Abstract
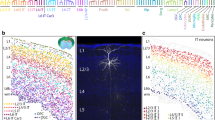
The study aimed at investigating the dynamics of the distribution and localization of the gap junction protein connexin-43 (Cx43) in rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells at different stages of postnatal ontogenesis to assess morphological signs of age-related changes in intercellular interactions. The work was performed on Wistar rats aged 4 and 18 months using immunohistochemical methods. Glial cells were detected using antibodies to glutamine synthetase, and Iba-1 marker was used for macrophages. It has been established that connexin-43-containing structures are identified predominantly in satellite glial cells of young and aging animals. Sensory neurons, as well as DRG macrophages, of the examined age groups do not contain connexin-43. When analyzing age-related changes in intercellular contacts in the DRG of rats, it was found that areas enriched with connexin-43, corresponding to plaques of protein channels that ensure metabolic interaction of satellite glial cells in the dorsal root ganglia, became more numerous with age. This fact may indicate activation of interaction between glial cells in the sensory ganglia during rat aging.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Adamczyk, A., Glial–neuronal interactions in neurological disorders: molecular mechanisms and potential points for intervention, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2023, vol. 24, p. 6274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076274
Almad, A.A., Doreswamy, A., Gross, S.K., Richard, J.P., Huo, Y., Haughey, N., and Maragakis, N.J., Connexin 43 in astrocytes contributes to motor neuron toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Glia, 2016, vol. 64, p. 1154. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22989
Basu, R. and Das Sarma, J., Connexin 43/47 channels are important for astrocyte/oligodendrocyte cross-talk in myelination and demyelination, J. Biosci., 2018, vol. 43, p. 1055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9811-0
Brocardo, L., Acosta, L.E., Piantanida, A.P., and Rela, L., Beneficial and detrimental remodeling of glial connexin and pannexin functions in rodent models of nervous system diseases, Front. Cell Neurosci., 2019, vol. 13, p. 491. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00491
Chew, S.S., Johnson, C.S., Green, C.R., and Danesh-Meyer, H.V., Role of connexin 43 in central nervous system injury, Exp. Neurol., 2010, vol. 225, p. 250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.07.014
Dublin, P. and Hanani, M., Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: their possible contribution to inflammatory pain, Brain Behav. Immun., 2007, vol. 21, p. 592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2006.11.011
Fukuda, T., Structural organization of the gap junction network in the cerebral cortex, Neuroscientist, 2007 vol. 13, p. 199. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858406296760
Grigorev, I.P. and Korzhevskii, D.E., Current technologies for fixation of biological material for immunohistochemical analysis (review), Mod. Technol. Med., 2018, vol. 10. № 2, p. 156. https://doi.org/10.17691/stm2018.10.2.19
Hanani, M., Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: from form to function, Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev., 2005, vol. 48, p. 457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.09.001
Hanani, M., Role of satellite glial cells in gastrointestinal pain, Front. Cell Neurosci., 2015, vol. 9, p. 412. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00412
Hanani, M. and Spray, D.C., Glial cells in autonomic and sensory ganglia, in Neuroglia, New York: Oxford Academic, 2012, 3rd ed., pp., 122–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/med/9780199794591.003.0011
Hanani, M. and Spray, D.C., Emerging importance of satellite glia in nervous system function and dysfunction, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2020, vol. 21, p. 485. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-020-0333-z
Hanani, M., Huang, T.Y., Cherkas, P.S., Ledda, M., and Pannese, E., Glial cell plasticity in sensory ganglia induced by nerve damage, Neuroscience, 2002, vol. 114, p. 279. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00279-8
Hanani, M, Spray, D.C., and Huang, T.Y., Age-related changes in neurons and satellite glial cells in mouse dorsal root ganglia, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2023, vol. 24, p. 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032677
Huang, T.Y., Hanani, M., Ledda, M., De Palo, S., and Pannese, E., Aging is associated with an increase in dye coupling and in gap junction number in satellite glial cells of murine dorsal root ganglia, Neuroscience, 2006, vol. 137, p. 1185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.10.020
Huang, T.Y., Belzer, V., and Hanani, M., Gap junctions in dorsal root ganglia: possible contribution to visceral pain, Eur. J. Pain, 2010, vol. 14, p. 49.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2009.02.005
Huang, X., Su, Y., Wang, N., Li, H., Li, Z., Yin, G., Chen, H., Niu, J., and Yi, C., Astroglial connexins in neurodegenerative diseases, Front. Mol. Neurosci., 2021, vol. 14, p. 657514. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2021.657514
Iacobas, D.A., Urban-Maldonado, M., Iacobas, S., Scemes, E., and Spray, D.C., Array analysis of gene expression in connexin-43 null astrocytes, Physiol. Genomics, 2003, vol. 15, p. 177. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00062.2003
Jasmin, L., Vit, J.P., Bhargava, A., and Ohara, P.T., Can satellite glial cells be therapeutic targets for pain control?, Neuron Glia Biol., 2010, vol. 6, p. 63. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1740925x10000098
Ji, R.R., Kawasaki, Y., Zhuang, Z.Y., Wen, Y.R., and Decosterd, I., Possible role of spinal astrocytes in maintaining chronic pain sensitization: review of current evidence with focus on bFGF/JNK pathway, Neuron Glia Biol., 2006, vol. 2, p. 259.
