Abstract
Background
Glucose is the main carbon source of E. coli and a typical substrate in production processes. The main glucose uptake system is the glucose specific phosphotransferase system (Glc-PTS). The PTS couples glucose uptake with its phosphorylation. This is achieved by the concomitant conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to pyruvate. The Glc-PTS is hence unfavorable for the production of succinate as this product is derived from PEP.
Results
We studied, in a systematic manner, the effect of knocking out the Glc-PTS and of replacing it with the glucose facilitator (Glf) of Zymomonas mobilis on succinate yield and productivity. For this study a set of strains derived from MG1655, carrying deletions of ackA-pta, adhE and ldhA that prevent the synthesis of competing fermentation products, were constructed and tested in two-stage cultivations. The data show that inactivation of the Glc-PTS achieved a considerable increase in succinate yield and productivity. On the other hand, aerobic growth of this strain on glucose was strongly decreased. Expression of the alternative glucose transporter, Glf, in this strain enhanced aerobic growth but productivity and yield under anaerobic conditions were slightly decreased. This decrease in succinate yield was accompanied by pyruvate production. Yield could be increased in both Glc-PTS mutants by overexpressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck). Productivity on the other hand, was decreased in the strain without alternative glucose transporter but strongly increased in the strain expressing Glf. The experiments were complemented by flux balance analysis in order to check the observed yields against the maximal theoretical yields. Furthermore, the phosphorylation state of EIIAGlc was determined. The data indicate that the ratio of PEP to pyruvate is correlating with pyruvate excretion. This ratio is affected by the PTS reaction as well as by further reactions at the PEP/pyruvate node.
Conclusions
The results show that for optimization of succinate yield and productivity it is not sufficient to knock out or introduce single reactions. Rather, balancing of the fluxes of central metabolism most important at the PEP/pyruvate node is important.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Biotechnological production of fine chemicals has gained increasing interest during the last years. Succinate has been ranked within the top 12 bio-based products by the US Department of Energy [1] and hence there are numerous efforts to produce succinate biotechnologically. Under anaerobic conditions, succinate is formed by E. coli as one of the products of mixed acid fermentation together with acetate, lactate, formate and ethanol [2]. Under aerobic conditions, succinate is an intermediate of the tricarboxylic acid cycle but it is not excreted. As succinate is produced only in minor amounts during natural fermentation, different strategies have been developed in order to improve the efficiency of succinate production by E. coli. Common to anaerobic strategies is prohibiting the production of the competing fermentation products acetate, formate and lactate by deletion of genes involved in their production (Fig. 1). This is often complemented by overexpression of endogenous or heterologous genes catalyzing oxaloacetate production from PEP or pyruvate to enhance metabolic fluxes towards succinate (see [3,4,5,6] and references therein). A major problem of all these strategies is that prohibiting the production of competing fermentation products strongly impairs growth under fermentative conditions. Hence, most engineered strains are incapable of fermentative growth in defined medium with glucose as sole carbon source. Many studies have hence been performed with complex media or have applied two stage strategies with an aerobic growth phase followed by an anaerobic production phase. Usage of complex medium however complicates the analysis of strain behavior as it is basically unknown which medium components are used and how they affect fluxes in the cell [7,8,9]. Also it complicates the calculation of yields.
Scheme of anaerobic glucose metabolism in E. coli. Shown are reactions involved in anaerobic glucose metabolism. Only reactions important for the study at hand are shown. Deletions present in all mutant strains are marked by red crosses. Grey arrows indicate that the respective fermentation products are absent or strongly reduced in the mutant strains. The blue arrows marks the Glc-PTS that is present in some of of the strains. The red arrow indicates the reaction catlyzed by Pck, while the green arrow indicates the reaction of the Ppc. ATP and NAD are not show in the figure with exeption of the ATP gained by Pck
Apart from anaerobic strategies of succinate production also aerobic and microaerobic strategies have been applied. In these strategies the production of acetate is prohibited, accompanied by a block in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and an enhancement of the glyoxylate shunt [10,11,12,13]. Aerobic strategies were motivated to overcome the severe growth problems of succinate production strains under anaerobic conditions. The mayor drawback of aerobic strategies is the low maximal theoretical yield of only 1 mol succinate per mol of glucose [11], which is significantly lower than for anaerobic conditions.
The Glc-PTS represents the major glucose uptake system in E. coli. It couples uptake with concomitant phosphorylation of glucose. The phosphodonor of the PTS is phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) which is converted to pyruvate by this reaction (Fig. 1). The phosphoryl group from PEP is transferred by a phosphoryl transfer chain consisting of the PTS proteins EI, HPr, EIIAGlc and EIICBGlc until it ultimately is transferred to the incoming substrate glucose [14]. Mutations in ptsG, the gene encoding the EIICBGlc, were isolated as spontaneous mutations leading to higher succinate production rates. This mutation was also predicted to be favorable by theoretical methods [6, 11, 15, 16].
One mole of PEP is converted to pyruvate for each mole of internalized and phosphorylated glucose. PEP is an essential precursor of succinate and this is why inactivation of the PTS improves succinate production in E. coli [8, 17]. Strains lacking the Glc-PTS or the PTS in general are characterized by slow growth and low glucose uptake rates. Besides the Glc-PTS, glucose can be taken up by several other uptake systems, both PTS-systems (ManXYZ) [18] and non-PTS systems, the most important being MglABC, GalP and MalEFG [19,20,21,22]. Under natural conditions these systems can replace the PTS only marginally. Wang and coworkers [23] reported that overexpression of galactose permease (galP) in a PTS− strain led to improved succinate production. Another strategy for improving cell growth and glucose uptake, and therefore also for increasing succinate production in PTS mutants, is the usage of the glucose facilitator protein, Glf of Z. mobilis [24,25,26], that allows an efficient uptake of glucose into cells by facilitated diffusion.
Although mutations of the Glc-PTS as well as introduction of alternative glucose transporters have been reported in a number of different studies, to our knowledge no systematic analysis of the effects of glucose uptake on succinate production have been reported.
In this article, we systematically compared a set of E. coli strains, distinguished by differences in glucose uptake, for the production of succinate in a two-stage strategy. Different knockout strains were analyzed for their growth capabilities, glucose consumption as well as the production of succinate and other by-products. A two-stage strategy was chosen to profit from the high theoretical yield under anaerobic conditions while at the same time circumvent the severe anaerobic growth defects of the test strains.
Common to all strains are knock outs of ldhA, ackA-pta and adhE. The strains differ with respect to glucose uptake: while one of the strains, KBM151101, still has the native Glc-PTS, this system (ptsG) was deleted in SB2. It is unknown which system is used for glucose uptake in SB2. To improve glucose uptake, the glucose facilitator, Glf, from Z. mobilis was introduced into SB2, giving rise to strain KBM1673. In addition, we overexpressed PEP carboxylase (Ppc) or PEP carboxykinase (Pck), important enzymes in the PEP to oxaloacetate conversion in the test strains.
