Abstract
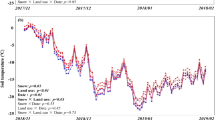
The effects of snow regimes (including the depth and duration of snow cover) on soil N dynamics and microbial activity in situ were explored in the alpine belt of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Deeper snow-cover reduced NH +4 -N content, microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen, fungi count, and enzyme activities, whereas did not change net N mineralization. No differences in N pools in the soil, microbial biomass, microbial counts, and enzyme activity were found under the different duration of snow cover, showing that accumulation and release in soil N pools did not be significantly changed by earlier continuous snow cover.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACIA: Arctic Climate Impact Assessment, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 2005.
Björk, R.G. and Molau, U., Ecology of alpine snowbeds and the impact of global change, Arctic Antarctic Alpine Res., 2007, vol. 39, pp. 34–43.
Brookes, P.C., Landman, A., Pruden, G., et al., Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil, Soil Biol. Biochem., 1985, vol. 17, pp. 837–842.
Brooks, P.D. and Williams, M.W., Snowpack controls on nitrogen cycling and export in seasonally snow-covered catchments, Hydrol. Process, 1999, vol. 13, pp. 2177–2190.
Brooks, P.D., Williams, M.W., and Schmidt, S.K., Snowpack controls on soil nitrogen dynamics in the Colorado alpine, in Biogeochemistry of Snow-Covered Catchments: International Association of Hydrological Sciences Publication 228, Tonnessen, K., Williams, M., and Tranter, M., Eds., Wallingford: IAHS, 1995, pp. 283–292.
Brooks, P.D., Williams, M.W., and Schmidt, S.K., Microbial activity under alpine snowpacks, Niwot Ridge, Colorado, Biogeochemistry, 1996, vol. 32, pp. 93–113.
Brooks, P.D., Schmidt, S.K., and Williams, M.W., Winter production of CO2 and N2O from alpine tundra: Environmental controls and relationship to inter-system C and N fluxes, Oecologia, 1997, vol. 110, pp. 403–413..
Brooks, P.D., Williams, M.W., and Schmidt, S.K., Inorganic nitrogen and microbial biomass dynamics before and during spring snowmelt, Biogeochemistry, 1998, vol. 43, pp. 1–15.
Buckeridge, K.M. and Grogan, P., Deepened snow alters soil microbial nutrient limitations in arctic birch hummock tundra, Appl. Soil Ecol., 2008, vol. 39, pp. 210–222.
Buckeridge, K.M., Cen, Y.P., Layzell, D.B., et al., Soil biogeochemistry during the early spring in low arctic mesic tundra and the impacts of deepened snow and enhanced nitrogen availability, Biogeochemistry, 2010, vol. 99, pp. 127–141.
Campbell, J.L., Mitchell, M.J., Groffman, P.M., et al., Winter in northeastern North America: A critical period for ecological processes, Front. Ecol. Environ., 2005, vol. 3, pp. 314–322.
Chapin, F.S., Sturm, M., Serreze, M.C., et al., Role of land-surface changes in Arctic summer warming, Science, 2005, vol. 310, pp. 657–660.
Edwards, K.A., McCulloch, J., Kershaw, G.P., et al., Soil microbial and nutrient dynamics in a wet Arctic sedge meadow in late winter and early spring, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2006, vol. 38, pp. 2843–2851.
Goodrich, L.E., The influence of snow cover on the ground thermal regime, Can. Geotech. J., 1982, vol. 19, pp. 421–432.
Grogan, P. and Jonasson, S., Controls on annual nitrogen cycling in the understory of a subarctic birch forest, Ecology, 2003, vol. 84, pp. 202–218.
Guan, S.Y., Soil Enzyme and Its Research Method, Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1986 (In Chinese).
IPCC: Climate Change 2007, Geneva, Switzerland: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2007.
Jones, D.L. and Willett, V.B., Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2006, vol. 38, pp. 991–999.
Lipson, D.A., Schmidt, S.K., and Monson, R.K., Carbon availability and temperature control the post-snowmelt decline in alpine soil microbial biomass, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2000, vol. 32, pp. 441–448.
Mulvaney, R.L., Nitrogen inorganic forms, in Methods of Soil Analysis, part 3: chemical Methods, Sparks, D.L., Ed., Madison, WI: Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy, 1996.
Schimel, J.P., Bilbrough, C., and Welker, J.M., Increased snow depth affects microbial activity and nitrogen mineralization in two Arctic tundra communities, Soil Biol. Biochem, 2004, vol. 36, pp. 217–227.
Serreze, M.C., Walsh, J.E., Chapin, F.S., et al., Observational evidence of recent change in the northern high-latitude environment, Clim. Change, 2000, vol. 46, pp. 159–207.
Steven, F.O. and Billings, W.D., Drought tolerance and water use by plants along an alpine topographic gradient, Oecologia, 1981, vol. 50, pp. 325–331.
Sulkava, P. and Huhta, V., Effects of hard frost and freezethaw cycles on decomposer communities and N mineralisation in boreal forest soil, Appl. Soil Ecol., 2003, vol. 22, pp. 225–239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, H., Peng, Y., Yan, W. et al. Effect of snow depth and snow duration on soil N dynamics and microbial activity in the alpine areas of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Russ J Ecol 45, 263–268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106741361404016X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106741361404016X