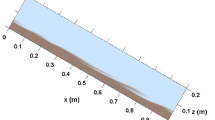
Abstract.
In this paper we presents a detailed description of granular flow down a flat, narrow chute using discrete element method simulations, with emphasis on the influence of sidewalls on the flow. The overall phase diagram is provided and it is found that there are four flow regimes (no flow, bulk flow, surface flow, and gas flow). The H̃stop curve is very complicated and quite different from that in the case without sidewalls. The effective friction coefficient \( \mu_{{\rm w}}\) increases with pile height H̃ and a surface flow occurs when the inclination angle \( \theta\) exceeds a critical value. The profile of \( \mu_{{\rm w}}\) shows that the \( \mu (I)\) rheology is valid in boundary layers. Furthermore, \( \mu_{{\rm w}}\) increases with the velocity of particles and there is a saturation to a nonzero value in static heap. For small H̃, the static heap vanishes and there is a bulk flow. A similarity between basal particles and sidewall particles indicates a universal role of the boundaries. In this bulk flow, there is a transition of the velocity profile with wall friction \( \mu_{{\rm ps}}\). When \( \mu_{{\rm ps}}\) is large, the velocity is linear and decreases with increasing height. With small \( \mu_{{\rm ps}}\), the velocity is nonlinear and the flow rate is roughly proportional to H̃3/2.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Bagnold, Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 225, 49 (1954)
L.E. Silbert et al., Phys. Rev. E 64, 051302 (2001)
S. Ogawa, A. Umemura, N. Oshima, Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 31, 483 (1980)
J.T. Jenkins, S.B. Savage, J. Fluid Mech. 130, 187 (1983)
M.W. Richman, Acta Mech. 75, 227 (1988)
P. Jop, Y. Forterre, O. Pouliquen, J. Fluid Mech. 541, 167 (2005)
K. Hui et al., J. Fluid Mech. 145, 223 (1984)
J.T. Jenkins, M.W. Richman, J. Fluid Mech. 171, 53 (1986)
M.Y. Louge, S.C. Keast, Phys. Fluids 13, 1213 (2001)
G.D.R. MiDi, Eur. Phys. J. E 14, 341 (2004)
D.M. Hanes, O.R. Walton, Powder Technol. 109, 133 (2000)
L.E. Silbert et al., Phys. Fluids 14, 2637 (2002)
R. Delannay et al., Nat. Mater. 6, 99 (2007)
J. Rajchenbach, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 144302 (2003)
T. Borzsonyi, R.E. Ecke, Phys. Rev. E 74, 061301 (2006)
W.T. Bi et al., Phys. Fluids 18, 123302 (2006)
A.J. Holyoake, J.N. McElwaine, J. Fluid Mech. 710, 35 (2012)
O. Pouliquen, Phys. Fluids 11, 542 (1999)
P.C. Johnson, P. Nott, R. Jackson, J. Fluid Mech. 210, 501 (1990)
O.R. Walton, Mech. Mater. 16, 239 (1993)
C.S. Campbell, C.E. Brennen, J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 52, 172 (1985)
N. Brodu, P. Richard, R. Delannay, Phys. Rev. E 87, 022202 (2013)
N. Brodu et al., J. Fluid Mech. 769, 218 (2015)
N. Taberlet et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 064301 (2003)
N. Taberlet, P. Richard, R. Delannay, Comput. Math. Appl. 55, 230 (2008)
P. Richard et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 248002 (2008)
D. Gollin, D. Berzi, E.T. Bowman, Granular Matter 19, 56 (2017)
R.D. Mindlin, J. Appl. Mech. 16, 259 (1949)
Y. Tian et al., Comput. Chem. Eng. 104, 231 (2017) (Suppl. C)
V.J.-L. Ralaiarisoa et al., EPJ Web of Conferences 140, 03081 (2017)
T. Weinhart et al., Granular Matter 14, 531 (2012)
G. Yang, Influence of Inclined Angles on the Stability of Inclined Granular Flows Down Rough Bottoms, in Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Discrete Element Methods, edited by X. Li, Y. Feng, G. Mustoe (Springer Singapore, Singapore, 2017) pp. 647--657
T.S. Komatsu et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 1757 (2001)
D. Bonamy, F. Daviaud, L. Laurent, Phys. Fluids 14, 1666 (2002)
N. Taberlet et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 264301 (2003)
Y. Forterre, O. Pouliquen, J. Fluid Mech. 486, 21 (2003)
A.V. Orpe, D.V. Khakhar, J. Fluid Mech. 571, 1 (2007)
C. Jérome et al., J. Stat. Mech.: Theor. Exp. 2008, P03009 (2008)
L. Sarno, Experimental Investigation on the Effects of the Fixed Boundaries in Channelized Dry Granular Flows (Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017)
L. Sarno et al., Phys. Fluids 26, 103303 (2014)
L. Sarno et al., Adv. Water Resour. 100, 183 (2017)
W. Losert et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1428 (2000)
D.M. Mueth, Phys. Rev. E 67, 011304 (2003)
P.K. Haff, J. Rheol. 30, 931 (1986)
E. Azanza, F. Chevoir, P. Moucheront, J. Fluid Mech. 400, 199 (1999)
R. Artoni, P. Richard, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 158001 (2015)
R. Artoni et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 238002 (2012)
V. Kumaran, S. Bharathraj, Phys. Fluids 25, 070604 (2013)
H. Ahn, C. Brennen, Channel flows of granular materials and their rheological implications, in Particulate Two-Phase Flow, edited by M.C. Roco (Butterworth-Heinemann, 1993) pp. 210--243
H. Ahn, C.E. Brennen, R.H. Sabersky, J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 59, 109 (1992)
T.G. Drake, J. Fluid Mech. 225, 121 (1991)
S. Courrech du Pont et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 048003 (2005)
R.M. Nedderman, C. Laohakul, Powder Technol. 25, 91 (1980)
P. Richard et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 248002 (2008)
Y. Khidas et al., Eur. Phys. J. E 10, 387 (2003)
T.G. Drake, J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth Planets 95, 8681 (1990)
Y. Forterre, O. Pouliquen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5886 (2001)
W.T. Bi et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 17, S2457 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
The EPJ Publishers remain neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Yang, G., Lin, P. et al. Inclined granular flow in a narrow chute. Eur. Phys. J. E 42, 40 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11796-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2019-11796-8