To understand the observed behavior in more detail, the growth assays were complemented by determination of the intracellular ATP levels and by determination of the phosphorylation state of EIIAGlc. The experimental studies were completed by theoretical analyses of optimal growth and product formation of the strains using flux balance analysis (FBA). The data illustrate that the type of glucose uptake indeed is important for achieving a high succinate yield but besides this, it is also important to balance fluxes especially at the pyruvate/PEP node.
Methods
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
Strains used in this study were E. coli MG1655 and mutants thereof listed in Table 1. Mutant strains were constructed by homologous recombination [27] or by P1 transduction [28]. To integrate the glucose facilitator, Glf, of Zymomonas mobilis into the genome of E. coli, gene glf, encoding the glucose facilitator, was amplified together with glk from plasmid pF-71 (kind gift of G. Sprenger, University of Stuttgart). The constitutive scrK promoter was amplified from pCS26-scrK [29] and fragments were cloned into pAH162 [30] using the Gibson Assembly Cloning Kit from NEB. glk was deleted from the construct using the Q5 site directed mutagenesis kit from NEB. The corresponding plasmid pAH162-scrKP-glf was integrated into the chromosome of SB2 as described by Haldimann and Wanner [30]. For construction of pPckA the coding sequence of pckA was amplified from chromosomal DNA of MG1655 and cloned into the expression vector pRR48c [31]. Primers used for plasmid and strain constructions are indicated in Additional file 1: Table S1.
E. coli cells from agar plates were grown in LB0 medium (10 g/l tryptone, 5 g/l yeast extract, 5 g/l NaCl) for 5–6 h at 37 °C. Afterwards the culture was diluted 1:100 or 1:50 into minimal salts medium [33] with 4 g/l glucose and incubated aerobically on a rotatory shaker (250 rpm) at 37 °C for 8–12 h. The culture in mid exponential growth phase was centrifuged and the washed cells were inoculated to 109 cells/ml into 50 ml fresh minimal medium containing 4 g/l glucose and 2 g/l NaHCO3. For anaerobic cultivations the culture was split into aliquots and cells were incubated in tightly sealed 5 ml glass vials at 37 °C without agitation.
Analytical techniques
Optical density (OD420) was determined spectrophotometrically at 420 nm (Ultrospec3000, Amersham, Bioscience). An OD420 of 1 corresponds to 5*108 cells/ml. To assure a linear correlation of OD420 and biomass, cell cultures were diluted before the measurement to obtain a measurement value between OD 0.05 and 0.5. The culture samples were harvested by quick centrifugation (2 min) and supernatants were used for further analysis. For organic acids measurements such as succinate, pyruvate, formate, acetate and orotate the supernatant was filtered and analyzed by HPLC using an Agilent 1100 Series system equipped with DAD detector (Agilent Technologies) and an Inertsil ODS-3 column (Gil Science Inc.). As mobile phase 0.1M NH4H2PO4, pH 2.6 solution was used at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. Concentrations in the samples were calculated based on standard solutions run under identical conditions.
The amounts of glucose, ethanol and acetate were determined using the respective enzymatic test kits d-glucose-HK, ethanol and acetc acid of Megazyme International Ireland.
Glucose uptake was determined by linear regression analysis by the method of least squares based on glucose levels determined in the interval between 0 and 48 h. Yield and productivity were determined independently. Yield was determined by plotting the time series of glucose concentrations in the medium against the concentrations of succinate at the given time points. Yield was estimated from the line of best fist applying total least square regression analysis to this biomass-glucose diagram. Uptake rate for glucose and production rate for succinate were determined analogously from the time course data.
Determination of EIIAGlc phosphorylation
The EIIAGlc phosphorylation state was determined by SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting as described [29, 34]. Samples were taken from mid-exponential phase under aerobic conditions and after 4 h of cultivation under anaerobic conditions, respectively.
Measurement of ATP concentration in cells
100 µl of growing culture was immediately quenched in 900 µl of boiling water and the mixture was incubated at 99 °C for 10 min. Afterwards the sample was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min and the ATP concentration of the supernatant was determined using the ATPLite kit (PerkinElmer) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. The concentration was normalized by taking into account the cell density in the respective sample.
Gene expression analysis by RT-qPCR
About 1.5*109 cells from exponential aerobic growth phase or after 2–4 h incubation in the anaerobic phase were quenched in twice the volume of RNA protect Bacterial Reagent (Qiagen), vortexed for 5 s and incubated at room temperature for 5 min. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded and the pellet was stored at − 80 °C. RNA was prepared using the Master Pure RNA Purification Kit (Epicentre). RNA concentration and purity was determined using the NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific).
mRNA was transcribed into cDNA by using the RevertAid H Minus First Strand cDNA synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Quantitative PCR of different cDNA samples was performed using the MesaGreen qPCR Master Mix Plus (Eurogenetec) with SYBR Green as detection agent and the Rotor-Gene 6000 (Corbett Life Science). Sequences of the primers used are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. Amplification conditions were: 95 °C for 10 min, 40 cycles at 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. A negative control without template was conducted for each primer pair in each PCR run and a control for DNA contamination was performed for each RNA sample used. Quantification was performed by relative quantification to housekeeping genes (rpoD, yhbc and ihfB) applying the ΔΔCt method [39, 40] with efficiency correction.
Flux balance analysis
Flux Balance Analysis (FBA) was carried out using the CobraToolbox v2.0 [35] and an adapted version of the included ecoli_core_model [36].
The exact model structure is given in the Additional file 2. The Cobra Toolbox was run in MATLAB 2014b using Gurobi optimizer version 6.5.0.
Simulation of EIIAGlc phosphorylation
To analyze the measured phosphorylation levels of EIIAGlc we used a mathematical model that considers substrate uptake for PTS and for non-PTS carbohydrates [37]. The model was developed for aerobic growth. It describes glycolysis with a reduced number of components and reactions. It comprises five components: glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, PEP, pyruvate and EIIAGlc. The components are linked by five reactions: substrate uptake, representative reaction of the upper part of glycolysis, pyruvate kinase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and by-product excretion. In case of PTS sugars, the uptake reaction requires 1 mol of PEP and produces 1 mol of pyruvate. The model was validated with experimental data for different growth rates and shows satisfactory agreement between simulation and experimental data [37]. The main outputs of the simulations are relationships between the steady-state values of the components as a function of the growth rate μ. In this way, a characteristic curve for the degree of phosphorylation of EIIAGlc in dependence on the growth rate is obtained.
