Abstract
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a progressive interstitial inflammatory disease with a high mortality rate. Patients with PF commonly experience a chronic dry cough and progressive dyspnoea for years without effective mitigation. The pathogenesis of PF is believed to be associated with dysfunctional macrophage polarization, fibroblast proliferation, and the loss of epithelial cells. Thus, it is of great importance and necessity to explore the interactions among macrophages, fibroblasts, and alveolar epithelial cells in lung fibrosis, as well as in the pro-fibrotic microenvironment. In this review, we discuss the latest studies that have investigated macrophage polarization and activation of non-immune cells in the context of PF pathogenesis and progression. Next, we discuss how profibrotic cellular crosstalk is promoted in the PF microenvironment by multiple cytokines, chemokines, and signalling pathways. And finally, we discuss the potential mechanisms of fibrogenesis development and efficient therapeutic strategies for the disease. Herein, we provide a comprehensive summary of the vital role of macrophage polarization in PF and its profibrotic crosstalk with fibroblasts and alveolar epithelial cells and suggest potential treatment strategies to target their cellular communication in the microenvironment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a group of progressive terminal lung diseases that do not currently have an effective treatment. Each year in Europe alone, the number of new cases diagnosed with idiopathic PF (IPF) is more than 40,000 [1], and the average survival of patients with PF is normally 3–5 years after diagnosis [2], although the course of disease varies among individuals. Nonspecific syndromes, such as dry cough and progressive dyspnoea, may cause clinicians to fail to consider the diagnosis of PF in practice [3]. Typically, advanced age (normally > 65 years) is considered a high-risk factor [4] for the development of PF. The aging population globally and increasing rates of hospital admissions also indicate the burden of this disease. Pharmacologic treatments, such as pirfenidone [5] and nintedanib [6], mitigate the worsening of lung function but do not improve the average survival. Therefore, the need for more effective and safe treatments remains a challenge for the management of PF.
Based on the latest research on laboratory animals and clinical experiments, the pathological progress of PF is not only an outcome of chronic inflammatory disorders, but also an unbalanced epithelial damage/injury response following many types of tissue injuries in the lung microenvironment [7]. In parallel, histopathological studies [8] have demonstrated dysregulated macrophage polarization and abnormal proliferation of non-immune cells, such as alveolar epithelial cells (AECs), fibroblasts, and mesenchymal stem cells. Many cellular crosstalk events, which occur intermittently and repeatedly over time, drive uncontrolled senescence, metabolism, and other processes, leading to aberrant wound repair [9]. Following injury to the alveolar epithelium, dysfunction of lung homeostasis, cytokines, and growth factors drive signalling to initiate various repair and immune pathways that contribute to the fibrotic microenvironment, which is characterised by macrophage recruitment, fibroblast accumulation, and extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition. Recent evidence indicates that macrophages exhibit anti-fibrotic properties as a result of the delivery of exosomes to AECs and lung fibroblasts [10] or polarization among different phenotypes [11]. The findings, coupled with experimental data showing that macrophage polarization participates in the lung fibrotic microenvironment and progression through the secretion and submission of pro-fibrotic mediators among nonimmune cells, has increased interest on the role of crosstalk between macrophages and non-immune cells in PF.
In this review, we discuss the latest studies that have shown the unique role of macrophage polarization and the activation of non-immune cells in the pathogenesis and progression of PF, their cellular crosstalk at the molecular level, and various signalling pathways and mechanisms that may be involved in lung fibrosis. Finally, we provide perspective on the remaining questions and future treatment targets within the scope of macrophage polarization and cellular crosstalk in the PF microenvironment.
Macrophage polarization promotes fibrotic progression
It has been long established that macrophages are the primary messengers in chronic inflammation and fibrotic progression [12], which induce injury and abnormal signals. Several single-cell RNA sequencing studies have investigated the heterogeneity within alveolar macrophages (AMs), fibroblasts, and epithelial cells in the lungs of human donors with PF [13]. These studies have shown that AMs consist of two distinct populations: tissue-resident AMs and monocyte-derived AMs [14]. Single-cell reports have further demonstrated that the selective deletion of pro-fibrotic genes in monocyte-derived AMs accelerates progressive fibrosis. When epithelial injury promotes fibrosis during COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the accumulation of monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) has performed a more profibrotic transcriptional gene sets than other macrophage populations [15] against foreign stimulation of the immune system and are activated into different phenotypes. Apart from the classical pro-inflammatory M1 and alternative anti-inflammatory/pro-fibrotic M2 types, many other phenotypes (such as M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d) participate in cell communication between macrophages and the lung microenvironment by regulating tissue regeneration and growth factor levels [16]. Current investigations of AM behaviour normally fall under the M1–M2 paradigm, which establishes that macrophages can exhibit opposite phenotypes in various disease states by repolarization [16].
The role of macrophages in PF
Resident tissue macrophages, which are widely recognized for their essential roles in host defense, inflammatory response, and microenvironment homeostasis, consist of AMs in the alveolar space and interstitial macrophages (IMs) in the pulmonary interstitial matrix [17]. Nevertheless, resident tissue macrophages would be replaced by MDMs under the stimulation of inflammation or injury, and the MDMs may take over the function of resident tissue macrophages. As observed in respiratory viral infective models [18], excessive and uncontrolled release of proinflammatory cytokines by monocyte-derived AMs can accelerate lung injury than original AMs. Consequently, the overactivation of macrophages may play a critical role in PF pathogenesis.
As the only cell population exposed to air, AMs are key cells that induce early biological effects in the lungs. By using the CD11b-diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) in transgenic mice to establish an IL-13-dependent model, Borthwick et al. [19] demonstrated that lung fibrosis and inflammation crucially rely on monocyte-derived AMs to maintain type-2 immunity, and AMs may harness this role by regulating chemokine production and recruiting effector T cells to the lungs. AMs produce various growth factors or cytokines that influence the maintenance of immune responses; however, both biophysical and biochemical signals can also regulate the phenotypes of AMs to facilitate the progression of PF. Usually, the ECM is a structural scaffold for cells to adhere to and receive mechanical stimulation, and its pathological remodelling leads to the transformation of AMs. After seeding with radiation-induced decellularised ECM, AMs polarise to M1 but not M2 via the integrin-dependent activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) [20], which aggravates the infiltration of inflammatory cells. In addition to normal inflammatory signals, inflammasomes (e.g., NLRP3) that undergo pyroptosis also contribute to the activation and pro-fibrotic effects of AMs [21, 22]. Furthermore, they accumulate IL-1b and IL-18 in macrophages and thereby stimulate the release of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), which directly triggers fibrosis progression [23].
The pro-fibrotic property of AMs is related to lipid metabolic imbalance, including the ‘cellular response to fatty acids’ and ‘positive regulation of lipid metabolic processes’ [24]. In a murine model, Romero et al. [25] observed that the mRNA levels of lipogenic genes decreased after bleomycin injury but bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) lipid levels increased. When co-cultured with the BAL lipid extraction, AMs have been observed to polarise into the M2 phenotype and display excessive production of TGF-β. The authors deduced that abnormal lipid surfactants accumulated and were oxidised in the alveolar space and then mediated the transformation of AMs into foam cells, leading to the final pro-fibrotic phenotype. It has also been reported that apolipoprotein E (ApoE) from monocyte-derived AMs impairs the progression of lung fibrosis by inducing Collagen I phagocytosis in vitro and in vivo; this process depends on the key lipid receptor low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 [26]. These findings suggest that the modulation of the lipid metabolism process through AMs may be a novel target for treating PF.
