrations in aliphatic ethers and/or in secondary alcohols in T. hirsuta X-13-treated samples illustrated that more easily degradable materials were produced after the demethylation and side chain oxidation of lignin. In addition, the reduction of intensity of the bands at 618 cm−1 ascribed to stretching vibrations of the C–S bond linked to the aromatic ring indicated a side chain oxidation of lignin. These significant variations of FTIR spectra on T. hirsuta X-13-treated lignin relative to control indicated that lignin structure was largely destructed by this fungus strain, which further demonstrated its impressive ligninolytic capacity.
GC–MS analysis
To investigate the degradation products from alkaline lignin by T. hirsuta X-13, GC–MS analysis was carried out. The low molecular weight metabolic compounds identified from the peaks of the total ion chromatograms (Additional file 8: Figure S4) are listed in Table 2. A total of 12 aromatics and 3 fatty acids were identified from the lignin samples after 13 days of T. hirsuta X-13 treatment, and only 4 aromatics were obtained from the control group. Among these aromatic compounds, 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde, gentisic acid, 2,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid, 3,5-ditert-butylphenol, 4,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxyacetophenone, 4‑hydroxyphenylacetic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid were only observed in T. hirsuta X-13-treated sample, suggesting the occurrence of lignin depolymerization by the strain treatment. Meanwhile, the presence of three long-chain fatty acid compounds, i.e., dodecanedioic acid, 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid and hexadecanoic acid in T. hirsuta X-13-treated sample might indicate that the generated aromatic compounds derived from lignin structure were further converted to fatty acid compounds via aromatic ring cleavage by the strain [38, 39]. However, further studies are needed to elucidate the metabolic pathway of fatty acids during the lignin degradation by T. hirsuta X-13. In addition, the predomination of aromatic acid compounds in the identified products implied the splitting of the aliphatic side chains of lignin units by T. hirsuta X-13. These suggested that the lignin structure was deeply destructed by the strain, which was consistent with FTIR analysis results.
It is noticeable that there were three unique aromatic compounds, i.e., acetovanillone, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and vanillin identified in the control group. These three aromatic compounds were the canonical aromatic metabolites presented in bacterial lignin degradation process [15, 25, 40, 41]. Moreover, vanillin generated from Cα–Cβ oxidative cleavage of β-aryl ether components of lignin was the major metabolite in lignin degradation process of many lignin-degrading microorganisms [1]. The presence of these three aromatic compounds in the control group suggested that the partial oxidation and degradation of lignin occurred during the production process [15, 37]. While the absence of these three aromatic compounds in lignin-derived metabolites of T. hirsuta X-13-treated group indicated the catabolism of these compounds by the strain for growth.
Acetovanillone could be converted to ferulic acid or vanillin by C–C coupling reaction, while this compound was found to be resistant for some bacteria [42]. That acetovanillone and its intermediate metabolites (ferulic acid and vanillin) were not detected suggested the strong degradation and metabolism capacity of T. hirsuta X-13 for lignin and its aromatic units. The appearance of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid corresponding with the absence of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid implied that Cα–Cβ cleavage might exist during the 4-hydroxybenzoic acid degradation by T. hirsuta X-13 [43]. It has been reported that the Cα–Cβ cleavage for lignin or aromatic compounds could be catalyzed by laccase [37, 44]. This was in line with the above results of enzymatic analysis that laccase activities were detected across the whole process of lignin degradation by T. hirsuta X-13.
SEM analysis
To investigate the morphological changes of alkaline lignin after degraded by T. hirsuta X-13, SEM analysis was performed to observe the surface microstructure of lignin samples. As shown in Fig. 4, the surface structure of control lignin samples and after T. hirsuta X-13 treatment revealed a dramatic distinction. The control lignin samples consist of large fragments with smooth flat surface structure (Fig. 4a, b). However, the particle size of lignin treated by T. hirsuta X-13 was reduced with smaller fragments generated (Fig. 4c). Moreover, the surface of treated lignin turned rugged with more cracks (Fig. 4d). The remarkable changes of treated lignin particle size and surface also confirmed that the lignin was severely degraded by T. hirsuta X-13.
