Abstract
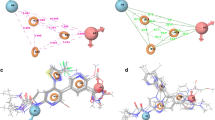
Searching for a specific inhibitor of pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylase (PyNP) was a central objective of the work. The search was carried out by modeling protein–ligand complexes via molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD), which make it possible to calculate the protein–ligand binding energy ΔGbind. The following compounds were selected as possible inhibitors: 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxythymidine (d4T), 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-ioduracil (fiauridine, FIAU), 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-uracil (FAU), and 2-pyrimidin-2-yl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylic acid (PIA). A preliminary estimate of the binding energy was obtained by the linear interaction energy (LIE) method, and a more accurate calculation was carried out by the free energy perturbation (FEP) method in the GROMACS software package. The calculation results showed that PIA and d4T bind to the active site of Bacillus subtilis PyNP (BsPyNP) with higher affinities as compared with the other putative inhibitors. PIA binds less strongly to human thymidine phosphorylase (hTP). This was assumed to minimize the possible side effects of this compound used for therapeutic purposes.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Friedkin, M. and Roberts, D., J. Biol. Chem., 1954, vol. 207, pp. 245–256.
Liekens, S., Bronckaers, A., and Balzarini, J., Lancet Oncol., 2009, vol. 10, pp. 628–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(09)70037-3
Bronckaers, A., Balzarini, J., and Liekens, S., Biochem. Pharmacol., 2008, vol. 76, pp. 188–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.04.019
Vande Voorde, J., Gago, F., Vrancken, K., Liekens, S., and Balzarini, J., Biochem. J., 2012, vol. 445, pp. 113–123. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20112225
Balaev, V.V., Prokofev, I.I., Gabdoulkhakov, A.G., Betzel, C., and Lashkov, A.A., Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun., 2018, vol. 74, pp. 193–197. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053230x18002935
Van Rompay, A.R., Johansson, M., and Karlsson, A., Pharmacol. Ther., 2003, vol. 100, pp. 119–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.07.001
Lipinski, C.A., Lombardo, F., Dominy, B.W., and Feeney, P.J., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2001, vol. 46, pp. 3–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-409x(00)00129-0
Balaev, V.V., Lashkov, A.A., Prokofev, I.I., Gabdulkhakov, A.G., Seregina, T.A., Mironov, A.S., Betzel, C., and Mikhailov, A.M., Crystallogr. Rep., 2016, vol. 61, pp. 830–841. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774516050023
Korb, O., Stützle, T., and Exner, T.E., Swarm Intell., 2007, vol. 1, pp. 115–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11721-007-0006-9
Goodsell, D.S. and Olson, A.J., Proteins, 1990, vol. 8, pp. 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.340080302
Korb, O., Stützle, T., and Exner, T.E., J. Chem. Inf. Model, 2009, vol. 49, pp. 84–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci800298z
Metropolis, N. and Ulam, S., J. Am. Stat. Assoc., 1949, vol. 44, pp. 335–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1949.10483310
Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V., and Colorni, A., IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern., 1996, vol. 26, pp. 29–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/3477.484436
Van Der Spoel, D., Lindahl, E., Hess, B., Groenhof, G., Mark, A.E., and Berendsen, H.J.C., J. Comput. Chem., 2005, vol. 26, pp. 1701–1718. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20291
Jo, S., Kim, T., Iyer, V.G., and Im, W., J. Comput. Chem., 2008, vol. 29, pp. 1859–1865. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20945
MacKerell, A.D., Bashford, D., Bellott, M., Dunbrack, R.L., Evanseck, J.D., Field, M.J., Fischer, S., Gao, J., Guo, H., Ha, S., Joseph-McCarthy, D., Kuchnir, L., Kuczera, K., Lau, F.T., Mattos, C., Michnick, S., Ngo, T., Nguyen, D.T., Prodhom, B., Reiher, W.E., Roux, B., Schlenkrich, M., Smith, J.C., Stote, R., Straub, J., Watanabe, M., Wiórkiewicz-Kuczera, J., Yin, D., and Karplus, M., J. Phys. Chem. B., 1998, vol. 102, pp. 3586–3616. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp973084f
Huang, J., Rauscher, S., Nawrocki, G., Ran, T., Feig, M., de Groot, B.L., Grubmüller, H., and MacKerell, A.D. Jr., Nat. Methods, 2017, vol. 14, pp. 71–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4067
Petersen, H.G., J. Chem. Phys., 1995, vol. 103, pp. 3668–3679. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.470043
Parrinello, M. and Rahman, A., J. Appl. Physics, 1981, vol. 52, pp. 7182–7190. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.328693
Bussi, G. and Parrinello, M., Computer Physics Comm., 2008, vol. 179, pp. 26–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2008.01.006