Compared with AMs, IMs were only discovered a few decades ago, which is partly due to the small number of cells and the inability to collect them from samples such as bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) [27]. Using single-cell transcriptome technology, various subsets of IMs have been isolated from normal murine lungs [28], and two IMs subpopulations arising from tissue-recruited monocytes express higher levels of genes contributing to wound healing, repair, and fibrosis. Simultaneously, it has been identified that the secreted levels of IL-6 and IL-10, as well as IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) were higher in IMs than in AMs, which suggests that IMs are an anti-inflammatory phenotype in disease [29]. Moreover, IMs isolated from radiation-induced lung fibrosis mouse models exhibit a pro-fibrotic ability by activating myofibroblast differentiation, and the specific depletion of IMs has been shown to inhibit fibrotic progress in vivo [30]. IM isolated from murine models have demonstrated higher expression of arginase (Arg)-1, a marker of the M2 phenotype, than AMs, and IMs with specific depletion with a CSF1R neutralising antibody exerts anti-fibrotic activity. However, it is still unclear whether macrophages have the same characteristics and transformation properties in humans as in mice. The role of these cells after chronic inflammation also remains unclear [31].
Modulation of macrophage polarization in PF
Considering macrophages are highly heterogeneous plastic cells in the microenvironment, they are believed to play vital roles not only in pulmonary homeostasis but also in inflammatory and fibrotic progression. Macrophages can transform from one phenotype to another, or even vice versa, under cytokine stimulation [32]. According to the classic M1/M2 macrophage paradigm, researchers normally use the term ‘polarization’ to define this perturbation of macrophages with multiple stimuli producing various patterns of gene and protein expression [33]. A growing body of evidence supports the role of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis of PF.
M1 macrophage polarization mostly activates inflammatory processes which can be classically induced by LPS and IFN-γ. By inducing and releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines with chemokines such as IL-1β and TNF- α, M1 macrophage can mediate tissue injury and initiate an inflammatory response [34]. Myocyte enhancer factor 2C can modulate M1 macrophage polarization in an IL-12-dependent manner [35]. Moreover, using public mouse transcriptomic data, Orecchioni et al. analysed and compared different gene signatures between activated M1 macrophages in vivo and in vitro and demonstrated that M1-polarised mice responded by upregulating many pro-inflammatory genes that are positively correlated with IL12/arginase [36]. Upregulated genes, both in vivo and in vitro, were actively involved in the modulation and polarization of macrophages. Interestingly, their expression is mediated by the Janus kinase (Jak2) JAK/signal and signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat1/Stat2) pathway [37]. The findings were further supported by studies indicating that JAK inhibitors (e.g., ruxolitinib, tofacitinib, and itacitinib) can exert anti-inflammatory effects on M1 macrophages and modulate lung fibrogenesis in a model of HOCl-induced ILD by diminishing the expression of polarised markers and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as CD86, MHCII, IL-6, and TNFα [38]. Thus, the polarization of M1 macrophages in lung injury serves as an indicator of a modest inflammatory response with high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with Th1/Th2 immune responses [39]. Nevertheless, a sustained inflammatory response would provoke the progression of interstitial fibrosis. In the early stages of inflammation and aberrant healing, there is enrichment of pro-fibrotic exudate macrophages [40] and polarization from AMs to M1 macrophages, as observed in microscopic sections [41]. Another study found that the Mo and/or Cd induced injury may cause macrophages to polarise toward M1 via the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway, leading to lung fibrosis progression by increasing the expression levels of TGF-β1, Smad2, and Smad3 [42]. Collectively, the experimental data verify the specific role of M1 macrophage polarization in the early inflammatory features of PF; however, it is still unclear whether M1 macrophage polarization participates in other phenotypes that promote lung fibrosis. The mechanical contributions of the matrix, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction to M1 macrophage polarization require further investigation.
Cumulative evidence has shown that the M2 rather than the M1 phenotype is dominant during the pathological process of PF [43]. From the favoured conceptual model of the lung fibrotic progress, it has been posited that M2 macrophage polarization promotes the secretion of pro-fibrotic mediators, especially TGF-β, which lead to the deposition of interstitial fibrosis [44]. Wang et al. demonstrated a dramatic increase in the number of M2 macrophages in the BALF and lung tissues of mice with fibrosis induced by high tidal volume–mechanical ventilation [45]. The results also showed that persistent tilt polarization toward M2 macrophages was associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) by upregulating the expression of TGF-β1 and p-Smad2/3. In that regard, AMs have been shown to promote SiO2-induced PF in a series of chain reactions including those undergoing M2 polarization, synthesising into TGF-β1 precursors, and then transforming into myofibroblasts [46]. However, multiple studies have investigated the modulative effects of cytokines and immune cells on M2 macrophages in the lung microenvironment. The polarization of macrophages toward the M2 phenotype can be induced by Th2 cytokines such as IL-4 and 13 [47]. Moreover, NKT cells have been shown to exhibit a protective role in a bleomycin-induced model by decreasing the Th2 milieu, inhibiting M2 polarization, and eventually alleviating PF [48]. Several independent lines of evidence suggest that the dysregulated action of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) implicated in PF may play a central role in its associated pathogenesis. MMP-10 can promote macrophage migration and induce macrophage polarization into an M2 phenotype through the upregulation of collagenase activity [49]. In bleomycin-treated mice, excessive MMP-28 expression polarises M1 macrophages into M2 phenotypes and activates fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, boosting fibrotic progression [50]. Such events ultimately disrupt the balance between pro-fibrotic and anti-fibrotic mediators, resulting in an aberrant repair process in PF [51].
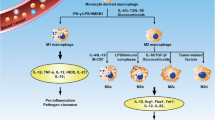
Furthermore, macrophage polarization is widely believed to be a dynamic process. In this regard, hyperactive cytokines and immune cells in the lung microenvironment contribute to pro-fibrotic polarization of macrophages, which aggravates the imbalance between the M1 and M2 phenotypes, eventually leading to progressive PF. This complementary relationship between various macrophages could be a target for future treatment strategies. Specifically, blocking specific macrophage-polarised pathways may aid in the treatment of PF. All significant mechanisms and regulators mentioned above in macrophage polarization through PF progress are illustrated in Fig. 1 and Table 1.
