Abstract
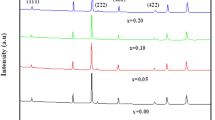
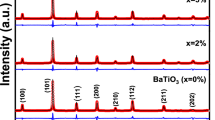
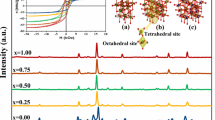
Modifying the properties of spinel ferrites by doping allows significantly expanding their application in various fields of science and industry. The present work reports results of the study of Ni1–xCoxFe2O4 ceramic samples (x = 0-1 with a step of 0.1) prepared by solid phase synthesis. The morphology and size of the particles of the synthesized powders are determined. The monophase character of the synthesized materials is confirmed by X-ray powder diffraction. The unit cell parameter a,b,c increase from 8.3375(3) Å to 8.3819(4) Å upon the substitution of nickel by cobalt. The differential scanning calorimetry data indicate heat capacity jumps corresponding to a thermal second-order phase transition. The phase transition temperature depends on the ceramics composition and decreases monotonically from 596 °C to 530 °C as nickel is replaced by cobalt.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. Kesavan, M. Pichumani, S.-M. Chen, and C.-S. Ko. Surfactant-assisted (CTAB, PVA, PVP) thermal decomposition synthesis of strontium spinel ferrite nanocrystals for electrochemical sensing of cytostatic drug flutamide. Mater. Today Chem., 2022, 26, 101045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.101045
T. Rafique, M. Atif, A. U. Rehman, H. Wahab, W. Khalid, Z. Ali, and M. Nadeem. Colossal permittivity, resistive and magnetic properties of zinc substituted manganese ferrites. J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 923, 166454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166454
V. J. Angadi, I. S. Yahia, H. Y. Zahran, M. C. Oliveira, E. Longo, S. P. Kubrin, S. O. Manjunatha, R. A. P. Ribeiro, and M. H. Ghozza. Effect of Eu3+ on the structural, magnetic and Mössbauer spectroscopy studies of copper ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2022, 562, 169789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169789
Z. Gao, J. Zhu, Q. Zhu, C. Wang, and Y. Cao. Spinel ferrites materials for sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation process: A review. Sci. Total Environ., 2022, 847, 157405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157405
Y. Slimani, R. Sivakumar, S. S. Meena, R. Vignesh, G. Yasin, E. Hannachi, M. A. Almessiere, Z. Trabelsi, K. M. Batoo, A. Baykal, N. Sfina, S. Brini, S. E. Shirsath, I. Ercan, and B. Özçelik. BaTiO3/(Co0.8Ni0.1Mn0.1Fe1.9Ce0.1O4) composites: Analysis of the effect of Co0.8Ni0.1Mn0.1Fe1.9Ce0.1O4 doping at different concentrations on the structural, morphological, optical, magnetic, and magnetoelectric coupling properties of BaTiO3. Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(20), 30499-30509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.06.330
T. Zhong, X. Li, M. Wu, and J.-M. Liu. Room-temperature multiferroicity and diversified magnetoelectric couplings in 2D materials. Natl. Sci. Rev., 2020, 7(2), 373-380. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz169
C. Priese and J. Töpfer. The effect of microstructure on the initial permeability of Ni-Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2022, 560, 169581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169581
S. Kanithan, N. Arun Vignesh, K. M. Katubi, P. S. Subudhi, E. Yanmaz, J. Arockia Dhanraj, N. S. Alsaiari, khamael M. Abualnaja, M. Sukumar, M. Sundararajan, S. Baskar, S. Sahu, and C. S. Dash. Enhanced optical, magnetic, and photocatalytic activity of Mg2+ substituted NiFe2O4 spinel nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct., 2022, 1265, 133289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133289
M. Thavarani, M. C. Robert, S. B. Prasath, N. Pavithra, P. Christuraj, and S. Saravanakumar. Effect of mediator on the auto combustion synthesis, magnetic properties, and electron density distribution of spinel ferrite Mn0.05Zn0.95Fe2O4. Brazilian J. Phys., 2022, 52(5), 177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-022-01181-w
D. Parajuli, N. Murali, A. V. Rao, A. Ramakrishna, S. Y. Mulushoa, and K. Samatha. Structural, dc electrical resistivity and magnetic investigation of Mg, Ni, and Zn substituted Co–Cu nano spinel ferrites. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng., 2022, 42, 106-114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2022.07.009
C. Srinivas, M. Deepty, S. A. V. Prasad, G. Prasad, E. R. Kumar, S. S. Meena, N. V. Seetala, D. D. Willams, and D. L. Sastry. Study of structural, vibrational, elastic and magnetic properties of uniaxial anisotropic Ni–Zn nanoferrites in the context of cation distribution and magnetocrystalline anisotropy. J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 873, 159748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159748
S. Ruiz-Gómez, A. Mandziak, L. Martín-García, J. E. Prieto, P. Prieto, C. Munuera, M. Foerster, A. Quesada, L. Aballe, and J. de domain wall pinning in cobalt ferrite microstructures. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 600, 154045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154045
K. Pubby, P. Sharma, and S. B. Narang. Structural, magnetic, dielectric, microwave absorption, and optical characterization of Ni0.1Co0.9(MnZr)xFe2–2xO4/BaySr1–yFe12O19. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2020, 31(1), 599-609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02564-7
S. Gaba, P. S. Rana, and A. Kumar. Influence of La3+ ion doping on structural and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel route. AIP Conf. Proc., 2019, 2093, 020036. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5097105
