Abstract
Background
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the principal pathogen that causes biofilm formation. Biofilms are associated with infectious diseases and antibiotic resistance. This study employed proteomic analysis to identify differentially expressed proteins after coculture of E. coli with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) microcapsules.
Methods
To explore the relevant protein abundance changes after E. coli and LGG coculture, label-free quantitative proteomic analysis and qRT-PCR were applied to E. coli and LGG microcapsule groups before and after coculture, respectively.
Results
The proteomic analysis characterised a total of 1655 proteins in E. coli K12MG1655 and 1431 proteins in the LGG. After coculture treatment, there were 262 differentially expressed proteins in E. coli and 291 in LGG. Gene ontology analysis showed that the differentially expressed proteins were mainly related to cellular metabolism, the stress response, transcription and the cell membrane. A protein interaction network and Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis indicated that the differentiated proteins were mainly involved in the protein ubiquitination pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Conclusions
These findings indicated that LGG microcapsules may inhibit E. coli biofilm formation by disrupting metabolic processes, particularly in relation to energy metabolism and stimulus responses, both of which are critical for the growth of LGG. Together, these findings increase our understanding of the interactions between bacteria under coculture conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Biofilms are complex bacterial community structures that can attach to surfaces. They connect to a surface via extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), which form a matrix composed primarily of polysaccharides, proteins and DNA; this encapsulates the bacteria [1]. Biofilms not only cause economic losses but also present a public health hazard. This is because the bacteria present within biofilms are much more resistant to antibiotics, disinfectants [2] and host immune system effectors [3]. Therefore, it is critical to develop effective non-toxic—or less toxic—antifungal agents with novel modes of action.
A recent study suggested that probiotic supernatants have antibiofilm formation properties [4], which implies that probiotics may inhibit biofilm formation through cell-cell communication. However, there has been little progress in this field to date. In our previous study, bacteria immobilised in microcapsules showed superior biofilm inhibition capacity compared to probiotic sterile culture supernatant. Accordingly, a Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) microcapsule–planktonic Escherichia coli (E. coli) coculture model was established to evaluate the biofilm inhibition effect [5]. However, the possible antibiofilm molecular mechanisms of LGG microcapsules have not yet been investigated.
Proteomic analysis for global protein identification is a powerful tool and has emerged as an important approach for extracting detailed information on cellular regulatory mechanisms at the protein level. Label-free quantitative proteomics provides a straightforward option for large-scale analysis of biological samples. In contrast to label-based methods, label-free quantitative proteomics has several advantages as it is cost-effective and does not require expensive labeling reagents. Also, label-free quantitative proteomics is not time-consuming compared to some label-based methods as these require tedious labeling steps [6]. For all these reasons, label-free quantitative proteomics has gained widespread acceptance in biomedical research, such as for the analysis of bodily fluids (blood, plasma, saliva, and urine), cell lines and tissues [7, 8].
In the present study, coculture experiments and proteomic analyses were performed to further advance understanding of such interactions and the potential underlying mechanisms. A label-free quantitative proteomic approach was used to identify proteins with significantly changed expression profiles during the E. coli and LGG microcapsule coculture process. Ultimately, these findings will contribute to an increased understanding of the possible molecular action of LGG microcapsules against E. coli biofilm formation and provide a powerful platform for future mechanistic studies of bacterial interactions.
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains and materials
LGG and E. coli K12MG165 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC 53103 and ATCC 47076). LGG was cultured in a modified MRS broth in which glucose was replaced by galactose under anaerobic conditions at 37 °C. E. coli strains were cultured at 37 °C in Luria-Bertani broth [9]. Cell suspensions were subsequently used as described below.
Sodium alginate was purchased from the Qingdao Crystal Salt Bioscience and Technology Corporation (Qingdao, Shandong, China). Chitosan was degraded from raw chitosan using the chemical method (Yuhuan Ocean Biomaterials Corporation, China). All other reagents and solvents were of analytical grade and were used without further purification.
Preparation of LGG microcapsules
LGG alginate beads were prepared using the emulsification/internal gelation technique, as described previously [10]. Briefly, sodium alginate powder was dissolved in 0.9% (w/v) NaCl solution to obtain a final concentration of 1.5% (w/v). The cell pellet was obtained by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 5 min. The cells and micro-crystalline CaCO3 powder were finely dispersed in sterile sodium alginate solution. Then, the alginate-calcium salt-cell suspension and 200 mL of liquid paraffin containing 0.5% (v/v) Span 85 were stirred in a turbine reactor at 200 rpm for 30 min. After 30 min of emulsification, glacial acetic acid was added for gelification following which 500 mL of deionised water was added with stirring for 30 min at 200 rpm. The cell-entrapped calcium alginate beads with an initial cell number of about 1.0 × 106 CFU/mL beads were then rinsed with 1% (v/v) Tween 80 solution and distilled water and were then stored in water at 4 °C.
Preparation of LGG alginate–chitosan microcapsules
Chitosan solution was dissolved in 0.1 M acetate buffer. The cell-entrapped calcium alginate beads were immersed in 0.5% (w/v) chitosan solution by gently shaking at a bead/solution ratio of 1:5 (v/v). After rinsing and liquefication for 6 min using 0.055 M sodium citrate, the cell-entrapped alginate-chitosan microcapsules were formed.
