Abstract
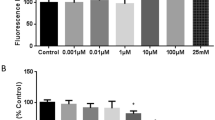
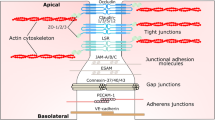
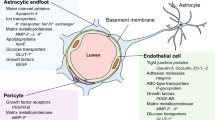
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) provides optimal conditions for the functioning of brain neurons. The barrier properties of the cerebrovascular (CV) endothelium are determined by the claudin family of proteins and occludin, which are major molecular determinants of selective intercellular transport. Plasma membrane lipids play an important role in forming the structure of tight junctions, being combined with these proteins into lipid rafts. The development of neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders correlates with changes in claudin levels in the CV endothelium. We studied the effect of methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MbCD), which causes destabilization of the plasma membrane lipid phase, on claudin-1, -5 and occludin levels in rat brain tissue. Male rats were injected intravenously with MbCD at a dose of 5 mg/kg of body weight, and 30 min later, brain tissue was prepared for Western blot and immunohistochemistry. MbCD induced a significant decrease in the claudin-5 level in the frontal lobes of the rat brain, while claudin-1 and occludin levels remained unchanged. Immunohistochemistry and confocal laser microscopical image analysis confirmed that changes in claudin-5 localization are confined to the CV endothelium. Since claudin-5 is a major contributor to the impermeability of the CV endothelium, we can assume that a change in the orderliness of the raft lipid phase may lead to an increase in intercellular permeability. The results suggest that the lipid environment is an important molecular component of the tight junction in the rat brain CV endothelium, which may be implicated in the maintenance and regulation of the barrier properties of the BBB.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sheikov N, McDannold N, Sharma S, Hynynen K (2008) Effect of focused ultrasound applied with an ultrasound contrast agent on the tight junctional integrity of the brain microvascular endothelium. Ultrasound Med Biol 34:1093–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2007.12.015
Ahishali B, Kaya M (2021) Evaluation of Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity Using Vascular Permeability Markers: Evans Blue, Sodium Fluorescein, Albumin-Alexa Fluor Conjugates, and Horseradish Peroxidase. Methods Mol Biol 2367:87–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2020_316
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030
Nico B, Ribatti D (2012) Morphofunctional aspects of the blood-brain barrier. Curr Drug Metab 13:50–60. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920012798356970
Petrov AM, Kasimov MR, Zefirov AL (2016) Brain Cholesterol Metabolism and Its Defects: Linkage to Neurodegenerative Diseases and Synaptic Dysfunction. Acta Naturae 8(1):58–73.
Anchisi L, Dessì S, Pani A, Mandas A (2013) Cholesterol homeostasis: A key to prevent or slow down neurodegeneration. Front Physiol 3:486. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00486
Günzel D, Yu AS (2013) Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol Rev 93:525–569. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00019.2012
Tsukita S, Tanaka H, Tamura A (2019) The Claudins: From Tight Junctions to Biological Systems. Trends Biochem Sci 44:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.09.008
Markov AG, Aschenbach JR, Amasheh S (2015) Claudin clusters as determinants of epithelial barrier function. IUBMB Life 67:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1347
Zahraoui A, Louvard D, Galli T (2000) Tight junction, a platform for trafficking and signaling protein complexes. J Cell Biol 151:F31–36. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.151.5.f31
Lee DB, Jamgotchian N, Allen SG, Abeles MB, Ward HJ (2008) A lipid-protein hybrid model for tight junction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F1601–1612. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00097.2008
Martín Del Valle EM (2004) Cyclodextrins and their uses: A review. Process biochemistry 39:1033–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00258-9
Dos Santos AG, Bayiha JC, Dufour G, Cataldo D, Evrard B, Silva LC, Deleu M, Mingeot-Leclercq MP (2017) Changes in membrane biophysical properties induced by the Budesonide/Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1859:1930–1940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.06.010
Du J, Liu X, Zhang Y, Han X, Ma C, Liu Y, Guan L, Qiao L, Lin J (2022) The Effects of Combined Therapy With Metformin and Hydroxypropyl-beta-Cyclodextrin in a Mouse Model of Niemann-Pick Disease Type C1. Front Pharmacol 12:825425. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.825425
Atışa M, Akcana U, Yılmazb CU, Orhanc N, Düzgüna P, Ceylana UD, Arıcand N, Karahüseyinoğlue S, Şahine GN, Ahıshalıf B, Kaya M (2019) Effects of methyl-beta-cyclodextrin on blood-brain barrier permeability in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats. Brain Res 1715:148–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2019.03.024
Lambert D, O’Neill CA, Padfield PJ (2007) Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin increases permeability of Caco-2 cell monolayers by displacing specific claudins from cholesterol rich domains associated with tight junctions. Cell Physiol Biochem 20:495–506. https://doi.org/10.1159/000107533
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, Seo Y, Sasaki H, Hashimoto N, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 161:653–660. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200302070
Greene C, Hanley N, Campbell M (2020) Blood-brain barrier associated tight junction disruption is a hallmark feature of major psychiatric disorders. Transl Psychiatry 10:373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-01054-3
