Abstract
Biochar is a carbon negative soil amendment that can promote crop growth. However, the effects of biochar on different plant species and cultivars within a species are not well understood, nor is the underlying basis of biochar-mediated plant growth promotion. This knowledge is critical for optimal use of biochar and for breeding biochar-responsive plants. Here, we investigated the genotype-specific effects of biochar on two cultivars of Solanum lycopersicum (tomato), and two wild relatives of tomato, Solanum pimpinellifolium, and Solanum pennelli, in two types of biochar. Biochar promoted shoot growth in all genotypes independent of biochar type but had genotype-dependent effects on other plant traits. Germination tests, exogenous GA4 application and mutant analysis indicated a role for GA in biochar-mediated plant growth promotion. Together, our results suggest that biochar promotes growth partially through stimulation of the GA pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Biochar is a carbon negative soil amendment produced from pyrolysis of organic material. Its potential for mitigating climate change and improving agricultural soils was recognized after the discovery of Terra Preta soil in the Amazon, where soils conditioned with black carbon additions thousands of years ago by native residents continue to be more fertile and carbon-rich than surrounding soils even today1,2. Today, soil amendment with biochar is being evaluated as a strategy for improving soil fertility, while simultaneously sequestering carbon and reducing greenhouse gas emissions3. Overall, modern biochars appear to promote plant growth4, though some studies have documented mixed or even negative effects of biochar5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13.
Research on how biochar promotes plant growth has focused on its positive impacts on soil characteristics, nutrient availability (reviewed in refs4,14) and the soil microbial community (reviewed in ref.15). Additionally, several groups have demonstrated that biochar is effective in controlling foliar and soil-borne pathogens with both biotrophic and necrotrophic lifestyles on multiple host crops (reviewed in refs16,17). However, others have shown a neutral or negative effect of biochar on disease progress18,19,20,21. Evidence indicates that differences in environment as well as biochar feedstock and production conditions each play a role in biochar’s effectiveness4. A recent meta-analysis of biochar studies showed that biochar’s effect on total plant biomass differs between annual and perennial crops4, suggesting that the effect of biochar on crop growth promotion may be dependent on crop species. Although the complexity of determinants underlying the agricultural outcomes of biochar amendment is not fully understood, further insight into the differences in biochar response both between and within species could improve biochar’s use in agriculture and lead to breeding for biochar responsiveness.
The bulk of biochar research on agricultural productivity has thus far focused on biochar’s effects on overall shoot growth and yield in major crops4,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29. Fewer studies have examined the effects of biochar on particular growth traits that impact yield, such as germination, shoot or root architecture30,31,32,33,34. Understanding how specific growth traits are impacted by biochar addition will lead to improved uses for biochar, such as in germination potting mixes for use in greenhouse applications.
The applicability of such data is maximized by understanding the plant signaling pathways underlying the positive effects of biochar on plant growth. Microarray-based genome-wide transcriptional analysis in Arabidopsis35 demonstrated that biochar application increased transcription of auxin- and brassinosteroid- related genes with a concurrent decrease in defense-related genes, which the authors suggested indicated a tradeoff between growth and defense in biochar-grown plants. Further elucidation of the underlying basis for how biochar functions to promote growth and influence disease will lead to improved practices for biochar use and potentially new synergistic applications with other horticultural or agronomic practices.
In this study, our objectives were to understand the species-specific, within-species (e.g. cultivar), and trait-specific aspects of biochar-mediated plant growth promotion. We hypothesized that biochar would promote growth independent of crop species and plant trait. To test this, we first examined the effect of two different biochars on various growth traits of two cultivars of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and two species that are wild tomato relatives (S. pimpinellifolium and S. pennellii) in greenhouse conditions. Surprisingly, we found that although biochar promotes shoot growth independent of genotype, it has genotype-specific effects on other traits. Based on these results, we then aimed to understand the underlying basis for these phenotypes. The effects of biochar on plant growth suggested the involvement of the gibberellin (GA) pathway. We hypothesized that this pathway may play a role in biochar-mediated plant growth promotion. To further investigate this, we used hormone assays and mutant analysis. These experiments revealed a functional role for GA pathways in biochar-induced growth promotion.
