Abstract
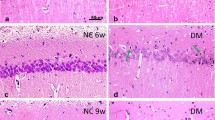
Cognitive dysfunction is a high incidence of diabetes mellitus (DM). However, the relationship between DM-induced cognitive defect and neuronal network oscillations is still unknown. In this study, adult male C57BL/6 J mice were intraperitoneally injected with streptozotocin (STZ) to duplicate DM. After 12 weeks, local field potentials were recorded in the perforant fiber pathway (PP) and dentate gyrus (DG) regions. Data showed that mice in the STZ group exhibited impairment of spatial learning and memory by the Morris Water Maze test. The low gamma (LG) and high gamma (HG) power were increased in the PP and DG areas of the STZ group. Moreover, the phase synchronization and the information flow at theta and LG rhythms between the PP and DG areas were decreased, and the theta-LG phase-amplitude coupling strength was markedly reduced in the PP region, DG region, and the PP–DG pathway in the STZ group. Additionally, the concentration of glutamate was increased by the high-performance liquid chromatography. Moreover, the NR2B and PSD95 expressions were markedly reduced, and the Akt/GSK-3β pathway was inhibited. Interestingly, the expressions of mGluRIIs (mGluR2 and mGluR3) were significantly decreased. The reduction of mGluRIIs may limit their function, such as restricting presynaptic glutamate release and reversing the dysfunction of NR2B via Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. In conclusion, our data suggest that DM alters the hippocampal neural network partly related to the dysfunction of mGluRIIs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beauquis J, Roig P, De Nicola AE, Saravia F (2009) Neuronal Plasticity and Antidepressants in the Diabetic Brain. Neuroimmunomodulation Fundam Biol Therapy. 1153:203–208
Brigman JL, Wright T, Talani G, Prasad-Mulcare S, Jinde S, Seabold GK, Mathur P, Davis MI, Bock R, Gustin RM, Colbran RJ, Alvarez VA, Nakazawa K, Delpire E, Lovinger DM, Holmes A (2010) Loss of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors in CA1 hippocampus and cortex impairs long-term depression, reduces dendritic spine density, and disrupts learning. J Neurosci 30:4590–4600
Csicsvari J, Jamieson B, Wise KD, Buzsaki G (2003) Mechanisms of gamma oscillations in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. Neuron 37:311–322
Ford JM, Roach BJ, Hoffman RS, Mathalon DH (2008) The dependence of P300 amplitude on gamma synchrony breaks down in schizophrenia. Brain Res 1235:133–142
Fritschy JM, Mohler H (1995) GABAA-receptor heterogeneity in the adult rat brain: differential regional and cellular distribution of seven major subunits. J Comp Neurol 359:154–194
Hiyoshi T, Kambe D, Karasawa J (2014) Chaki SDifferential effects of NMDA receptor antagonists at lower and higher doses on basal gamma band oscillation power in rat cortical electroencephalograms. Neuropharmacology 85:384–396
Johnson NW, Ozkan M, Burgess AP, Prokic EJ, Wafford KA, O’Neill MJ, Greenhill SD, Stanford IM, Woodhall GL (2017) Phase-amplitude coupled persistent theta and gamma oscillations in rat primary motor cortex in vitro. Neuropharmacology 119:141–156
Jones NC, Reddy M, Anderson M, Salzberg MR, O’Brien TJ, Pinault D (2012) Acute administration of typical and atypical antipsychotics reduces EEG γ power, but only the preclinical compound LY379268 reduces the ketamine-induced rise in γ power. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15(5):657–668
Kalcza-Janosi K, Lucas A, Barkai L, Szamoskozi I (2013) Cognitive functions in type 1 and type 2 diabetes metaanalysis. Orv Hetil 154:694–699
Kehrer C, Dugladze T, Maziashvili N, Wojtowicz A, Schmitz D, Heinemann U, Gloveli T (2007) Increased inhibitory input to CA1 pyramidal cells alters hippocampal gamma frequency oscillations in the MK-801 model of acute psychosis. Neurobiol Dis 25:545–552
Kitamura T, Sun C, Martin J, Kitch LJ, Schnitzer MJ, Tonegawa S (2015) Entorhinal cortical ocean cells encode specific contexts and drive context-specific fear memory. Neuron 87(6):1317–1331
Lemercier CE, Holman C, Gerevich Z (2017) Aberrant alpha and gamma oscillations ex vivo after single application of the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Schizophr Res 188:118–124
Muir KW (2006) Glutamate-based therapeutic approaches: clinical trials with NMDA antagonists. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:53–60
Nakazono T, Lam TN, Patel AY, Kitazawa M, Saito T, Saido TC, Igarashi KM (2017) Impaired in vivo gamma oscillations in the medial entorhinal cortex of knock-in alzheimer model. Front Syst Neurosci 11:48
