Abstract
Background
Diabetes-related foot lesions are a major cause of non-traumatic lower limb amputations and are associated with a high re-amputation rate. Lesions can cause hindrance in activities of daily living, reduce physical function, and lower a patient’s quality of life. Physical therapy is necessary to prevent these limitations. Thus far, there has been limited investigation into the re-amputation rate in patients who have undergone physical therapy. This study aimed to elucidate modifiable risk factors for re-amputation in patients with minor amputations who were treated with physical therapy during their hospitalization.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of 245 consecutive hospitalized patients who presented to our Wound Care Center between January 2015 and February 2018 and received physical therapy after a minor amputation. Participants were identified from admission records to surgical and physical therapy units stored in the electronic medical records. We examined re-amputations that occurred in the ipsilateral lower extremity during the 1-year post-discharge outpatient period. The maximum follow-up period was set at 1 year. We used Cox proportional hazards analysis to examine factors affecting the risk of re-amputation.
Results
Of the 129 patients enrolled, 42 patients (32.5%) underwent re-amputations during an average observation period of 6.2 months (range, 2.1 to 10.9 months). The factors associated with re-amputation were a requirement for hemodialysis, ankle dorsiflexion angle, and the Functional Independence Measure (FIM) ambulation score.
Conclusions
In diabetes patients with minor amputations, a requirement for hemodialysis, ankle dorsiflexion angle, and the FIM ambulation score were shown to be modifiable risk factors for re-amputation. This emphasizes that maintaining vascular endothelial function through lower limb muscle exercises for hemodialysis, improving ankle mobility, and relieving plantar pressure during walking are necessary to reduce the risk of re-amputation. Patients with these risk factors should be encouraged to participate in physical therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In a survey of lower limb amputations in Japan, the amputation rate in the 1960s was 1.6/100,000 patients, and 70% of the amputations were caused by trauma; however, in the 2000s, the amputation rate was reported to be 5.8/100,000 patients, and the cause was peripheral circulatory disturbances in 66.2% of cases [1]. A prognostic study of amputee patients reported that the mean age of patients with foot amputations was 72.4 years and that the re-amputation rate was 18.2% [2].
A report examining the prognosis after minor amputation reported that 31.5% of patients required re-amputation within 2 years [3]. These reports indicate that amputees are older and have a higher short-term re-amputation rate.
After minor amputation, a patients’ quality of life is reduced, with limitations on their daily activities [4]. In addition, metabolic functions and microcirculatory systems are often impaired [5, 6], and postoperative rest can cause a disuse syndrome, such as lower limb muscle atrophy and reduced physical endurance, leading to a decreased walking ability and limitation in social life. With the decline in walking ability, nursing care may be required for daily life, which may increase social security costs.
In addition, plantar pressure relief during walking and maintaining ankle range of motion (ROM) plays an important role in preventing ulcers that may be a precursor for amputation [7, 8]. Previous studies have shown that the risk factors for re-amputation after minor amputation cases are age [9], wound depth [10], history of peripheral arterial disease [11], and wound infection [12].
Physical therapy may be required to prevent a decline in physical function, activities of daily living, and quality of life. However, there has been limited investigation into re-amputation in patients who have required physical therapy. Therefore, the present study aimed to elucidate modifiable risk factors of re-amputation in patients with a history of minor amputations who received physical therapy during their hospitalization.
Methods
Study design and participants
This single-center retrospective cohort study was conducted in the Wound Care Center of Oita Oka Hospital, a community medical support hospital with a multidisciplinary foot care team.
A total of 245 consecutive inpatients who presented to our Wound Care Center between January 2015 and February 2018 and who received physical therapy after revascularization and a minor amputation were included. Participants were identified using information from the admission records (to surgical and physical therapy units) stored electronically. We examined re-amputations in the ipsilateral lower extremity during the 1-year post-discharge outpatient care period.
In this study, a diabetes-related foot was defined as a plantar ulcer associated with neuropathy and peripheral artery disease in patients with diabetes [13]. The amputation region was defined as a minor amputation of the toes, rays, and metatarsal bones. Amputation below and above the knee was defined as major amputation [14]. We excluded patients with the following: (1) infection after minor amputation, (2) major amputation (below and above the knee), (3) death following discharge due to systemic complications, (4) use of a wheelchair for mobility before admission, (5) severe progression of dementia, (6) missing data, and (7) patients who did not visit the hospital for regular outpatient visits (1, 3, 6, or 12 months) after discharge. The reason for excluding patients with postoperative infections was that if an obvious wound infection appeared postoperatively, the rehearsal intervention was discontinued in view of the spread of infection. Patients who had difficulty in undergoing continuous physical therapy due to infection were excluded.
