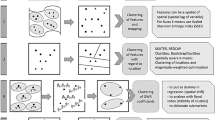
Abstract—
The article provides an overview of the use of computed tomography in the study of soils from the first works to the present time. The development of computed tomography in the field of hardware and methods for processing tomographic data—from the first attempts to analyze soil structure using tomographic sections of low quality to modern methods of segmentation and analysis of volumetric structures using specialized software, correlation functions and neural networks—is discussed. The purpose of the article is to show the possibilities of methods for processing tomographic data in relation to studies of soil structure and to analyze possible trends of their further development. The article presents examples from the world experience of using computed tomography for a broad variety of soils, shows various methods of data segmentation that have been used from the first studies to the recent ones. The specific terminology coined in the course of the evolution of the method and various morphometric indicators for 2D and 3D images are presented, and a forecast of the prospects for the method in the near future is given.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. B. Skvortsova, K. M. Gerke, D. V. Korost, and K. N. Abrosimov, “The pore space arrangement in podzolic horizons of loamy soils (analysis of 2D and 3D images),” Byull. Pochv. Inst. im. V.V. Dokuchaeva, No. 71, 65–79 (2013).
E. B. Skvortsova and N. V. Kalinina, “Micromorphometric types of the pore space in virgin and plowed loamy soils,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 37, 980–991 (2004).
Explanatory Dictionary of Soil Science, Ed. by A. A. Rode (Nauka, Moscow, 1975) [in Russian].
K. N. Abrosimov, K. M. Gerke, I. N. Semenkov, and D. V. Korost, “Otsu’s algorithm in the segmentation of pore space in soils based on tomographic data,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 54, 560–571 (2021).
S. H. Anderson and C. J. Gantzer, “Determination of soil water content by X-ray computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging,” Irrig. Sci. 10 (1), 63–71 (1989).
L. A. G. Aylmore and J. M. Hainsworth, “The use of computed assisted tomography to determine spatial distribution of soil water content,” Aust. J. Soil Res. 21, 435–443 (1983).
A. Bacq-Labreuil, J. Crawford, S. J Mooney, A. L. Neal, E. Akkari, C. McAuliffe, X. Zhang, M. Redmile-Gordon, and K. Ritz, “Effects of cropping systems upon the three-dimensional architecture of soil systems are modulated by texture,” Geoderma 332, 73–83 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.07.002
T. G. Baychev, A. P. Jivkov, A. Rabbani, A. Q. Raeini, Q. Xiong, T. Lowe, and P. J. Withers, “Reliability of algorithms interpreting topological and geometric properties of porous media for pore network modeling,” Transp. Porous Media 128, 271–301 (2019).
A. A. Belik, A. A. Kokoreva, A. G. Bolotov, A. V. Dembovetskii, V. N. Kolupaeva, D. V. Korost, and A. N. Khomyak, “Characterizing macropore structure of agrosoddy-podzolic soil using computed tomography,” Open Agric. 5, 888–897 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1515/opag-2020-0080
C. Bilger, M. Aboukhedr, K. Vogiatzaki, and R. S. Cant, “Evaluation of two-phase flow solvers using Level Set and Volume of Fluid methods,” J. Comput. Phys. 345, 665–686 (2017).
B. Biswal, C. Manwart, and R. Hilfer, “Three-dimensional local porosity analysis of porous media,” Phys. A (Amsterdam) 255, 221–241 (1998).
D. Braz, R. T. Lopes, and L. M. G. Motta, “Dual-energy computerized tomography in compacted soil,” Geotech. Geol. Eng. 18, 221–238 (2000).
Y. Capowiez, A. Pierret, P. Monestiez, and L. Belzunces, “Evolution of burrow systems after the accidental introduction of a new earthworm species into a Swiss pre-alpine meadow,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 31, 494–500 (2000).
Y. Capowiez, S. Sammartino, and E. Michel, “Using X-ray tomography to quantify earthworm bioturbation non-destructively in repacked soil cores,” Geoderma 162, 124–131 (2011).