Results
Biochar promotes shoot growth in a genotype-independent manner
In order to test the effects of biochar addition on different tomato genotypes, we performed a full factorial greenhouse experiment on two S. lycopersicum cultivars, S. pimpinellifolium, and S. pennellii with two different types of biochar at 4% weight weight−1 and a control 0% application rate. The two biochars significantly differed in their pH, organic matter content, and mineral composition (Table 1). We performed two trials and measured shoot growth traits after eight weeks of growth. The first trial was performed from December to late February and the second from late March to late May. For simplicity, the two S. lycopersicum cultivars and two wild species will be referred to as four genotypes. Biochar was a significant effect in the model for both shoot length and fresh weight (Table 2). Genotype was also significant for both shoot growth parameters, reflecting the different growth patterns between genotypes (Table 2). Interestingly, the p-value for the interaction between genotype and trial was 0.098 for shoot length and 0.06 for shoot fresh weight, suggesting that the trial may have impacted growth of some genotypes. This may have been due to environmental differences between the two trials, with the first trial conducted during the winter months with shorter days compared to the second trial in the spring. The biochar*genotype interaction was not significant for either model, indicating that the effects of biochar on shoot length and fresh weight are genotype-independent. Because the effects of biochar were independent of genotype, we used one genotype (H7996) to examine the effect of each biochar on leaf nutrient content (Table S1). Results showed very small to no differences in the levels of N and C between control and biochar treated H7996 plants, but decreased levels of potassium (K).
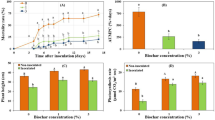
Overall, both types of biochar (Premium and Ultra) significantly promoted shoot weight and shoot length over the control plants (Table 2; Fig. 1). Premium biochar increased shoot weight by an average of 33.1% (±6.9%) and shoot length by 8.0% (±2.6%). Ultra biochar increased shoot weight by 50.9% (±11.6%) and shoot length by 9.2% (±3.1%). Ultra biochar promoted shoot weight, but not shoot length, significantly more than Premium biochar (Fig. 1).
Biochar promotes shoot length and shoot weight in a genotype-independent manner. Graphs of (a) shoot length and (b) shoot fresh weight, showing the effects of biochar addition and genotype. ‘Control’ indicates no biochar addition, while ‘Premium’ and ‘Ultra’ represent 4% (w w−1) soil amendment with indicated biochar. Because a significant interaction between genotype and biochar addition was not observed (Table 2), here we compared the effect of different biochar types with the control. For this, data from different genotypes were pooled within each biochar and within the control. A post-hoc Tukey’s honestly significant differences test comparing biochar types and the control indicated significant differences between control and biochar amendments for both shoot length and weight. Abbreviations: H7996 – Solanum lycopersicum cv. Hawaii7996. M82 – S. lycopersicum cv. M82. WV – S. pimpinellifolium accession West Virginia700. SP – S. pennellii accession LA0716.
Biochar amendment affects germination and time to flowering in a genotype-specific manner
In order to further investigate biochar’s role in other growth traits, we examined the effect of biochar on germination. Seeds from all four genotypes were planted with or without 4% Premium biochar and were measured for germination over a 10 day period. Area under the germination progress curves (AUGPC) for each of the four genotypes revealed that Premium biochar increased germination rate in H7996 and SP (Fig. 2a,d). Overall germination increased for SP by nearly 20% (Fig. 2d). AUGPC differences for germination in M82 between biochar-grown and control seeds were p < 0.1, suggesting a possibly similar, but weaker trend to H7996. These results suggest a species-specific effect of biochar on germination, as only 2 (S. lycopersicum and S. pennellii) out of 3 species showed a germination phenotype with biochar addition. Consistent with our observations that biochar affects GA-related traits, we observed both a decrease in days to flowering and an increase in the number of flowers at eight weeks in the second trial of the greenhouse experiment (Fig. S1). A summary of the effect of biochar in different Solanum species and within a given Solanum species is in Fig. 3.
Premium biochar reduces time to germination and increases germination percentage in two tomato genotypes. (a–d) Percent germination over time in genotypes H7996, WV, M82, and SP, respectively, in 0 and 4% Premium biochar amended potting mix. Results in (a–d) are the averages of 54 seeds/treatment with four biological replicates. Error bars represent one standard error. P value represents mixed model ANOVA comparing Area Under the Germination Curve (AUGPC) values between biochar-treated and un-treated pots for each genotype. P value was considered significant at p < 0.05 (bold). Abbreviations: H7996 – Solanum lycopersicum cv. Hawaii7996. M82 – S. lycopersicum cv. M82. WV – S. pimpinellifolium accession West Virginia700. SP – S. pennellii accession LA0716.
Summary of the effects of biochar on growth traits, separated by plant genotype. Gray boxes indicate that biochar had a positive effect on that trait for that genotype. White boxes indicate no effect. Flowering traits for SP are marked N/A because control SP plants had not flowered by the end of the experiment, so no statistical analysis could be performed.