Palva JM, Palva S, Kaila K (2005) Phase synchrony among neuronal oscillations in the human cortex. J Neurosci 25:3962–3972
Qiao Z, Xie K, Liu K, Li G (2014) Decreased neuronal bursting and phase synchrony in the hippocampus of streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/626108
Ribeiro FM, Vieira LB, Pires RG, Olmo RP, Ferguson SS (2017) Metabotropic glutamate receptors and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Res 115:179–191
Shipton OA, Paulsen O (2014) GluN2A and GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptors in hippocampal plasticity. Philos Trans Royal Soc B-Biolog Sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0163
Steffenach HA, Witter M, Moser MB, Moser EI (2005) Spatial memory in the rat requires the dorsolateral band of the entorhinal cortex. Neuron 45:301–313
Ster J, Mateos JM, Grewe BF, Coiret G, Corti C, Corsi M, Helmchen F, Gerber U (2011) Enhancement of CA3 hippocampal network activity by activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(24):9993–9997
Tang ZJ, Zou W, Yuan J, Zhang P, Tian Y, Xiao ZF, Li MH, Wei HJ, Tang XQ (2015) Antidepressant-like and anxiolytic-like effects of hydrogen sulfide in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through inhibition of hippocampal oxidative stress. Behav Pharmacol 26:427–435
Tyszkiewicz JP, Gu Z, Wang X, Cai X, Yan Z (2004) Group II metabotropic glutamate receptors enhance NMDA receptor currents via a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism in pyramidal neurons of rat prefrontal cortex. J Physiol 554:765–777
van Groen T, Miettinen P, Kadish I (2003) The entorhinal cortex of the mouse: organization of the projection to the hippocampal formation. Hippocampus 13(1):133–149
Wang B, Wu Q, Lei L, Sun H, Michael N, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ge B, Wu X, Xin Y, Zhao J, Li S (2019) Long-term social isolation inhibits autophagy activation, induces postsynaptic dysfunctions and impairs spatial memory. Exp Neurol 311:213–224
Witter MP, Wouterlood FG, Naber PA, Van Haeften T (2000) Anatomical organization of the parahippocampal-hippocampal network. Ann N Y Acad Sci 911:1–24
Xi D, Li YC, Snyder MA, Gao RY, Adelman AE, Zhang W, Shumsky JS, Gao WJ (2011) Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist ameliorates MK801-induced dysfunction of NMDA receptors via the Akt/GSK-3beta pathway in adult rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:1260–1274
Xiao TL, Guan X, Nie L, Wang S, Sun L, He T, Huang YJ, Zhang JB, Yang K, Wang JP, Zhao JH (2014) Rapamycin promotes podocyte autophagy and ameliorates renal injury in diabetic mice. Mol Cell Biochem 394:145–154
Xu X, Liu C, Li Z, Zhang T (2015) Effects of hydrogen sulfide on modulation of theta-gamma coupling in hippocampus in vascular dementia rats. Brain Topogr 28:879–894
Yanovsky Y, Ciatipis M, Draguhn A, Tort AB, Brankack J (2014) Slow oscillations in the mouse hippocampus entrained by nasal respiration. J Neurosci 34:5949–5964
Yener GG, Guntekin B, Oniz A, Basar E (2007) Increased frontal phase-locking of event-related theta oscillations in Alzheimer patients treated with cholinesterase inhibitors. Int J Psychophysiol 64:46–52
Zheng C, Zhang T (2013) Alteration of phase-phase coupling between theta and gamma rhythms in a depression-model of rats. Cogn Neurodyn 7:167–172
Zheng C, Zhang T (2015) Synaptic plasticity-related neural oscillations on hippocampus-prefrontal cortex pathway in depression. Neuroscience 292:170–180
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Key Technology R&D Program of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Tianjin (20YFZCSY00460), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070988, 81771979), Nankai University 111 project (202210055434, 202210055912, 202210055434).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
Nankai University, 202210055434, Liu Chunhua, 202210055912, Liu Chunhua, 202210055434, Liu Chunhua, Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology of China, 20YFZCSY00460, Liu Chunhua, National Natural Science Foundation of China, 81771979, Tao Zhang, 32070988, Tao Zhang
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sreedharan Sajikumar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Li, Q., Wu, Z. et al. The dysfunction of mGluRIIs is involved in the disorder of hippocampal neural network in diabetic mice model. Exp Brain Res 240, 2491–2498 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-022-06433-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-022-06433-4