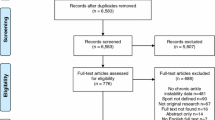
The date of death within 1 year after the minor amputation was confirmed by the medical information from the cooperating medical institutions. Finally, 129 patients were enrolled in this study (Fig. 1).
Data collection and definition
We collected basic data on all patients by reviewing electronic medical records and structured interviews that were conducted when they were admitted for the first amputation. The structured interview involved questions on age, sex, current medical history, cognitive functioning, pre-hospitalization living conditions, and mobility. Measurement items included participants’ basic and medical information, including physical function. Basic information included age, sex, body mass index (BMI), hospitalization days, physical therapy duration, the average length of daily physical therapy in minutes, non-weight-bearing duration, comorbidities (hypertension, heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), and the requirement (or no requirement) for hemodialysis.
The medical information included laboratory parameters including serum albumin, serum hemoglobin, blood glucose, C-reactive protein, white blood cell counts, and estimated glomerular filtration rate [15].
For data collection, we divided the patients into four groups as follows: The estimated eGFR (1) ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2, (2) 45–59.9 mL/min/1.73 m2, (3) 30–44.9 mL/min/1.73 m2, and (4) < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Lower limb blood flow data (skin perfusion pressure and ankle-brachial pressure index), Wound, Ischemia, foot Infection (WIfI) classification system [16], amputation region (toe, ray, and transmetatarsal) [14], foot deformity (Charcot’s joint [17], hallux valgus [18], hammer toe [19], and claw toe [20]). The deformity was determined by experienced plastic and orthopedic surgeons specializing in treating diabetes-related foot lesions based on X-ray images and clinical indicators.
X-ray radiographs were taken periodically before surgery and at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. As the only hospital specializing in podiatry in the prefecture, we regularly perform imaging evaluations as part of our regular practice. Based on the imaging findings, a multidisciplinary wound care team conference is held to evaluate the treatment strategy and degree of progression of the deformity. Physical function was determined by knee extension muscle strength [21], ROM in the ankle joint [22], presence or absence of plantar sensory disorder [23], and ambulation status were evaluated using the Functional Independence Measure (FIM) movement parameter ambulation score [24]. The measurement methods and definitions of the study items are shown in Table 1.
Main study outcome
In this study, all patients with minor amputations were followed up, with data collected from electronic medical records, for 1 year after surgery or until death. The endpoint was the presence or absence of re-amputation within 1 year after surgery. Re-amputation was defined as an amputation on the same side of the limb as the initial amputation. To detect the presence or absence of re-amputation, the operative information in the electronic medical record was checked; in addition, the date of amputation and the site of surgery were identified. Our Wound Care Center is the only facility of its kind in the prefecture; therefore, post-discharge outpatient follow-up is basically limited to our facility. As a rule, outpatient visits to the hospital are conducted at intervals of 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after discharge.
Physical therapy program
Physical therapy was provided to patients to improve their physical function and walking ability. The first postoperative day started with strength training and ROM exercises of the hip and knee joints, which were performed according to the level of pain experienced by the patient. Additionally, a walking practice started after wound healing. The physiotherapy session and physical function measurements were performed by two experienced staff physiotherapists.
Statistical analysis
Mann-Whitney U-test, t-test, and χ2 test were used to compare background characteristics and indices of physical function between the two groups with re-amputation histories versus groups with no re-amputation histories, depending on the data characteristics. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was also performed after adjusting for confounders by inputting sex [2], age [10], serum albumin levels [25], and knee extension muscle strength [26] as covariates with reference to items that were significant in univariate analysis and previous studies to identify factors associated with re-amputation. To account for multicollinearity in this process, variables considered clinically significant were left in the model if the absolute value of the correlation coefficients between the independent variables was greater than 0.7. In addition, incomplete data sets (missing data) were excluded from the multivariate Cox regression analysis for case-pair-wise deletions.
The incidence of the presence or absence of re-amputation was calculated using Kaplan-Meier curves for the extracted factors. Differences between groups were estimated using the log-rank test. All statistical analyses were performed using R version 3.2.5 (R Foundation for Statistics Computing, Vienna, Austria). The significance level was set to P < 0.05.