Schematic overview of major mechanisms and key regulators in macrophage polarization, fibroblast activation and AEC transformation within PF microenvironment. (IL: interleukin; ECM: extracellular matrix; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-beta; TNF α: Tumor Necrosis Factor-α; NF κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells; NLRP3: NLR Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3; ApoE: apolipoprotein E; LPR1: lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; TLR: Toll-like receptors; CSF1R: clinically available colony-stimulating factor receptor-1; LPS: lipopolysaccharides; IFN-γ: interferon-γ; MEF2C: myocyte enhancer factor 2 C; STAT6: Signal Transducer And Activator Of Transcription 6; MMP: matrix metalloproteinases; CXCR4: C-X-C receptor 4; CXCL: C-X-C motif ligand; ECM: extracellular matrix; YAP: Yes-Associated Protein; TAZ: Tafazzin; FMT: fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transformation; PI3K: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; FAP: fibroblast activation protein; JNK: JUN N -terminal kinases; ECM: extracellular matrix; JNK: JUN N -terminal kinases; WISP-1: WNT1inducible-signaling pathway protein 1; SASP: senescence-associated secretory phenotype; IGF-1: insulin like growth factor 1; JAK/STAT: Janus tyrosine Kinase-Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription; MFN: mitochondrial fusion proteins mitofusin)
The role of cellular crosstalk in the PF microenvironment
Activation of fibroblasts in PF
Considering chronic epithelial injury and dysfunctional healing both trigger the fibrotic process, fibroblasts, one of the major non-immune cell types involved in wound healing, play a critical role in the PF microenvironment. Based on scRNA-seq analysis and DNA methylation of PF fibroblast phenotypes, activated myofibroblasts are increasingly viewed as heterogeneous, with profibrotic properties [52, 53]. The activation of unremitting fibroblasts in PF consists of fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transformation (FMT), migration, resistance to apoptotic clearance, and excessive deposition of ECM proteins. Further research has highlighted the potential application of myofibroblasts as a primary indicator of ECM deposition in fibrosis and as PF effector cells with a fibroblast-synthesizing capacity [54, 55]. In addition, previous in vitro studies have shown that several chemokines, including CCL12, CXCL4, and CCL1 [56,57,58], drive the fibrotic process by recruiting and activating fibroblasts at different PF stages. Furthermore, there is a strong link between ECM stiffness and TGF-β1-induced fibroblast differentiation, which suggests the capacity of the ECM to dictate FMT processes and promote progressive PF [59]. Recent reports have also indicated that the close association between long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and PF development contributes to fibroblast activation, particularly by acting as key mediators, similar to lncIAPF [60], lncPFAR [61], and lncRNA DNM3OS [62], which regulate autophagy or cellular crosstalk. The evolving concept with fibroblast activation mechanisms underlying PF is regulated by multiple signalling pathways simultaneously. For example, the Notch signalling cascade has been involved in lung myofibroblast differentiation [63]; particularly, the deficiency of Notch3 has protected lung tissues from fibrotic injury by reducing collagen deposition and α-SMA-positive myofibroblast release following bleomycin administration [64, 65]. In view of the significance of Notch3 in the activation of fibroblasts, it might be a therapeutic target inhibiting Notch3 against PF. Furthermore, the inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) on fibroblast activation protein would suppress the production of hydroxyproline (a major building block of collagen), reduce collagen deposition, and increase mice survival [66]. The reactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is also associated with pro-fibrotic cellular functions, including EMT and myofibroblast differentiation in the PF microenvironment [67]. Therefore, stimulation of the above signalling molecules or pathways may impact the initiation of the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts in the lung interstitium, and delineation of the communication between macrophages and fibroblasts throughout PF would lead to better and more specific medication-based treatment strategies. All significant mechanisms and regulators mentioned above in the activation of fibroblasts through PF progress are illustrated in Fig. 1 and Table 2.
Macrophage-fibroblast crosstalk in PF
Several metabolites and soluble paracrine factors produced by macrophages are conventionally viewed as essential mediators in the biological switch between macrophage polarization and fibroblast activation, or macrophage-fibroblast crosstalk, in the pathological progression of PF. S100a4, also known as fibroblast-specific protein-1, was initially regarded as a protein specifically expressed by fibroblasts, whereas current experiments indicate that it can induce mesenchymal progenitor cell fibrogenicity in idiopathic PF [76] and also coincides with the presence of macrophages [77]. S100a4 expression was significantly up-regulated by M2 polarised AMs from IFN-γR−/− mice with MHV-68. Conditioned media with the presence of recombinant S100a4 protein increase the production of pro-fibrotic cytokines such as α-SMA and collagen I in primary mouse lung fibroblasts after 24 and 48 h of exposure, which ultimately promotes the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis via fibroblast activation, migration, and FMT [78]. Overall, the results suggest that S100a4 released from macrophages contributes to PF by promoting fibroblast differentiation. Nevertheless, the abundant expression of CX3CR1 in macrophages has prompted researchers to evaluate the role of the CX3CL1–CX3CR1 axis in PF [79]. Although CX3CR1 deficiency may not have an impact on the macrophage population after BLM administration, it can still affect macrophage polarization, and subsequent fibrotic progresses, such as myofibroblast activation. By utilising co-culture models to analyse the interaction between macrophages and fibroblasts, Li et al. have explained the mechanisms underlying macrophage-induced PF that macrophage-derived TSLP and MMP9 jointly contribute to lung fibrosis by promoting EMT process and fibroblasts migration [80].
In some conditions, neither pro-inflammatory cytokine deficiency nor steroid and immunosuppressive therapies can limit PF. Based on the current research, it is vital to consider the possibility that the presence of an immunoregulatory microenvironment, which mainly comprises regulatory lymphocytes and myeloid cells, may be associated with lung pathological processes. Within the type-2 immune response, IL-10 is an inducer of fibrogenic particles, especially M2-like and Th2-like pro-fibrotic cells [81]. Consistent with the major profibrogenic cytokine TGF-β1, it has been found that the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 is produced by alveolar macrophages, and another study further demonstrated that IL-10 suppresses lung fibrosis in a TGF-β1-dependent manner, wherein the overexpression of IL-10 simultaneously regulates the M2 polarization via the CCL2/CCR2 axis [82]. In this regard, it has been suggested that immunoregulatory cytokines, typically TGF-β1 and IL-10, are major participants in the pro-fibrotic microenvironment, which trigger a series of fibroproliferative wound healing processes and are relevant to inappropriate communication between M2-like polarised macrophages and activated fibroblasts in lung tissues [83]. In both the BLM-induced rat and fluorescein isothiocyanate-induced mouse models, chronic exposure to microcystin-leucine arginine (LR) contributed to an amelioration of PF [84]. Further in vivo data indicated that microcystin-LR, as an immune regulator, can attenuate macrophage polarization toward the CD206 + M2-like phenotype, thereby blocking UPRER signal transduction in stressed cells, which may be a mechanism underlying the inhibition of pulmonary EMT and FMT. The difference between macrophage subpopulations in normal and fibrotic lungs supports the idea of a specific role of innate immune factors in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. To emphasise this point, co-localisation and causal modelling have been utilised to verify macrophages that highly express SPP1 and MERTK (SPP1hi), and these identified macrophages are crucial in accelerating the activation of myofibroblasts in lung tissues and in the upregulation of stress response-associated genes [85]. Emerging evidence indicates that ER stress induces various pro-fibrotic functions through inducing interactions between myofibroblasts and macrophage polarization. Germline mutations have induced ER stress and activated a signalling network known as the unfolded protein response (UPR), which could also be regulated by PI3K and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) [86, 87].
Considering intercellular communication through metabolites has been previously defined in cancer cells and carcinoma-associated fibroblasts [88], it is necessary to provide insight into the role of immunomodulators in PF as an intercellular message between macrophages and fibroblasts. Glycolytic escalation in lung fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells are responsible for the pathological progression of lung fibrosis [89]. Subsequent analysis has indicated that there is a significant increase in glycolytic-related lactate in the conditioned media of TGF-β1-induced lung myofibroblasts and mice BALFs [90]. Macrophages treated with myofibroblast-conditioned media have switched to pro-fibrotic phenotypes with a high level of selected pro-fibrotic mediators which establish myofibroblast glycolysis and accelerate the pro-fibrotic activity of macrophages in lung fibrosis. Fatty acid (FA) metabolism in cells regulates various biological activities [91] and energy production through FA oxidation. Altered contents and profiles of FA metabolism have been identified in patients with PF and in animal models, suggesting its critical role in the development of pro-fibrotic phenotypes in macrophages and fibroblasts/myofibroblasts [92]. For example, the polarization of macrophages to the M2 phenotype is not only dependent upon the energy provided by FA [93] but also activated by the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ, which was initially recognised in adipose tissue for its role in FA storage [94]. Additionally, cell lineage tracing to lung fibroblasts in mice has shown that both large quantities of pro-fibrotic cytokines from polarised macrophages and PPAR-γ can induce phenotype switching between lipofibroblasts and myofibroblasts during the progression and resolution phases of lung fibrosis [95]. Exosomes and their enriched microRNAs (miRNAs) have collectively merged as potent modulators in complex networks that communicate between neighbouring or distant cells [96], and their utility as biomarkers of PF has been explored [97]. To investigate whether macrophage-derived exosomes are able to transfer anti-fibrotic miR-142-3p to target cells, Guiot et al. co-cultured MRC5 cells with purified THP1 macrophage-derived exosomes for 24 h and treated the cells with TGF-β for 4 h [10]. They found that the delivery of miR-142-3p from macrophage-derived exosomes to fibroblasts can reduce TGFβ-R1 transcription the expression of and pro-fibrotic genes, which may eventually slow the progression of PF. Although there are still several challenges to overcome before pharmacological application [98], exosomal miRNAs have been found to be potential biomarkers for fibrogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic intervention in lung fibrosis [99].