The model was adapted to the various mutant strains used in this study and to the anaerobic case. In case the PTS is missing, the uptake reaction was decoupled from PEP to pyruvate conversion. To mimic the mutations, the drain of by-products e.g. acetate or lactate was omitted. In this way, the modifications focus on the pyruvate node and its drain in biosynthesis. To validate the model for the anaerobic case, the uptake rate is taken as input into the model and only the kinetic parameter for the pyruvate drain reaction was fitted to get a good agreement of the measured degree of phosphorylation of EIIAGlc with the simulation results. In the anaerobic case, only one growth rate was analyzed for each mutant. Therefore, each curve generated in the simulation could be verified with only one data point. Since under anaerobic conditions the flux through glycolysis is higher than during aerobic growth, the maximal uptake rate for strains with a PTS was increased by 30%. The simulation also allows us to determine the PEP/pyruvate ratio. The analysis of the characteristic curves for the PEP/pyruvate ratio is the basis for a correlation with the pyruvate produced by the strains during the experiment.
Results
Characterization of aerobic growth in isogenic mutant strains with different glucose uptake systems
As described in the introduction, there are numerous studies dealing with improving succinate production in E. coli. While these studies describe improvements of succinate production by knock-out or overexpression of multiple genes, a systematic investigation of the effects of a certain knock-out is lacking. ptsG or ptsI were knocked out in several strategies [8, 11, 17, 38,39,40,41,42]. These mutations dramatically slow down growth with glucose as carbon source and hence diminish productivity. We investigated, in a systematic way, the effects of knocking out ptsG and of introducing an alternative glucose transporter on succinate production. The strain analyzed, KBM151101, has deletions in adhE, ldhA and ackA-pta (Fig. 1). As KBM151101 is not able to grow anaerobically in mineral salts medium with glucose as sole carbon source, a two-stage cultivation strategy was employed. Strain SB2 was constructed by knocking out ptsG in KBM151101. In strain KBM1673 we replaced the Glc-PTS with the PTS-independent glucose facilitator, Glf, of Z. mobilis. This transporter enables uptake of glucose by facilitated diffusion and is hence independent of ATP, PEP or proton gradient. Glucose uptake via Glf should not affect energy charge.
We first analyzed growth of the wild-type strain and the mutants under aerobic batch conditions, in minimal medium with glucose (Table 2). The mutant KBM151101 showed a similar growth behavior as the wild-type. As the deletions in KBM151101 affect the anaerobic fermentative pathways, this is in agreement with current knowledge. As expected, SB2, the ΔptsG strain incapable of uptaking glucose by the glucose-PTS, grew significantly slower on glucose (µ = 0.26 h−1, compared to µ = 0.72 h−1 for MG1655). In KBM1673 the introduction of Glf from Z. mobilis complemented the ptsG deletion, although not completely. Glf is hence able to largely replace PtsG in glucose uptake.
Characterization of anaerobic growth and succinate production
Two-stage cultivations are useful if growth during the production phase is impaired or slow. During the first phase, the cells are maintained in an environment favorable for fast growth and for biomass accumulation, while no or only low amounts of product are produced. This phase is then followed by a second, production phase. In this case, growth of the mutant strains under fermentative conditions is impaired. Hence, an aerobic growth phase was introduced before the culture was shifted to an anaerobic succinate production phase. Cells from mid-exponential aerobic growth were harvested by centrifugation and incubated anaerobically in fresh minimal medium with 4 g/l glucose and 2 g/l carbonate. The anaerobic growth behavior of E. coli MG1655 and the mutants is presented in Fig. 2. While MG1655 continued to grow in the second, anaerobic stage (μ = 0.4 h−1), the cell number of KBM151101 decreased slowly but clearly (Fig. 2). In contrast, the ptsG mutant, SB2, grew after the shift, albeit extremely slow (µ = 0.02 h−1). Growth stopped after about 10 h in the anaerobic phase, but the cell number was not decreasing until the end of the experiment. Notably, the Glf+ derivative, KBM1673, showed an intermediated behavior. Cell numbers of these strains stayed almost constant during the anaerobic phase.
Course of biomass concentrations during the anaerobic phase of two-stage cultivation. Shown are biomass measurements for the wild tpye MG1655 (black), KBM151101 (red), SB2 (green) and KBM1673 (blue). Biomass concentration is plotted on a logarythmically scaled axis. At the start of the anaerobic phase, all strains were inoculated to the same cell density (OD420 ~ 2). While MG1655 shows quick anaerobic growth, growth of all mutant strains is strongly impaired. The data shown are derived from one exemplary experiment. At least three repeats have been carried out for all strains amd average data concerning growth rates are given in Table 3
Glucose consumption rates and by-product yields for the second phase of two-stage cultivations are presented in Table 3. The anaerobic glucose consumption rates of all mutant strains were significantly lower than that of MG1655. While KBM151101 consumed only small amounts of glucose, SB2 carrying the ptsG deletion showed improved anaerobic glucose utilization. This was against expectation and hints to differences in the expression of glucose uptake systems or alternative metabolic pathways in ptsG mutants compared to KBM151101 under anaerobic conditions. SB2 synthesized succinate as a major anaerobic fermentation product with a high yield of 1.3 mol/mol glucose. The anaerobic glucose uptake rate of KBM1673, expressing Glf, was higher than that of KBM151101, but unexpectedly did not reach the uptake rate of SB2. Also, succinate production rates were intermediary for this strain. The data imply that in the anaerobic phase of two stage cultivations glucose uptake is possible by expression of (a) so far unknown uptake system(s) and that the presence of uptake systems which are efficient under aerobic conditions (like Glf) does not necessarily improve anaerobic glucose uptake in strains unable to grow.
Notably, succinate yield is inversely linked to pyruvate production (Table 3). KBM1673 produced significant amounts of pyruvate while no pyruvate production was detected for SB2. Pyruvate production is hence not only influenced by PTS uptake of glucose but is also related to the uptake rate by non-PTS systems and to the fluxes in central metabolism.
Overexpression of PEP carboxykinase and PEP carboxylase
PEP carboxykinase (Pck) and PEP carboxylase (Ppc) are important gluconeogenic or anaplerotic enzymes, respectively. Both enzymes are able to catalyze the carboxylation of PEP to oxaloacetate. Compared to Ppc, Pck requires higher concentrations of CO2 to catalyze the reaction of PEP to oxaloacetate [43,44,45]. Oxaloacetate production by Pck is accompanied by the gain of one molecule of ATP. Previous publications showed an increase in succinate production resulting from overexpression of the native E. coli ppc gene [32, 46]. Introduction of the gene encoding Pck of A. succinogenes into E. coli or overexpression of the native E. coli pck gene improved succinate production [43, 47], too. Overexpression of Pck provides the cells with additional ATP and leads to better growth [44].