J. S. Ghodake, R. C. Kambale, T. J. Shinde, P. K. Maskar, and S. S. Suryavanshi. Magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of Co2+ substituted nickel–zinc ferrites with the emphasis on initial permeability studies. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2016, 401, 938-942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.11.009
A. Riaz, M. A. Khan, M. Junaid, S. Gulbadan, A. Manzoor, S. R. Ejaz, G. A. Ashraf, H. H. Somaily, M. Morsi, and T. Alshahrani. Effect of Nd3+ ions on structural, spectral, magnetic, and dielectric properties of Co–Zn soft ferrites synthesized via sol-gel technique. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2022, 290, 126519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126519
R. Díaz-Pardo and R. Valenzuela. Characterization of magnetic phases in nanostructured ferrites by electron spin resonance. In: Advanced Electromagnetic Waves / Ed. S.O. Bashir. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech, 2015. https://doi.org/10.5772/61508
C. Suchomski, B. Breitung, R. Witte, M. Knapp, S. Bauer, T. Baumbach, C. Reitz, and T. Brezesinski. Microwave synthesis of high-quality and uniform 4 nm ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals for application in energy storage and nanomagnetics. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol., 2016, 7, 1350-1360. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.7.126
D. A. Vinnik, D. P. Sherstyuk, V. E. Zhivulin, D. E. Zhivulin, A. Y. Starikov, S. A. Gudkova, D. A. Zherebtsov, D. A. Pankratov, Y. A. Alekhina, N. S. Perov, S. V. Trukhanov, E. L. Trukhanova, and A. V. Trukhanov. Impact of the Zn–Co content on structural and magnetic characteristics of the Ni spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(13), 18124-18133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.070
D. P. Sherstyuk, A. Y. Starikov, V. E. Zhivulin, D. A. Zherebtsov, S. A. Gudkova, N. S. Perov, Y. Alekhina, K. A. Astapovich, D. A. Vinnik, and A. V. Trukhanov. Effect of Co content on magnetic features and SPIN states in Ni–Zn spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int., 2021, 47(9), 12163-12169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.063
P. P. Mohapatra, H. K. Singh, M. S. R. N. Kiran, and P. Dobbidi. Co substituted Ni–Zn ferrites with tunable dielectric and magnetic response for high-frequency applications. Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(19), 29217-29228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.197
H.-S. Guo, L. Zhang, Y.-L. Yan, J. Zhang, J. Wang, S.-Y. Wang, L.-Z. Li, and X.-H. Wu. Effect of lanthanum substitution on structural, magnetic, and electric properties of Ni–Zn–Co ferrites for radio frequency and microwave devices. Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(15), 22516-22522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.275
N. Kumar, Archana, R. K. Singh, V. Kumar, and S. B. Das. Tuning in structural, optoelectronic, magnetic and ferroelectric properties of NiFe2O4 ceramics engineering nanomaterials by substitution of rare earth element, Pr3+ prepared by sol-gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2022, 33(9), 6131-6149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07790-0
X. Xie, B. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Ni, X. Sun, and W. Du. Spinel structured MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Mn, Zn) and their composites for microwave absorption: A review. Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 428, 131160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131160
H. E. Swanson, H. F. McMurdie, M. C. Morris, E. H. Evans, and B. Paretzkin. Standard X-ray Diffraction Powder Patterns: Section 9. Data for 63 Substances. Report. Washington, D.C., USA: National Bureau of Standards, Department of Commerce, 1971.
P. Sowjanya, N. P. Kumar, A. Chelvane, and M. V. R. Reddy. Synthesis and analysis of low field high magnetostrictive Ni–Co ferrite for magneto-electric energy harvesting applications. Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2022, 279, 115674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.115674
Atomistic Simulation Group. Database of Ionic Radii. Radii for Ni. http://abulafia.mt.ic.ac.uk/shannon/radius.php?Element=Ni
Atomistic Simulation Group. Database of Ionic Radii. Radii for Co. http://abulafia.mt.ic.ac.uk/shannon/radius.php?Element=Co
M. S. R. Prasad, B. B. V. S. V. Prasad, and B. Rajesh Babu. Magnetic, structural and dc electrical resistivity studies on the divalent cobalt substituted Ni–Zn ferrite system. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B, 2015, 29(12), 1550067. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0217979215500678
S. A. Gudkova, D. A. Vinnik, V. E. Zhivulin, A. S. Chernukha, D. A. Zherebtsov, E. A. Trofimov, A. V. Trukhanov, S. V. Trukhanov, M. Kalandija, A. S. Semisalova, N. S. Perov, A. V. Senin, N. S. Zabeivorota, and G. G. Mikhailov. Synthesis, structure and properties of barium and barium lead hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2019, 470, 101-104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.11.114
Funding
This work was funded by a subsidy for the Strategic Academic Leadership Program Priority 2030 (Science and Universities).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2023, published in Zhurnal Strukturnoi Khimii, 2023, Vol. 64, No. 9, 117238.https://doi.org/10.26902/JSC_id117238
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherstyuk, D.P., Zhivulin, V.E., Starikov, A.Y. et al. CORRELATION BETWEEN CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AND CURIE TEMPERATURE OF A NICKEL-COBALT FERRITE. J Struct Chem 64, 1743–1750 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476623090172
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476623090172