Transformation of alveolar epithelial cells in PF
In the alveolar lumen, alveolar epithelial cell type I (ATI), alveolar epithelial cell type II (ATII), and interalveolar septa mix in the continuous epithelium lining in the alveolar surface. Histopathological evidence has shown that aberrant epithelial cells, especially hyperplasia, and a lack of ATI cells, are some of the defining features of IPF, suggesting that the variability of ATII cells, which develop into ATI phenotypes, might add a heavy burden to fibrotic lung tissues due to mesenchymal expansion [100, 101]. In addition, there is consensus that ATII cells maintain alveolar niche homeostasis by the secretion of surfactant and to act as progenitor cells for regeneration or differentiation into ATI phenotypes in PF pathogenesis [102]. Recent reports have further demonstrated that EMT-associated signalling and senescence pathways regulate ATII cell transformation during fibrotic airway injury and remodelling. EMT in ATII cells is a progressive process, along with the deficiency of E-cadherin and other cytokines, as well as the alteration of cell migration, adhesion, and expression of ECM components, which are sustained by specific signalling pathways, such as the TGF-β/SMAD2/3 signalling loop [68] and Wnt/β-catenin pathways [69]. Furthermore, Hippo and Notch signalling in dysregulated ATII cells promote both ATII plasticity for transdifferentiation into a pro-fibrotic phenotype and epithelial diminished renewal by transmitting mechanical tension from alveolar epithelium to myofibroblasts [70, 71, 103]. Cell senescence, which is observed in lung fibrosis, has been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in the pathogenic alterations of ATII cells [104]. The fibrotic capacity of senescent ATII cells can mediate signals to mesenchymal cells within the same PF microenvironment via the acquisition of a specific senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) or epithelium-derived triple type 2 cytokines [72, 105]. In addition, upregulation of the IL-6 pathway by JAK/STAT signalling has been shown to drive senescent gene transcription both in IPF epithelial cells and fibroblasts [73, 74]. Meanwhile, the loss of IGF-1 receptor in radiation-induced model has inhibited the capacity of senescent ATII cells to polarise macrophages into the M2 phenotype via IL-13, one of the central SASPs in the PF microenvironment [75]. Furthermore, several cell-autonomous factors are involved in the exhaustion of ATII cell self-renewal and their capacity to recruit inflammatory cells, especially AMs [106]. The above evidence largely suggests that alveolar epithelial cells have a direct role in the fibrotic microenvironment and cellular crosstalk. All significant mechanisms and regulators mentioned above in the transformation of alveolar epithelial cells through PF progress are illustrated in Fig. 1 and Table 2.
Crosstalk between macrophages and the alveolar epithelium in PF
As the alveolar epithelium lies at the interface between the external environment and internal haemostasis, repeated exposure to injury and stimulation requires accurate modulation of inflammatory reactions in response to pro-fibrotic cellular crosstalk. In the PF microenvironment, polarised macrophages participate in a complex crosstalk network with alveolar epithelial cells, particularly ATII cells, via several mechanisms and cytokines. The addition of IL-4 and IL-13 to bone marrow-derived macrophage media has been found to be an M2-polarising reagent [107]. Thus, Hult et al. chose a combination of IL-4 and IL-13 to acquire M2 culture media and found that the expression of fibrotic factors (platelet-derived growth factor alpha, connective tissue growth factor) and antiapoptotic mediators (COX and BCL2) were upregulated in ATII cells treated with M2 culture media [108]. However, the differences in apoptosis between AEC cultured in M1 or M2 media are limited, suggesting that AEC apoptosis relies on juxtacrine signalling from macrophages in the pro-fibrotic microenvironment. Furthermore, by comparing macrophage populations from murine strains with different fibrosis-prone properties, Chung et al. observed that superoxide production from the M2 phenotype partially depends on NOX2 in fibrotic progenesis, and the significant increase in these superoxides promotes M2 macrophages to induce alveolar epithelial cell senescence, which ultimately increases the susceptibility of a patient to radiation-induced lung fibrosis [109]. Importantly, the infiltration of macrophages might be the first step of the early PF stage due to their aggregation occurring earlier than the EMT process. Li et al. analysed macrophage-secreted cytokine levels after bleomycin treatment, and the data indicated that the inhibited PI3K/Akt signalling was involved in the macrophage-induced EMT progress between alveolar epithelial cells and fibroblasts within the PF microenvironment [110]. Spontaneously, the key genetic variant in IPF pathogenesis could also alleviate the fibrotic crosstalk between macrophages and AECs, in which keratin 8 knockdown in murine IPF models downregulated the expression of macrophage chemokines and further inhibited macrophage-induced transitional AEC senescence from bleomycin exposure [111]. Based on a co-culture system consisting of macrophages, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts, Ni et al. demonstrated that the knockout of STING signalling in macrophages impairs M1 polarization and inhibits the fibrotic response in fibroblasts, which emphasises the significance of STING signalling in the cellular crosstalk between macrophages, lung epithelial cells, and fibroblasts [112].
As described above, AECs have been found to have a direct role in pro-fibrotic macrophage activation; however, the mechanisms underlying macrophage polarization and recruitment that depend on epithelial signalling or cytokines in the PF microenvironment have not yet been fully elucidated. Epithelial cells have been implicated in the migration of pathological macrophages. In a recent in vivo study, bleomycin-induced AEC insult led to a significant increase in CCL2 and CCL12; in such cases, monocyte-oriented macrophages were recruited by these chemokines in the lung and ultimately promoted the exudate phenotype associated with lung fibrosis [113]. Evidence supporting this cellular crosstalk comes from an early fibrotic in vivo study, wherein the migration of bleomycin-treated Ly6C monocytes was promoted to inflamed tissues by CCL2 secreted from epithelial cells and subsequently differentiated into increased interstitial macrophages [114]. Additionally, for the purpose of exploring the significant capacity of GM-CSF in fibrogenic AM compartments and surfactants [115], Gschwand et al. analysed the expression of its receptor Csf2 in perinatal and adult mouse lungs. Subsequent data demonstrated that timed expression of GM-CSF in ATII cells switched on the differentiation of foetal AMs, and the absence of ATII-derived Csf2 led to AM population atrophy [116].