Characterisation of microcapsules
Microcapsule size was examined with a Counter Coulter LS130 particle size analyser, which has a size range of 0.1 to 1000 μm. Optical images were observed under a Nikon Eclipse TE2000 Inverted Research Microscope (Nikon Corp., Japan).
Biofilm thickness detection by confocal microscopy
Biofilm thickness was detected according to a previously published method, with minor modification [11]. After incubation, the microscope slides with biofilm from each group were gently rinsed with deionised water to remove unattached cells and then stained with SYTO9/propidium iodide according to the instructions of the L13152 LIVE/DEAD BacLight bacterial viability kit (Invitrogen Molecular Probes, USA). After staining for 30 min, sterile PBS was used to remove the planktonic dyes and bacteria, and the stained coverslips were visualised under a confocal laser scanning microscope (Leica SP8, Germany) at an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and 200× magnification. Three-dimensional biofilm images were obtained using CLSM software. Image stacks of three random spots were collected from three sets of biofilm samples and saved in “tif” format.
Preparation of cell samples and experimental grouping
Briefly, LGG microcapsules were cocultured with planktonic E. coli for 48 h for biofilm inhibition, as reported previously [5]. At the end of coculture, the biofilm was meticulously scraped off the well wall using a sterile scalpel. The E. coli cells in the biofilm were collected by sonication using high-intensity focused ultrasound (UTR2000, Hielscher); these were denoted as group A. Group A was lysed in medium containing 4% w/v sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), 0.1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), and 100 mM Tris-HCl at pH 8.2. At the same time, the LGG microcapsules were collected after coculture and the entrapped LGG cells were released from the microcapsules according to a previously described method [12]; these were denoted as group B. E. coli pure culture (denoted as group C) and 48 h LGG microcapsules pure culture (denoted as group D) were used as the negative controls.
Protein extraction and digestion
To the samples was added 1 mL of lysis buffer containing 8 M urea and 10% protease inhibitor and the resulting mixture carefully transferred 1.5 mL microfuge tubes. The samples were sonicated using a probe sonicator, then centrifuged at 14,000×g for 30 min, following which the supernatant was collected. The protein concentration was determined using the Bradford method and the remainder of the sample was frozen to − 80 °C.
From each sample, 50 μg of total protein was used for further analysis. The samples were diluted with ammonium bicarbonate (ABC) buffer, which allowed for a steady pH value of approximately 7.0 for eight times, and then reduced with 200 mM of DTT solution and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. The samples were digested overnight with trypsin (trypsin:protein = 1:25) at 37 °C. After concentration using a Speedvac (Thermo Savant SPD121P, Thermo Scientific, Wohlen, Switzerland), each sample was reconstituted in 3% acetonitrile (ACN) and 0.1% formic acid (FA).
Protein fractionation by reverse-phase liquid chromatography
The next day, 50 μL of 0.1% formic acid (FA) was added to the incubated mixture to terminate the digestion. A C18 column was washed with 100% ACN followed by 0.1% FA and centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 3 min. The Eppendorf (EP) tube was replaced and the sample (≤ 30 μg) was added and then centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 3 min. The samples were washed once with 100 μL of pH 10 water. After this process, the sample was eluted with 10 gradients of ACN in pH 10 water at the following concentrations: 6% (i.e. 60 μL ACN, 940 μL pH 10 water), 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 25, 30, 35 and 50%. Next, the eluent from the 6, 12, 15, 25 and 35% gradients were combined in one tube while the 9, 18, 21, 30 and 50% gradients were combined in another tube, thus dividing the sample into two fractions. The sample fractions were then lyophilised and stored at − 80 °C until loading.
Peptide identification by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
Samples were injected onto an in-house pulled and packed tip column (length 8 cm) carrying Magic C18 AQ beads (3 μm bead size, 200 Å pore size; Bishoff Chromatography, Leonberg, Germany), 75 μm ID, 375 OD capillary, coupled to an Eksigent nanoLC-1D device (ABSciex, Zug, Switzerland). They were then separated using a binary solvent system with a flow rate of 200 nL/min, eluted using a gradient from 2 to 30% B over 60 min (A:1% ACN, 0.1% FA, B: 100% ACN, 0.1% FA) and acquired using an LTQ Orbitrap (ThermoScientific, Wohlen, Switzerland) equipped with a nanospray ion source running a standard collision-induced data-dependent (CID-DDA) method of one survey (MS) scan followed by ten dependent scans (MS/MS) looped throughout the run. The survey scan was acquired from 300 to 2000 m/z units in profile mode with a resolution of 30,000 in the Orbitrap. The dependent scans were acquired in centroid mode in the ion trap with a collision energy of 35, activation energy of 0.25 and 30 ms activation time, excluding singly charged ions for fragmentation. Dynamic exclusion was applied with a list size of 500 that was repeated every 30 s and with a duration of 90 s.