Kettenmann, H., Faissner, A., and Trotter, J., Neuron-glia interactions in homeostasis and degeneration, in Comprehensive Human Physiology, Greger, R. and Windhorst, U., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 1996. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-60946-6_27
Kettenmann, H., Hanisch, U.K., Noda, M., and Verkhratsky, A., Physiology of microglia, Physiol. Rev., 2011, vol. 91, p. 461.
Kim, Y.S., Choi, J., and Yoon, B.-E., Neuron-glia interactions in neurodevelopmental disorders, Cells, 2020, vol. 9, p. 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102176
Koike, T., Tanaka, S., Hirahara, Y., Oe, S., Kurokawa, K., Maeda, M., Suga, M., Kataoka, Y., and Yamada, H., Morphological characteristics of p75 neurotrophin receptor-positive cells define a new type of glial cell in the rat dorsal root ganglia, J. Comp. Neurol., 2019, vol. 527, p. 2047. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.24667
Kolos, E.A. and Korzhevskii, D.E., Glutamine synthetase-containing cells of the dorsal root ganglion at different stages of rat ontogeny, Russ. J. Dev. Biol., 2018, vol. 49, p. 179. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360418030049
Korzhevskii, D.E., Sukhorukova, E.G., Gilerovich, E.G., Petrova, E.S., Kirik, O.V., and Grigorev, I.P., Advantages and disadvantages of zinc-ethanol-formaldehyde as a fixative for immunocytochemical studies and confocal laser microscopy, Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 2014, vol. 44, p. 542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-014-9948-8
Korzhevskii, D.E., Sukhorukova, E.G., Kirik, O.V., and Grigorev, I.P., Immunohistochemical demonstration of specific antigens in the human brain fixed in zinc-ethanol-formaldehyde, Eur. J. Histochem., 2015, vol. 59, p. 233. https://doi.org/10.4081/ejh.2015.2530
Li, F., Li, L., Song, X.Y., Zhong, J.H., Luo, X.G., Xian, C.J., and Zhou, X.F., Preconditioning selective ventral root injury promotes plasticity of ascending sensory neurons in the injured spinal cord of adult rats—possible roles of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, TrkB and p75 neurotrophin receptor, Eur. J. Neurosci, 2009, vol. 30, p. 1280. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06920.x
Lin, S.H., Lu, C.Y., Muhammad, R., Chou, W.Y., Lin, F.C., Wu, P.C., Lin, C.R., and Yang, L.C., Induction of connexin 37 expression in a rat model of neuropathic pain, Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res., 2002, vol. 99, p. 134.
Marshall, A. and Duchen, L.W., Sensory system involvement in infantile spinal muscular atrophy, J. Neurol. Sci., 1975, vol. 26, p. 349. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-510x(75)90207-5
Martinelli, C., Sartori, P., Ledda, M., and Pannese, E., Gap junctions between perineuronal satellite cells increase in number with age in rabbit spinal ganglia, J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol., 2004, vol. 36, p. 17.