Biochar water extracts affect S. pennellii seedling growth traits
After observing the effect of biochar on growth under controlled growth conditions, we hypothesized that this phenotype was due to a direct effect of chemicals present in the biochar. In order to test this hypothesis, we made water extracts of both biochars and measured growth of S. pennellii (SP) on agar plates (Fig. S2). We chose SP because it is the most amenable to growth on agar plates and responded highly to biochar amendment. Seedlings treated with Ultra and Premium biochar extracts exhibited higher seedling weight and longer hypocotyls compared to the control (Fig. S2a,b). Root length was only affected by Premium water extracts compared to the control (Fig. S2c). These results suggest that biochar’s growth promoting effects in the greenhouse trials come at least in part from water-soluble compounds present in the biochar.
We hypothesized that Premium biochar may contain karrikins, germination promoting compounds found in smoke and other biochars36 that require the GA pathway to promote germination37. GC-MS analysis was performed on ethyl acetate extracts of ground Premium biochar to detect the presence of karrikins. However, no karrikins were detected in Premium biochar (Fig. S3).
Biochar amendment increases response to exogenous GA in one tomato genotype
Because the growth phenotypes observed above (shoot length, germination, flowering time) were reminiscent of growth mediated through the gibberellin (GA) pathway, we asked whether biochar promoted plant growth through the GA pathway. To examine this, we first tested whether exogenous GA treatment differentially affected plants grown with or without biochar. We examined the effects of exogenous GA4 treatment on shoot growth in all four tomato genotypes grown with or without Premium biochar (Fig. 4). Our results show a positive, interactive effect of biochar and GA4 treatment on both shoot fresh weight and shoot length in one genotype, M82, suggesting that biochar stimulates the GA pathway (Fig. 4c,g). This effect appears to be within-species specific as the interaction effect was observed in M82 and not H7996, both S. lycopersicum cultivars (Fig. 4a,c,e,g). Full model results are in Table S1. A summary of the species- and within-species specific effects of biochar can be found in Fig. 3.
Exogenous gibberellin (GA4) application and Premium biochar (BC) amendment interact synergistically to increase the shoot biomass and length of M82 tomato plants. Least Square (LS) Mean interaction plots for each species show relationship between GA4 application and BC amendment for (a–d) shoot fresh weight and (e,f) shoot length. The experiment was repeated in four trials, and trial was included as a random factor in the model. Shoot weight and length values were square root transformed to meet homogeneity of variance and normality assumptions. Values represented in the figure are not transformed. P values represent significance of BC × GA4 interaction in the full model analysis. The interaction effect was considered statistically different at p < 0.05. Error bars represent one standard error. Abbreviations: H7996 – Solanum lycopersicum cv. Hawaii7996. M82 – S. lycopersicum cv. M82. WV – S. pimpinellifolium accession West Virginia700. SP – S. pennellii accession LA0716. Full model results are in Table S1.
Biochar induced growth promotion requires an intact GA biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
In order to further evaluate the role of GA in biochar induced growth promotion, mutant analysis was performed. Because few tomato GA deficient mutants without severe growth defects exist, the Arabidopsis GA biosynthesis mutant ga3ox1-3 was used. ga3ox1-3 is defective in Gibberellin 3-oxidase 1 (At1g15550), which is involved in the production of bioactive GA4 during the vegetative growth stage38. We hypothesized that if biochar promoted plant growth through the GA pathway, a mutant defective in GA biosynthesis would be less responsive to biochar. Growth assays on plates with biochar extracts showed that the GA pathway is required for a hypocotyl growth response to water extracts of biochar (Fig. 5, Table S2). Premium biochar extracts promoted hypocotyl growth in Col-0, the wild-type background for ga3ox1-3 (Fig. 5). However, no significant difference was found in hypocotyl growth between control and Premium biochar extract-treated ga3ox1-3 seedlings (Fig. 5). This result suggests that GA is at least partially responsible for biochar growth promotion in Arabidopsis.
Premium biochar water extracts promote hypocotyl growth in WT Col-0, but not in ga3ox1-3 mutant. Hypocotyl length of Col-0 or ga3ox1-3 seedlings plated with Premium biochar water extract vs. sterile water treatment. Results represent the averages of three plates/treatment of 7–29 seeds/plate with two biological replicates performed. Square root transformed values were used for statistical analysis to meet homogeneity of variance assumption. Values represented in the figure are not transformed. Significant differences between all genotype and treatment combinations determined by Tukey’s honest significant differences at p < 0.05 indicated by differing letters. Error bars represent one standard error. Full model results can be found in Table S2.