Results
Of the 129 patients enrolled, 42 (32.5%) underwent re-amputation during an average observation period of 6.2 months (range, 2.1 to 10.9 months). Demographic and medical information of the patients is shown in Table 2. The re-amputation group exhibited significantly higher rates of hemodialysis and the FIM ambulation score than the no re-amputation group. Patients in the no re-amputation group demonstrated better ankle dorsiflexion ROM. Univariate Cox regression analysis showed that hemodialysis, ankle dorsiflexion angle, and the FIM ambulation score were potential risk factors for re-amputation. Subsequently, multivariate Cox regression analysis adjusted for age, sex, serum albumin level, and knee extension muscle strength as covariates showed that hemodialysis (HR 2.20, 95% CI 1.12–4.34), ankle dorsiflexion angle (HR 5.82, 95% CI 2.93–11.58), and the FIM ambulation score (HR 3.85, 95% CI 2.00–7.39) were identified as significant risk factors for re-amputation (Table 3). The Kaplan-Meier curves illustrated in Figs. 2, 3, and 4 show the cumulative incidence of re-amputation after minor amputation. Survival analysis using Kaplan-Meier log-rank test showed that the requirement for hemodialysis (Fig. 2), ankle dorsiflexion angle (Fig. 3), and the FIM ambulation score (Fig. 4) were significantly associated with survival (P < 0.05).
Discussion
The present study examined factors that influence re-amputation within 1 year of discharge in patients who had undergone minor amputations. We revealed that the requirement for hemodialysis, ankle dorsiflexion angle, and the FIM ambulation score were associated with re-amputation in this patient population significantly (P < 0.05). The re-amputation rate was 32.5% within 1 year of discharge, similar to previous findings [27].
Regarding the relationship between hemodialysis and re-amputation, it has been reported that hemodialysis caused periodic fluid fluctuations and worsened microcirculation, thereby promoting blood circulation disorders [28]. Miyajima et al. reported that hemodialysis was also an independent risk factor of major limb amputation [29]. Okamoto et al. reported that approximately 40% of 140 patients who had undergone hemodialysis had peripheral arterial disease [30]. These findings were similar to this study. We, therefore, determined that patients who had undergone hemodialysis may have undergone re-amputation due to peripheral arterial disease. However, it has been reported that diabetes patients on dialysis often have severe calcification of central arteries; thus, accurate ABI values may not be obtained, and they pseudo-normalize [31]. Therefore, we believe that the risk of peripheral vascular disease may be underestimated in the results of this study.
Regarding the association between ankle dorsiflexion angle and re-amputation, Fernando reported that the incidence of ulcers in patients with diabetes, who had limited joint ROM, was as high as 65%, compared to 5% of those with an unrestricted ROM [32]. Lavery et al. reported that minor amputations are a risk factor for ulcer recurrence [33]. In the present study, the recurrence of ulceration after a minor amputation may have led to re-amputation.
Furthermore, Eduardo et al. reported that patients with diabetes who had minor amputations had an average ankle dorsiflexion angle of 9.6° [34]. The mean dorsiflexion angle in the re-amputation group in this study was 2.6°, which was very low compared to that reported in previous studies.
In this study, all patients received foot ROM training early after surgery, and the physical therapy duration was similar for both groups. It has been suggested that regular screening for preoperative range of motion limitations and postoperative ROM practice time should be expanded since interventions after surgery may not improve foot mobility sufficiently.
Secondly, about the association between the FIM ambulation score and re-amputation, the re-amputation group had a higher FIM ambulation score. The re-amputation group had a median FIM ambulation score of 6 and were able to ambulate independently to 50 m using walking aids. Therefore, post-discharge mobility is assessed mainly by walking distance, which may increase following re-amputation compared to that observed in the no re-amputation group.
In addition, a study reported that an increase in cumulative plantar tissue stress associated with the extent of walking distance resulted in wound formation [35]. Therefore, this report suggests that walking with a limited ankle ROM may lead to an increase in cumulative plantar tissue stress. Finally, this finding suggests that physical therapy after minor amputations should incorporate programs that maintaining vascular endothelial function through lower limb muscle exercises for hemodialysis and include activities that maintain ankle mobility. There is also a need to teach adequate plantar pressure relief methods during walking if there is a high risk of revision surgery.