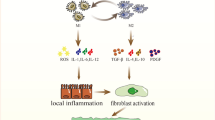
Alveolar epithelial cells are essential inducers and modulators of macrophage fibrotic activation and polarization. To determine whether senescent ATII cells influence AMs, Rana et al. analysed the alteration in secreted cytokines due to TGF-β1 induced ATII cell senescence and the key role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). Deletion of PAI-1 in senescent ATII cells not only inhibited the stimulatory capacity of ATII-oriented SASP on AM gene expression, but also attenuated the expression of fibrotic mediators (such as IL-4, IL-13, and PDGF) from TGF-β1 induced ATII cell senescence [117]. Liu et al. identified critical effects of AEC-derived exosomes on AM activation; specifically, LPS-induced exosomes from impaired AECs could be efficiently absorbed by AMs to induce the expressions of the inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, compared to control groups [118]. Choi et al. discovered increased transmembrane nerve injury-induced protein 1 (Ninj1) expression in bleomycin-induced AECs; the macrophage bond to the AECs was subsequently activated, indicating that Ninj1 may promote the activation of macrophages in a fibrotic murine model by boosting their interaction with impaired AECs [119]. According to bleomycin-induced in vivo and in vitro models, fibrosis-associated macrophage phenotypes are locally similar to those of ATII cells, contributing to paracrine-induced macrophage polarization. For example, sonic hedgehog secreted by ATII cells promotes the alternative activation of osteopontin-mediated macrophages in an autocrine or paracrine manner, thus justifying the epithelial cell-dependent mechanisms underlying M2 polarization and fibrotic pathogenesis [120]. To evaluate the potential role of 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) in radiation-induced murine fibrosis, Chung et al. compared the different levels of M2 phenotype biomarkers from primary macrophages cultured in ATII media between wild-type and 12-LOX-deficient mice and found that senescent ATII cells may facilitate macrophage polarization into the preferential M2 type via the 12-LOX dependent pathway in the PF microenvironment [121]. Hence, the crosstalk loop between macrophages and epithelial cells in lung tissues may be involved in the pathogenesis of PF by mediating cytokine, chemokine, and pro-fibrotic pathways within the PF microenvironment. All significant mechanisms and regulators mentioned above in cellular crosstalk through PF progress can be consulted in Fig. 2 and Table 3.
Schematic overview of major mechanisms and key regulators in cellular crosstalk within PF microenvironment. (FMT: fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transformation; ECM: extracellular matrix; TSLP: thymic stromal lymphopoietin; MMP9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; IL: interleukin; LR: leucine arginine; UPR: endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response; EMT: epithelial-mesenchymal transition; IRE1α: requiring enzyme 1α; CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein; PPAR-γ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; AEC: alveolar epithelial cell; IL: interleukin; ATII: alveolar epithelial cell type II; COX: Cyclooxygenase; BCL2: B-cell lymphoma-2; PI3K/Akt: Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases/ protein kinase B; STING: stimulator of interferon genes; GM-CSF: Granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor; PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; SASP: senescence-associated secretory phenotype; Ninj1: nerve injury-induced protein 1; Shh: Sonic hedgehog; 12-LOX: 12-lipoxygenase)
Conclusions and outlook
PF is a progressive and irreversible disease with an unknown cause that severely threatens the prognosis and quality of life of patients. Although small-molecule drugs such as pirfenidone or nintedanib are used widely in clinics, current Western medicine treatments only alleviate the decline of the patient’s lung function and cannot reverse the entire pathological process. The pathogenesis of lung fibrosis involves the abnormal repair of lung tissues, differentiation and proliferation of fibroblasts, and activation and inflammatory responses of immune cells, especially macrophages [122]. A review of the research has revealed a feedback loop between macrophage polarization and non-immune cell activities, including those of fibroblasts and AECs, which regulate pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic activities in PF. In the early stage of lung fibrosis, the polarised M1 phenotype may be dominant owing to its direct role in modulating the abnormal immune response to repetitive wound healing by regulating pro-inflammatory cytokines. Emerging evidence has demonstrated that the macrophage polarization into M2 phenotype can be induced by multiple cytokines, chemokines, inflammasomes, and even autophagy in the pulmonary fibrotic microenvironment; therefore, the M2 polarization ultimately promotes the expression of several mediators of epithelial injury and FMT, such as TGF-β1. Fibroblast proliferation can promote macrophage polarization via metabolic reprogramming or ER stress. AECs play two roles in the development of lung fibrosis development; first, their impaired self-renewal, abnormal senescence, and recruitment of inflammatory mediators directly contribute to fibrogenesis mechanisms; and second, their cellular crosstalk with local primary macrophages promotes Mo-M0 migration and M2 phenotype polarization after injury-induced stimuli, which are indirectly involved in the maintenance of the PF microenvironment. Thus, within the lung fibrosis microenvironment, pro-fibrotic macrophage polarization and its primary or subsequent dysfunctional crosstalk with AECs and fibroblasts contribute to the imbalance of immune homeostasis throughout the whole process of PF, which suggests a novel target for an anti-fibrotic approach.
Here, we summarise and highlight the complex dual role of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis, emphasising the therapeutic possibility of regulating cellular crosstalk between macrophages, AECs, and fibroblasts. However, several studies are still needed to develop treatments for patients experiencing PF-associated symptoms. Due to multiple setbacks in pure anti-inflammatory PF clinical trials, the investigation of macrophage regulation has been reoriented and we present a potential approach involving integration of macrophage polarization and cellular communication. Recent reports have similarly suggested that modulating cell–cell circuits may reset macrophage pools within inflammatory episodes [123]. Therefore, it may be worth exploring the strategies that directly inhibit or reprogram such fatal cellular communications rather than sample antibody-mediated therapies. Moreover, future studies should aim to clarify the phenotypic and functional heterogeneity underlying the crosstalk loop between macrophages and other immune cells via genetic, genomic, and metabolomic tools. Such studies could unravel several pharmacological targets for the treatment of PF with impressive safety and efficacy.
Availability of data and materials
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- PF:
-
Pulmonary fibrosis
- IPF:
-
Idiopathic PF
- AEC:
-
Alveolar epithelial cell
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- AM:
-
Alveolar macrophages
- IM:
-
Interstitial macrophage
- DTR:
-
Diphtheria toxin receptor
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-beta
- BAL:
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage
- BALF:
-
BAL fluid
- ApoE:
-
Apolipoprotein E
- IL-1Ra:
-
IL-1 receptor antagonist
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- FMT:
-
Fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transformation
- lncRNA:
-
Long noncoding RNA
- FAP:
-
Fibroblast activation protein
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- ATI/II:
-
Alveolar epithelial cell type I/II
- SASP:
-
Senescence-associated secretory phenotype
- TSLP:
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- PINK:
-
PTEN-induced putative kinase
- LR:
-
Leucine arginine
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- IRE1α:
-
Enzyme 1α
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- FA:
-
Fatty acid
- PPAR-γ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- 12-LOX:
-
12-Lipoxygenase
References
Navaratnam V, Fleming KM, West J, Smith CJ, Jenkins RG, Fogarty A, et al. The rising incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the U.K. Thorax. 2011;66(6):462–7.
Maher TM, Bendstrup E, Dron L, Langley J, Smith G, Khalid JM, et al. Global incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2021;22(1):197.
Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(19):1811–23.
Fernandez Perez ER, Daniels CE, Schroeder DR, St Sauver J, Hartman TE, Bartholmai BJ, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and clinical course of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a population-based study. Chest. 2010;137(1):129–37.
King TE, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2083–92.
Richeldi L, Kolb M, Jouneau S, Wuyts WA, Schinzel B, Stowasser S, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in patients with advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm Med. 2020;20(1):3.
Kobayashi Y, Tata A, Konkimalla A, Katsura H, Lee RF, Ou J, et al. Persistence of a regeneration-associated, transitional alveolar epithelial cell state in pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(8):934–46.
Yang F, Chang Y, Zhang C, Xiong Y, Wang X, Ma X, et al. UUO induces lung fibrosis with macrophage-myofibroblast transition in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;93:107396.
Perrot CY, Karampitsakos T, Herazo-Maya JD. Monocytes and macrophages: emerging mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023;325(4):C1046–57.
Guiot J, Cambier M, Boeckx A, Henket M, Nivelles O, Gester F, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes attenuate fibrosis in airway epithelial cells through delivery of antifibrotic miR-142-3p. Thorax. 2020;75(10):870–81.
Witherel CE, Abebayehu D, Barker TH, Spiller KL. Macrophage and fibroblast interactions in biomaterial-mediated fibrosis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(4):e1801451.
