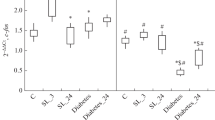
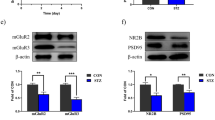
Abstract—We studied the effect of the peptide drug pinealon (Glu-Asp-Arg) at doses of 50, 100, and 200 ng/kg on the training of rats in the Morris maze and the maintenance of the acquired skill after the development of experimental diabetes. We also studied the changes in the subunit composition of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus in these experimental models. In the Morris water maze, spatial learning was evaluated for 3 days, and pinealon was administered for 5 days following animal training. After training, animals were injected once with streptozotocin at a dose of 50 mg/kg of rat body weight. Estimation of the maintenance of the acquired skill and molecular studies (using real-time PCR) were performed on day 21 after modeling of experimental diabetes. It was shown that pinealon has a dose-dependent effect on the parameters studied. The most positive effect on the maintenance of the developed skill during streptozotocin-induced diabetes was observed after pinealon administration at a dose of 100 ng/kg. At this dose, we observed the smallest changes in the expression level of the Grin1, Grin2b, and Grin2d genes relative to the control values, as well as increased values of Grin2a/Grin2b ratio compared to diabetic groups treated with pinealon at dosages of 50 or 200 ng/kg.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dedov, I.I., Shestakova, M.V., Vikulova, O.K., Zheleznyakova, A.V., and Isakov, M.A., Sakharnyi Diabet, 2018, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 144–159.
Nampoothiri, M., Reddy, N.D., and John, J., Behavioural Neurology, vol. 2014, p. 8.
Devaskar, S.U., Giddings, S.J., Rajakumar, P.A., Carnaghi, L.R., Menon, R.K., and Zahm, D.S., J. Biol. Chem., 1994, vol. 269, pp. 8445–8454.
Caruso, M.A. and Sheridan, M.A., Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 2011, vol. 173, pp. 227–247.
Baskin, D.G., Schwartz, M.W., Sipols, A.J., D’Alessio, D.A., Goldstein, B.J., and White, M.F., Endocrinology, 1994, vol. 34, pp. 1952–1955.
Baura, G.D., Foster, D.M., Kaiyala, K., Porte, D.Jr., Kahn, S.E., and Schwartz, M.W., Diabetes, 1996, vol. 45, pp. 86–90.
Blinov, D.V., Epilepsiya i paroksizmal’nye sostoyaniya, 2014, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 70–84.
Wu, L.-J., Xu, H., Ren, M., Cao, X., and Zhuo, M., Molecular Pain, 2007, vol. 3, p. 11.
Baez, M.V., Cercato, M.C., and Jerusalinsky, D.A., Neural Plasticity, 2018, Article ID 5093038.
Cercato, M.C., Vazquez, C.A., and Kornisiuk, E., Front. Behav. Neurosci., 2017, vol. 10, p. 242.
Shohami, E. and Biegon, A., CNS and Neurological Disorders–Drug Targets, 2014, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 567–573.
Bannerman, D.M., Niewoehner, B., and Lyon, L., J. Neuroscience, 2008, vol. 28, no. 14, pp. 3623–3630.
Tse, Y.C., Bagot, R.C., Hutter, J.A., Wong, A.S., and Wong, T.P., PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, no. 11, e27215.
Nampoothiri, LaiT.W., Zhang, S., and Wang, Y.T., Progress in Neurobiology, 2014, vol. 115, pp. P. 157–188.
Pomytkin, I., Costa-Nunes, J.P., and Kasatkin, V., CNS Neuroscience &Therapeutics, 2018, vol. 24, iss. 9. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12866
McNay, E.C. and Recknagel, A.K., Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 2011, vol. 96, pp. 432–342.
Kullmann, S., Heni, M., and Hallschmid, M., Physiol. Rev., 2016, vol. 96, pp. 1169–1209.
Qiu, J., Zhang, C., and Borgquist, A., Cell Metab., 2014, vol. 19, pp. 682–693.
Chen, W., Balland, E., and Cowley, M.A., Neuroendocrinology, 2017, vol. 104, pp. 364–381.
Morris, R.G., J. Neurosci. Met., 1984, vol. 11, pp. 47–60.
Szkudelski, T., Ibed, 2001, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 536–546.
Livak, K.J. and Schmittgen, T.D., Methods, 2001, vol. 25, pp. 402–408.
Karantysh, G.V., Abramchuk, V.A., Ryzhak, G.A., and Mendzheritskii, A.M., Fundamental’nye Issledovaniya, 2013, no. 6, pp. 1406–1410.
Mendzheritskii, A.M., Karantysh, G.V., Ryzhak, G.A., and Dem’yanenko, S.V., Uspekhi Gerontologii, 2014, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 94–97.
Aykut, U., Goncalves, G.H.M., and Li, W., Molecular Metabolism, 2015, vol. 4, no. 10, pp. 678–691.
Paoletti, P., Bellone, C., and Zhou, Q., Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2013, vol. 14, pp. 383–400.
Shang, Y., Zhang, J., and Huang, E.J., J. Neurosci., 2018, vol. 38, no. 16, pp. 4006–4019.
von Engelhardt, J., Bocklisch, C., Tonges, L., et al., Front. Cell. Neurosci., 2015, vol. 9, p. 95.
Cavallaro, S., D’Agata, V., Manickam, P., Dufour, F., and Alkon, D.L., Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2001, vol. 99, no. 25, pp. 16279–16284.
Zhang, L., Yu, W., Han, T.-Z., Xie, W., and Luo, Y., Sheng Li Xue Bao, 2006, vol. 58, no. 5, pp. 442–448.
Baez, M.V., Oberholzer, M.V., Cercato, M.C., Snitcofsky, M., Aguirre, A.I., and Jerusalinsky, D.A., PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 2, e55244.
Hepp, Y., Salles, A., Carbo-Tano, M., Pedreira, M.E., and Freudenthal, R., Learning and Memory, 2016, vol. 23, no. 8, pp. 427–434.
Shanmugasundaram, B., Sase, A., and Miklosi, A.G., Behav. Brain Res., vol. 289, no. 2015, pp. 157–168.
Liu, Y., Wong, T.P., and Aarts, M., J. Neurosci., 2007, vol. 27, no. 11, pp. 2846–2857.
Taghibiglou, C., Martin, H.G.S., and Lai, T.W., Nature Medicine, 2009, vol. 15, no. 12, pp. 1399–1406.
Funding
No external funding was used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement. Animal experiments were performed in compliance with the principles of the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for experiments or other scientific purposes (Strasbourg, March 18, 1986).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karantysh, G.V., Fomenko, M.P., Menzheritskii, A.M. et al. Effect of Pinealon on Learning and Expression of NMDA Receptor Subunit Genes in the Hippocampus of Rats with Experimental Diabetes. Neurochem. J. 14, 314–320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S181971242003006X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S181971242003006X