There are several limitations to this study. First, our results were obtained from a single institution. Similar findings derived from other facilities are needed to validate ours for generalizability. Second, the definition of re-amputation was limited to the original hospital only. Thirdly, it was not possible to evaluate the foot pressure. Further, patients who did not receive physical therapy were excluded. In addition, we did not investigate the living conditions and self-management status of patients after discharge from the hospital.
Moreover, the results may not be generalizable to all hospitalized patients with minor amputations; thus, further longitudinal studies with larger samples in multiple hospital settings are required to investigate the re-amputation rates in hospitalized patients with minor amputations.
Conclusions
Diabetes patients with minor amputations, a requirement for hemodialysis, ankle dorsiflexion angle, and the FIM ambulation score were shown to be modifiable risk factors of re-amputation. This highlights that maintaining vascular endothelial function through lower limb muscle exercises for hemodialysis, improving ankle mobility, and relieving plantar pressure during walking is necessary to reduce the risk of re-amputation. Patients with these risk factors should be encouraged to participate in physical therapy. Further studies with larger samples are needed to confirm our results.
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- FIM:
-
Functional Independence Measure
- ROM:
-
Range of motion
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- WIfI:
-
Wound, Ischemia, foot Infection
References
Ohmine S, Kimura Y, Saeki S, Hachisuka K. Community-based survey of amputation derived from the physically disabled person’s certification in Kitakyushu City, Japan. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2012;36:196–202.
Endoh S, Yamana H, Nakahara Y, Matsui H, Fushimi K, Yasunaga H, Haga N. Risk factors for in-hospital mortality and reamputation following lower limb amputation. Prog Rehabil. 2017;2:20170015.
Matsuzaki K, Miyamoto A, Hakamata N, Fukuda M, Yamauchi Y, Akita T, et al. Diabetic foot wounds in haemodialysis patients: 2-year outcome after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and minor amputation. Int Wound J. 2012;9:693–700.
NICE clinical guideline NG19. Diabetes. Diabetic foot problems: prevention and management. National Institute of Health and Care Excellence, 2016. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng19/resources/diabetic-foot-problems-prevention-and-management-pdf-1837279828933. Accessed 1 Oct 2020.
Anderson JL, Halperin JL, Albert N, Bozkurt B, Brindis RG, Curtis LH, et al. Management of patients with peripheral artery disease (compilation of 2005 and 2011 ACCF/AHA guideline recommendations): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1555–70.
Schaper NC, van Netten JJ, Apelqvist J, Bus SA, Hinchliffe RJ, Lipsky BA, IWGDF Editorial Board. Practical guidelines on the prevention and management of diabetic foot disease (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36:e3266.
Kanade RV, van Deursen RW, Harding K, Price P. Walking performance in people with diabetic neuropathy: benefits and threats. Diabetologia. 2006;49:1747–54.
Rao SR, Saltzman CL, Wilken J, Yak HJ. Increased passive ankle stiffness and reduced dorsiflexion range of motion in individuals with diabetes mellitus. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27:617–22.
Ohsawa S, Inamori Y, Fukuda K, Hirotuji M. Lower limb amputation for diabetic foot. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001;121:186–90.
Skoutas D, Papanas N, Georgiadis GS, Zervas V, Manes C, Maltezos E, et al. Risk factors for ipsilateral reamputation in patients with diabetic foot lesions. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2009;8:69–74.
Nerone VS, Springer KD, Woodruff DM, Atway SA. Reamputation after minor foot amputation in diabetic patients: risk factors leading to limb loss. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013;52:184–7.
Acar E, Kacıra BK. Predictors of lower extremity amputation and reamputation associated with the diabetic foot. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56:1218–22.
Alavi A, Sibbald RG, Mayer D, Goodman L, Botros M, Armstrong DG, et al. Diabetic foot ulcers Part I. Pathophysiology and prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:1-e.
Kim YK, Lee HS, Ryu JJ, In Lee H, Seo SG. Sarcopenia increases the risk for mortality in patients who undergo amputation for diabetic foot. J Foot Ankle Res. 2018;11:32.
Roshanravan B, Khatri M, Robinson-Cohen C, Levin G, Patel KV, de Boer IH, et al. A prospective study of frailty in nephrology-referred patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:912–21.
Mills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, Pomposelli FB, Schanzer A, Sidawy AN, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection (WIfI). J Vasc Surg. 2014;59:220–34.
Ergen FB, Sanverdi SE, Oznur A. Charcot foot in diabetes and an update on imaging. Diabet Foot Ankle. 2013;4:21884.