We hence tested the effect of overexpressing the native Pck and Ppc of E. coli in our test strains (Table 3). Introduction of Pck into SB2 and KBM1673 increased succinate yield by about 10%. Notably, Pck overexpression strongly increased productivity in KBM1673. In SB2, on the contrary, a slight drop in productivity was observed. Ppc overexpression had a low positive effect on succinate yield in KBM1673 but not in SB2 and productivity decreased in both strains with introduction of Ppc. Obviously, enhancement of the PEP to oxaloacetate reaction is positive for succinate productivity but only if catalyzed by Pck. This might be reasoned in the additional ATP generated by the Pck reaction.
Determination of ATP level and pck expression
ATP is an important factor determining growth and also succinate production. We measured the ATP levels of the mutant strains in the aerobic and anaerobic phase of two-stage cultivations. The aerobic ATP level was approximately the same in all strains (Fig. 3) with the only exception of SB2/pPck that shows a slightly lower ATP concentration. Based on ANOVA analysis this difference is not significant, though (Additional file 1: Figure S2) Under anaerobic conditions, the ATP concentration was highest in MG1655 reflecting its good growth under these conditions. The ATP levels of the mutant strains were lower than that of MG1655. The lowest concentration was observed for KBM151101. Based on ANOVA this difference can be regarded as significant (Additional file 1: Figure S2). This low ATP concentration could be the reason for growth impairment of this strain and also for the observed cell death during the second, anaerobic phase. SB2 and KBM1673 showed slightly lower ATP levels than MG1655 but significantly higher levels than KBM151101. It is tempting to speculate, that in these strains, especially in SB2, PckA is expressed in the anaerobic phase and allows for some flux from PEP to succinate coupled to ATP synthesis. For both strains overexpression of PckA results in slightly higher ATP levels probably reflecting increased PEP to oxaloacetate fluxes.
Measurement of ATP level of strains MG1655 and mutants. Shown are the concentrations of intracellular ATP in the different strains during the aerobic (blue) and anaerobic (red) phase of two-stage cultivations. Samples were taken during the exponential phase of aerobic growth and after 4 h in the anaerobic phase. Data are derived from two independent experiments with exception of MG1655 with only one repeat
To test the hypothesis of pckA being expressed in SB2, we performed Real Time RT PCR and determined pckA as well as ppc expression in the different mutants under aerobic as well as anaerobic conditions. As can be seen from Fig. 4, pckA is clearly upregulated in SB2 under aerobic as well as anaerobic conditions. Also for KBM1673 an upregulation of pckA is visible but only under aerobic conditions. ppc on the contrary is downregulated in KBM151101 and SB2 under anaerobic conditions.
Analysis of pckA and ppc expression by Real Time RT PCR. Shown are the relative expression levels of pckA (blue) and ppc (red) determined for the different strains under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Samples were taken from the exponential growth phase of the aerobic stage and after 4 h (mutant strains) or 2 h (MG1655 in the anaerobic stage. Gene expression was analysed by the ∆∆Ct method with normalization to three housekeeping genes and to MG1655 under the respective condition. Y-axes are plotted logarithmically to be able to show also downregulation
Evaluation of theoretical yields by flux balance analysis and conclusions for strain design
To understand the stoichiometric limits of succinate production, flux balance analysis was performed to determine theoretical yields (see Additional file 2). To calculate the maximal theoretical yield, only the pathways from substrates to the products were considered, but not growth. The general assumptions used here were anaerobic cultivation in minimal medium with glucose and carbonate. Glyoxylate shunt, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (Pdh) and phosphoenolpyruvate synthase (PpsA) were considered to be inactive. This was reasoned in the assumptions that Pdh is not active under anaerobic conditions. PDH is inhibited by NADH and under anaerobic conditions, PFL is responsible for the cleavage of pyruvate. PpsA is a gluconeogenic enzymes and is repressed in the presence of glucose to avoid futile cycling [48, 49]. The glyoxylate shunt is downregulated during batch growth with glucose as carbon source [50,51,52]. For the simulation of the mutant strains, the respective gene knock-outs were considered. With carbonate as second substrate and without considering growth, a maximal yield of 1.7 \(\frac{mol\, succinate}{mol \,glucose}\) is possible. However, to reach this value, glucose uptake is distributed on the PTS as well as on alternative (non-PTS) uptake systems with 71% uptake by the non-PTS system.
The importance of carbonate supplementation becomes obvious when comparing the theoretical optimum with and without carbonate addition. Without external CO2 supplementation, a yield of 1.3 \(\frac{mol \,succinate}{mol \,glucose}\) is possible, if optimal balance between carbonate formation by glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, formate cleavage, and carbonate fixation during anaplerosis is achieved. For this, at least 33% of glucose uptake need to be catalyzed by non-PTS uptake systems. However, the main glucose uptake system of E. coli is the PTS which requires that at least 50% of glucose derived PEP is converted to pyruvate for glucose uptake. This constraint reduces the maximum yield to 1 \(\frac{mol\, succinate}{mol \,glucose}\) independent of carbonate supplementation. Therefore, simulation studies indicate non-PTS uptake systems as highly favorable for succinate production. This prediction agrees well with the tremendous increase in product yield observed for SB2 compared to KBM151101.
In a second scenario, a slow growth of biomass was considered. Demanding a minimal biomass yield of 0.01 \(\frac{gDW}{mmol \,glucose}\) to achieve a viable cell population, the maximal theoretical succinate yield is reduced to 1.4 \(\frac{mol \,succinate}{mol \,glucose}\). This theoretical value is energy limited and requires acetate formation to supply sufficient ATP. One way to alleviate energy limitation is recruiting Pck for anaplerosis. Working in the reversed direction from PEP to oxaloacetate, Pck produces ATP. In contrast to Pck, the usual anaplerotic enzyme Ppc produces only inorganic phosphate and no ATP. Overexpression of Pck allows for a higher theoretical yield of 1.6 \(\frac{mol\, succinate}{mol \,glucose}\), while still maintaining a minimal biomass yield of 0.01 \(\frac{gDW}{mmol \,glucose}\). Under regular growth conditions Pck is regarded as a gluconeogenic enzyme whose expression is repressed in the presence of glucose [53, 54]. The carboxylating activity of Pck can occur in vivo, if the gene is overexpressed and if the carbonate concentration is high enough to shift the equilibrium towards oxaloacetate production [43, 55]. Our experiments showed a positive effect of Pck overexpression on succinate yield for SB2 and KBM1673. However, only for KBM1673 a positive effect on growth was observed.