2D-HSQC NMR characterization
To explore the changes in alkaline lignin structure during fungal treatment, 2D-HSQC NMR spectra analysis was employed. The 2D-HSQC NMR spectra of control lignin samples and after 7 and 13 days treatment by T. hirsuta X-13 are presented in Fig. 5. The correlation peaks of lignin from the spectra are assigned and listed in Table 3. As shown in Fig. 5a, signals from the aliphatic (δC/δH 80–140/6.0–8.0) and aromatic (δC/δH 50–80/2.5–6.0) regions of the spectra including methoxyls, β-O-4 (aryl ethers), β–β (resinols) and β-5 (phenylcoumarans) structures, pCA (p-coumarates), FA (ferulate), S-, G- and H-type units, were clearly detected in NMR spectra of control samples. The relative abundances of lignin interunit linkages and dominant aromatic units are listed in Table 4. It should be noted that compared to control, the intensities of signals of most of those structures were significantly decreased in the lignin residual after treated by T. hirsuta X-13 (Fig. 5). This might be due to that the lignin structure was greatly modified after the fungus strain treatment, which might severely impede the solubility of lignin residual in dimethyl sulfoxide.
2D-HSQC NMR spectra of the control (a) and treated lignin samples after 7 days (b) and 13 days (c) by T. hirsuta X-13. Chemical shift assignments are listed in Table 3. The main structures present in lignin: (A) β-aryl ether (β-O-4); (B) phenylcoumaran (β-5); (C) resinol (β–β); (I) cinnamyl alcohol; (G) guaiacyl; (S) syringyl; (FA) ferulate; (pCA) p-coumarate; (H) p-hydroxyphenyl
In aliphatic region, as listed in Table 4, the percentage of lignin interunit linkages greatly changed in T. hirsuta X-13-treated sample relative to control, suggesting that the interunit linkages in lignin might be severely deconstructed during T. hirsuta X-13 degradation. The condensation degree (β–β/β-O-4) of the lignin were largely decreased with the increment of incubation time of T. hirsuta X-13, which further confirmed the depolymerization of lignin by T. hirsuta X-13. In addition, the percentages of resinol (β–β) and cinnamyl alcohol were reduced with the increment of incubation time of T. hirsuta X-13, indicating that β–β and lignin end-groups were more susceptible to degrade by T. hirsuta X-13. C–C bonds including β–β were found to be more resistant to microorganism cleavage than ether bonds [45,46,47]. Though β–β cleavages pathway have been reported in the lignin degradation by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora, the used substrate was lignocellulosic biomass wheat straw instead of pure lignin in these study [19, 20]. The complicated composition of biomass might disturb the lignin utilization by the fungi and the polysaccharides components residues might affect the signals of lignin detection in NMR spectra [48, 49]. The employment of lignin as the sole carbon source for exploring the fungus lignin degradation pathway provided a controlled substrate for research. By using alkaline lignin as the sole carbon source, our results showed that β–β cleavage might occur during the lignin degradation process of T. hirsuta X-13. These results implied that the strain could substantially cleave the highly stable interunit linkage of lignin. Laccase has been found with capacity to break the lignin interunit linkages including β–β [37, 50, 51]. The secretion of laccase by T. hirsuta X-13 might be responsible for cleavage of this interunit linkage of lignin.
In the aromatic region, the percentage of G-type was more than twice those of S- and H-type units, suggesting that this alkaline lignin belongs to G-rich lignin (Table 4). Compared to control, the percentage of H-type unite in the lignin residual treated by T. hirsuta X-13 was decreased. While the percentages of G- and S-type units changed with opposite trends during the treatment of T. hirsuta X-13. The ratio of S/G declined in the lignin residual after degraded by T. hirsuta X-13 for 7 days relative to control, and the value of which increased from 0.35 up to 0.66 after 13 days treatment. A similar variation trend of S/G ratio was also obtained from the py-GC–MS analysis (Additional file 9: Table S3). The detected S/G ratio in py-GC–MS experiment was lower than that of 2D-HSQC NMR spectra analysis, which might be caused by that the demethylation reaction rate of S-type unit was faster than that of G-type unit in pyrolysis process [52]. This indicated that S-type unit was more susceptible to utilized by T. hirsuta X-13 in the first 7 days incubation, while it preferentially degraded G-type unit in the last 6 days of incubation. S-type unit was regarded as the most recalcitrant structure toward biodegradation than other two units, as it has two methoxyl groups with lower redox potential [53]. The preferential degradation of recalcitrant structure of S-type unit in the early stage might be attributed to the fast growth of fungus in the first 7 days incubation, which might secrete more relevant enzymes to attack the structure. The reduction of these basic lignin-derived aromatic units might be attributed to the further conversion into other aromatics or fatty acids via demethylation and cleavage of aromatic ring, which then consumed by the strain for growth [54]. The accumulation of certain toxic metabolic compounds derived from these lignin-derived aromatic units might contribute to the decline of fungal growth after 7 days incubation. Further studies focusing on quantitation and tracking of these aromatics are needed to elucidate the metabolism of lignin-derived aromatics by the fungus strain.