Dudek KA, Dion-Albert L, Lebel M, LeClair K, Labrecque S, Tuck E, Ferrer Perez C, Golden SA, Tamminga C, Turecki G, Mechawar N (2020) Molecular adaptations of the blood–brain barrier promote stress resilience vs. depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:3326–3336. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1914655117
Díaz-Coránguez M, Segovia J, López-Ornelas A, Puerta-Guardo H, Ludert J, Chávez B, Meraz-Cruz N, González-Mariscal L (2013) Transmigration of neural stem cells across the blood brain barrier induced by glioma cells. PLoS One 8:e60655. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060655
Velandia-Romero ML, Calderón-Peláez MA, Castellanos JE (2016) In Vitro Infection with Dengue Virus Induces Changes in the Structure and Function of the Mouse Brain Endothelium. PLoS One 11:e0157786. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157786
Buschmann MM, Shen L, Rajapakse H, Raleigh DR, Wang Y, Wang Y, Lingaraju A, Zha J, Abbott E, McAuley EM, Breskin LA, Wu L, Anderson K, Turner JR, Weber CR (2013) Occludin OCEL-domain interactions are required for maintenance and regulation of the tight junction barrier to macromolecular flux. Mol Biol Cell 24:3056–3068. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-09-0688
Zhang Y, Ding X, Miao C, Chen J (2019). Propofol attenuated TNF-α-modulated occludin expression by inhibiting Hif-1α/ VEGF/ VEGFR-2/ ERK signaling pathway in hCMEC/D3 cells. BMC Anesthesiol 19:127. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-019-0788-5
Tian J, Shi R, Liu T, She R, Wu Q, An J, Hao W, Soomro MH (2019) Brain Infection by Hepatitis E Virus Probably via Damage of the Blood-Brain Barrier Due to Alterations of Tight Junction Proteins. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:52. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00052
Markov AG, Fedorova AA, Kravtsova VV, Bikmurzina AE, Okorokova LS, Matchkov VV, Cornelius V, Amasheh S, Krivoi II (2020) Circulating Ouabain Modulates Expression of Claudins in Rat Intestine and Cerebral Blood Vessels. Int J Mol Sci 21:5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21145067
Albelda SM, Muller WA, Buck CA, Newmanll PJ (1991) Molecular and cellular properties of PECAM-1 (endoCAM/CD31): a novel vascular cell-cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol 114(5):1059–68. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.114.5.1059
Morita K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 147:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.147.1.185
Sugibayashi K, Onuki Y, Takayama K (2009) Displacement of tight junction proteins from detergent-resistant membrane domains by treatment with sodium caprate. Eur J Pharm Sci 36:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2008.09.011
Monnaert V, Tilloy S, Bricout H, Fenart L, Cecchelli R, Monflier E (2004) Behavior of α-, β-, and γ-Cyclodextrins and Their Derivatives on an in Vitro Model of Blood-Brain Barrier. J Pharm Experim Ther 310:745–751. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.067512
Saito AC, Higashi T, Fukazawa Y, Otani T, Tauchi M, Higashi AY, Furuse M, Chiba H (2021) Occludin and tricellulin facilitate formation of anastomosing tight-junction strand network to improve barrier function. Mol Biol Cell 32(8):722–738. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E20-07-0464
Hissa B, Pontes B, Roma PM, Alves AP, Rocha CD, Valverde TM, Aguiar PH, Almeida FP, Guimarães AJ, Guatimosim C, Silva AM, Fernandes MC, Andrews NW, Viana NB, Mesquita ON, Agero U, Andrade LO (2013) Membrane Cholesterol Removal Changes Mechanical Properties of Cells and Induces Secretion of a Specific Pool of Lysosomes. PLoS ONE 8:e82988. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082988
He WQ, Wang J, Sheng JY, Zha JM, Graham WV, Turner JR (2020) Contributions of Myosin Light Chain Kinase to Regulation of Epithelial Paracellular Permeability and Mucosal Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 21:993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030993
Zhang J, Li X, Yu H, Larre I, Dube PR, Kennedy DJ, Tang WHW, Westfall K, Pierre SV, Xie Z, Chen Y (2020) Regulation of Na/K-ATPase expression by cholesterol: isoform specificity and the molecular mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 319:C1107–C1119. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00083.2020
Funding
This work was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (RSF), grant no. 18-15-00043. The studies were carried out using the facilities of the “Center for Molecular and Cellular Technologies” Resource Center (project no. 109-14629) and the “Chromas” Center for Collective Use of Equipment (project no. 101-14625) at the St. Petersburg State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology (A.G.M., I.I.K.); data collection and processing (A.E.B., A.A.F.), manuscript writing and editing (A.G.M., A.E.B., A.A.F., I.I.K.).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have neither evident nor potential conflict of interest related to the publication of this article. A.G.M. is a member of the editorial board of the Russian Journal of Physiology.
Additional information
Translated by A. Polyanovsky
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2022, published in Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I.M. Sechenova, 2022, Vol. 108, No. 5, pp. 677–685https://doi.org/10.31857/S0869813922050089.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markov, A.G., Bikmurzina, A.E., Fedorova, A.A. et al. Methyl-beta-Cyclodextrin Alters the Level of Tight Junction Proteins in the Rat Cerebrovascular Endothelium. J Evol Biochem Phys 58, 849–855 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093022030188
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093022030188