In a third scenario, we considered a more natural objective function, namely the maximization of biomass. When considering the experimental validated strains, the best theoretical product yield is predicted for ptsG knockout plus pckA overexpression, predicting a product yield of 1.32 \(\frac{mol \,succinate}{mol\, glucose}\) and a biomass yield of 0.028 \(\frac{gDW}{mmol \,glucose}\). This theoretical biomass yield gives an upper boundary of growth, assuming that no limitations by maintenance metabolism, futile cycles and stress responses are present. However, while the corresponding strain KBM1673/pPckA almost reaches optimal biomass yield, there are other limitations on the flux: these limitations lead to the formation of pyruvate as a second fermentation product and thus decrease succinate yield. From FBA the reason for the pyruvate production by KBM1673/pPckA, that becomes obvious from the measurements, is not clear. One might speculate that the flux that can be channeled by Pck is too low to cope with the amount of PEP produced by glycolysis. The amount of PEP that can not be processed by Pck is converted to pyruvate and some fraction of this pyruvate is found in the outside medium.
Analysis of mutant behavior by metabolic flux analysis
The results above are valid for optimal behavior, and describe the stoichiometric possibilities of the strains. Next, we considered the experimentally obtained uptake rates as input into the model. For these studies, maximization of growth or the biomass function was taken as objective function. In all cases, except SB2, the simulated growth rate was slightly higher than the observed growth rate. For SB2, growth could only be explained if allowing for Pck activity. This finding was also supported by pckA expression analysis presented in Fig. 4 and by mRNA Seq analysis (data not shown). The simulated growth rates are slightly higher since FBA gives an upper limit growth, as mentioned previously. Also, in some cases the simulation predicts secretion of additional by-products like glutamate, which were not measured in our experiments.
To evaluate how efficiently the carbon source is converted into product by each strain, we calculated individual theoretical yields considering the observed growth rate and the respective genetic background (see Table 4). Comparing our strains to this adapted value shows, that especially SB2 and SB2/pPckA are close to optimal product formation.
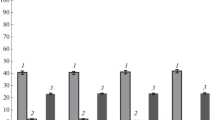
Metabolic flux analysis was also used to analyze in more detail the fluxes at the PEP and pyruvate node. For this analysis glucose uptake rates as well as the production rates of extracellular succinate and pyruvate were taken into account. As can be seen from Fig. 5 for strains giving good succinate yields, low fluxes from PEP to pyruvate and high fluxes from PEP to oxaloacetate are predicted. No clear correlation between the fluxes at the PEP-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node and productivity is visible. Apart from KBM151101, a higher flux to pyruvate seems to be correlated with pyruvate excretion. Most probably, Pck or Ppc activity are important for the fluxes at the PEP-pyruvate node. The amount of PEP that can not be converted to oxaloacetate by these enyzmes will by converted to pyruvate and partly excreted. Data for KBM151101 are to be treated with care. As this strain takes up only very small amounts of glucose, measurements of glucose uptake and also of products formed are faulty, due to the detection limit of the assays applied.
Flux ratio at node PEP. Bars show the relative flux from PEP to oxaloacetate (blue bars) and pyruvate (yellow bars) as determined by FBA; the hatched green part in the yellow bars indicate the fraction of the flux to pyruvate that is excreted into the medium as given by the measurement of extracellular pyruvate. Superimposed are shown the succinate yield (relative to the maximal yield obtained in this study) (red curve) and productivity (relative to the maximal productivity obtained in this study) (green curve)
Determination of EIIAGlc phosphorylation
EIIAGlc is a central regulator of carbon metabolism. The unphosphorylated EIIAGlc is an inhibitor for uptake of sugars such as maltose, lactose, and glycerol, an effect called catabolite repression [14]. Uptake of PTS substrates but also fast growth with non-PTS substrates results in a low EIIAGlc phosphorylation state [29, 56], because the PEP to pyruvate ratio is low during fast growth. We analyzed the EIIAGlc phosphorylation state in the different mutants in both stages of two-stage cultivations (Table 5). When grown on glucose, 95% of EIIAGlc in an E. coli wild-type strain is unphosphorylated [29]. This was also observed for KBM151101 during aerobic growth. SB2, the ptsG mutant, showed increased EIIAGlc phosphorylation under aerobic conditions, reflecting its slow growth and the lack of the Glc-PTS. KBM1673 shows an intermediary EIIAGlc phosphorylation level, reflecting its intermediary growth rate and maybe also the fact that glucose uptake in this strain is catalyzed by the PTS-independent Glf.
While the EIIAGlc phosphorylation state is in good agreement with the growth rates for aerobic growth, it is more difficult to interpret the data from the anaerobic phase (Table 5). The wild type MG1655 showed a low EIIAGlc phosphorylation level also under anaerobic conditions. Unexpectedly, a low EIIAGlc phosphorylation level was also observed for KBM151101, although this strain did not grow during the anaerobic phase. Slow growth is normally coupled to high EIIAGlc phosphorylation but not in this case. It has been hypothesized, that in addition to the PTS activity the EIIAGlc phosphorylation level also reflects the PEP to pyruvate ratio in the cell [29, 57]. Given the fact that KBM151101 excreted pyruvate, a high concentration of pyruvate is expected within the cell, and might explain the low EIIAGlc phosphorylation state. Intracellular pyruvate accumulation might also be responsible for the low EIIAGlc phosphorylation in KBM1673. In SB2, the EIIAGlc phosphorylation state was slightly lower under anaerobic than under aerobic conditions but still quite high. Again, this fits to the lack of pyruvate excretion by SB2.
To support the experimental findings, a simulation study was performed as described under Materials and Methods. For all strains, the experimentally determined glucose uptake rate and the degree of EIIAGlc phosphorylation was provided to the model. The simulation results for the PEP/pyruvate ratio are shown in Fig. 6.
Course of the degree of phosphorylation of EIIAGlc and PEP/pyruvate ratio over growth rate µ. Comparison of measurement and simulation. a Course of EIIAGlc ~ P over growth rate for the anaerobic case and strains with PTS system. b Course of PEP/pyruvate ratio over growth rate for the anaerobic case and strains with PTS system. c Course of EIIAGlc ~ P over growth rate for the anaerobic case and strains without PTS system. d Course of PEP/pyruvate ratio over growth rate for the anaerobic case and strains without PTS system. Green symbols are measured data points (see Tables 3, 5 in the main text)
As one can see, a low PEP/pyruvate ratio (~ 1 or below 1) is predicted for strains showing pyruvate production (KBM151101, KBM1673) while a PEP/pyruvate ratio of about 3 is predicted for strains showing no pyruvate production (SB2 and SB2/pPck). It might hence be concluded that a low PEP/pyruvate ration of about 1 can be associated with pyruvate excretion.