Conclusions
In summary, this study characterized the strong capacity of a newly isolated white-rot basidiomycete T. hirsuta X-13 for lignin degradation and provided a lignin degradation route insight into its ligninolysis. The maximum lignin degradation rate reached 39.8% after 11 days of treatment with this strain using alkaline lignin as the sole carbon source. Both Lac and MnP activities were observed across the whole incubation time. The employment of chemical analysis elucidated that the structure of lignin residual was severely destructed, and the cleavage of the interunit linkages of lignin including Cα–Cβ and β–β occurred in the ligninolysis routes of T. hirsuta X-13. These results suggested that T. hirsuta X-13 might be a promising candidate for application on lignin valorization, and the insight of its ligninolysis pathway could broaden the knowledge of lignin degradation mechanisms of fungi.
Methods
Ligninolytic fungus strain isolation
Rotten wood samples were collected from the forests of Yuelu Mountain in Changsha city, China. The samples were cut to 0.5 × 0.5 cm and was washed three times using sterile water. Then the samples were placed in the center of Petri dish containing enrichment medium. Potato dextrose broth (PDA) medium contained (g/L) potato extract (200), glucose (10), MgSO4 (1.5), KH2PO4 (3.0), vitamin B (0.05), agar (15) were used as enrichment medium. After cultivation of isolated fungus strains for 2 to 3 generations, the pure isolates obtained were further inoculated in the screen media for ligninolytic strain screening. The screen media included Azure B-containing and guaiacol-containing PDA medium which containing potato dextrose agar (PDA) supplemented with Azure B (0.1 g/L) or guaiacol (0.1 g/L), respectively. The strains produced the largest diameter of the decolorization zone in Azure B-containing PDA medium or colorization zone in guaiacol-containing PDA medium were selected for further study.
Microorganism identification
The isolated fungus was identified by morphological analysis and internal transcribed region sequence (ITS) fingerprinting. Total DNA of fungus strain was extracted using a Fungi Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China). Amplification of ITS region sequence was performed using ITS 1 forward (TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG) and ITS 4 reverse (TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC) as the primer. The amplified products were sequenced and analyzed by the NCBI BLAST algorithm tool. The phylogenetic analysis was conducted by MEGA 5.0 based on maximum likelihood algorithm.
Lignin degradation
To prepare fungus seed cultures, an agar square from fully grown mycelia on PDA medium was inoculated in 100 mL of basic medium contained (g/L) glucose 20.0, peptone 1.0, yeast extract 2.0, (NH4)2SO4 4.0, KH2PO4 1.0, K2HPO4 1.0, CaCl2 0.3 g/L, MgSO4 0.3, NaCl 0.1, and incubated at 28 °C for 7 days with shaking at 180 rpm. The seed cultures were centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 5 min to collect the fungus pellets. The collected pellets were washed three times with 0.9% NaCl to remove the cultures. Then the washed pellets were inoculated into lignin medium contained (g/L) (NH4)2SO4 4.0, KH2PO4 1.0, K2HPO4 1.0, NaCl 0.1, MgSO4 0.3, MnSO4 0.05, FeSO4 0.01, CuSO4 0.01, ZnSO4 0.01, CoCl2 0.005, Na2MoO4 0.001, KAl(SO4)2 0.001, H3BO3 0.01, alkaline lignin (from Norway spruce (Picea abies) wood) (CAS No. 8068-05-1, Catalog number 370959, Sigma-Aldrich) 3.0, and incubated at 28 °C with shaking at 180 rpm for 13 days. Cultures containing alkaline lignin without inoculating fungus strain were used as control and incubated in the same conditions as the fungal treatment. The culture sample was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, and the collected pellets were washed twice with deionized water to elute the absorbed lignin on the surface of fungus mycelium. The washed cell pellets were collected and dried at 45 °C for 48 h for mycelial biomass dry weight assay. The supernatant and eluent were collected and lyophilized completely. The dried powder was weighed for degradation rate calculation as the following formula:
where M0 is the initial lignin weight, and Mn is the nth day sampling lignin residue weight.