M. Y. M. Chiang, F. A. Landis, X. Wang, J. R. Smith, M. T. Cicerone, J. Dunkers, and Y. Luo, “Local thickness and anisotropy approaches to characterize pore size distribution of three-dimensional porous networks,” Tissue Eng., Part C 15, 65–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tec.2008.0298
A. Cormack, “Representation of a function by its line integrals, with some radiological applications,” J. Appl. Phys. 34 (9), 2722–2727 (1963).
S. Crestana, PhD Thesis (Säo Paulo, 1985).
CTan Usermanual: Morphometric Parameters Measured by Skyscan™ CT-Analyser Software (Bruker, Billerica, MA, 2013).
N. Dal Ferro, L. Sartori, G. Simonetti, A. Berti, and F. Morari, “Soil macro- and microstructure as affected by different tillage systems and their effects on maize root growth,” Soil Tillage Res. 140, 55–65 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.02.003
A. Demianov, O. Dinariev, and N. Evseev, “Density functional modeling in multiphase compositional hydrodynamics,” Can. J. Chem. Eng. 89 (2), 206–226 (2011).
P. Eichheimer, M. Thielmann, A. Popov, G. J. Golabek, W. Fujita, M. O. Kottwitz, and B. J. P. Kaus, “Pore-scale permeability prediction for Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids,” Solid Earth 10 (5), 1717–1731 (2019).
T. R. Elliot and R. J. Heck, “A comparison of optical and X-ray CT technique for void analysis in soil thin section,” Geoderma 141, 60–70 (2007).
E. T. Elliott and D. C. Coleman, “Let the soil work for us,” Ecol. Bull. 39, 23–32 (1998).
I. Fatt, “The network model of porous media I. Capillary pressure,” Trans. AIME 207, 144–159 (1956).
I. Fatt, “The network model of porous media II. Dynamic properties of a single size tube network,” Trans. AIME 207, 160–163 (1956).
I. Fatt, “The network model of porous media III. Dynamic properties of networks with tube radius distribution,” Trans. AIME 207, 164–181 (1956).
K. M. Gerke and M. V. Karsanina, “Improving stochastic reconstructions by weighing correlation functions in an objective function,” Europhys. Lett. 111 (5), 56002 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/111/56002
K. M. Gerke and M. V. Karsanina, “How pore structure non-stationarity compromises flow properties representativity (REV) for soil samples: pore-scale modelling and stationarity analysis,” Eur. J. Soil Sci., (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.13055
K. M. Gerke, M. V. Karsanina, and D. Mallants, “Universal stochastic multiscale image fusion: an example application for shale rock,” Sci. Rep. 5, 15880 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15880
K. M. Gerke, M. V. Karsanina, and E. V. Skvortsova, “Description and reconstruction of the soil pore space using correlation functions,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 45, 861–872 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229312090049
K. M. Gerke, E. V. Korostilev, K. A. Romanenko, and M. V. Karsanina, “Going submicron in the precise analysis of soil structure: a FIB-SEM imaging study at nanoscale,” Geoderma 383, 114739 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114739
K. M. Gerke, E. B. Skvortsova, and D. V. Korost, “Tomographic method of studying soil pore space: current perspectives and results for some Russian soils,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 45, 700–709 (2012).
K. M. Gerke, T. O. Sizonenko, M. V. Karsanina, E. V. Lavrukhin, V. V. Abashkin, and D. V. Korost, “Improving watershed-based pore-network extraction method using maximum inscribed ball pore-body positioning,” Adv. Water Res. 140, 103576 (2020).
K. M. Gerke, R. V. Vasilyev, S. Khirevich, D. Collins, M. V. Karsanina, T. O. Sizonenko, D. V. Korost, S. Lamontagne, and D. Mallants, “Finite-difference method Stokes solver (FDMSS) for 3D pore geometries: software development, validation and case studies,” Comput. Geosci. 114, 41–58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2018.01.005
S. N. Gorbov, O. S. Bezuglova, K. N. Abrosimov, E. B. Skvortsova, S. S. Tagiverdiev, and I. V. Morozov, “Physical properties of soils in Rostov agglomeration,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 49, 898–907 (2016).