Protein identification
The Uniprot_Escherichia coli (2019.4.20 download) database and the Uniprot_Lactobacillus rhamnosus (2019.7.25 download) database were used. The MS/MS data were processed using Maxquant 1.5.2.8 software and the identification parameters set with a precursor ion mass tolerance of ±15 ppm, fragment ion mass tolerance of ±0.5 Da, maximum of two missed cleavages, static modification with carboxyamidomethylation (57.021 Da) of the Cys residues, and dynamic modification with oxidation modification (+ 15.995 Da) of the Met residues. According to the primary data analyses, protein and peptide FDR were set to 0.01 (1%), the decoy database was set to revert and the minimum peptide number was 1 for the identified proteins. Data with p ≤ 0.05 and a difference ratio of ≥1.2 were selected for further analysis. The statistical analyses of the LC-MS/MS data were performed using Perseus (v1.4.1.3).
Bioinformatic analysis of identified proteins and prediction of promoters in intergenic regions
A functional category gene enrichment test was performed using Blast 2GO to determine whether there was enrichment in any functional subcategories. The number of differentially expressed proteins was imported into IPA (Ingenuity Pathway Analysis) software and used to perform protein biological pathway analysis based on the Gene Ontology (GO) and UniProt databases.
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis
LGG microcapsules were cocultured with planktonic E. coli for 48 h. The cells were then pelleted by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 5 min at 4 °C and then resuspended in 1 mL TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) for total RNA isolation, according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Residual genomic DNA was then removed by treating isolated RNA with a Turbo DNAfree kit (Ambion, Austin, TX). Then, cDNA was synthesised using the PrimeScript RT Master Mix (Takara), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. qRT-PCR amplifications were performed with at least three biological replicates using 2 × SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM II (DRR081A, Takara) with Stratagene MX3000P (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA). The housekeeping gene 16S rRNA was used as a control for normalisation. The qRT-PCR primers are provided in Table S1. The data were normalised against 16S rRNA and the p-values from Student’s t-tests are reported as follows: * ≤ 0.05, ** ≤ 0.01, and *** ≤ 0.001.
Detection of antibiotic resistance
The antibiotic resistance of the E. coli coculture with LGG microcapsules was determined using the inhibition zone method [13]. The E. coli culture before and after coculture was used as the test strain and inoculated into LB solid medium at 1% of the total amount. After solidification, 1 cm diameter filter paper with 500 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL or 5 μg/mL ampicillin (Amp) was impregnated on the inoculated agar plates and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. The blank medium was the negative control. After incubation, the diameter of the inhibition zone (accurate to 0.1 mm) was measured.
Results
The inhibition effect of LGG microcapsules on E. coli biofilm formation
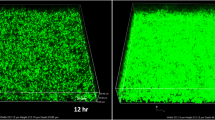
The LGG microcapsules appeared spherical, were well dispersed in the solution and were relatively uniform in size. Because of the high cell count of the microcapsules at the end of culturing, which resulted in the appearance of dark microcapsule density, the cells occupied almost all of the inner space (Fig. 1 a and b). The diameter of the microcapsules entrapped with LGG was about 200 μm (Fig. 1c). The observed reduction in the intensity of fluorescence provided evidence of biofilm inhibition, with the confocal software analysis showing that the E. coli biofilm thickness was decreased from 25.2 ± 1.3 μm to 12.3 ± 0.9 μm after coculture (Fig. 1d).
Optical images of LGG microcapsules produced by the emulsification/internal gelation technique (bar = 100 μm) at (a) 0 h culture and (b) 24 culture. c Size distribution of LGG microcapsules produced by the emulsification/internal gelation technique. d Confocal laser scanning microscopy images of E. coli biofilm formation after coculture with LGG microcapsules for 24 h
Global proteomic analysis of E. coli and LGG before and after coculture treatment
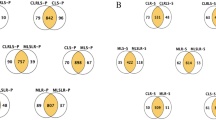
E. coli in the biofilm functional genome was evaluated at the proteome level in response to LGG microcapsules, before and after coculture. The experiments were performed in biological triplicates. Proteins from total bacterial lysates were extracted and digested in solution and the resulting peptides were analysed using LC-MS/MS [14]. In total, 76,382 matched spectra resulted in 12,236 matched peptides assembled into 1655 proteins in groups A and group C, and 58,028 matched spectra led to 10,321 matched peptides assembled into 1431 proteins in groups B and D (Additional files 1 and 2). Differential expression was considered as proteins that were significantly different with an ANOVA p-value < 0.05 and with at least a 1.2-fold change (cut-off value), as shown in the Venn diagram in Fig. 2a. For E. coli, there were 20 proteins not identified in group C but identified in group A, while 68 proteins identified in group C were not identified in group A. For LGG, there were 35 proteins not identified in group D but identified in group B, while there were 16 proteins identified in group D that were not identified in group B. Detailed information on these differentially expressed proteins is given in Additional files 3 and 4. Hierarchical cluster analysis was performed for the coculture and control groups. As shown in Fig. 2b, the common differentially expressed proteins in the coculture groups did not cluster with the ones in the control groups.