The decolorization of the lignin culture sample was assayed according to the standard method of the Canadian Pulp and Paper Association [55]. All assays were performed with three replicates.
Ligninolytic enzyme assay
Laccase (Lac) activity was detected by using 2,2,-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) as substrate and monitoring the production of ABTS radical at 420 nm (ε420 = 36,000 M−1 cm−1) according to the method of Nakagawa et al. [56]. Lignin peroxidase (LiP) activity was assessed by monitoring oxidation of veratryl alcohol to veratraldehyde at 310 nm (ε310 = 9300 M−1 cm−1) based on the method of Kirk et al. [57]. Manganese peroxidase (MnP) activity was assayed by monitoring oxidation of 2,6-dimethyl phenol to coerulignone at 469 nm (ε469 = 49,600 M−1 cm−1) according to method of Wariishi et al. [58]. The amount of enzyme needed to produce 1 μM product per minute under the assay conditions was defined as one unit of enzyme activity.
Secretory proteins extraction and identification
The culture samples of fungus strains incubated in lignin-containing medium was withdrawn at 7th day and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm, 4 °C for 10 min. The collected supernatant was filtered through 0.45-μm membranes and was lyophilized completely. The dried powder was resuspended in a buffer containing 8 M urea, 4% (w/v) 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl) dimethylammonio] propanesulfonate, 40 mM dithiothreitol. Protein concentration was determined by a non-interference protein assay kit (Sangon Bio-tech, Shanghai, China). The peptide obtained by trypsin digestion was subjected to nano-liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (nanoLC–MS/MS). NanoLC–MS/MS analysis was performed on an Orbitrap Fusion Tribrid MS (Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with an UltiMate 3000 system according to the procedure described in our previous work [59]. The obtained raw MS/MS data were processed by Maxquant proteomics software (Version 1.6.4) against UniProt proteomes of Trametes genus. The parameters used for peptide identification was set as described in our previous work [59].
GC–MS analysis
The cultures used for GC–MS analysis were pretreated as previously described [60]. The procedure of GC–MS test was performed as described by Chen et al. [40]. The obtained mass spectra were compared with that of the NIST library available in the instrument and the retention time to the original standards.
FTIR analysis
The chemical structure changes of lignin before and after treated by strain were investigated by FTIR analysis. Samples were ground with dry KBr prior to test. FTIR analysis was conducted on A Varian 2000 FTIR spectrometer range from 4000 to 400 cm−1 at 4 cm−1 spectral resolution for 32 scans.
SEM analysis
The collected lignin samples were freeze-dried, then covered with gold to prevent buildup of static charges. SEM analysis was carried out with a JEOL JSM-7900F scanning electron microscopy (Tokyo, Japan).
2D-HSQC NMR analysis
Approximately 50 mg of dried lignin powder was dissolved in 0.5 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-d6 in an NMR tube. To promote the lignin solubility, the NMR tube was dipped into an ultrasonic bath for 3 h. 2D-HSQC NMR analysis was conducted on a Bruker AVANCE 400 MHz NMR spectrometer (Bruker BioSpin, Rheinstetten, Germany). The spectra were collected at 25 °C using a Bruker standard pulse sequence “hsqcetgpsisp2”. The procedure was performed as described by Ma et al. with slight modification [45]. The spectral widths of 1H and 13C were 5000 Hz and 18,000 Hz, respectively. A total of 2048 collected complex points with 1.5 s recycle delay were acquired for 1H dimension. The number of transients was 64 for 13C dimension with 256 time increments. The 1JCH was set to 145 Hz. HSQC correlation peaks were assigned by comparison with the literature reports [37, 61,62,63,64]. Semiquantitative analysis of volume intergrals of HSQC correlation peaks was conducted by MestReNova 11.0.4 as described by Ma et al. [45].