J. T. Gostick, Z. A. Khan, T. G. Tranter, M. D.R. Kok, M. Agnaou, M. Sadeghi, and R. Jervis, “PoreSpy: A python toolkit for quantitative analysis of porous media images,” J. Open Source Software 4 (37), 1296 (2019).
J. T. Gostick, “Versatile and efficient pore network extraction method using marker-based watershed segmentation,” Phys. Rev. E 96 (2), (2017).
J. Gostick, M. Aghighi, J. Hinebaugh, T. Tranter, M. A. Hoeh, H. Day, B. Spellacy, M. H. Sharqawy, A. Bazylak, A. Burns, and W. Lehnert, “OpenPNM: a pore network modeling package,” Comput. Sci. Eng. 18 (4), 60–74 (2016).
Z. He, S. Zhang, J. Teng, Y. Yao, and D. Sheng, “A coupled model for liquid water-vapor-heat migration in freezing soils,” Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 148, 22–28 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.01.003
A. L. Herring, L. Andersson, S. Schlüter, A. Sheppard, and D. Wildenschild, “Efficiently engineering pore-scale processes: the role of force dominance and topology during nonwetting phase trapping in porous media,” Adv. Water Res. 79, 91–102 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.02.005
D. W. Holmes, J. R. Williams, P. Tilke, and C. R. Leonardi, “Characterizing flow in oil reservoir rock using SPH: absolute permeability,” Comput. Part. Mech. 3, 141–154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-015-0038-7
G. N. Hounsfield, “Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography). Description to system,” Br. J. Radiol. 46, 1016–1022 (1973).
D. Ivonin, T. Kalnin, E. Grachev, and E. Shein, “Quantitative analysis of pore space structure in dry and wet soil by integral geometry methods,” Geosciences 10 (9), 365–365 (2020).
N. Jarvis, M. Larsboand, and J. Koestel, “Connectivity and percolation of structural pore networks in a cultivated silt loam soil quantified by X-ray tomography,” Geoderma 287, 71–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.06.026
Y. Jiao, F. H. Stillinger, and S. Torquato, “Modeling heterogeneous materials via two-point correlation functions: basic principles,” Phys. Rev. 76, 031110 (2007).
M. Joschko, O. Graff, P. C. Müller, K. Kotzke, P. Lindner, D. P. Pretschner, and O. Larink, “A non-destructive method for the morphological assessment of earthworm burrow systems in three dimensions by X-ray computed tomography,” Biol. Fertil. Soils 11, 88–92 (1991).
M. V. Karsanina, K. M. Gerke, E. V. Skvortsova, A. L. Ivanov, and D. Mallants, “Enhancing image resolution of soils by stochastic multiscale image fusion,” Geoderma 314, 138–145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.055
M. V. Karsanina, K. M. Gerke, E. V. Skvortsova, and D. Mallants, “Universal spatial correlation functions for describing and reconstructing soil microstructure,” PLoS One 10 (5), e0126515 (2015).
M. V. Karsanina, E. V. Lavrukhin, D. S. Fomin, A. V. Yudina, K. N. Abrosimov, and K. M. Gerke, “Compressing soil structural information into parameterized correlation functions,” Eur. J. Soil Sci., (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.13025
S. Khirevich, I. Ginzburg, and U. Tallarek, “Coarse-and fine-grid numerical behavior of MRT/TRT lattice-Boltzmann schemes in regular and random sphere packings,” J. Comput. Phys. 281, 708–742 (2015).
N. Koebernick, K. R. Daly, S. D. Keyes, T. S. George, L. K. Brown, A. Raffan, L. J. Cooper, M. Naveed, A. G. Bengough, I. Sinclair, P. D. Hallett, and T. Roose, “High-resolution synchrotron imaging shows that root hairs influence rhizosphere soil structure formation,” New Phytol. 216 (1), 124–135 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14705
J. Koestel, “SoilJ: an ImageJ plug-in for the semiautomatic processing of three-dimensional X-ray images of soils,” Vadose Zone J. 17 (1), 170062 (2018).