Summarizing, the EIIAGlc phosphorylation levels reflect current knowledge for the aerobic growth phase. The data for the anaerobic phase seem to indicate that in non-growing cells or under anaerobic conditions EIIAGlc does not reflect glucose uptake but rather the potential accumulation of pyruvate inside the cell.
Discussion
In order to improve succinate productivity by metabolic engineering of central pathways in E. coli different strategies have been explored [17, 38, 58, 59]. Several genetic manipulations are necessary to obtain a good production strain, because wild-type E. coli produce only minor amounts of succinate [48]. Typical manipulations are the deletion of pathways leading to alternative fermentation products such as lactate, ethanol, formate and acetate. As a consequence of this manipulations, the strains show low anaerobic growth rates or are not able to grow on glucose in minimal medium at all [38]. Although theoretically anaerobic growth is feasible, it is hardly observed without addition of complex medium components. Hence, rich media are used in most studies for improving growth and succinate production [7, 9]. Succinate production in E. coli has been studied in a number of different theoretical studies (for a review see [6]). However, for most of them an experimental validation is lacking. Typically, the different strategies result in strains carrying multiple mutations but the effect of a single mutation often was not investigated.
In this work we compared different strains for their succinate production using mineral salts medium. Strain KBM151101, unable to produce the fermentation products acetate, ethanol and formate, but still having a functional glucose-PTS, was not able to grow under anaerobic conditions. In fact, biomass was even dropping anaerobically. In two-stage cultivations of KBM151101, pyruvate accumulation was observed coupled to low ATP levels. This indicates that fluxes in this strain are not balanced. Most probably, the inability of producing enough ATP is limiting succinate production. This is also indicated by flux analysis. As KBM151101 takes up glucose by the Glc-PTS, glucose uptake is coupled to a conversion of PEP to pyruvate. In order to fulfill growth requirements and to regenerate NAD, pyruvate would have to be converted back to PEP but this is not possible, due to a lack of ATP. Similar results have been reported in previous studies dealing with succinate production in E. coli. These studies used strain NZN111, which has two mutations in lactate dehydrogenase and pyruvate formate lyase [7, 60]. Although mutations in NZN111 and KBM151101 are different, they have a similar effect, as both strain are unable to synthesize the main fermentation products.
We implemented a further mutation in KBM151101 by knocking out the Glc-PTS. The resulting strain, SB2, produced succinate from glucose anaerobically with a high yield of 1.24 mol/mol (about 80% of the maximal theoretical yield). This compares well to yields obtained from studies using similar strains carrying the ptsI or ptsG mutation as well as pfl mutations [40,41,42] In theory, inactivation of ptsG increases the PEP pool, because uptake of glucose is no longer coupled to the conversion of PEP to pyruvate. PEP hence becomes available for the formation of succinate. This observation has been described previously for ptsG mutants of NZM111 [17, 44]. Our hypothesis is that two main factors account for this observation. First, the PTS mutation decouples glucose uptake from PEP to pyruvate conversion. This enables fluxes from PEP to succinate without the need to input ATP for PEP synthase reaction. This is underlined by the results of flux analyses that predict improved succinate production as soon as part of the glucose is taken up by non-PTS systems. Secondly, Pck activity is needed to achieve high succinate yields. Flux analysis assigns an important function to PckA, too. This enzyme is able to couple PEP to oxaloacetate conversion with ATP synthesis. Our second hypothesis hence is that pckA is expressed in SB2. This hypothesis is supported by gene expression analyses, showing an increased pckA RNA level in SB2 compared to KBM151101 (Fig. 4). Pck is generally regarded as a gluconeogenic enzyme, which is not expressed in the presence of glucose [53, 54, 61]. Also pckA is known to be under control of CsrA [62]. It is hence tempting to speculate that deletion of ptsG, reducing glucose uptake, and the lack of ATP observed for KBM151101 under anaerobic conditions (Fig. 3) provoke expression of pckA in SB2, allowing for improved growth or survival, which is coupled to a high succinate yield. PckA overexpression in cells of SB2 decreased glucose uptake and succinate production rates, but increased succinate yield (Table 3). A positive effect of pckA overexpression was also reported by Kwon [43]. They observed this positive effect only in the presence of high carbonate concentrations, an observation that was verified by our experiments (data not shown).
In strains with ptsG deletion, the glucose facilitator protein, Glf, and the glucokinase, Glk, of Z. mobilis allow for improved glucose uptake [25, 63, 64]. Strain KBM1673, the Glf+ derivative of SB2, had a higher glucose utilization rate under aerobic condition than its parent strain, SB2. Contrary to expectation, glucose uptake rate as well as succinate yield and productivity of KBM1673 in the anaerobic phase decreased compared to SB2. This was due to significant excretion of pyruvate (Table 3). FBA (Fig. 5) shows that this strain is characterized by relatively high fluxes from PEP to pyruvate. We hypothesize that due to the presence of an efficient glucose uptake system that allows for a high growth rate in the aerobic preculture, an expression of pckA is either not possible or that the amount of Pck available is too low to direct the main flux towards succinate. In fact, we observed a lower expression of pckA for KBM1673 under anaerobic conditions than for SB2 (Fig. 4). Instead, the accumulating PEP is converted to pyruvate, a reaction that allows the cell to synthesize ATP, too. Pyruvate production might hence be considered an overflow reaction. A significant fraction of pyruvate is found in the outside medium (Table 3, Fig. 5). If the flux through Pck is enhanced by overexpression of the enzyme, high succinate productivity is achieved. An alternative explanation for the increased pyruvate production might be the involvement of an alternative PTS in intracellular glucose phosphorylation. In this case the respective PTS system would not be able to transport extracellular glucose but to phosphorylate glucose that accumulates intracellularly due to the presence and activity of Glf.
Figure 5 summarizes our theoretical and experimental findings. The bars represent the ratio of the fluxes at node PEP and shows that strains with a high yield (red curve) direct the flux mainly from PEP to oxaloacetate while a smaller part is going to pyruvate. Strain KBM1673 with PckA shows the highest productivity, however, as can be seen in Fig. 5, a large fraction from the flux to pyruvate is excreted, which can be interpreted as metabolic overflow. This points to a bottleneck in the drain from pyruvate to acetyl-CoA (the non-hatched part in the yellow bars is nearly equal for all strains except KBM151101).