a Venn diagram summarising the common and differentially expressed proteins before and after coculture. b Hierarchical cluster of proteins differentially expressed in (a) E. coli before coculture (group C) and after coculture (group A), and (b) LGG before coculture (group D) and after coculture (group D). Red represents high expression and blue represents low expression. Two main clusters of proteins can be observed, one upregulated (right) and the other downregulated (left)
The next focus was on the common differentially expressed proteins identified both before and after coculture. As shown in Table 1 and Fig. S1, for E. coli a total of 262 differentially expressed proteins were identified in groups A and C, among which 31 proteins were upregulated and 231 proteins were downregulated. For LGG, 291 proteins were identified in groups B and D, among which 104 proteins were upregulated and 187 proteins were downregulated. The top 10 most differentially expressed proteins in both strains are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
Functional categorisation of common differentially expressed proteins in E. coli and LGG
The possible functions of the common differentially expressed proteins were investigated. The functions of the regulated bacterial proteins were enriched according to GO terms, with the redundant GO terms summarised and unified.
Functional categorisation of common differentially expressed E. coli proteins
A total of 358, 356 and 50 GO terms relating to molecular function, biological processes and cellular components, respectively, were generated based upon the upregulated proteins in E. coli after coculture; a total of 56, 57 and 26 GO terms, respectively, were generated based upon the downregulated proteins. Among the GO terms for biological processes, “cellular response to DNA damage stimulus” (22.75%) was the most common function in upregulated proteins in the E. coli coculture group. Among the GO terms for cellular components, the most common upregulated proteins belonged to “cytosol” (33.86%), while the most common downregulated proteins belonged to “plasma membrane” (12.58%). For molecular function, 13.51% of up- and 11.69% of downregulated proteins were related to “4 iron, 4 sulphur cluster binding” and “ATPase activity”, respectively (Fig. 3).
Annotation of overall regulated bacterial protein functions by enrichment of Gene Ontology (GO) terms. Based on the classifications of the GO annotation, the overall bacterial functions were categorised into biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components, and are displayed in histogram format. The number of GO terms for each of the three categories is shown and the proportion of each specific subcategory is also provided. Subcategories with GO terms less than 1% are classified as “other”
Functional categorisation of common differentially expressed LGG proteins
A total of 211, 138 and 20 GO terms for molecular function, biological processes and cellular components, respectively, were generated: 85, 50 and 10 GO terms, respectively, were related to upregulated proteins in LGG after coculture, while 150, 102 and 15 GO terms, respectively, were related to downregulated proteins. Among the GO terms for biological processes, “carbohydrate metabolic process” (22.75%) was the most common function in upregulated proteins in the coculture group. Among the GO terms for cellular components, the most common upregulated proteins belonged to “cytoplasm” (33.86%), while the most common downregulated proteins belonged to “ATP binding” (12.58%). For molecular function, 17.92% of up- and 16.55% of downregulated proteins were related to “oxidoreductase activity” and “structural constituent of ribosome”, respectively (Fig. 3).
Pathway analysis
As shown in Table 4, in E. coli the common differentially expressed upregulated proteins were enriched in the fatty acid biosynthesis, biotin metabolism and nitrogen metabolism pathways and the common differentially expressed downregulated proteins were enriched in the purine metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation and protein export signaling pathways. However, in LGG strains, as shown in Table 5, there were no upregulated pathways enriched in the KEGG analysis, and the common downregulated signaling pathways were galactose metabolism, amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism, and metabolic pathways. By exploring the possible global protein-protein interactions (PPIs; Fig. 4), and in combination with Tables 2 and 3, several genes in E. coli and LGG were identified for subsequent analysis.
Confirmation of the target proteins of E. coli and LGG at the mRNA level in the coculture model
qRT-PCR analysis of selected targets was conducted to validate the observed differentially expressed protein levels (Fig. 5). In line with the findings from the global proteomic analysis, increased bioD2, panD and ygiW mRNA levels in E. coli were observed. The mRNA levels of bamE and dnaK, which encode downregulated expression at the transcription level, were also quantified. Additionally, given the extensive effect of LGG microcapsules on biofilm inhibition, the mRNA expression levels of purD and purM were found to be upregulated 3.1-fold and 7.3-fold, respectively. The mRNA levels of murB, murF and ackA were also decreased after coculture with E. coli for 48 h.
Relative mRNA expression of selected targets from global proteomics analysis. Total RNA isolated from coculture treatment or pure culture of E. coli and LGG was reversed transcribed and cDNA was quantified by qRT-PCR using target-specific primers. The data represents the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments normalised to 16S RNA. Statistically significant differences between coculture treatment and pure culture treatment, as determined by Student’s t-test analysis (unpaired, two-tailed), are represented as *p ≤ 0.5, **p ≤ 0.1 and ***p ≤ 0.01
Antibiotic resistance
The antibiotic resistance of E. coli obtained from pure culture and after coculture with LGG microcapsules was determined. The results showed that the E. coli antibiotic resistance was concentration-dependent: the inhibition zone of the E. coli pure culture was 9.1 ± 1.2 mm, 2.1 ± 0.2 mm and 0.2 ± 0.03 mm at the three decreasing Amp concentrations, respectively; furthermore, the inhibition zone of E. coli after coculture was 11.1 ± 0.93 mm, 3.4 ± 0.76 mm and 0.98 ± 0.03 mm, respectively, each of which was significantly larger than the inhibition zone of the E. coli pure culture at different Amp concentrations. Negative controls did not show any inhibitory effect on the growth of tested bacteria (Fig. 6). Antibiogram results revealed that E. coli after coculture with LGG microcapsules showed increased susceptibility to Amp compared with pure E. coli culture.
