Abstract
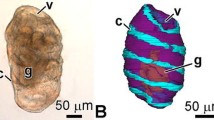
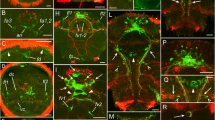
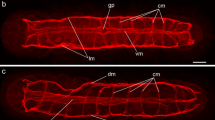
For the first time using laser confocal microscopy and histochemical and immunocytochemical methods (detection of F-actine, catecholamines, acetylcholintransferase, substance P and FMRFamide) in combination with classical histological methods and electron microscopy of whole-mount preparations, the structure and patterns of formation of the nervous, muscular, and digestive systems in early postlarval development (from 2 days to 4 months) in the opisthobranch mollusk Cadlina laevis were studied. Heterochronies manifested in positive allometry of the sensory organs, ganglia of the central nervous system, and the pharyngeal region of the digestive system in relation to overall body size in juvenile specimens compared to adult animals were detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbour, M.A., Note on the distribution and food preference of Cadlina laevis (Nudibranchia: Chromodoridae), Nautilus, 1979, vol. 93, nos. 2–3, pp. 61–62.
Bickell, L. and Kempf, S., Larval and metamorphic morphogenesis in the nudibranch Melibe leonine (Mollusca: Opisthobranchia), Biol. Bull., 1983, vol. 165, pp. 119–138.
Boyd, P.J., Osborne, N.N., and Walker, R.J., Localization of a substance P-like material in the central and peripheral nervous system of the snail Helix aspersa, Histochemistry, 1986, vol. 84, no. 1, pp. 97–103.
Bullock, T.H. and Horridge, G.A., Structure and Function in the Nervous System of Invertebrates, San Francisco: Calif.: W.H. Freeman, 1965.
Carroll, S.B., Evo-devo and an expanding evolutionary synthesis: a genetic theory of morphological evolution, Cell, 2008, vol. 134, pp. 25–36.
Chase, R., Lessons from snail tentacles, Chem. Senses, 1986, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 411–426.
Croll, R.P., Catecholamine-containing cells in the central nervous system and periphery of Aplysia californica, J. Comp. Neurol., 2001, vol. 441, no. 2, pp. 91–105.
Croll, R.P. and Voronezhskaya, E.E., Early FMRFamidelike immunoreactive cells in gastropod neurogenesis, Acta Biol. Hung., 1995, vol. 46, nos. 2–4, pp. 295–303.
Croll, R.P., Voronezhskaya, E.E., Hiripi, L., and Elekes, K., Development of catecholaminergic neurons in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis: II. postembryonic development of central and peripheral cells, J. Comp. Neurol., 1999, vol. 404, no. 3, pp. 297–309.
Fominykh, M.Ya., Sensitive nerve cells in the epithelium and subepithelial connective tissue of trunk segments of polychaetes Nephthys hombergii and Harmathoe imbricate, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 1982, vol. 18, no. 52, pp. 507–513.
Furness, J.B., Costa, M., and Wilson, A.J., Water-stable fluorophores, produced by reaction with aldehyde solutions, for the histochemical localization of catechol- and indolethylamines, Histochemistry, 1977, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 159–170.
Hernádi, L. and Elekes, K., Topographic organization of serotonergic and dopaminergic neurons in the cerebral ganglia and their peripheral projection patterns in the head areas of the snail Helix pomatia, J. Comp. Neurol., 1999, vol. 411, no. 2, pp. 274–287.
Kempf, S.C., Chun, G.V., and Hadfield, M.G., An immunocytochemical search for potential neurotransmitters in larvae of Phestilla sibogae (Gastropoda, Opisthobranchia), Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Pt C: Comp. Pharmacol., 1992, vol. 101, no. 2, pp. 299–305.
Kononenko, N.L. and Zhukov, V.V., Neuroanatomical and immunocytochemical studies of the head retractor muscle innervation in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis L., Zoology (Jena), 2005, vol. 108, no. 3, pp. 217–237.
Kristof, A. and Klussmann-Kolb, A., Neuromuscular development of Aeolidiella stephanieae Valdez, 2005 (Mollusca, Gastropoda, Nudibranchia), Front. Zool., 2010, vol. 7, no. 10, p. 5.