Funes SC, Rios M, Escobar-Vera J, Kalergis AM. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology. 2018;154(2):186–95.
Reyfman PA, Walter JM, Joshi N, Anekalla KR, McQuattie-Pimentel AC, Chiu S, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of human lung provides insights into the pathobiology of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;199(12):1517–36.
Misharin AV, Morales-Nebreda L, Reyfman PA, Cuda CM, Walter JM, McQuattie-Pimentel AC, et al. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages drive lung fibrosis and persist in the lung over the life span. J Exp Med. 2017;214(8):2387–404.
Wang H, Gao Y, Wang L, Yu Y, Zhang J, Liu C, et al. Lung specific homing of diphenyleneiodonium chloride improves pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting macrophage M2 metabolic program. J Adv Res. 2023;44:213–25.
Tarique AA, Logan J, Thomas E, Holt PG, Sly PD, Fantino E. Phenotypic, functional, and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;53(5):676–88.
Liu G, Zhai H, Zhang T, Li S, Li N, Chen J, et al. New therapeutic strategies for IPF: Based on the “phagocytosis-secretion-immunization” network regulation mechanism of pulmonary macrophages. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109230.
Li F, Piattini F, Pohlmeier L, Feng Q, Rehrauer H, Kopf M. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages autonomously determine severe outcome of respiratory viral infection. Sci Immunol. 2022;7(73):eabj5761.
Borthwick LA, Barron L, Hart KM, Vannella KM, Thompson RW, Oland S, et al. Macrophages are critical to the maintenance of IL-13-dependent lung inflammation and fibrosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2016;9(1):38–55.
Zhang Y, Zhu L, Hong J, Chen C. Extracellular matrix of early pulmonary fibrosis modifies the polarization of alveolar macrophage. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109179.
Liu W, Han X, Li Q, Sun L, Wang J. Iguratimod ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the EMT process and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113460.
Sayan M, Mossman BT. The NLRP3 inflammasome in pathogenic particle and fibre-associated lung inflammation and diseases. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016;13(1):51.
Wang J, Lai X, Yao S, Chen H, Cai J, Luo Y, et al. Nestin promotes pulmonary fibrosis via facilitating recycling of TGF-β receptor I. Eur Respir J. 2022;59(5):2003721.
Cheng H, Feng D, Li X, Gao L, Tang S, Liu W, et al. Iron deposition-induced ferroptosis in alveolar type II cells promotes the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021;1867(12):166204.
Romero F, Shah D, Duong M, Penn RB, Fessler MB, Madenspacher J, et al. A pneumocyte-macrophage paracrine lipid axis drives the lung toward fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;53(1):74–86.
Cui H, Jiang D, Banerjee S, Xie N, Kulkarni T, Liu RM, et al. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophage apolipoprotein E participates in pulmonary fibrosis resolution. JCI Insight. 2020;5(5):e134539.
Ogawa T, Shichino S, Ueha S, Matsushima K. Macrophages in lung fibrosis. Int Immunol. 2021;33(12):665–71.
Chakarov S, Lim HY, Tan L, Lim SY, See P, Lum J, et al. Two distinct interstitial macrophage populations coexist across tissues in specific subtissular niches. Science. 2019;363(6432):eaau0964.
Hoppstadter J, Diesel B, Zarbock R, Breinig T, Monz D, Koch M, et al. Differential cell reaction upon Toll-like receptor 4 and 9 activation in human alveolar and lung interstitial macrophages. Respir Res. 2010;11(1):124.
Meziani L, Mondini M, Petit B, Boissonnas A, Thomas de Montpreville V, Mercier O, et al. CSF1R inhibition prevents radiation pulmonary fibrosis by depletion of interstitial macrophages. Eur Respir J. 2018;51(3):1702120.
Shi T, Denney L, An H, Ho LP, Zheng Y. Alveolar and lung interstitial macrophages: definitions, functions, and roles in lung fibrosis. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110(1):107–14.
Xue J, Schmidt SV, Sander J, Draffehn A, Krebs W, Quester I, et al. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation. Immunity. 2014;40(2):274–88.
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA, Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(1):14–20.
Zhang L, Wang Y, Wu G, Xiong W, Gu W, Wang CY. Macrophages: friend or foe in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respir Res. 2018;19(1):170.
Zhao X, Di Q, Liu H, Quan J, Ling J, Zhao Z, et al. MEF2C promotes M1 macrophage polarization and Th1 responses. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(4):540–53.
Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB, Ley K. Macrophage polarization: different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. classically and M2(LPS-) vs. alternatively activated macrophages. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1084.
Gough DJ, Levy DE, Johnstone RW, Clarke CJ. IFNgamma signaling-does it mean JAK-STAT? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008;19(5–6):383–94.
Lescoat A, Lelong M, Jeljeli M, Piquet-Pellorce C, Morzadec C, Ballerie A, et al. Combined anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory properties of JAK-inhibitors on macrophages in vitro and in vivo: Perspectives for scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;178:114103.
Noubissi Nzeteu GA, Schlichtner S, David S, Ruppenstein A, Fasler-Kan E, Raap U, et al. Macrophage differentiation and polarization regulate the release of the immune checkpoint protein V-Domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:837097.
Zhang Z, Wu X, Han G, Shao B, Lin L, Jiang S. Altered M1/M2 polarization of alveolar macrophages is involved in the pathological responses of acute silicosis in rats in vivo. Toxicol Ind Health. 2022;38(12):810–8.
Xiang GA, Zhang YD, Su CC, Ma YQ, Li YM, Zhou X, et al. Dynamic changes of mononuclear phagocytes in circulating, pulmonary alveolar and interstitial compartments in a mouse model of experimental silicosis. Inhal Toxicol. 2016;28(9):393–402.
Huang G, Luo J, Guo H, Wang X, Hu Z, Pu W, et al. Molybdenum and cadmium co-exposure promotes M1 macrophage polarization through oxidative stress-mediated inflammatory response and induces pulmonary fibrosis in Shaoxing ducks (Anas platyrhyncha). Environ Toxicol. 2022;37(12):2844–54.
Rao LZ, Wang Y, Zhang L, Wu G, Zhang L, Wang FX, et al. IL-24 deficiency protects mice against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by repressing IL-4-induced M2 program in macrophages. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(4):1270–83.
Young LR, Gulleman PM, Short CW, Tanjore H, Sherrill T, Qi A, et al. Epithelial-macrophage interactions determine pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. JCI Insight. 2016;1(17):e88947.
Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhang N, Xia J, Zhan Q, Wang C. Potential role of M2 macrophage polarization in ventilator-induced lung fibrosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105795.
Zhang ZQ, Tian HT, Liu H, Xie R. The role of macrophage-derived TGF-β1 on SiO(2)-induced pulmonary fibrosis: a review. Toxicol Ind Health. 2021;37(4):240–50.
Rahal OM, Wolfe AR, Mandal PK, Larson R, Tin S, Jimenez C, et al. Blocking interleukin (IL)4- and IL13-mediated phosphorylation of STAT6 (Tyr641) decreases M2 polarization of macrophages and protects against macrophage-mediated radioresistance of inflammatory breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;100(4):1034–43.
Grabarz F, Aguiar CF, Correa-Costa M, Braga TT, Hyane MI, Andrade-Oliveira V, et al. Protective role of NKT cells and macrophage M2-driven phenotype in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(2):491–504.
Craig VJ, Zhang L, Hagood JS, Owen CA. Matrix metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;53(5):585–600.
Atamas SP. MMP28 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: beyond the extracellular matrix. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018;59(1):5–6.