Discussion
Biofilm formation is associated with resistance to antibiotic therapy and therefore continues to be a major health threat in both hospital and community settings [15, 16]. We previously reported that probiotic LGG microcapsules could inhibit E. coli biofilm formation without causing antibiotic resistance. Probiotics have many benefits for human health and are used both therapeutically and in the food industry [17]. These findings prompted the present evaluation of the mechanism of action underlying the inhibitory effect of LGG microcapsules on antibacterial biofilm formation.
This study demonstrated that, after coculture treatment, there were 1655 and 1431 proteins expressed in E. coli and LGG strains, respectively. Overall, 262 and 291 common differentially expressed proteins, respectively, exhibited greater than 2-fold changes in expression compared to the control group.
Effects of LGG microcapsules on biofilm formation capacity and the metabolism of E. coli in coculture
There are four major steps involved in biofilm formation: (i) initial adhesion or attachment (reversible); (ii) early development of biofilm structure (irreversible); (iii) maturation of the developed biofilm; and, (iv) dispersion of cells from the biofilm to return to the planktonic state. Many genes and proteins are involved in the complex process of biofilm formation [18]. Proteomics result also revealed some proteins with functions relating to biofilm formation and development. For example, OmpA protein is associated with biofilm formation [19], and an association between biofilm formation, structure and the expression levels of genes relating to biofilm formation and biofilm-specific resistance was found in Acinetobacter baumannii Strains isolated from burn infections in Ahvaz, Iran. Furthermore, some other proteins have been reported in relation to biofilm formation and development, such as Dnak [20] and RpoA [21]. It is assumed that the downregulation of these proteins in E. coli after coculture with LGG microcapsules decreased the initial adhesion or attachment ability of E. coli, which resulted in decreased biofilm thickness (Fig. 1d).
Proteomic analysis detected differentially expressed E. coli proteins before and after coculture. These differences were related to cellular responses to DNA damage stimulus and cell wall organisation. Thus, these findings indicated that the proteins involved in response to the environment changed during coculture. Based on this, the stress response of E. coli was focused on in the coculture model. Accordingly, increased mRNA levels of the bioD2 gene were observed. The bioD2 protein is an ATP-dependent dethiobiotin synthetase that encodes a homolog of dethiobiotin synthetase, which is the penultimate enzyme in the biotin synthesis pathway. Therefore, it is likely that this upregulated bioD2 expression in the presence of LGG microcapsules enhanced the degrader’s requirement for biotin, which is synthesised de novo under the acidic, osmotic and oxidative stress conditions with the involvement of different isozymes. This explanation was supported by the upregulated expression observed in both the proteomics and qRT-PCR analyses and was further validated by the inhibitory effect of LGG microcapsules on E. coli biofilm formation.
Aspartate 1-decarboxylase (PanD) is the only enzyme capable of β-alanine synthesis in E. coli. In bacteria, fungi and plants, β-alanine is a precursor to pantothenate which, in turn, is a required metabolite for the synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) in all organisms [22]. Research indicates that chloroplast engineering of the beta-alanine pathway by overexpression of E. coli panD enhances thermotolerance of photosynthesis and biomass production following high-temperature stress [23].
During the coculture process, E. coli strains were frequently confronted by acid stress produced by LGG metabolism. The ygiW protein is reported to be involved in the stress response associated with exposure to H2O2, cadmium and acid [24]. An earlier study also reported that the expression of functional YgiW and QseC proteins is necessary for optimal biofilm growth of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans [25]. Comparison of the expression levels of the ygiW gene between LGG microcapsules and coculture conditions revealed a 4.0-fold change.
Proteomic analysis revealed the downregulation of several virulence-related proteins, including bamE and dnaK, when E. coli was treated with LGG microcapsules. The most downregulated protein, bamE (MHC class II analog protein, log2FC = − 9.2), is an integral outer membrane β-barrel protein (OMP) that is assembled by the beta-barrel assembly machine (Bam) complex in Gram-negative bacteria [26]. Another downregulated protein, DnaK, is an important factor in all three antibiotic-related persister formation pathways. The decreased persistence phenotype, as well as the growth defect of dnaK, seem to depend on functional (p) ppGpp [27]. Heterogeneous expression of the dnaK gene in Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris can significantly enhance the resistance of host bacteria E. coli against heat and acid stresses [28]. Furthermore, the DnaK protein has also been reported to play an important role in bacterial biofilm formation [29, 30].
EPS is the characteristic that distinguishes biofilms from planktonic bacteria. The EPS matrix is the medium through which bacterial cells are attached to the surface and facilitate cell-to-cell as well as cell-to-surface interactions. It provides support to biofilm cells and gives the biofilm a three-dimensional architecture, thus providing a protective as well as structural role. Water is one of the major components of the EPS, along with extrapolymeric polymers, proteins, nucleic acids, nutrients, lipids and other metabolites. An EPS inhibition effect has been reported in many papers [31]. However, in the present study no differentially expressed proteins that were downregulated in E. coli in the coculture model related to EPS formation.