Martinelli, C., Sartori, P., De Palo, S., Ledda, M., and Pannese, E., Increase in number of the gap junctions between satellite neuroglial cells during lifetime: an ultrastructural study in rabbit spinal ganglia from youth to extremely advanced age, Brain Res. Bull., 2005, vol. 67, p. 19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2005.05.021
Martinelli, C., Sartori, P., De Palo, S., Ledda, M., and Pannese, E., The perineuronal glial tissue of spinal ganglia. Quantitative changes in the rabbit from youth to extremely advanced age, Anat. Embryol. (Berl.), 2006, vol. 211, p. 455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-006-0097-x
Miyazaki, I. and Asanuma, M., Neuron-astrocyte interactions in Parkinson’s disease, Cells, 2020, vol. 9, p. 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9122623
Meyer, K. and Kaspar, B.K., Glia-neuron interactions in neurological diseases: testing non-cell autonomy in a dish, Brain Res., 2017, vol. 1656, p. 27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.051
Nadeau, J.R., Wilson-Gerwing, T.D., and Verge, V.M., Induction of a reactive state in perineuronal satellite glial cells akin to that produced by nerve injury is linked to the level of p75NTR expression in adult sensory neurons, Glia, 2014, vol. 62, p. 763. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22640
Obata, K., Katsura, H., Sakurai, J., Kobayashi, K., Yamanaka, H., Dai, Y., Fukuoka, T., and Noguchi, K., Suppression of the p75 neurotrophin receptor in uninjured sensory neurons reduces neuropathic pain after nerve injury, J. Neurosci., 2006, vol. 26, p. 11974. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3188-06.2006
Ohsawa, K., Imai, Y., Kanazawa, H., Sasaki, Y., and Kohsaka, S., Involvement of Iba1 in membrane ruffling and phagocytosis of macrophages/microglia, J. Cell Sci., 2000, vol. 113, p. 3073. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.113.17.3073
Orellana, J.A., von Bernhardi, R., Giaume, C., and Sáez, J.C., Glial hemichannels and their involvement in aging and neurodegenerative diseases, Rev. Neurosci., 2012, vol. 23, p. 163. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2011-0065
Orellana, J.A., Retamal, M.A., Moraga-Amaro, R., and Stehberg, J., Role of astroglial hemichannels and pannexons in memory and neurodegenerative diseases, Front. Integr. Neurosci., 2016, vol. 10, p. 26. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2016.00026
Pannese, E., The satellite cells of the sensory ganglia, Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol., 1981 vol. 65, p. 1.
Pannese, E., The structure of the perineuronal sheath of satellite glial cells (SGCs) in sensory ganglia, Neuron Glia Biol., 2010, vol. 6, p. 3. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1740925X10000037
Pannese, E., Ledda, M., Cherkas, P.S., Huang, T.Y., and Hanani, M., Satellite cell reactions to axon injury of sensory ganglion neurons: increase in number of gap junctions and formation of bridges connecting previously separate perineuronal sheaths, Anat. Embryol. (Berl.), 2003, vol. 206, p. 337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-002-0301-6
Pierezan, F., Mansell, J., Ambrus, A., and Hoffmann, R.A., Immunohistochemical expression of ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 in cutaneous histiocytic proliferative, neoplastic and inflammatory disorders of dogs and cats, J. Comp. Pathol., 2014, vol. 151, p. 347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.07.003
Procacci, P., Magnaghi, V., and Pannese, E., Perineuronal satellite cells in mouse spinal ganglia express the gap junction protein connexin43 throughout life with decline in old age, Brain Res. Bull., 2008, vol. 75, p. 562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.09.007
Retamal, M.A., Riquelme, M.A., Stehberg, J., and Alcayaga, J., Connexin43 hemichannels in satellite glial cells, can they influence sensory neuron activity?, Front. Mol. Neurosci., 2017, vol. 10, p. 374. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00374
Rodjakovic, D., Salm, L., and Beldi, G., Function of connexin-43 in macrophages, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, vol. 22, p. 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms2203141
Schmitt, L.-I., Leo, M., Kutritz, A., Kleinschnitz, C., and Hagenacker, T., Activation and functional modulation of satellite glial cells by oxaliplatin lead to hyperexcitability of sensory neurons in vitro, Mol. Cell. Neurosci., 2020, vol. 105, p. 103499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2020.103499
Tsuda, M., Inoue, K., and Salter, M.W., Neuropathic pain and spinal microglia: a big problem from molecules in “small” glia, Trends Neurosci., 2005, vol. 28, p. 101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2004.12.002
Wu, A., Green, C.R., Rupenthal, I.D., and Moalem-Taylor, G., Role of gap junctions in chronic pain, J. Neurosci. Res., 2012, vol. 90, p. 337. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22764
Xing, J., Wang, H., Chen, L., Wang, H., Huang, H., Huang, J., and Xu, C., Blocking Cx43 alleviates neuropathic pain in rats with chronic constriction injury via the P2X4 and P38/ERK-P65 pathways, Int. Immunopharmacol., 2023, vol. 114, p. 109506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109506
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 23-25-10003, https://rscf.ru/project/23-25-10003) and the St. Petersburg Science Foundation, Russia in accordance with agreement no. 23-25-10003 dated May 5, 2023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.A. Kolos: developing a research plan, performing immunohistochemical reactions, analyzing the material, writing the text of the article; D.E. Korzhevsky: editing the text of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
All studies were conducted in accordance with the principles of biomedical ethics as set out in the Declaration of Helsinki of 1964 and its subsequent amendments. They were also approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Experimental Medicine (St. Petersburg, Russia), protocol no. 4/22 of September 29, 2022.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by I. Fridlyanskaya
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations: PNS—peripheral nervous system; Cx43—connexin-43; DRG—dorsal root ganglion.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolos, E.A., Korzhevsky, D.E. Gap Junction Protein Connexin-43 in a Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion. Cell Tiss. Biol. 18, 189–198 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X23700049
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X23700049