Abstract
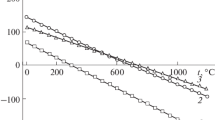
The processes of drying and reduction of red mud in the pure state and with coal additions in vacuum or in gaseous media (helium, hydrogen) have been experimentally studied by thermogravimetry using a Setaram TAG24 thermogravimetric analyzer. The minimum total weight loss (∼20%) is observed for red mud samples without additives in forevacuum, and the maximum loss (∼38%) is detected in samples with coal. It is demonstrated that, for this type of red mud with iron oxide Fe2O3, water molecules are bonded in the form of iron hydroxide Fe2O3 · 3H2O rather than goethite FeOOH. The peak of magnetite formation is observed in differential thermogravimetry (DTG) curve in the range 270–400°C. The simulation of the magnetite dehydration and formation rates under experimental conditions in the relevant temperature ranges agrees with the experimental data. A peak of wustite formation in hydrogen above ∼600°C is recorded in a DTG curve, and the removal of one-third of sodium oxide, which is likely not to be fixed into strong sodium alumosilicate, is observed in the range 800–1000°C. The peak detected in the DTG curve of the mud with charcoal in helium in the range 350–450°C is similar to the peak of hematite reduction in magnetite in a hydrogen atmosphere. The most probable source of hydrogen-containing gases in this temperature range consists of the residual hydrocarbons of charcoal. The reduction reactions of disperse iron oxides with coal proceed only at temperatures above 600°C. These processes occur in the same temperature range (600–900°C) both in forevacuum and in a helium atmosphere. It is experimentally demonstrated that sintering process occurs in the mud in the temperature range 450–850°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. I. Smirnov, T. V. Molchanova, L. I. Vodolazov, and V. I. Peganov, “Methods of processing of red muds,” Tsvetn. Met., No. 8, 64–69 (2002).
G. I. Gazaleeva, S. L. Orlov, A. G. Savin, and V. N. Zakirnichnyi, “Promising trends of beneficiation of technogenic wastes,” Ekol. Prom-st Ross., No. 1, 13–16 (2013).
O. A. Teplov and Yu. A. Lainer, “Rate of the reduction of the iron oxides in red mud by hydrogen and converted gas,” Russian Metallurgy (Metally), No. 1, 28–36 (2013).
O. A. Teplov, “Kinetics of the low-temperature hydrogen reduction of magnetite concentrates,” Russian Metallurgy (Metally), No. 1, 13–29 (2012).
O. A. Teplov, “Kinetics of the low-temperature hydrogen reduction of single-crystal magnetite,” Russian Metallurgy (Metally), No. 11, 833–844 (2010).
S. I. Filippov, Theory of Metallurgical Processes (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1967).
JANAF Thermochemical Tables (NBS, Washington, 1971).
V. P. Eliutin, Yu. A. Pavlov, V. P. Poliakov, and S. B. Sheboldaev, Interaction of Metal Oxides with Carbon (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1976).
O. A. Teplov, L. I. Leont’ev, I. G. Voropaev, and V. G. Diubanov, “Zinc containing metallurgical muds: thermogravimetric study and development of disposal technology,” Stal’, No. 10, 123–127 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.A. Teplov, N.L. Korenovskii, Yu.A. Lainer, 2015, published in Metally, 2015, No. 1, pp. 14–21.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teplov, O.A., Korenovskii, N.L. & Lainer, Y.A. Thermogravimetric study of the dehydration and reduction of red mud. Russ. Metall. 2015, 12–18 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029515010127
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029515010127