In summary, it is believed that the LGG microcapsules inhibited E. coli biofilm formation and decreased antibiotic resistance mainly through the disruption of cell metabolism and by decreasing the expression of stress-related proteins.
Effects of E. coli on the growth and metabolism of LGG microcapsules in coculture
Proteomic analysis indicated that E. coli coculture with LGG microcapsules elicited a cellular response in LGG and E. coli strains that was related to a certain intracellular mechanism. Coculture with LGG microcapsules places environmental stress on E. coli and this, in turn, raises a cellular response in LGG as well [32]. For LGG, the possible responses to E. coli coculture include physiological and developmental changes, reprogramming of the resistance gene or proteins, and alterations to how energy is supplemented. In the present study, proteomic analysis revealed that coculture with E. coli significantly upregulated two nucleotide metabolism–related genes, purD and purM. The pur-operon (purEKCSQLFMNHD) is responsible for the catalysis of de novo synthesis of inosine monophosphate (IMP) from phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate [33]. In Staphylococcus aureus, purine biosynthesis enzymes have been closely implicated in the virulence, persistence and tolerance of stresses such as antibiotic resistance [34, 35]. Such extensive effects could be attributed to the potential modulation of transcription of the operon by bacteria-secreted extracellular compounds. In another study, purD and purF mutants were constructed in macrophage-like RAW264.7 and HeLa cells. The purD and purF mutants showed significantly decreased intracellular survival, and complementation of these mutants with intact copies of the purD or purF genes of Brucella abortus strain RB51 restored these defects. These findings suggest that genes encoding the early stages of purine biosynthesis (purD and purF) are required for intracellular survival and virulence of the RB51 strain [36]. Therefore, it may be that LGG strains maintain intracellular survival and homeostasis by upregulating the purD and purM genes.
Coculture of LGG microcapsules with E. coli appeared to downregulate murB gene expression and to completely abolish expression of the murF gene. Bacteria generally synthesise their own active form of N-acetylmuramic acid, UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid [37], and the MurB enzyme (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyruvate enol ether reductase) plays an important role in the biosynthesis of this substance [38]. The MurB enzyme converts UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyruvate enol ether to UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid by reducing its double bond [39]. Inhibition of the MurB enzyme reduces or blocks the synthesis of peptidoglycan, resulting in an incomplete bacterial cell wall; this eventually leads to the production of lytic bacteria under the pressure of permeation [40]. Therefore, downregulation of the murB and murF genes implies suppressed LGG cell membrane biosynthesis, to some extent, when LGG was cocultured with E. coli.
Metabolism refers to the basic physiological processes that maintain a living organism. Coculture of LGG microcapsules with E. coli was associated with the downregulation of metabolism-related genes. Acetate presumably provides a relevant nutrient for Enterobacteria as well as other bacteria [41, 42]. In E. coli, the primary pathway of acetate production involves two enzymes that are intimately connected to central metabolism, phosphotransacetylase (Pta) and acetate kinase (AckA) [43]. During exponential growth, acetyl-CoA, the product of glycolysis and the consumable substrate for the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, can be converted into acetylphosphate (AcP) by Pta and then into acetate by AckA. E. coli also takes up acetate, using the Pta-AckA pathway in reverse, resulting in the synthesis of acetyl-CoA. This pathway typically operates at high extracellular acetate concentrations (≥ 8 mM) [44]. Disruption of the Pta-AckA pathway during overflow metabolism causes a significant reduction in the growth rate and viability of the bacteria, although this is not due to intracellular ATP depletion [45, 46]. Hence, downregulation of the ackA gene will affect LGG metabolism.
Conclusions
As far as is known, the present study is the first published attempt to determine protein expression differences associated with a probiotic E. coli in situ coculture. Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis indicated that E. coli and microencapsulated LGG may impact cellular metabolism, the stress response, transcription, and the cell membrane through regulating the expression of PanD, YgiW, BioD2, DamE and DnaK proteins in E. coli, and PurD, PurM, AckA, MurB, MurF and RpoC proteins in LGG. The coculture with LGG microcapsules also decreased the E. coli resistance to Amp. Taken together, these findings further understanding of the possible molecular action of LGG microcapsules against E. coli biofilm formation. Future studies will focus on the analysis of posttranslational modifications of differentially expressed proteins as well as endogenous protein complexes and protein-protein interactions.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [figshare] repository, [https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.11923542].
References
Monnappa AK, Dwidar M, Seo JK, Hur JH, Mitchell RJ. Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and invasion into human epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:3811.
Hetrick EM, Shin JH, Paul HS, Schoenfisch MH. Anti-biofilm efficacy of nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14):2782–9.
Beloin C, Roux A, Ghigo JM. Escherichiaia coli biofilms. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;322:249–89.
Matsuda Y, Cho O, Sugita T, Ogishima D, Takeda S. Culture supernatants of Lactobacillus gasseri and L. crispatus inhibit Candida albicans biofilm formation and adhesion to HeLa cells. Mycopathologia. 2018;183(4):691–700.