Py-GC/MS analysis
Analytical pyrolysis coupled to gas chromatography with mass spectrometeric detection was conducted as previously described with some modification [60]. Briefly, pyrolysis was performed at 500 °C for 1 min on PY-3030D pyrolyzer (Frontier Lab, Japan) coupled with a gas chromatography/mass spectrometer (7890B-5977A, Agilent Technologies, Germany). The chromatography was programmed from 40 °C to 150 °C at 5 °C/min, followed by 10 °C/min to 280 °C, and then held for 20 min. The chromatographic signals were identified by comparing the experimental mass spectrum with those reported in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) library. The relative abundance of each identified pyrolysate was calculated as the percentage of the sum of all peak areas.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed by Origin 9.0 software, and the experimental data were presented as the replicate mean ± standard deviation (SD).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information file.
Abbreviations
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GC–MS:
-
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron micrographs
- 2D-HSQC NMR:
-
Two-dimensional heteronuclear single quantum coherence NMR
- PDA:
-
Potato dextrose agar
- ITS:
-
Internal transcribed region sequence
- Lac:
-
Laccase
- LiP:
-
Lignin peroxidase
- MnP:
-
Manganese peroxidase
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- CGMCC:
-
China General Microbiological Culture Collection
- G:
-
Guaiacyl group
- S:
-
Syringyl group
- H:
-
p-Hydroxyphenyl group
- pCA:
-
p-Coumarates
- FA:
-
Ferulate
- py-GC–MS:
-
Pyrolysis gas chromatography–mass spectrometry
References
Bugg TD, Ahmad M, Hardiman EM, Rahmanpour R. Pathways for degradation of lignin in bacteria and fungi. Nat Prod Rep. 2011;28:1883–96.
Cho EJ, Trinh LTP, Song Y, Lee YG, Bae H-J. Bioconversion of biomass waste into high value chemicals. Bioresour Technol. 2020;298:122386.
Galbe M, Wallberg O. Pretreatment for biorefineries: a review of common methods for efficient utilisation of lignocellulosic materials. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019;12:294.
Yu X, Wei Z, Lu Z, Pei H, Wang H. Activation of lignin by selective oxidation: an emerging strategy for boosting lignin depolymerization to aromatics. Bioresour Technol. 2019;291:121885.
Weiss R, Guebitz GM, Pellis A, Nyanhongo GS. Harnessing the power of enzymes for tailoring and valorizing lignin. Trends Biotechnol. 2020;38:1215–31.
Venkatesagowda B. Enzymatic demethylation of lignin for potential biobased polymer applications. Fungal Biol Rev. 2019;33:190–224.
Wong SS, Shu R, Zhang J, Liu H, Yan N. Downstream processing of lignin derived feedstock into end products. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49:5510–60.
Chen Z, Wan C. Biological valorization strategies for converting lignin into fuels and chemicals. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;73:610–21.
Janusz G, Pawlik A, Sulej J, Swiderska-Burek U, Jarosz-Wilkolazka A, Paszczynski A. Lignin degradation: microorganisms, enzymes involved, genomes analysis and evolution. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017;41:941–62.
Kamimura N, Sakamoto S, Mitsuda N, Masai E, Kajita S. Advances in microbial lignin degradation and its applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019;56:179–86.
Asina F, Brzonova I, Voeller K, Kozliak E, Kubatova A, Yao B, et al. Biodegradation of lignin by fungi, bacteria and laccases. Bioresour Technol. 2016;220:414–24.
Jensen KA, Houtman CJ, Ryan ZC, Hammel KE. Pathways for extracellular fenton chemistry in the brown rot Basidiomycete Gloeophyllum trabeum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67:2705–11.
Arantes V, Milagres AMF, Filley TR, Goodell B. Lignocellulosic polysaccharides and lignin degradation by wood decay fungi: the relevance of nonenzymatic Fenton-based reactions. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;38:541–55.
Ravi K, García-Hidalgo J, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Lidén G. Conversion of lignin model compounds by Pseudomonas putida KT2440 and isolates from compost. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;101:5059–70.