A. N. Kravchenko, W. C. Negassa, A. K. Guber, and M. L. Rivers, “Protection of soil carbon within macro-aggregates depends on intra-aggregate pore characteristics,” Sci. Rep. 5, 291 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16261
E. V. Lavrukhin, K. M. Gerke, K. A. Romanenko, K. N. Abrosimov, and M. V. Karsanina, “Assessing the fidelity of neural network-based segmentation of soil XCT images based on pore-scale modelling of saturated flow properties,” Soil Tillage Res. 209 (15), 104942 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.104942
M. P. Lebedeva, D. L. Golovanov, V. A. Shishkov, A. L. Ivanov, and K. N. Abrosimov, “Microscopic and tomographic studies for interpreting the genesis of desert varnish and the vesicular horizon of desert soils in Mongolia and the USA,” Bol. Soc. Geol. Mex. 71 (1), 21–42 (2019).
M. Leue, D. Uteau-Puschmann, S. Peth, J. Nellesen, R. Kodešová, and H. H. Gerke, “Separation of soil macropore types in three-dimensional x-ray computed tomography images based on pore geometry characteristics,” Vadose Zone J. 18, 1–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2018.09.0170
W. B. Lindquist, S.-M. Lee, D. A. Coker, K. W. Jones, and P. Spanne, “Medial axis analysis of void structure in three-dimensional tomographic images of porous media,” J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth 101, 8297–8310 (1996).
M. Lucas, S. Schlüter, H.-J. Vogel, and D. Vetterlein, “Soil structure formation along an agricultural chronosequence,” Geoderma 350, 61–72 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.04.041
L. Luo, H. Lin, and S. Li, “Quantification of 3-D soil macropore networks in different soil types and land uses using computed tomography,” J. Hydrol. 39 (1–2), 53–64 (2010).
Z. Ma and S. Torquato, “Precise algorithms to compute surface correlation functions of two-phase heterogeneous media and their applications,” Phys. Rev. E 98 (1), 013307 (2018).
Z. Ma and S. Torquato, “Generation and structural characterization of Debye random media,” Phys. Rev. E 102 (4), 043310 (2020).
X. Miao, K. M. Gerke, and T. O. Sizonenko, “A new way to parameterize hydraulic conductances of pore elements: a step forward to create pore-networks without pore shape simplifications,” Adv. Water Res. 105, 162–172 (2017).
S. J. Mooney, T. P. Pridmore, J. Helliwell, and M. J. Bennett, “Developing X-ray computed tomography to non-invasively image 3D root systems architecture in soil,” Plant Soil 352 (1–2), 1–22 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-1039-9
W. C. Negassa, A. K. Guber, A. N. Kravchenko, T. L. Marsh, B. Hildebrandt, and M. L. Rivers, “Properties of soil pore space regulate pathways of plant residue decomposition and community structure of associated bacteria,” PLoS One 10, e0123999 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123999
A. Odgaard and H. J. Gundersen, “Quantification of connectivity in cancellous bone, with special emphasis on 3-D reconstructions,” Bone 14 (2), 173–182 (1993).
W. Oh and B. Lindquist, “Image thresholding by indicator kriging,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21, 590–602 (1999).
N. Otsu, “A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms,” IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 9, 62–66 (1979). https://doi.org/101109/TSMC19794310076
M. Pagliai and N. Vignozzi, “Soil pore system as an indicator of soil quality,” Adv. GeoEcol. 35, 71–82 (2002).
A. M. Petrovic, J. E. Siebert, and P. E. Rieke, “Soil bulk density analysis in three dimensions by computed tomographic scanning,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46 (3), 445–450 (1982). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600030001x
R. L. Peyton, B. A. Haeffner, S. H. Anderson, and C. J. Gantzer, “Applying X-ray CT to measure macropore diameters in undisturbed soil cores,” Geoderma 53 (3–4), 329–340 (1992).