In summary, this study demonstrates that it is possible to achieve a good succinate yield with minimal number of interventions also for cultivation in minimal media. To achieve high succinate yields, it is important to direct a significant flux through Pck, in order to gain ATP and in order to avoid disadvantageous pyruvate production. A high succinate yield was achieved by an engineered strain SB2 with Pck overexpression by using two-stage cultivations. This strain reaches a succinate yield of 1.4 mol/mol glucose, which is near to the theoretical maximum that could be achieved (theoretical maximum 1.7 mol/mol glucose). A lower yield but a much better productivity was achieved in KBM1673 with pckA overexpression. Based on our results a further strain improvement would require to fine-tune incoming glycolytic fluxes with the fluxes at the PEP/pyruvate node, especially with fluxes through Pck to avoid pyruvate accumulation and to allow for ATP and succinate synthesis.
References
Werpy T, Petersen G. Top value added chemicals from biomass: volume I—results of screening for potential candidates from sugars and synthesis gas. Washington: US Department of Energy; 2004.
Sawers RG, Clark DP. Fermentative pyruvate and acetyl-coenzyme a metabolism. EcoSal Plus. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1128/ecosalplus.3.5.3.
Thakker C, Martinez I, San KY, Bennett GN. Succinate production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol J. 2012;7:213–24.
Förster AH, Gescher J. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for production of mixed-acid fermentation end products. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014;2:16.
Ahn JH, Jang Y-S, Lee SY. Production of succinic acid by metabolically engineered microorganisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016;42:54–66.
Valderrama-Gomez MA, Kreitmayer D, Wolf S, Marin-Sanguino A, Kremling A. Application of theoretical methods to increase succinate production in engineered strains. Bioproc Biosys Eng. 2017;40:479–97.
Stols L, Donnelly MI. Production of succinic acid through overexpression of NAD+-dependent malic enzyme in an Escherichia coli mutant. Appl Environ Micrbiol. 1997;63:2695–701.
Vemuri GN, Eiteman MA, Altman E. Effects of growth mode and pyruvate carboxylase on succinic acid production by metabolically engineered strains of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Micrbiol. 2002;68:1715–27.
Sánchez AM, Bennett GN, San K-Y. Novel pathway engineering design of the anaerobic central metabolic pathway in Escherichia coli to increase succinate yield and productivity. Metab Eng. 2005;7:229–39.
Lin H, Bennett GN, San K-Y. Genetic reconstruction of the aerobic central metabolism in Escherichia coli for the absolute aerobic production of succinate. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2005;89:148–56.
Lin H, Bennett GN, San K-Y. Metabolic engineering of aerobic succinate production systems in Escherichia coli to improve process productivity and achieve the maximum theoretical succinate yield. Metab Eng. 2005;7:116–27.
Skorokhodova AY, Gulevich AY, Morzhakova AA, Shakulov RS, Debabov VG. Comparison of different approaches to activate the glyoxylate bypass in Escherichia coli K-12 for succinate biosynthesis during dual-phase fermentation in minimal glucose media. Biotechnol Lett. 2013;35:577–83.
Skorokhodova AY, Morzhakova AA, Gulevich AY, Debabov VG. Manipulating pyruvate to acetyl-CoA conversion in Escherichia coli for anaerobic succinate biosynthesis from glucose with the yield close to the stoichiometric maximum. J Biotechnol. 2015;214:33–42.
Deutscher J. The mechanisms of carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008;11:87–93.
Chatterjee R, Millard CS, Champion K, Clark DP, Donnelly MI. Mutation of the ptsG gene results in increased production of succinate in fermentation of glucose by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67:148–54.
Zhao Y, Wang CS, Li FF, Liu ZN, Zhao GR. Targeted optimization of central carbon metabolism for engineering succinate production in Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol. 2016;16:52.
Chatterjee R, Millard CS, Champion K, Clark DP, Donnelly MI. Mutation of the ptsG Gene results in increased production of succinate in fermentation of glucose by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Micrbiol. 2001;67:148–54.
Hunter IS, Kornberg HL. Glucose transport of Escherichia coli growing in glucose-limited continuous culture. Biochem J. 1979;178:97–101.
McDonald TP, Walmsley AR, Henderson PJ. Asparagine 394 in putative helix 11 of the galactose-H+ symport protein (GalP) from Escherichia coli is associated with the internal binding site for cytochalasin B and sugar. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:15189–99.
Death A, Ferenci T. The importance of the binding-protein-dependent Mgl system to the transport of glucose in Escherichia coli growing on low sugar concentrations. Res Microbiol. 1993;144:529–37.
Death A, Ferenci T. Between feast and famine: endogenous inducer synthesis in the adaptation of Escherichia coli to growth with limiting carbohydrates. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:5101–7.
Ferenci T. Adaptation to life at micromolar nutrient levels: the regulation of Escherichia coli glucose transport by endoinduction and cAMP. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1996;18:301–17.
Wang QZ, Wu CY, Chen T, Chen X, Zhao XM. Expression of galactose permease and pyruvate carboxylase in Escherichia coli ptsG mutant increases the growth rate and succinate yield under anaerobic conditions (vol 28, pg 89, 2006). Biotechnol Lett. 2006;28:203–203.
Gosset G. Improvement of Escherichia coli production strains by modification of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. Microb Cell Fact. 2005;4:14.
Tang J, Zhu X, Lu J, Liu P, Xu H, Tan Z, Zhang X. Recruiting alternative glucose utilization pathways for improving succinate production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;97:2513–20.
Li J, Li Y, Cui Z, Liang Q, Qi Q. Enhancement of succinate yield by manipulating NADH/NAD+ ratio and ATP generation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;101:3153–61.
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:6640–5.
Thomason LC, Costantino N, Court DL. E. coli genome manipulation by P1 transduction. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142727.mb0117s79.
Bettenbrock K, Sauter T, Jahreis K, Kremling A, Lengeler JW, Gilles E-D. Correlation between growth rates, EIIACrr phosphorylation, and intracellular cyclic AMP levels in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:6891–900.
Haldimann A, Wanner BL. Conditional-replication, integration, excision, and retrieval plasmid-host systems for gene structure-function studies of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 2001;183:6384–93.
Parkinson JS, Houts SE. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982;151(1):106–13.
Kwon YD, Kwon OH, Lee HS, Kim P. The effect of NADP-dependent malic enzyme expression and anaerobic C4 metabolism in Escherichia coli compared with other anaplerotic enzymes. J Appl Microbiol. 2007;103:2340–5.
Tanaka S, Lerner SA, Lin EC. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967;93:642–8.
Takahashi H, Inada T, Postma P, Aiba H. CRP down-regulates adenylate cyclase activity by reducing the level of phosphorylated IIA(Glc), the glucose-specific phosphotransferase protein, in Escherichia coli. Mol Genet Genom. 1998;259:317–26.
Schellenberger J, Que R, Fleming RM, Thiele I, Orth JD, Feist AM, Zielinski DC, Bordbar A, Lewis NE, Rahmanian S, et al. Quantitative prediction of cellular metabolism with constraint-based models: the COBRA Toolbox v2.0. Nat Protoc. 2011;6:1290–307.
