Abstract
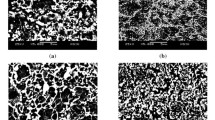
The regular patterns of the formation of an ultrafine-grained structure in heat-treated relaxation-resistant high-temperature chrome–molibdenum steel during equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) have been shown. The importance of this work is in a deeper understanding of the theoretical concepts and practical aspects of structure formation upon ECAP and in the possibility of expanding the field of application of this steel by creating advanced technological processes for producing ultrafine-grained semifinished and finished products showing a qualitatively new level of physical and mechanical properties. ECAP and heat treatment have been used for the first time to form an ultrafine-grained structure in the investigated steel. Submicrocrystalline structures formed in materials have been shown to substantially enhance the complex of mechanical properties, bringing the material closer to those of the high-strength class. The proposed technologies allow the manufacture of defect-free volume workpieces with a uniform ultrafine-grained structure and various combinations of strength and plasticity.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. G. Raab and M. V. Chukin, “The development of a new method of severe plastic deformation by drawing with shear,” in Actual problems of physical metallurgy of steels and alloys: Materials of the XXI Ural School of Metallurgical Scientists, Magnitogorsk (2012), pp. 20–21.
M. Yu. Murashkin, E. V. Bobruk, A. R. Kil’mametov, and R. Z. Valiev, “Structure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy 6061 subjected to equal-channel angular pressing in parallel channels,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 108, 415–423 (2009).
G. G. Kurapov, E. P. Orlova, I. E. Volokitina, and A. Turdaliev, “Plasticity as a physical-chemical process of deformation of crystalline solids,” J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 51, 451–457 (2016).
R. Z. Valiev and I. V. Aleksandrov, Bulk Nanostructured Materials: Production, Structure, Properties (IKTs “Akademkniga”, Moscow, 2007) [in Russian]
F. Z. Utyashev, Modern Methods of Severe Plastic Deformation: A Tutorial (UGATU, Ufa, 2008) [in Russian].
S. N. Lezhnev, I. E. Volokitina, and A. V. Volokitin, “Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of steel during pressing–drawing,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 118, 1167–1170 (2017).
A. A. Gazder, TorreF. Dalla, C. F. Gu, C. H. Davies, and E. V. Pereloma, “Microstructure and texture evolution of bcc and fcc metals subjected to equal channel angular extrusion,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 415, 126–139 (2006).
R. Z. Valiev and T. G. Langdon, “Achieving exceptional grain refinement through severe plastic deformation: new approaches for improving the processing technology,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 42, 2942–2951 (2011).
A. B. Nayzabekov, S. N. Lezhnev, and I. E. Volokitina, “Change in copper microstructure and mechanical properties with deformation in an equal channel stepped die,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 57, 3–5 (2015).
E. G. Astafurova, G. G. Zakharova, E. V. Naydenkin, S. V. Dobatkin, and G. I. Raab, “Influence of equal-channel angular pressing on the structure and mechanical properties of low-carbon steel 10G2FT,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 110, 260–268 (2010).
A. I. Korshunov, Physico-Mechanical Properties of Materials after Eequal-Channel Angular Pressing. Features of anifestation: A Monograph (RFYaTs–VNIIEF, Sarov, 2013) [in Russian].
I. Yu. Khmelevskaya, R. D. Karelin, S. D. Prokoshkin, V. A. Andreev, V. S. Yusupov, M. M. Perkas, V. V. Prosvirnin, A. E. Shelest and V. S. Komarov, “Effect of the quasi-continuous equal-channel angular pressing on the structure and functional properties of Ti–Ni-based shape-memory alloys,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 118, 279–287 (2017).
L. E. Kar’kina, T. A. Zubkova, and I. L. Yakovleva, “Dislocation structure of cementite in granular pearlite after cold plastic deformation,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 114, 234–241 (2013).
V. Bratova and E. N. Borodin, “Comparison of dislocation density based approaches for prediction of defect structure evolution in aluminium and copper processed by ECAP,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 631, 10–17 (2015).
M. Kawasaki, Z. Horita, and T. G. Langdon, “Microstructural evolution in high purity aluminum processed by ECAP,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A 631, 143–150 (2009).
A. B. Naizabekov and V. A. Andreyashchenko, “Influence of sample inverting on the microstructure during ECA-pressing,” in VIII All-Russian Scientific Practical Conference with International Participation “Innovative Technologies and Economics in Engineering”. Yurga, Kemerov. oblast, Russia (Yurga Technol. Inst., Tomsk. Politekh. Univ., Yurga, 2009), pp. 72–76.
S. Lezhnev, I. Volokitina, and T. Koinov, “Research of influence equal channel angular pressing on the microstructure of copper,” J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 49, 621–630 (2014).
A. Naizabekov, S. Lezhnev, E. Panin, and I. Volokitina, “New combined technology of deformation “rolling–equal channel angular pressing”, allowing to obtain metals and alloys with sub-ultra-fine-grained structure,“ in Severe Plastic Deformation Techniques, Ed. by M. Cabibbo (IntechOpen, London, 2017), pp. 175–191.
A. Mishra, B. K. Kad, F. Gregori, and M. A. Meyers, “Microstructural evolution in copper subjected to severe plastic deformation: Experiments and analysis,” Acta Mater. 55, 13–28 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by T. Gapontseva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayzabekov, A.B., Volokitina, I.E. Effect of the Initial Structural State of Cr–Mo High-Temperature Steel on Mechanical Properties after Equal-Channel Angular Pressing. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 120, 177–183 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X19020133
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X19020133