Lehman, H.K. and Price, D.A., Localization of FMRFamidelike peptides in the snail Helix aspersa, J. Exp. Biol., 1987, vol. 131, pp. 37–53.
Lloyd, P.E. and Church, P.J., Cholinergic neuromuscular synapses in Aplysia have low endogenous acetylcholinesterase activity and a high-affinity uptake system for acetylcholine, J. Neurosci., 1994, vol. 14, no. 11, pt 1, pp. 6722–6733.
Marois, R. and Carew, T.J., The gastropod nervous system in metamorphosis, J. Neurobiol., 1990, vol. 21, no. 7, pp. 1053–1071.
Martynov, A.V. and Schröbl, M., Phylogeny and evolution of corambid nudibranchs (Mollusca: Gastropoda), Zool. J. Linn. Soc., 2011, vol. 163, pp. 585–604.
Martynov, A.V., From “tree-thinking” to “cycle-thinking”: ontogenetic systematics of nudibranch molluscs, Thalassas, 2011, vol. 27, pp. 193–224.
Martynov, A.V., Ontogenetic systematics: the synthesis of taxonomy, phylogenetics, and evolutionary developmental biology, Paleontol. J., 2012, vol. 46, pp. 833–864.
Moroz, L., Nezlin, L., Elofsson, R., and Sakharov, D., Serotonin-and FMRFamide-immunoreactive nerve elements in the chiton Lepidopleurus asellus (Mollusca, Polyplacophora), Cell Tiss. Res., 1994, vol. 275, no. 2, pp. 277–282.
Ovsyannikov, V.I., Neiromediatory i gormony v zheludochnokishechnom trakte (integrativnye aspekty) (Neurotransmitters and Hormones in the Gastrointestinal Tract (Integrative Aspects)), St. Petersburg, 2003.
Perron, F.E. and Turner, R.D., Development, metamorphosis, and natural history of the nudibranch Doridella obscura Verrill (Corambidae: Opisthobranchia), J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol., 1977, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 171–185.
Punin, M.Yu., Kishechnaya regulyatornaya sistema bespozvonochnykh zhivotnykh i ee predpolagaemaya evolyutsiya u mnogokletochnykh (Intestinal Regulatory System of Invertebrates and Its Presumable Evolution in Metazoans), Tr. ZIN RAN, 2001, vol. 290.
Quinlan, E.M., Arnett, B.C., and Murphy, A.D., Feeding stimulants activate an identified dopaminergic interneuron that induces the feeding motor program in Helisoma, J. Neurophysiol., 1997, vol. 78, no. 2, pp. 812–824.
Romeis, B., Mikroskopische, Technik, Munchen: Leibniz-Verlag, 1948.
Romeis, B., Mikroskopicheskaya tekhnika (Microscopic Techniques), Sokolov, I.I., Ed., Moscow: Izd. Inostr. Lit., 1953.
Schot, L.P., Boer, H.H., Swaab, D.F., and Van Noorden, S., Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic neurons in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis with antisera raised to biologically active peptides of vertebrates, Cell Tiss. Res., 1981, vol. 216, no. 2, pp. 273–291.
Suzuki, H., Kimura, T., Sekiguchi, T., and Mizukami, A., FMRF amide-like-immunoreactive primary sensory neurons in the olfactory system of the terrestrial mollusc, Limax marginatus, Cell Tiss. Res., 1997, vol. 289, no. 2, pp. 339–345.
Thompson, T.E., Direct development in a nudibranch, Cadlina laevis, with a discussion of developmental processes in Opisthobranchia, J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. Unit. Kingdom, 1967, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 1–22.
De la Torre, J.C. and Surgeon, J.W., A methodological approach to rapid and sensitive monoamine histofluorescence using a modified glyoxylic acid technique: the SPG method, Histochemistry, 1976, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 81–93.
Voronezhskaya, E.E., Hiripi, L., Elekes, K., and Croll, R.P., Development of catecholaminergic neurons in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis: I. Embryonic development of dopamine-containing neurons and dopamine-dependent behaviors, J. Comp. Neurol., 1999, vol. 404, no. 3, pp. 285–296.