L. F. Pires, J. A.R. Borges, J. A. Rosa, M. Cooper, R. J. Heck, S. Passoni, and W. L. Roque, “Soil structure changes induced by tillage systems,” Soil Tillage Res. 165, 66–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.07.010
L. F. Pires, W. L. Roque, J. A. Rosa, and S. J. Mooney, “3D analysis of the soil porous architecture under long term contrasting management systems by X-ray computed tomography,” Soil Tillage Res. 191, 197–206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.02.018
L. Pogosyan, K. Abrosimov, K. Romanenko, J. Marquez, and S. Sedov, “How is the fragipan incorporated in the pore space architecture of a boreal retisol?” Soil Res. 57 (6), 566–574 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1071/SR18239
L. Pogosyan, A. Gastelum, B. Prado, J. Marquez, K. Abrosimov, K. Romanenko, and S. Sedov, “Morphogenesis and quantification of the pore space in a tephra-palaeosol sequence in Tlaxcala, central Mexico,” Soil Res. 57 (6), 559–565 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1071/SR18185
V. Pot, X. Zhong, and P. C. Baveye, “Effect of resolution, reconstruction settings, and segmentation methods on the numerical calculation of saturated soil hydraulic conductivity from 3D computed tomography images,” Geoderma 362, 114089 (2020).
M. Prodanović and S. L. Bryant, “A level set method for determining critical curvatures for drainage and imbibition,” J. Colloid Interface Sci. 304 (2), 442–458 (2006).
E. Rabot, M. Wiesmeier, S. Schlüter, and H.-J. Vogel, “Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: a review,” Geoderma 314, 122–137 (2018).
A. Q. Raeini, B. Bijeljic, and M. J. Blunt, “Generalized network modeling: Network extraction as a coarse-scale discretization of the void space of porous media,” Phys. Rev. E 96 (1), 013312 (2017).
A. Q. Raeini, M. J. Blunt, and B. Bijeljic, “Modeling two-phase flow in porous media at the pore scale using the volume-of-fluid method,” J. Comput. Phys. 231, 5653–5668 (2012).
P. Renard and D. Allard, “Connectivity metrics for subsurface flow and transport,” Adv. Water Res. 51, 168–196 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.12.001
M. R. Rokhforouz and H. A. Akhlaghi Amiri, “Phase-field simulation of counter-current spontaneous imbibition in a fractured heterogeneous porous medium,” Phys. Fluids 29 (6), 062104 (2017).
K. A. Romanenko, E. B. Skvortsova, and V. A. Rozhkov, “Form and orientation of soil pores as indicators of a structural soil organization,” IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 368, 012041 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/368/1/012041
K. A. Romanenko, V. V. Rogov, A. V. Yudina, K. N. Abrosimov, E. B. Skvortsova, and A. N. Kurchatova, “Frozen soils and sediments microstructure x-ray tomography study: methods, approaches, perspectives,” Dokuchaev Soil Bull. 83, 103–117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.19047/0136-1694-2016-83-103-117
T. Romanis, S. Sedov, S. Lev, M. Lebedeva, K. Kondratev, A. Yudina, K. Abrosimov, A. Golyeva, and D. Volkov, “Landscape change and occupation history in the Central Russian Upland from Upper Palaeolithic to medieval: paleopedological record from Zaraysk Kremlin,” Catena 196, 104873 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104873
V. A. Rozhkov, Soil Informatics (Agropromizdat, Moscow, 1989) [in Russian].
V. Shabro, C. Torres-Verdín, F. Javadpour, and K. Sepehrnoori, “Finite-difference approximation for fluid-flow simulation and calculation of permeability in porous media,” Transp. Porous Media 94, 775–793 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-0024-y
F. San José Martínez, F. J. Muñoz Ortega, F. J. Caniego Monreal, A. N. Kravchenko, and W. Wang, “Soil aggregate geometry: measurements and morphology,” Geoderma 237–238, 36–48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.08.003
A. Y. Sasov, “The investigation of the microstructure of soils by computed tomography,” Vestn. Mosk. Univ., Ser. Geol. 3, 56–62 (1987).
S. Schlüter, C. Großmann, J. Diel, G.-M. Wu, S. Tischer, A. Deubel, and J. Rücknagel, “Long-term effects of conventional and reduced tillage on soil structure, soil ecological and soil hydraulic properties,” Geoderma 332, 10–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.07.001
S. Schlüter, U. Weller, and H.-J. Vogel, “Segmentation of X-ray microtomography images of soil using gradient masks,” Comput. Geosci. 36 (10), 1246–1251 (2010).