Hansson, T., Marelius, J., and Åqvist, J., J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des., 1998, vol. 12, pp. 27–35. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007930623000
Aldeghi, M., Heifetz, A., Bodkin, M.J., Knapp, S., and Biggin, P.C., Chem. Sci., 2016, vol. 7, pp. 207–218. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5sc02678d
Lashkov, A.A., Tolmachev, I.V., Eistrikh-Heller, P.A., and Rubinsky, S.V., Crystallogr. Rep., vol. 66, pp. 861–865. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774521050126
Rocklin, G.J., Mobley, D.L., Dill, K.A., and Hunenberger, P.H., J. Chem. Phys., 2013, vol. 139, p. 184103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4826261
Boresch, S., Tettinger, F., Leitgeb, M., and Karplus, M., J. Phys. Chem. B, vol. 107, pp. 9535–9551. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0217839
Wennberg, C.L., Murtola, T., Pall, S., Abraham, M.J., Hess, B., and Lindahl, E., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2015, vol. 11, pp. 5737–5746. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00726
Abraham, M.J., Murtola, T., Schulz, R., Pall, S., Smith, J.C., Hess, B., and Lindahl, E., SoftwareX, 2015, vol. 1, pp. 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
Shirts, M.R. and Chodera, J.D., J. Chem. Phys., 2008, vol. 129, p. 124105. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2978177
Zwanzig, R.W., J. Chem. Phys., 1954, vol. 22, pp. 1420–1426.
Jurrus, E., Engel, D., Star, K., Monson, K., Brandi, J., Felberg, L.E., Brookes, D.H., Wilson, L., Chen, J., Liles, K., Chun, M., Li, P., Gohara, D.W., Dolinsky, T., Konecny, R., Koes, D.R., Nielsen, J.E., Head-Gordon, T., Geng, W., Krasny, R., Wei, G., Holst, M.J., McCammon, J.A., and Baker, N.A., Protein Sci., 2018, vol. 27, pp. 112–128. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3280
Balaev, V.V., Prokofev, I.I., Gabdoulkhakov, A.G., Betzel, C., and Lashkov, A.A., X-ray Structure of the Complex Pyrimidine-Nucleoside Phosphorylase from Bacillus subtilis at 1.88 Å. Worldwide Protein Data Bank, 2018.
Kandil, S., Pannecouque, C., Chapman, F.M., Westwell, A.D., and McGuigan, C., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2019, vol. 29, p. 126721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.126721
Institute of Medicine, Committee to Review the Fialuridine (FIAU/FIAC) Clinical Trials., Review of the Fialuridine (FIAU) Clinical Trials. National Academies Press, 1995, p. 280.
Kirkwood, J.G., J. Chem. Phys. Am. Inst. Phys., 1935, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 300–313.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work was carried out using the infrastructure of the High-Throughput Calculations and Big Data Collective Access Center (Informatika Center, Informatics and Management Federal Research Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow). Regulations of the Informatika Center are available at http://www.frccsc.ru/ckp.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 19-29-12054, calculations by the FEP method) and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (state contract with the Crystallography and Photonics Federal Research Center, molecular docking and MD simulations).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by T. Tkacheva
Abbreviations: AD, Autodock; BsPyNP, Bacillus subtilis pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase; d4T, 2',3'- didehydro-3'-deoxythymidine; FAU, 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-uracil; FEP, free energy perturbation; FIAU, fiauridine (1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-ioduracil); ΔGbind, protein–ligand binding energy; ΔGcoul, free energy of coupling the Coulomb interaction; ΔGvdw, free energy of coupling the van der Waals interaction defined as the Lennard-Jones potential; ΔΔGDSF, discrete bound finite-size solvent correction; ΔΔGNET, correction for net charge interaction due to periodicity; ΔGrest, restrained binding free energy; ΔΔGRIP, correction for residual integrated potential effects; ΔΔGUSV, correction for under solvation due to periodicity; hTP, human thymidine phosphorylase; LIE, linear interaction energy; MhPyNP, Mycoplasma hyorhinis pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase; PIA, 2-pyrimidin-2-yl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylic acid; PL, PLANTS; PME, particle mesh Ewald; PyNP, pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase; RMSD, root-mean-square deviation; TI, thermodynamic integration; MD, molecular dynamics
Corresponding author: phone: +7 (916) 875-27-80.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eistrikh-Heller, P.A., Rubinsky, S.V., Samygina, V.R. et al. Calculation of Free Energy of Binding for Widely Specific Pyrimidine-Nucleoside Phosphorylase and Suspected Inhibitors. Russ J Bioorg Chem 48, 1262–1272 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162022060103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162022060103