Abstract
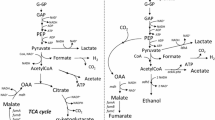
Escherichia coli strain NZN111, which is unable to grow fermentatively because of insertional inactivation of the genes encoding pyruvate: formate lyase and the fermentative lactate dehydrogenase, gave rise spontaneously to a chromosomal mutation that restored its ability to ferment glucose. The mutant strain, named AFP111, fermented glucose more slowly than did its wild-type ancestor, strain W1485, and generated a very different spectrum of products. AFP111 produced succinic acid, acetic acid, and ethanol in proportions of approx 2:1:1. Calculations of carbon and electron balances accounted fully for the observed products; 1 mol of glucose was converted to 1 mol of succinic acid and 0.5 mol each of acetic acid and ethanol. The data support the emergence in E.coli of a novel succinic acid:acetic acid:ethanol fermentation pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gottschalk, G. (1985),Bacterial Metabolism, 2nd ed. Springer series in microbiology, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Clark, D. P. (1989),FEMS Microb. Rev. 63, 223–234.
Bock, A. and Sawers, G. (1996), inEscherichia coli and Salmonella, Neidhardt, F. C., et al., eds. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp. 262–282.
Samuelov, N. S., Lamed, R., Lowe, S., and Zeikus, J. G. (1991),Appl, Environ. Microbiol. 57, 3013–3019.
Guettler, M. V., Jain, M. K., and Rumler, D. (1996), in USPatent and Trademark Office, patent no. 5573931, Michigan Biotechnology Institute.
Millard, C. S., Chao, Y. -P., Liao, J. C., and Donnelly, M. I. (1996),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 1808–1810.
Stols, L. and Donnelly, M. I. (1997),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 2695–2701.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., and Maniatis, T. (1989),Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Mat-Jan, F., Kiswar, A. Y., and Clark, D. P. (1989),J. Bacteriol. 171, 342–348.
Balch, W. and Wolfe, R. S. (1976),Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 32, 781–791.
Bunch, P. K., Mat-Jan, F., Lee, N., and Clark, D. P. (1997),Microbiology 143, 187–195.
Boernke, W. E., Millard, C. S., Stevens, P. W., Kakar, S. N.; Stevens, F. J., and Donnelly, M. I. (1995),Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 322, 43–52.
Gupta, S. and Clark, D. P. (1989),J. Bacteriol. 171, 3650–3655.
Postma, P. W., Lengeler, J. W., and Jacobsen, G. R. (1996), inEscherichia coli and Salmonella, Neidhardt, F. C., et al., eds. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp. 1149–1174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donnelly, M.I., Millard, C.S., Clark, D.P. et al. A novel fermentation pathway in anEscherichia coli mutant producing succinic acid, acetic acid, and ethanol. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 70, 187–198 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920135
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920135