Shi Y, Chai L, Tang C, Yang Z, Zhang H, Chen R, et al. Characterization and genomic analysis of kraft lignin biodegradation by the beta-proteobacterium Cupriavidus basilensis B-8. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013;6:1.
Sainsbury PD, Hardiman EM, Ahmad M, Otani H, Eltis LD, Bugg TDH. Breaking down lignin to high-value chemicals: the conversion of lignocellulose to vanillin in a gene deletion mutant of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8:2151–6.
Martínez AT, Rencoret J, Nieto L, Jiménez-Barbero J, Gutiérrez A, del Río JC. Selective lignin and polysaccharide removal in natural fungal decay of wood as evidenced by in situ structural analyses. Environ Microbiol. 2011;13:96–107.
Yelle DJ, Kapich AN, Houtman CJ, Lu F, Timokhin VI, Fort RC, et al. A highly diastereoselective oxidant contributes to ligninolysis by the white rot basidiomycete Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80:7536–44.
van Erven G, Hilgers R, Waard Pd, Gladbeek E-J, van Berkel WJH, Kabel MA. Elucidation of in situ ligninolysis mechanisms of the selective white-rot fungus Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2019;7:16757–64.
van Erven G, Wang J, Sun P, de Waard P, van der Putten J, Frissen GE, et al. Structural motifs of wheat straw lignin differ in susceptibility to degradation by the white-rot fungus Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7:20032–42.
Ponnusamy VK, Nguyen DD, Dharmaraja J, Shobana S, Banu JR, Saratale RG, et al. A review on lignin structure, pretreatments, fermentation reactions and biorefinery potential. Bioresour Technol. 2019;271:462–72.
Sharma A, Aggarwal NK, Yadav A. Isolation and screening of lignolytic fungi from various ecological niches. Univ J Microbiol Res. 2017;5:25–34.
Milenković I, Tomšovský M, Karadžić D, Veselinović M. Decline of Paulownia tomentosa caused by Trametes hirsuta in Serbia. For Pathol. 2018;48:e12438.
Dhakar K, Pandey A. Laccase production from a temperature and pH tolerant fungal strain of Trametes hirsuta (MTCC 11397). Enzyme Res. 2013;2013:869062.
Zhu D, Zhang P, Xie C, Zhang W, Sun J, Qian WJ, et al. Biodegradation of alkaline lignin by Bacillus ligniniphilus L1. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017;10:44.
Asina FNU, Brzonova I, Kozliak E, Kubátová A, Ji Y. Microbial treatment of industrial lignin: successes, problems and challenges. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;77:1179–205.
Ulmer DC, Leisola MSA, Schmidt BH, Fiechter A. Rapid degradation of isolated lignins by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983;45:1795–801.
Li C, Chen C, Wu X, Tsang CW, Mou J, Yan J, et al. Recent advancement in lignin biorefinery: with special focus on enzymatic degradation and valorization. Bioresour Technol. 2019;291:121898.
Zhang Y, Tang B, Du G. Self-induction system for cellulase production by cellobiose produced from glucose in Rhizopus stolonifer. Sci Rep. 2017;7:10161.
Monjed MK, Achour B, Robson GD, Pittman JK. Improved saccharification of Chlorella vulgaris biomass by fungal secreted enzymes for bioethanol production. Algal Res. 2021;58:102402.
Vasina DV, Moiseenko KV, Fedorova TV, Tyazhelova TV. Lignin-degrading peroxidases in white-rot fungus Trametes hirsuta 072. Absolute expression quantification of full multigene family. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0173813.
Vasina DV, Pavlov AR, Koroleva OV. Extracellular proteins of Trametes hirsuta st. 072 induced by copper ions and a lignocellulose substrate. BMC Microbiol. 2016;16:106.
Moiseenko KV, Glazunova OA, Savinova OS, Vasina DV, Zherebker AY, Kulikova NA, et al. Relation between lignin molecular profile and fungal exo-proteome during kraft lignin modification by Trametes hirsuta LE-BIN 072. Bioresour Technol. 2021;335:125229.
Savinova OS, Moiseenko KV, Vavilova EA, Tyazhelova TV, Vasina DV. Properties of two laccases from the Trametes hirsuta 072 multigene family: twins with different faces. Biochimie. 2017;142:183–90.