S. Schlüter, U. Weller, and H.-J. Vogel, “Soil-structure development including seasonal dynamics in a long-term fertilization experiment,” J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 174, 395–403 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201000103
E. V. Shein, E. B. Skvortsova, A. V. Dembovetskii, K. N. Abrosimov, L. I. Il’in, and N. A. Shnyrev, “Pore-size distribution in loamy soils: a comparison between microtomographic and capillarimetric determination methods,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 49, 315–325 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229316030091
E. B. Skvortsova, E. V. Shein, K. N. Abrosimov, K. M. Gerke, D. V. Korost, K. A. Romanenko, V. S. Belokhin, and A. V. Dembovetskii, “Tomography in soil science,” Dokuchaev Soil Bull. 86, 28–34 (2016). https://doi.org/10.19047/0136-1694-2016-86-28-34
A. S. Sorokin, K. N. Abrosimov, M. P. Lebedeva, and G. S. Kust, “Composition and structure of aggregates from compacted soil horizons in the southern steppe zone of European Russia,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 49, 326–337 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229316030108
A. V. Suzdaleva, E. V. Shein, N. V. Verkhovtseva, and K. N. Abrosimov, “Physical and microbiological aspects of the soil seedbed in the early formation of the barley root system (Hordeum vulgare L.): tomographic studies,” IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 941, 012032 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/941/1/012032
C. O. Tan, D. Kuppens, and R. Gupta, “Dual-energy CT,” in Neuroimaging Techniques in Clinical Practice: Physical Concepts and Clinical Applications (Springer-Verlag, Cham, 2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48419-4_7
E. W. Tollner and C. Murphy, “Factors affecting soil x-ray absorption coefficients with computer tomography,” Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 34 (3), 1047–1053 (1991).
S. Torquato, Random Heterogeneous Materials: Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties (Springer-Verlag, New York, 2002).
J. K. Torrance, T. Elliot, R. Martin, and R. J. Heck, “X-ray computed tomography of frozen soil,” Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 53, 75–82 (2008).
R. A. Victor, M. Prodanović, and C. Torres-Verdín, “Monte Carlo approach for estimating density and atomic number from dual-energy computed tomography images of carbonate rocks,” J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth 122 (12), 9804–9824 (2017).
H.-J. Vogel, “Morphological determination of pore connectivity as a function of pore size using serial sections,” Eur. J. Soil Sci. 48, 365–377 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1997.tb00203.x
H.-J. Vogel, “Topological characterization of porous media,” in Morphology of Condensed Matter: Physics and Geometry of Spatially Complex Systems (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2002), pp. 75–92.
H.-J. Vogel, U. Weller, and S. Schlüter, “Quantification of soil structure based on Minkowski functions,” Comput. Geosci. 36, 1236–1245 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2010.03.007
IUSS Working Group WRB, World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, World Soil Resources Reports No. 106 (UN Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, 2014).
Y. S. Yang, K. Y. Liu, S. Mayo, A. Tulloh, M. B. Clennell, and T. Q. Xiao, “A data-constrained modeling approach to sandstone microstructure characterization,” J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 105, 76–83 (2013).
A. V. Yudina and K. A. Romanenko, “Mechanistic understanding of soil hierarchical structure,” in Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly (Vienna, 2019). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26167.16809
Z. Zhang, K. Liu, H. Zhou, H. Lin, D. Li, and X. Peng, “Three-dimensional characteristics of biopores and non-biopores in the subsoil respond differently to land use and fertilization,” Plant Soil 428, 453–467 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3689-3
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 19-74-10070; the equipment of the Center for Collective Use “Functions and Properties of Soils and Soil Cover” at the V.V. Dokuchaev Soil Science Institute (registration number 441994, https://ckp-rf.ru/ckp/441994/) was used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by D. Konyushkov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abrosimov, K.N., Gerke, K.M., Fomin, D.S. et al. Tomography in Soil Science: From the First Experiments to Modern Methods (A Review). Eurasian Soil Sc. 54, 1385–1399 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229321090027
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229321090027