Nishimura A, Fukuda A, Nakazora S, Uchida A, Sudo A, Kato K, et al. Prevalence of hallux valgus and risk factors among Japanese community dwellers. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19:257–62.
DiPreta JA. Metatarsalgia, lesser toe deformities, and associated disorders of the forefoot. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98:233–51.
Schrier JC, Verheyen CC, Louwerens JW. Definitions of hammer toe and claw toe: an evaluation of the literature. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2009;99:194–7.
Hirano M, Katoh M, Gomi M, Arai S. Validity and reliability of isometric knee extension muscle strength measurements using a belt-stabilized hand-held dynamometer: a comparison with the measurement using an isokinetic dynamometer in a sitting posture. J Phys Ther Sci. 2020;32:120–4.
Lázaro-Martínez JL, Aragón-Sánchez J, Alvaro-Afonso FJ, García-Morales E, García-Álvarez Y, Molines-Barroso RJ. The best way to reduce reulcerations: if you understand biomechanics of the diabetic foot, you can do it. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2014;13:294–319.
Feng Y, Schlösser FJ, Sumpio BE. The Semmes Weinstein monofilament examination as a screening tool for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Vasc Surg. 2009;50:675–82.
Ottenbacher KJ, Hsu Y, Granger CV, Fiedler RC. The reliability of the functional independence measure: a quantitative review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996;77:1226–32.
Eneroth M, Apelqvist J, Stenström A. Clinical characteristics and outcome in 223 diabetic patients with deep foot infections. Foot Ankle Int. 1997;18:716–22.
Nomura T, Kawae T, Kataoka H, Ikeda Y. Aging, physical activity, and diabetic complications related to loss of muscle strength in patients with type 2 diabetes. Phys Ther Res. 2018;21:33–8.
Izumi Y, Satterfield K, Lee S, Harkless LB. Risk of reamputation in diabetic patients stratified by limb and level of amputation: a 10-year observation. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:566–70.
Shimazaki M, Matsuki T, Yamauchi K, Iwata M, Takahashi H, Genda S, et al. Assessment of lower limb ischemia with measurement of skin perfusion pressure in patients on hemodialysis. Ther Apher Dial. 2007;11:196–201.
Miyajima S, Shirai A, Yamamoto S, Okada N, Matsushita T. Risk factors for major limb amputations in diabetic foot gangrene patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;71:272–9.
Okamoto K, Oka M, Maesato K, Ikee R, Mano T, Moriya H, et al. Peripheral arterial occlusive disease is more prevalent in patients with hemodialysis: comparison with the findings of multidetector-row computed tomography. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48:269–76.
Ohtake T, Oka M, Ikee R, Mochida Y, Ishioka K, Moriya H, et al. Impact of lower limbs’ arterial calcification on the prevalence and severity of PAD in patients on hemodialysis. J Vasc Surg. 2011;53:676–83.
Fernando DJ, Masson EA, Veves A, Boulton AJ. Relationship of limited joint mobility to abnormal foot pressures and diabetic foot ulceration. Diabetes Care. 1991;14:8–11.
Lavery LA, Lavery DC, Quebedeax-Farnham TL. Increased foot pressures after great toe amputation in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:1460–2.
Simón-Pérez E, Simón-Pérez C, Alonso-Peña D, Pontón-Cortina A, Chicharro-Luna E, Martínez-Nova A, et al. Stiffness degree of ankle range of motion in diabetic patients with atypical amputation. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2020;66:216–21.
Maluf KS, Mueller MJ. Comparison of physical activity and cumulative plantar tissue stress among subjects with and without diabetes mellitus and a history of recurrent plantar ulcers. Clin Biomech. 2003;18:567–5.
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of the Department of Rehabilitation, Oita Oka Hospital, for their assistance, and Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SI and TH were involved in study conception and design, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, and drafting the manuscript. KS, MF, and MO were involved in data interpretation and contributed to drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in Brazil in 2013), and approval was obtained from the Ethical Committee of the Oita Oka Hospital (approval number: B0018). In place of informed consent from every participant, consent was sought by publishing details of the study on the homepage of the research institute website, as well as on-site posting in the facility.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Imaoka, S., Sato, K., Furukawa, M. et al. Re-amputation in patients with diabetes-related minor amputations who underwent physical therapy during their hospitalization. J Foot Ankle Res 14, 14 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13047-021-00454-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13047-021-00454-y