Song HY, Zhang JB, Qu JL, Liu JJ, Yin PY, Zhang GX, Shang D. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microcapsules inhibit Escherichiaia coli biofilm formation in coculture. Biotechnol Lett. 2019;41(8–9):1007–14.
Abdallah C, Dumas-Gaudot E, Renaut J, Sergeant K. Gel-based and gel-free quantitative proteomics approaches at a glance. Int J Plant Genomics. 2012;2012:494572.
Yan W, Chen SS. Mass spectrometrybased quantitative proteomic profiling. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2005;4(1):27–38.
Megger DA, Bracht T, Meyer HE, Sitek B. Label-free quantification in clinical proteomics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834(8):1581–90.
Dekeersmaecker SC, Vanderleyden J. Constraints on detection of autoinducer-2 (AI-2) signaling molecules using Vibrio harveyi as a reporter. Microbiology. 2003;149(Pt 8):1953–6.
Song HY, Yu WT, Liu XD, Ma XJ. Improved probiotic viability in stress environments with post-culture of alginate-chitosan microencapsulated low density cells. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;108:10–6.
Zhang JY, Poh CL. Regulating exopolysaccharide gene wcaF allows control of Escherichiaia coli biofilm formation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13127.
Xue WM, Yu WT, Liu XD, Wang HW, Ma XJ. Chemical method of breaking the cell-loaded sodium alginate/chitosan microcapsule. Chem J Chin Univ. 2004;25:1342–6.
Wu J, Xu GQ, Jin YY, Sun C, Zhou L, Lin GD, Xu R, Wei L, Fei H, Wang D, et al. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus sp GFP-2, a novel Bacillus strain with antimicrobial activities, from Whitespotted bamboo shark intestine. AMB Express. 2018;8(1):84.
Silva JC, Gorenstein MV, Li GZ, Vissers JP, Geromanos SJ. Absolute quantification of proteins by LCMSE: a virtue of parallel MS acquisition. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5(1):144–56.
Rasmussen RV, Fowler VG, Skov R, Bruun NE. Future challenges and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia with emphasis on MRSA. Future Microbiol. 2011;6(1):43–56.
Grundmann H, Aires-de-Sousa M, Boyce J, Tiemersma E. Emergence and resurgence of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a public-health threat. Lancet. 2006;368(9538):874–85.
Vieco-Saiz N, Belguesmia Y, Raspoet R, Auclair E, Gancel F, Kempf I, Drider D. Benefits and inputs from lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters during food-animal production. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:57.
Sharma G, Sharma S, Sharma P, Chandola D, Dang S, Gupta S, Gabrani R. Escherichiaia coli biofilm: development and therapeutic strategies. J Appl Microbiol. 2016;121(2):309–19.
Amin M, Navidifar T, Shooshtari FS, Rsahno M, et al. Association between biofilm formation, structure, and the expression levels of genes related to biofilm formation and biofilm-specific resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from burn infection in Ahvaz. Iran Infect Drug Resist. 2019;12:3867–81.
Jain S, Smyth D, O’ Hagan BMG, Heap JT, McMullan G, Minton NP, Ternan NG. Inactivation of the dnaK gene in Clostridium difficile 630 △erm yields a temperature-sensitive phenotype and increases biofilm-forming abiligy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):17522.
Wang C, Zhang QL, Wang Y, Tang XD, An YN, Li SL, Xu HY, et al. Comparative proteomics analysis between biofilm and planktonic cells of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Comparative study. 2019;40(20):2736–46.
Webb ME, Smith AG, Abell C. Biosynthesis of pantothenate. Nat Prod Rep. 2004;21(6):695–721.
Fouad WM, Altpeter F. Transplastomic expression of bacterial L-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase enhances photosynthesis and biomass production in response to high temperature stress. Transgenic Res. 2009;18(5):707–18.
Lee J, Hiibel SR, Reardon KF, Wood TK. Identification of stress-related proteins in Escherichiaia coli using the pollutant cis-dichloroethylene. J Appl Microbiol. 2010;108(6):2088–102.
Juárez-Rodríguez MD, Torres-Escobar A, Demuth DR. ygiW and qseBC are co-expressed in Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and regulate biofilm growth. Microbiology. 2013;159(Pt 6):989–1001.
Rigel NW, Ricci DP, Silhavy TJ. Conformation-specific labeling of BamA and suppressor analysis suggest a cyclic mechanism for β-barrel assembly in Escherichiaia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(13):5151–6.
Liu S, Wu N, Zhang S, Yuan Y, Zhang W, Zhang Y. Variable persister gene interactions with (p) ppGpp for persister formation in Escherichiaia coli. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:1795.
Xu X, Jiao L, Feng X, Ran J, Liang X, Zhao R. Heterogeneous expression of DnaK gene from Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris improves the resistance of Escherichiaia coli against heat and acid stress. AMB Express. 2017;7(1):36.
Grudniak AM, Wlodkowska J, Wolska KI. Chaperone DnaJ influences the formation of biofilm by Escherichiaia coli. Pol J Microbiol. 2015;64(3):279–83.