Wägele, H., Klussmann-Kolb, A., Verbeek, E., and Schröbl, M., Flashback and foreshadowing—a review of the taxon Opisthobranchia, Org. Divers. Evol., 2013, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 133–149.
Wanninger, A., Comparative lophotrochozoan neurogenesis and larval neuroanatomy: recent advances from previously neglected taxa, Acta Biol. Hung., 2008, vol. 59(suppl.), pp. 127–136.
Wanninger, A., Shaping the things to come: ontogeny of lophotrochozoan neuromuscular systems and the tetraneuralia concept, Biol. Bull., 2009, vol. 216, no. 3, pp. 293–306.
Webster, M. and Zelditch, M.L., Evolutionary modifications of ontogeny: heterochrony and beyond, Paleobiology, 2005, vol. 31, pp. 354–372.
Wollesen, T., Wanninger, A., and Klussmann-Kolb, A., Neurogenesis of cephalic sensory organs of Aplysia californica, Cell Tiss. Res., 2007, vol. 330, no. 2, pp. 361–379.
Wollesen, T., Wanninger, A., and Klussmann-Kolb, A., Myogenesis in Aplysia californica (Cooper, 1863) (Mollusca, Gastropoda, Opisthobranchia) with special focus on muscular remodeling during metamorphosis, J. Morphol., 2008, vol. 269, no. 7, pp. 776–789.
Wyeth, R.C. and Croll, R.P., Peripheral sensory cells in the cephalic sensory organs of Lymnaea stagnalis, J. Comp. Neurol., 2011, vol. 519, no. 10, pp. 1894–1913.
Yablokov, A.V. and Yusufov, A.G., Evolyutsionnoe uchenie (Evolutionary Theory), Moscow: Vyssh. Shk., 1976.
Zaitseva, O.V., Characteristics of the neuronal composition of the central nervous system of nudibranch mollusks, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 1978, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 497–503.
Zaitseva, O.V., Structural organization receptor elements and organs of the land mollusks Pomatias elegans (Prosobranchia), Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 1997, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 533–540.
Zaitseva, O.V., The structural organization of the sensory system of statocysts of nudibranchs and characteristics of intersensory interactions, Morfologiya, 1999, vol. 115, no. 6, pp. 26–32.
Zaitseva, O.V., Dominant structural and functional adaptations of distant chemosensory systems in phylogenesis of Gastropoda, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2000a, vol. 86, no. 8, pp. 995–1006.
Zaitseva, O.V., Projection connections and a hypothetical scheme of the structural organization of the procerebrum of terrestrial mollusks, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2000b, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 470–483.
Zaitseva, O.V., Morphological characteristic of ommatophore olfactory organs in gastropod mollusks (principle of evolutionary parallelism), Proc. Zool. Inst. Russ. Acad. Sci., St. Petersburg, 2002, vol. 296, pp. 171–176.
Zaitseva, O.V., Comparative study of nervous elements and their interaction with the endocrine glands and the muscle retractors in the ommatophores of snails and slugs, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2004, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 556–568.
Zaitseva, O.V. and Bocharova, L.S., Sensory cells in the head skin of pond snails. Fine structure of sensory endings, Cell Tiss. Res., 1981, vol. 220, no. 4, pp. 797–807.
Zaitseva, O.V. and Kuznetsova, T.V., Distribution of acetylcholinesterase activity in the digestive system of the gastropod molluscs Littorina littorea and Achatina fulica, Morfologiya, 2008, vol. 133, no. 1, pp. 55–59.
Zaitseva, O.V. and Markosova, T.G., Acetylcholine, nitric oxide and their possible colocalization in regulatory cells of the digestive system of gastropods, Dokl. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2008, vol. 421, no. 1, pp. 248–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.V. Zaitseva, A.N. Shumeev, T.A. Korshunova, A.V. Martynov, 2015, published in Izvestiya Akademii Nauk, Seriya Biologicheskaya, 2015, No. 3, pp. 237–247.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaitseva, O.V., Shumeev, A.N., Korshunova, T.A. et al. Heterochronies in the formation of the nervous and digestive systems in early postlarval development of opisthobranch mollusks: Organization of major organ systems of the arctic dorid Cadlina laevis . Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 42, 186–195 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359015030152
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359015030152