Reyes-Rivera J, Terrazas T. Lignin analysis by HPLC and FTIR. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1544:193–211.
Xu Z, Qin L, Cai M, Hua W, Jin M. Biodegradation of kraft lignin by newly isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas putida, and Ochrobactrum tritici strains. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018;25:14171–81.
Zhu D, Liang N, Zhang R, Ahmad F, Zhang W, Yang B, et al. Insight into depolymerization mechanism of bacterial laccase for lignin. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2020;8:12920–33.
Morya R, Sharma A, Kumar M, Tyagi B, Singh SS, Thakur IS. Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis and characterization: a proteogenomic and process optimization study for biovalorization of industrial lignin. Bioresour Technol. 2021;320:124439.
Linger JG, Vardon DR, Guarnieri MT, Karp EM, Hunsinger GB, Franden MA, et al. Lignin valorization through integrated biological funneling and chemical catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:12013–8.
Chen Y, Chai L, Tang C, Yang Z, Zheng Y, Shi Y, et al. Kraft lignin biodegradation by Novosphingobium sp. B-7 and analysis of the degradation process. Bioresour Technol. 2012;123:682–5.
Morya R, Kumar M, Singh SS, Thakur IS. Genomic analysis of Burkholderia sp. ISTR5 for biofunneling of lignin-derived compounds. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019;12:277.
Ravi K, Abdelaziz OY, Nobel M, Garcia-Hidalgo J, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Hulteberg CP, et al. Bacterial conversion of depolymerized Kraft lignin. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019;12:56.
Abdelaziz OY, Brink DP, Prothmann J, Ravi K, Sun M, Garcia-Hidalgo J, et al. Biological valorization of low molecular weight lignin. Biotechnol Adv. 2016;34:1318–46.
Christopher LP, Yao B, Ji Y. Lignin biodegradation with laccase-mediator systems. Front Energy Res. 2014;2:12.
Ma F, Huang X, Ke M, Shi Q, Chen Q, Shi C, et al. Role of selective fungal delignification in overcoming the saccharification recalcitrance of bamboo culms. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2017;5:8884–94.
Ma R, Guo M, Zhang X. Recent advances in oxidative valorization of lignin. Catal Today. 2018;302:50–60.
Patil ND, Yao SG, Meier MS, Mobley JK, Crocker M. Selective cleavage of the Cα–Cβ linkage in lignin model compounds via Baeyer-Villiger oxidation. Org Biomol Chem. 2015;13:3243–54.
Hedenstrom M, Wiklund-Lindstrom S, Oman T, Lu F, Gerber L, Schatz P, et al. Identification of lignin and polysaccharide modifications in Populus wood by chemometric analysis of 2D NMR spectra from dissolved cell walls. Mol Plant. 2009;2:933–42.
Tarasov D, Leitch M, Fatehi P. Lignin-carbohydrate complexes: properties, applications, analyses, and methods of extraction: a review. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018;11:269.
Rico A, Rencoret J, del Río JC, Martínez AT, Gutiérrez A. Pretreatment with laccase and a phenolic mediator degrades lignin and enhances saccharification of Eucalyptus feedstock. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018;11:269.
Rencoret J, Pereira A, Marques G, del Río JC, Martínez ÁT, Gutiérrez A. A commercial laccase-mediator system to delignify and improve saccharification of the fast-growing Paulownia fortunei (Seem.) Hemsl. Holzforschung. 2018;73:45–54.
van Bergen PF, Poole I, Ogilvie TMA, Caple C, Evershed RP. Evidence for demethylation of syringyl moieties in archaeological wood using pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2000;14:71–9.
Martinez AT, Camarero S, Gutiérrez A, Bocchini P, Galletti GC. Studies on wheat lignin degradation by Pleurotus species using analytical pyrolysis. J Anal Appl pyrolysis. 2001;58:401–11.
Lubbers RJM, Dilokpimol A, Visser J, Makela MR, Hilden KS, de Vries RP. A comparison between the homocyclic aromatic metabolic pathways from plant-derived compounds by bacteria and fungi. Biotechnol Adv. 2019;37:107396.
