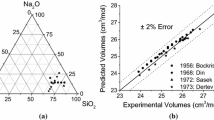
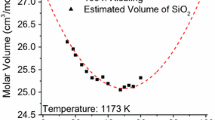
Abstract
A structural based model is proposed to represent the molar volume of silicate melts in terms of both temperature and composition. The model links the molar volume to the internal structure of melts through the concentrations of non-bridging oxygen present in the slag. A previous proposed structural thermodynamic model is used to calculate the content of oxygen ions. The molar volume model requires only one or two parameters to obtain a good agreement between experimental and calculated data for the SiO2–Na2O, SiO2–CaO, SiO2–MgO, SiO2–MnO, and SiO2–PbO binary systems. The molar volume of ternary systems is calculated with the model assuming a linear function of the parameters from binary systems; however, the content of non-oxygen bridges is calculated using the thermodynamic model for ternary systems. Comparison is made between the experimental and model results for the SiO2–CaO–MnO, SiO2–Na2O–PbO and SiO2–CaO–MgO systems.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mills, K.C., Karagagge, S., Lee, P.D., Yuang, L. and Shahbazian, F., Calculation of physical properties for use in models of continuous casting process-Part 1: Mould slags, ISIJ Int., 2016, vol. 56, pp. 264–273.
Rabukhin, A.I., Structural interpretation of the concentration dependences of molar volume in lead silicate glasses, Glass Ceram., 2000, vol. 57, pp. 338–341.
Thibodeau, E., Gheribi, A.E., and Jung, I.-H., A structural molar volume model for oxide melts, Part I: Li2O–Na2O–K2O–MgO–CaO–MnO–PbO–Al2O3–SiO2 melts-binary systems, Metall. Mater. Trans., B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 1147–1164.
Thibodeau, E., Gheribi, A.E., and Jung, I-H., A structural molar volume model for oxide melts Part II: Li2O–Na2O–K2O–MgO–CaO–MnO–PbO–Al2O3–SiO2 melts-ternary systems, Metall. Mater. Trans., B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 1165–1186.
Pelton, A.D. and Blander, M., Thermodynamic analysis of ordered liquid solutions by a modified quasichemical approach—Applications to silicate slags, Metall. Mater. Trans., B, 1986, vol. 17, pp. 805–815.
Lin, P.L. and Pelton, A.D., A structural model for binary silicate systems, Metall. Trans., B, 1979, vol. 10, pp. 667–676.
Romero-Serrano, A. and Pelton, A.D. Extensions of a structural model for binary silicate systems, Metall. Mater. Trans., B, 1995, vol. 26, pp. 305–315.
López-Rodríguez, J., Romero-Serrano, A., Hernández-Ramírez, A., Pérez-Labra, M., Cruz-Ramírez, A., and Rivera-Salinas, E., Use of a structural model to calculate the viscosity of liquid silicate systems, ISIJ Int., 2018, vol. 58, pp. 220–226.
Gutiérrez, J., Romero-Serrano, A., Plascencia, G., Chávez, F., and Vargas, R., Thermodynamic model for ternary silicate systems, ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 664–669.
Tomlinson, J.W., Heynes, M.S.R., and Bockris, J.O.M., The structure of liquid silicates Part 2. Molar volumes and expansivities, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1958, vol. 54, pp. 1822–1833.
Courtial, P. and Dingwell, D.B., Nonlinear composition dependence of molar volume of melts in the CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 system, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1995, vol. 59, pp. 3685–3695.
Sokolov, V.I., Popel, S.I., and Esin, O.A., Density and molar volume of slags, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., 1970, vol. 13, pp. 10–15.
Fujino, S., Hwang, C., and Morinaga, K., Density, surface tension, and viscosity of PbO–B2O3–SiO2 glass melts, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2004, vol. 87, pp. 10–16.
Ouchi, Y., Yoshida, T., and Kato, E., Densities of ternary lead-silicate melts, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1977, vol. 41, pp. 865–874.
Ito, H. and Yanagase, T., Studies on lead silicate melts, Trans. Jpn. Inst. Melts, 1960, vol. 1, pp. 115–120.
Hino, M., Ejima, T., and Kameda, M., Surface tension and density of liquid lead silicate, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1967, vol. 31, pp. 113–119.
Courtial, P. and Dingwell, D.B., Densities of melts in the CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 system, Am. Mineral., 1999, vol. 48, pp. 465–476.
Gogiberidze, Y.M., Kekelidze, M.A., and Mikiashvili, S.M., Interfacial tension at the boundary between Fe–P alloys and MnO–SiO2 melts, Soobshch. Akad. Nauk Gruz. SSR, 1963, vol. 32, pp. 117–124.
Segers, L., Fontana, A., and Winand, R., Poids specifiques et volumes molaires de melanges d’oxydes fondus du systeme CaO–SiO2–MnO, Electrochim. Acta, 1978, vol. 23, pp. 1275–1280.
Bockris, J.O.M., Tomlinson, J.W., and White, J.L., The structure of the liquid silicates: Partial molar volumes and expansivities, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1956, vol. 52, pp. 299–310.
Heidtkamp, G., and Endell, K. The dependence of density and viscosity on temperature in the system soda–silica, Glastech. Ber., 1936, vol. 14, pp. 89–103.
Shartsis, L., Spinner, S., and Capps, W., Density, expansivity, and viscosity of molten alkali silicates, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1952, vol. 35, pp. 155–160.
Coenen, M., Density of cord glasses at high temperatures, Glastech. Ber., 1966, vol. 39, pp. 81–89.
Kekelidze, T.M., Mikiashvili, S.M., Dzhincharadze, T.I., and Khomeriki, R.V., Density and surface tension of oxide melts of the manganese oxide–calcium oxide–silica and manganese oxide–calcium oxide–silica–alumina systems, Izv. Akad. Nauk Gruz. SSR, Ser. Khim., 1978, vol. 4, pp. 240–244.
Lee, J., Hoai, L.T., Choe, J., and Park, J.H., Density measurements of CaO–MnO–SiO2 slags, ISIJ Int., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 2145–2148.
Hino, M., Ejima, T., and Kameda, M., Surface tension, density and viscosity of PbO–Na2O–SiO2 ternary melts, J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1968, vol. 32, pp. 809–814.
Licko, T. and Danek, V., Densities of melts in the system calcium silicate–calcium magnesium silicate (CaMgSi2O6)–calcium magnesium silicate (Ca2MgSi2O7), Phys. Chem. Glasses, 1982, vol. 23, pp. 67–71.
Lange, R.L. and Carmichael, I.S.E., Thermodynamic properties of silicate liquids with emphasis on density, thermal expansion and compressibility, Rev. Miner. Geochem., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 25–64
Ghiorso, M.S., and Kress, V.C., An equation of state for silicate melts. II. Calibration of volumetric properties at 105 Pa, Am. J. Sci., 2004, vol. 304, pp. 679–751.
Myssen, B.O., Structure and Properties of Silicate Melts, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1988.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors wish to thank the Institutions CONACyT, SNI, COFAA and IPN for the support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonio Romero-Serrano, López-Rodríguez, J., Hernández-Ramírez, A. et al. Evaluation of Molar Volume of Silicate Systems Using a Structural Model. Glass Phys Chem 45, 195–201 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659619030088
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659619030088