Veen SVD, Abee T. HrcA and DnaK are important for static and continuous-flow biofilm formation and disinfectant resistance in listeria monocytogenes. Microbiology (Reading). 2010;156(Pt 12):3782–90.
Vijayakumar K, Thirunanasambandham R. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural inhibits acinetobacter baumannii biofilms: an in vitro study. Arch Microbiol. 2020; Online ahead of print.
Dahl JU, Koldewey P, Salmon L, Horowitz S, Bardwell JC, Jakob U. HdeB functions as an acid-protective chaperone in bacteria. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(16):9950.
Diether M, Nikolaev Y, Allain FH, Sauer U. Systematic mapping of protein-metabolite interactions in central metabolism of Escherichiaia coli. Mol Syst Biol. 2019;15(8):e9008.
Kriegeskorte A, Block D, Drescher M, Windmüller N, Mellmann A, Baum C, Neumann C, et al. Inactivation of thyA in Staphylococcus aureus attenuates virulence and has a strong impact on metabolism and virulence gene expression. MBio. 2014;5(4):e01447–14.
Yee R, Cui P, Shi W, Feng J, Zhang Y. Genetic screen reveals the role of purine metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus persistence to rifampicin. Antibiotics (Basel). 2015;4(4):627–42.
Truong QL, Cho Y, Barate AK, Kim S, Watarai M, Hahn TW. Mutation of purD and purF genes further attenuates Brucella abortus strain RB51. Microb Pathog. 2015;79:1–7.
Karl HS, Otto K. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1973;37(2):258.
Benson TE, Walsh CT, Hogle JM. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase. Protein Sci. 1994;3(7):1125–7.
Lees WJ, Benson TE, Hogle JM, Walsh CT. (E)-enolbutyryl-UDP-N-acetylglucosamine as a mechanistic probe of UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase (MurB). Biochemistry. 1996;35(5):1342–51.
Weidel W, Pelzer H. Bagshaped macromolecules - a new outlook on bacterial cell walls. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1964;26:193–232.
Rowland I, Gibson G, Heinken A, Scott K, Swann J, Thiele I, Tuohy K. Gut microbiota functions: metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(1):1–24.
Wolfe AJ. The acetate switch. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005;69(1):12–50.
De Mets F, Van Melderen L, Gottesman S. Regulation of acetate metabolism and coordination with the TCA cycle via a processed small RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(3):1043–52.
Enjalbert B, Millard P, Dinclaux M, Portais JC, Létisse F. Acetate fluxes in Escherichiaia coli are determined by the thermodynamic control of the Pta-AckA pathway. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42135.
Marshall DD, Sadykov MR, Thomas VC, Bayles KW, Powers R. Redox imbalance underlies the fitness defect associated with inactivation of the Pta-AckA pathway in Staphylococcus aureus. J Proteome Res. 2016;15(4):1205–12.
Sadykov MR, Thomas VC, Marshall DD, Wenstrom CJ, Moormeier DE, Widhelm TJ, Nuxoll AS, et al. Inactivation of the Pta-AckA pathway causes cell death in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 2013;195(13):3035–44.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The materials used in this manuscript were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81601734). The proteomic analysis work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81873156) and the Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 20180530062) supported the publishing charges.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Song HY and Shang D designed and planned the study. Lou N and Liu Jian J conducted the experiments. Xiang H contributed the analytical tools and analysed the data. Song HY wrote the manuscript. All authors were involved in editing the manuscript and all made substantial contributions to the content and approved the final version.
Authors’ information
Dong Shang is a professor in First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. He performed his research as a senior visiting scholar at Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals and the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) in Pennsylvania, USA. Currently, he is Chief Surgeon of the Department of General Surgery, Pancreatic-Biliary Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, as well as the leader of the National Clinical Key Specialist-Department of Acute Abdominal Surgery, at the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. His fields of expertise are the clinical and experimental biomedical sciences of pancreatic disease, including the molecular mechanism and innovative drug development of AP, CP, and PC.
Huiyi Song is an associate professor in First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. Her current research interests include understanding the biomaterials-bio interactions and using nanotechnologies for immunotherapy, anti-resistant bacterial coating.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
: Table S1. Primers used in this study.
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
Volcano plots of differentially expressed proteins after E. coli and LGG microcapsule coculture. Volcano plots were generated based on the fold-change of protein levels using averaged spectral counts from biological triplicates. The x-axis indicates a log2-fold change and the y-axis indicates -log10 p-values based on Student’s t-test. The horizontal line indicates a p-value < 0.5 and the vertical lines represent a fold-change > 1.5. In all plots, the green dots represent upregulated proteins in the upper left quadrant, whereas downregulated proteins are shown as red dots in the upper right quadrant. Black dots indicate proteins for which differences in abundance were not statistically significant.
Additional file 3: Table S2.
Most highly differentially upregulated and downregulated proteins in E. coli after coculture.
Additional file 4: Table S3.
Most highly differentially upregulated and downregulated proteins in LGG microcapsules after coculture.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H., Lou, N., Liu, J. et al. Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis of the inhibition effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on Escherichia coli biofilm formation in co-culture. Proteome Sci 19, 4 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12953-021-00172-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12953-021-00172-0