Orth JD, Fleming RM, Palsson BO. Reconstruction and use of microbial metabolic networks: the core Escherichia coli metabolic model as an educational guide. EcoSal Plus. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1128/ecosalplus.10.2.1.
Kremling A, Bettenbrock K, Gilles ED. Analysis of global control of Escherichia coli carbohydrate uptake. BMC Syst Biol. 2007;1:42.
Donnelly MI, Millard CS, Clark DP, Chen MJ, Rathke JW. A novel fermentation pathway in an Escherichia coli mutant producing succinic acid, acetic acid, and ethanol. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1998;70–72:187–98.
Jantama K, Haupt MJ, Svoronos SA, Zhang X, Moore JC, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO. Combining metabolic engineering and metabolic evolution to develop nonrecombinant strains of Escherichia coli C that produce succinate and malate. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2008;99:1140–53.
Zhang X, Jantama K, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO. Reengineering Escherichia coli for succinate production in mineral salts medium. Appl Environ Micrbiol. 2009;75:7807–13.
Yu JH, Zhu LW, Xia ST, Li HM, Tang YL, Liang XH, Chen T, Tang YJ. Combinatorial optimization of CO2 transport and fixation to improve succinate production by promoter engineering. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016;113:1531–41.
Meng J, Wang B, Liu D, Chen T, Wang Z, Zhao X. High-yield anaerobic succinate production by strategically regulating multiple metabolic pathways based on stoichiometric maximum in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact. 2016;15:141.
Kwon DY, Lee SY, Kim P. Influence of gluconeogenic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PCK) expression on succinic acid fermentation in Escherichia coli under high bicarbonate condition. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006;16:1448–52.
Zhang X, Jantama K, Moore JC, Jarboe LR, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO. Metabolic evolution of energy-conserving pathways for succinate production in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:20180–5.
Krebs A, Bridger WA. The kinetic properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase of Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem. 1980;58:309–18.
Millard CS, Chao YP, Liao JC, Donnelly MI. Enhanced production of succinic acid by overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:1808–10.
Kim P, Laivenieks M, Vieille C, Zeikus JG. Effect of overexpression of actinobacillus succinogenes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase on succinate production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Micrbiol. 2004;70:1238–41.
Cooper RA, Kornberg HL. The direct synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate from pyruvate by Escherichia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967;168:263–80.
Chao YP, Patnaik R, Roof WD, Young RF, Liao JC. Control of gluconeogenic growth by pps and pck in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:6939–44.
Fischer E, Sauer U. A novel metabolic cycle catalyzes glucose oxidation and anaplerosis in hungry Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:46446–51.
Prasad Maharjan R, Yu PL, Seeto S, Ferenci T. The role of isocitrate lyase and the glyoxylate cycle in Escherichia coli growing under glucose limitation. Res Microbiol. 2005;156:178–83.
Oh MK, Liao JC. Gene expression profiling by DNA microarrays and metabolic fluxes in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog. 2000;16:278–86.
Goldie H. Regulation of transcription of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase locus: studies with pck-lacZ operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1984;159:832–6.
Goldie H, Medina V. Physical and genetic analysis of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (pckA) locus from Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1990;220:191–6.
Lu S, Eiteman MA, Altman E. Effect of CO2 on succinate production in dual-phase Escherichia coli fermentations. J Biotechnol. 2009;143:213–23.
Hogema BM, Arents JC, Bader R, Eijkemans K, Inada T, Aiba H, Postma PW. Inducer exclusion by glucose 6-phosphate in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1998;28:755–65.
Hogema BM, Arents JC, Bader R, Eijkemans K, Yoshida H, Takahashi H, Aiba H, Postma PW. Inducer exclusion in Escherichia coli by non-PTS substrates: the role of the PEP to pyruvate ratio in determining the phosphorylation state of enzyme IIAGlc. Mol Microbiol. 1998;30:487–98.
Gokarn RR, Evans JD, Walker JR, Martin SA, Eiteman MA, Altman E. The physiological effects and metabolic alterations caused by the expression of Rhizobium etli pyruvate carboxylase in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001;56:188–95.
Vemuri GN, Eiteman MA, Altman E. Succinate production in dual-phase Escherichia coli fermentations depends on the time of transition from aerobic to anaerobic conditions. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002;28:325–32.
Singh A, Lynch MD, Gill RT. Genes restoring redox balance in fermentation-deficient E. coli NZN111. Metab Eng. 2009;11:347–54.
Goldie AH, Sanwal BD. Genetic and physiological characterization of Escherichia coli mutants deficient in phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase activity. J Bacteriol. 1980;141:1115–21.
Romeo T, Gong M, Liu MY, Brun-Zinkernagel AM. Identification and molecular characterization of csrA, a pleiotropic gene from Escherichia coli that affects glycogen biosynthesis, gluconeogenesis, cell size, and surface properties. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:4744–55.
Snoep JL, Arfman N, Yomano LP, Fliege RK, Conway T, Ingram LO. Reconstruction of glucose uptake and phosphorylation in a glucose-negative mutant of Escherichia coli by using Zymomonas mobilis genes encoding the glucose facilitator protein and glucokinase. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:2133–5.
Parker C, Barnell WO, Snoep JL, Ingram LO, Conway T. Characterization of the Zymomonas mobilis glucose facilitator gene product (glf) in recombinant Escherichia coli: examination of transport mechanism, kinetics and the role of glucokinase in glucose transport. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:795–802.
Authors’ contributions
LK planned, carried out and evaluated the wet lab experiments, and helped in preparing the manuscript. DK performed flux analyses and evaluated experimental data. AK designed the study, performed mathematical modeling studies, and helped in preparing the manuscript. KB designed the study, planned and evaluated wet lab experiments, and prepared the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We thank Andrea Schütze for excellent technical support and Alexandra Blitz and Miguel Valderrama Gomez for their input und support in the modeling and simulation tasks. We thank Prof. Sprenger (University of Stuttgart) for providing a plasmid encoding glf from Z. mobilis.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by the German Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung FKZ 031A127 A and B.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primers used in this study. Table S2. Single measurements of EIIAGlc phosphorylation state during two-stage cultivations. Figure S1. Pictures of chemiluminescence detection of Western Blots. Figure S2. Results from ANOVA analysis of intracellular ATP levels.
Additional file 2.
Model structure and FBA results for the different strains.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Kyselova, L., Kreitmayer, D., Kremling, A. et al. Type and capacity of glucose transport influences succinate yield in two-stage cultivations. Microb Cell Fact 17, 132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0980-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0980-1