Geng Y, Li L, Yan J, Liu K, Yang A, Zhang L, et al. PEAR1 regulates expansion of activated fibroblasts and deposition of extracellular matrix in pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7114.
Xie T, Wang Y, Deng N, Huang G, Taghavifar F, Geng Y, et al. Single-cell deconvolution of fibroblast heterogeneity in mouse pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2018;22(13):3625–40.
Yang IV, Pedersen BS, Rabinovich E, Hennessy CE, Davidson EJ, Murphy E, et al. Relationship of DNA methylation and gene expression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;190(11):1263–72.
Habermann AC, Gutierrez AJ, Bui LT, Yahn SL, Winters NI, Calvi CL, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals profibrotic roles of distinct epithelial and mesenchymal lineages in pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Adv. 2020;6(28):eaba1972.
Rajasekar P, Patel J, Clifford RL. DNA methylation of fibroblast phenotypes and contributions to lung fibrosis. Cells. 2021;10(8):1977.
Chen YT, Chang FC, Wu CF, Chou YH, Hsu HL, Chiang WC, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling activates pericyte-myofibroblast transition in obstructive and post-ischemic kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2011;80(11):1170–81.
Affandi AJ, Carvalheiro T, Ottria A, de Haan JJ, Brans MAD, Brandt MM, et al. CXCL4 drives fibrosis by promoting several key cellular and molecular processes. Cell Rep. 2022;38(1):110189.
Liu SS, Liu C, Lv XX, Cui B, Yan J, Li YX, et al. The chemokine CCL1 triggers an AMFR-SPRY1 pathway that promotes differentiation of lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and drives pulmonary fibrosis. Immunity. 2021;54(9):2042-56.e8.
Upagupta C, Shimbori C, Alsilmi R, Kolb M. Matrix abnormalities in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(148):180033.
Zhang J, Wang H, Chen H, Li H, Xu P, Liu B, et al. ATF3 -activated accelerating effect of LINC00941/lncIAPF on fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation by blocking autophagy depending on ELAVL1/HuR in pulmonary fibrosis. Autophagy. 2022;18(11):2636–55.
Zhao X, Sun J, Chen Y, Su W, Shan H, Li Y, et al. lncRNA PFAR promotes lung fibroblast activation and fibrosis by targeting miR-138 to regulate the YAP1-twist axis. Mol Ther. 2018;26(9):2206–17.
Savary G, Dewaeles E, Diazzi S, Buscot M, Nottet N, Fassy J, et al. The long noncoding RNA DNM3OS is a reservoir of FibromiRs with major functions in lung fibroblast response to TGF-β and pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200(2):184–98.
Gajjala PR, Madala SK. Notch3: a new culprit in fibrotic lung disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021;64(4):403–4.
Xu K, Nieuwenhuis E, Cohen BL, Wang W, Canty AJ, Danska JS, et al. Lunatic Fringe-mediated notch signaling is required for lung alveogenesis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;298(1):L45-56.
Vera L, Garcia-Olloqui P, Petri E, Vinado AC, Valera PS, Blasco-Iturri Z, et al. Notch3 deficiency attenuates pulmonary fibrosis and impedes lung-function decline. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021;64(4):465–76.
Hettiarachchi SU, Li YH, Roy J, Zhang F, Puchulu-Campanella E, Lindeman SD, et al. Targeted inhibition of PI3 kinase/mTOR specifically in fibrotic lung fibroblasts suppresses pulmonary fibrosis in experimental models. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(567):eaay3724.
Katoh M. Multi-layered prevention and treatment of chronic inflammation, organ fibrosis and cancer associated with canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling activation (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(2):713–25.
Wu H, Yu Y, Huang H, Hu Y, Fu S, Wang Z, et al. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis is caused by elevated mechanical tension on alveolar stem cells. Cell. 2021;184(3):845–6.
Ruaro B, Salton F, Braga L, Wade B, Confalonieri P, Volpe MC, et al. The history and mystery of alveolar epithelial type II cells: focus on their physiologic and pathologic role in lung. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2566.
Parimon T, Yao C, Stripp BR, Noble PW, Chen P. Alveolar epithelial type II cells as drivers of lung fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2269.
Tsao PN, Matsuoka C, Wei SC, Sato A, Sato S, Hasegawa K, et al. Epithelial notch signaling regulates lung alveolar morphogenesis and airway epithelial integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(29):8242–7.
Waters DW, Blokland KEC, Pathinayake PS, Burgess JK, Mutsaers SE, Prele CM, et al. Fibroblast senescence in the pathology of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018;315(2):L162–72.
Phan THG, Paliogiannis P, Nasrallah GK, Giordo R, Eid AH, Fois AG, et al. Emerging cellular and molecular determinants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(5):2031–57.
Pedroza M, Le TT, Lewis K, Karmouty-Quintana H, To S, George AT, et al. STAT-3 contributes to pulmonary fibrosis through epithelial injury and fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation. FASEB J. 2016;30(1):129–40.
Chung EJ, Kwon S, Reedy JL, White AO, Song JS, Hwang I, et al. IGF-1 receptor signaling regulates type II pneumocyte senescence and resulting macrophage polarization in lung fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021;110(2):526–38.
Xia H, Herrera J, Smith K, Yang L, Gilbertsen A, Benyumov A, et al. Hyaluronan/CD44 axis regulates S100A4-mediated mesenchymal progenitor cell fibrogenicity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021;320(5):L926–41.
Zhang W, Ohno S, Steer B, Klee S, Staab-Weijnitz CA, Wagner D, et al. S100a4 is secreted by alternatively activated alveolar macrophages and promotes activation of lung fibroblasts in pulmonary fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1216.
Li Y, Bao J, Bian Y, Erben U, Wang P, Song K, et al. S100A4(+) macrophages are necessary for pulmonary fibrosis by activating lung fibroblasts. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1776.
Ishida Y, Kimura A, Nosaka M, Kuninaka Y, Hemmi H, Sasaki I, et al. Essential involvement of the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of fibrocyte and M2 macrophage migration. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16833.
Li G, Jin F, Du J, He Q, Yang B, Luo P. Macrophage-secreted TSLP and MMP9 promote bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;366:10–6.
Liu F, Liu J, Weng D, Chen Y, Song L, He Q, et al. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells depletion may attenuate the development of silica-induced lung fibrosis in mice. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e15404.
Gharaee-Kermani M, McCullumsmith RE, Charo IF, Kunkel SL, Phan SH. CC-chemokine receptor 2 required for bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Cytokine. 2003;24(6):266–76.
Huaux F. Interpreting immunoregulation in lung fibrosis: a new branch of the immune model. Front Immunol. 2021;12:690375.
Wang J, Xu L, Xiang Z, Ren Y, Zheng X, Zhao Q, et al. Microcystin-LR ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis via modulating CD206(+) M2-like macrophage polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(2):136.
Morse C, Tabib T, Sembrat J, Buschur KL, Bittar HT, Valenzi E, et al. Proliferating SPP1/MERTK-expressing macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2019;54(2):1802441.
Hsu HS, Liu CC, Lin JH, Hsu TW, Hsu JW, Su K, et al. Involvement of ER stress, PI3K/AKT activation, and lung fibroblast proliferation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14272.
Burman A, Tanjore H, Blackwell TS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in pulmonary fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2018;68–69:355–65.
Bertero T, Oldham WM, Grasset EM, Bourget I, Boulter E, Pisano S, et al. Tumor-stroma mechanics coordinate amino acid availability to sustain tumor growth and malignancy. Cell Metab. 2019;29(1):124-40.e10.
Xie N, Tan Z, Banerjee S, Cui H, Ge J, Liu RM, et al. Glycolytic reprogramming in myofibroblast differentiation and lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192(12):1462–74.