Shintani N, Shoda M. Decolorization of oxygen-delignified bleaching effluent and biobleaching of oxygen-delignified kraft pulp by non-white-rot fungus Geotrichum candidum Dec 1. J Environ Sci. 2013;25:S164–8.
Nakagawa Y, Sakamoto Y, Kikuchi S, Sato T, Yano A. A chimeric laccase with hybrid properties of the parental Lentinula edodes laccases. Microbiol Res. 2010;165:392–401.
Kirk TK, Croan S, Tien M. Production of multiple ligninases by Phanerochaete chrysosporium effect of selected growth conditions and use of a mutant strain. Enzyme Microb Technol. 1986;8:27–32.
Wariishi H, Valli K, Gold MH. Manganese(II) oxidation by manganese peroxidase from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:23688–95.
Ma J, Yue H, Li H, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Wang X, et al. Selective delignification of poplar wood with a newly isolated white-rot basidiomycete Peniophora incarnata T-7 by submerged fermentation to enhance saccharification. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021;14:135.
Ma J, Zhang K, Huang M, Hector SB, Liu B, Tong C, et al. Involvement of Fenton chemistry in rice straw degradation by the lignocellulolytic bacterium Pantoea ananatis Sd-1. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016;9:211.
Rencoret J, Pereira A, del Río JC, Martínez ÁT, Gutiérrez A. Delignification and saccharification enhancement of sugarcane byproducts by a laccase-based pretreatment. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2017;5:7145–54.
Zhao C, Huang J, Yang L, Yue F, Lu F. Revealing structural differences between alkaline and kraft lignins by HSQC NMR. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2019;58:5707–14.
Mattsson C, Andersson S-I, Belkheiri T, Åmand L-E, Olausson L, Vamling L, et al. Using 2D NMR to characterize the structure of the low and high molecular weight fractions of bio-oil obtained from LignoBoostTM kraft lignin depolymerized in subcritical water. Biomass Bioenerg. 2016;95:364–77.
Giummarella N, Pylypchuk IV, Sevastyanova O, Lawoko M. New structures in Eucalyptus kraft lignin with complex mechanistic implications. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng. 2020;8:10983–94.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900087), the Project of International Cooperation Base of Science and Technology Innovation on Forest Resource Biotechnology of Hunan Province (2018WK4008), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2020JJ5974, 2021JJ31151), Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (2017YFE0108100), Outstanding Youth Project of Hunan Provincial Education Department (18B169) and Aid Program for Science and Technology Innovative Team of Hunan Province (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JSM designed the experiments, carried out lignin degradation experiment, performed data analysis and drafted the manuscript. QL performed lignin structure characterization experiments. YJW, HMY, YHZ, MLS and SXW participated in FTIR, GC–MS and SEM analysis experiments and data processing. JSZ performed fungal strains isolation and identification and data analysis. GQL provided the original idea, supervised the research and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Detection of colorization and decolorization zone by T. hirsuta X-13 on guaiacol-containing (a and b) and Azure B-containing (c and d) PDA medium. A and C, control; B and D, inoculated with T. hirsuta X-13.
Additional file 2: Figure S2.
Morphologic analysis of T. hirsuta X-13. (a) Colony morphology of T. hirsuta X-13 grown on PDA medium plate. (b) Microscopic photograph of T. hirsuta X-13 mycelium.
Additional file 3: Table S1.
The percentage of main components in alkaline lignin.
Additional file 4:
The identified proteins from secretome of T. hirsuta X-13 in lignin-containing medium.
Additional file 5:
Functional classification of identified proteins from secretome of T. hirsuta X-13.
Additional file 6: Figure S3.
Distribution of the identified proteins based on functional classification.
Additional file 7: Table S2.
Identification of proteins involved in lignin degradation in the secretome of T. hirsuta X-13 in lignin-containing medium.
Additional file 8: Figure S4.
The total ion chromatograms of the control (a) and lignin samples treated with T. hirsuta X-13 for 13 days (b).
Additional file 9: Table S3.
The identified pyrolysates from lignin samples before and after treated by T. hirsuta X-13 at different time with relative peak areas.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Li, Q., Wu, Y. et al. Elucidation of ligninolysis mechanism of a newly isolated white-rot basidiomycete Trametes hirsuta X-13. Biotechnol Biofuels 14, 189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-021-02040-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-021-02040-7