Abstract
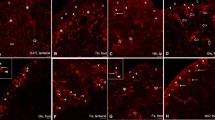
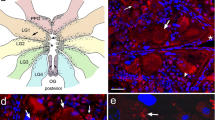
The distribution of serotonin-like and FMRFamide-like immunoreactive (5HT-ir and FMRFa-ir, respectively) neurons in the nervous system of the chiton Lepidopleurus asellus (Mollusca, Polyplacophora) was studied using an immunocytochemical technique. The neurons were distributed in characteristic patterns in the central nervous system, the 5HT-ir neurons predominating in the ventral (pedal) cords and FMRFa-ir neurons in the lateral cords. In the body wall including the foot, a tight network of 5HT-ir and FMRFa-ir nerve fibers is found, the former being mostly attributed to the musculature whereas the latter seems to be associated with the blood sinuses. Intraepithelial neurons of both types are abundant in the fore-and hindgut. The presence and general distribution in the central and peripheral nervous system of the 5HT-ir and FMRFa-ir elements seems thus to be similar in simple and advanced molluscs. The relationship between these neurons and their targets in the body also appears to be well conserved in molluscs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brusca RC, Brusca GJ (1990) Invertebrates. Sinauer, Sunderland, Mass
Cardot J, Fellman D (1983) Immunofluorescent evidence of an FMRFamide-like peptide in the peripheral nervous system of the gastropod mollusc Helix aspersa. Neurosci Lett 43:167–172
Caunce M, McKenzie JP, Tripp J, Winlow W (1988) Serotonergic innervation of the pedal epidermis of Lymnaea. In: Salanki J, S-Rozsa K (eds) Neurobiology of invertebrates: transmitters, modulators and receptors, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, pp 691–692
Cooke IRC, Gelperin A (1988) Distribution of FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of the slug Limax maximus. Cell Tissue Res 253:69–76
Cottrell GA, Price DA, Doble KE, Hettle S, Sommerville J, Mac-Donald M (1992) Identified Helix neurons: mutually exclusive expression of the tetrapeptide and heptapeptide members of the FMRFamide family. Biol Bull 183:113–122
Croll RP (1988) Distribution of the monoamines within the central nervous system of the juvenile pulmonate snail, Achatina fulica. Brain Res 460:29–49
Croll RP, Chiasson BJ (1989) Postembryonic development of serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Comp Neurol 280:122–142
Croll RP, Lo RYC (1986) Distribution of serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the periwinkle, Littorina littorea (Gastropoda, Prosobranchia, Mesogastropoda). Biol Bull 171:426–440
Dahl E, Falck B, Mecklenburg C von, Myhrberg H, Rosengren E (1966) Neuronal localisation of dopamine and 5-HT in some mollusca. Z Zellforsch 71:489–498
Elekes K, Nässel DR (1990) Distribution of FMRFamide-like immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the snail Helix pomatia. Cell Tissue Res 262:177–190
Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1992) Relationships among the FMRFamide-like peptides. Progr Brain Res 92:25–37
Griffond B, Boer HH, Wijdenes J (1986) Localization and function of an FMRFamide-like substance in the aorta of Helix aspersa. Cell Tissue Res 246:303–307
Hernadi L (1992) Relationships between the distribution of serotonergic cell bodies and the running of vascular elements in the central nervous system of the snail, Helix pomatia. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 103:85–92
Hernadi L, Elekes K, S-Rozsa K (1989) Distribution of serotonincontaining neurons in the central nervous system of the snail Helix pomatia. Comparison of immunocytochemical and 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine labelling. Cell Tissue Res 257:313–323
Hyman LH (1967) The invertebrates, vol 6, part 1. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kemenes G, Elekes K, Hiripi L, Benjamin PR (1989) Distribution of serotonin and serotonin-containing neurons in fixed and native ganglia of the snail Lymnaea stagnalis: a comparative study applying four techniques. J Neurocytol 18:193–208
Lehman HK, Price DA (1987) Localization of FMRFamide-like peptides in the snail Helix aspersa. J Exp Biol 131:37–53
Marchand CR, Colard C (1991) Presence of cells and fibers immunoreactive toward antibodies to different peptides or amines in the digestive tract of the snail Helix aspersa. J Morphol 207:185–190
Osborne NN, Cottrell GA (1971) Distribution of biogenic amines in the slug, Limax maximus. Z Zellforsch 112:15–30
Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1989) The hunting of the FaRPs: the distribution of FMRFamide-related peptides. Biol Bull 177:198–205
Roberts MH, Speh JC, Moore RY (1989) The central nervous system of Bulla gouldiana: peptide localization. Peptides 9:1323–1334
Sakharov DA (1974) The genealogy of neurons (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow
Sakharov DA (1976) Nerve cell homologies in gastropods. In: J Salanki (ed) Neurobiology of invertebrates. Gastropoda brain. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, pp 27–40
Sakharov DA (1990) Integrative function of serotonin common to distantly related invertebrate animals. In: Gustafsson M, Reuter M (eds) The early brain. Abo Akademi, Abo, pp 73–88
Schot LPC, Boer HH (1982) Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic cells in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis with antiserum to the molluscan cardioactive tetrapeptide, FMRFamide. Cell Tissue Res 225:347–354
Schot LPC, Boer HH, Swaab DF, Van Noorden S (1981) Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic neurons in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis with antisera raised to biologically active peptides of vertebrates. Cell Tissue Res 216:273–291
Soinila S, Mpitsos GJ (1991) Immunohistochemistry of diverging and converging neurotransmitter systems in molluscs. Biol Bull 181:484–499
Takayanagi H, Takeda N (1988) FMRFamide immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the snail, Achatina fulica. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 88:263–268
Walker RJ (1986) Transmitters and modulators. In: Willows AOD (ed) The Mollusca, vol 9, part 2. Academic Press, London New York, pp 279–485
Walker RJ (1992) Neuroactive peptides with an RFamide or Famide carboxyl terminal. Comp Biochem Physiol [C] 102:213–222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moroz, L., Nezlin, L., Elofsson, R. et al. Serotonin-and FMRFamide-immunoreactive nerve elements in the chiton Lepidopleurus asellus (Mollusca, Polyplacophora). Cell Tissue Res 275, 277–282 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319425
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319425