Cui H, Xie N, Banerjee S, Ge J, Jiang D, Dey T, et al. Lung myofibroblasts promote macrophage profibrotic activity through lactate-induced histone lactylation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021;64(1):115–25.
de Carvalho C, Caramujo MJ. The various roles of fatty acids. Molecules. 2018;23(10):2583.
Yang F, Ma Z, Li W, Kong J, Zong Y, Wendusu B, et al. Identification and immune characteristics of molecular subtypes related to fatty acid metabolism in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front Nutr. 2022;9:992331.
Namgaladze D, Brüne B. Macrophage fatty acid oxidation and its roles in macrophage polarization and fatty acid-induced inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1861(11):1796–807.
Kökény G, Calvier L, Hansmann G. PPARγ and TGFβ-major regulators of metabolism, inflammation, and fibrosis in the lungs and kidneys. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(19):10431.
El Agha E, Moiseenko A, Kheirollahi V, De Langhe S, Crnkovic S, Kwapiszewska G, et al. Two-way conversion between lipogenic and myogenic fibroblastic phenotypes marks the progression and resolution of lung fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(2):261-73.e3.
Li S, Zhang J, Feng G, Jiang L, Chen Z, Xin W, et al. The emerging role of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages in pulmonary fibrosis: insights into miRNA delivery. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15(10):1276.
Makiguchi T, Yamada M, Yoshioka Y, Sugiura H, Koarai A, Chiba S, et al. Serum extracellular vesicular miR-21-5p is a predictor of the prognosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2016;17(1):110.
Kaur G, Maremanda KP, Campos M, Chand HS, Li F, Hirani N, et al. Distinct exosomal miRNA profiles from BALF and lung tissue of COPD and IPF patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11830.
Santos-Álvarez JC, Velázquez-Enríquez JM, García-Carrillo R, Rodríguez-Beas C, Ramírez-Hernández AA, Reyes-Jiménez E, et al. miRNAs contained in extracellular vesicles cargo contribute to the progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an in vitro aproach. Cells. 2022;11(7):1112.
Flaherty KR, Travis WD, Colby TV, Toews GB, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, et al. Histopathologic variability in usual and nonspecific interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(9):1722–7.
Selman M, Pardo A. The leading role of epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Signal. 2020;66:109482.
Confalonieri P, Volpe MC, Jacob J, Maiocchi S, Salton F, Ruaro B, et al. Regeneration or repair? The role of alveolar epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Cells. 2022;11(13):2095.
Liu F, Lagares D, Choi KM, Stopfer L, Marinković A, Vrbanac V, et al. Mechanosignaling through YAP and TAZ drives fibroblast activation and fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;308(4):L344–57.
Chin C, Ravichandran R, Sanborn K, Fleming T, Wheatcroft SB, Kearney MT, et al. Loss of IGFBP2 mediates alveolar type 2 cell senescence and promotes lung fibrosis. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4(3):100945.
Xu X, Zhang J, Dai H. IL-25/IL-33/TSLP contributes to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: do alveolar epithelial cells and (myo)fibroblasts matter? Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020;245(10):897–901.
Hussell T, Bell TJ. Alveolar macrophages: plasticity in a tissue-specific context. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(2):81–93.
Rui Y, Han X, Jiang A, Hu J, Li M, Liu B, et al. Eucalyptol prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and M2 macrophage polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;931:175184.
Hult EM, Gurczynski SJ, Moore BB. M2 macrophages have unique transcriptomes but conditioned media does not promote profibrotic responses in lung fibroblasts or alveolar epithelial cells in vitro. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021;321(3):L518–32.
Chung EJ, Kwon S, Shankavaram U, White AO, Das S, Citrin DE. Natural variation in macrophage polarization and function impact pneumocyte senescence and susceptibility to fibrosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(19):7692–717.
Li S, Gao S, Jiang Q, Liang Q, Luan J, Zhang R, et al. Clevudine attenuates bleomycin-induced early pulmonary fibrosis via regulating M2 macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;101(Pt B):108271.
Wang F, Ting C, Riemondy KA, Douglas MT, Foster KM, Patel N, et al. Regulation of epithelial transitional states in murine and human pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(22):e165612.
Ni J, Guo T, Zhou Y, Jiang S, Zhang L, Zhu Z. STING signaling activation modulates macrophage polarization via CCL2 in radiation-induced lung injury. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):590.
Yang J, Agarwal M, Ling S, Teitz-Tennenbaum S, Zemans RL, Osterholzer JJ, et al. Diverse injury pathways induce alveolar epithelial cell CCL2/12, which promotes lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020;62(5):622–32.
Yamada Z, Nishio J, Motomura K, Mizutani S, Yamada S, Mikami T, et al. Senescence of alveolar epithelial cells impacts initiation and chronic phases of murine fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:935114.
Fabre T, Barron AMS, Christensen SM, Asano S, Bound K, Lech MP, et al. Identification of a broadly fibrogenic macrophage subset induced by type 3 inflammation. Sci Immunol. 2023;8(82):eadd8945.
Gschwend J, Sherman SPM, Ridder F, Feng X, Liang HE, Locksley RM, et al. Alveolar macrophages rely on GM-CSF from alveolar epithelial type 2 cells before and after birth. J Exp Med. 2021;218(10):e20210745.
Rana T, Jiang C, Liu G, Miyata T, Antony V, Thannickal VJ, et al. PAI-1 regulation of TGF-β1-induced alveolar type II cell senescence, SASP secretion, and SASP-mediated activation of alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020;62(3):319–30.
Liu F, Peng W, Chen J, Xu Z, Jiang R, Shao Q, et al. Exosomes derived from alveolar epithelial cells promote alveolar macrophage activation mediated by miR-92a-3p in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:646546.
Choi S, Woo JK, Jang YS, Kang JH, Hwang JI, Seong JK, et al. Ninjurin1 plays a crucial role in pulmonary fibrosis by promoting interaction between macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17542.
Hou J, Ji J, Chen X, Cao H, Tan Y, Cui Y, et al. Alveolar epithelial cell-derived Sonic hedgehog promotes pulmonary fibrosis through OPN-dependent alternative macrophage activation. Febs j. 2021;288(11):3530–46.
Chung EJ, Reedy JL, Kwon S, Patil S, Valle L, White AO, et al. 12-Lipoxygenase is a critical mediator of type II pneumocyte senescence, macrophage polarization and pulmonary fibrosis after irradiation. Radiat Res. 2019;192(4):367–79.
Heukels P, Moor CC, von der Thüsen JH, Wijsenbeek MS, Kool M. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir Med. 2019;147:79–91.
Guilliams M, Svedberg FR. Does tissue imprinting restrict macrophage plasticity? Nat Immunol. 2021;22(2):118–27.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank the Young Qihuang Scholars Training Project (qnqhxz-02), the Shandong Province Taishan Scholar Project (No. tsqn202306393) and the Natural Foundation of Shandong Province (Grants nos. ZR2020MH353) for their support.
Funding
This work was supported by the Young Qihuang Scholars Training Project, Grants nos. qnqhxz-02, the Shandong Province Taishan Scholar Project No. tsqn202306393 and the Natural Foundation of Shandong Province, Grants nos. ZR2020MH353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bo-wen Zhou analyzed the data, wrote, edited and revised the manuscript, Xin-hua Jia , Hua-man Liu and Fei Xu revised the manuscript and participated in the preparation of the review. All the authors read carefully and participated in the manuscript, contributing to the improvement of language and grammar.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Bw., Liu, Hm., Xu, F. et al. The role of macrophage polarization and cellular crosstalk in the pulmonary fibrotic microenvironment: a review. Cell Commun Signal 22, 172 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-024-01557-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-024-01557-2