Discussion
Here we provide evidence that biochar-mediated growth promotion acts in part through the GA pathway. Further, we show that while the shoot length and fresh weight growth promotion effect of biochar is genotype-independent, the effect of biochar on other traits such as germination, depends on genotype. We demonstrated that biochar and exogenous GA application acted synergistically to affect tomato shoot growth, but only in cultivar M82. Our study highlights the complexity of biochar-plant interactions and helps explain some of the apparent contradictions in the biochar literature. Differences in growth or disease outcomes are commonly reported for different types and rates of biochar13,18,24,31,32,33,39,40,41,42,43. Additionally, previous studies have observed the full range of germination responses to biochar, from an inhibitory to a stimulatory effect31,32,44,45,46,47. One reason for these discrepancies could be due to the differential effects of biochar on different traits and genotypes. We showed that while biochar affected overall shoot growth across all genotypes, germination was only positively affected in two of the studied genotypes.
The trait-dependent effects of biochar have not been well characterized31,32,42,48. Here we show that, depending on the genotype, biochar impacts some growth traits but not others (germination or response to GA application, for example). Solaiman et al. (2012) tested the effects of different levels of five different biochars on three plant species and observed differing effects dependent on trait observed, plant species, biochar amendment level, and biochar type. For example, in wheat, biochar amendment increased germination and seedling growth at low amendment levels, but had negative effects at higher concentrations31. For mung bean and clover, biochar amendment had a negative effect on germination regardless of amendment level. Providing further evidence that biochar affects plant growth in a trait-specific manner, biochar did have positive effects on mung bean and clover growth at low concentrations, despite its negative effect on germination in these species31. While it is still unclear why the effects of biochar depend on the trait, species and cultivar examined, our discovery of within-species (e.g. cultivar) variation opens the door to the potential for breeding for a positive biochar response.
To test the hypothesis that GA is involved in biochar-mediated plant growth promotion, we examined biochar response traits related to GA and performed mutant analysis. Exogenous GA4 application revealed a positive, interactive effect of Premium biochar and GA application on shoot growth in M82, indicating that biochar stimulates the GA pathway. Similarly, Premium biochar promoted germination in H7996 and SP with the largest effect occurring in SP with approximately a 20% increase in percent germination over the control. Our experiments with the ga3ox1-3 Arabidopsis mutant for GA biosynthesis supported the involvement of the GA pathway in biochar-mediated plant growth promotion. In another study, Soybean plants grown in 5% biochar exhibited upregulated transcription of β-1,4-glucanase, involved in cell wall expansion, which is a hallmark of GA-mediated growth21. Conversely, Viger et al. (2014) found evidence for upregulation of auxin and brassinosteroid pathways in Arabidopsis plants grown in biochar, though this may be due to differences in species response or the type of biochar used35. Our study supports evidence for a model by which biochar promotes tomato growth partly through stimulation of germination and growth through the GA pathway. Future work should focus on measuring hormone levels and transport in biochar-treated plants to further understand biochar’s influence on hormone pathways.
Biochar’s positive effects on shoot growth and germination, even under well-watered and fertilized conditions, suggest a direct effect of compounds present in the biochar on the plant. Our results showing that water-extracts of biochar promoted SP seedling growth confirmed this hypothesis. Though we were unable to identify karrikins in the biochar used here, recent studies have demonstrated that biochars contain bioactive compounds, including karrikins and humic substances products (HSP) which have been shown to have hormone-like effects on plant growth, including GA-like responses36,49,50,51. Alternatively, biochar’s effects on plant growth and defense may occur indirectly through its impacts on the soil microbial community. Biochar has been shown to shift root-associated communities toward microbes with plant-growth promoting or defense-promoting capabilities13,52,53,54. These altered communities may, in turn, impact plant growth and defense.
Our data supports a model in which biochar application stimulates the GA pathway in tomato and Arabidopsis. These data may lead to new potential applications for biochar, such as enhancing current horticultural practices like spraying exogenous GA on grapes for larger fruit production. We have also shown that while biochar generally promotes tomato growth under controlled greenhouse conditions, it affects specific traits such as germination in a genotype- and trait-specific manner. Future studies are needed to better understand how biochar affects plant hormone pathways and to examine how genetic differences influence plant responses to biochar in order to use biochar more effectively.
Methods
Biochar and Leaf Tissue Analysis
Premium and Ultra biochars were obtained from Black Owl Biochar in Washington state, USA (http://www.biocharsupreme.com/). Both were produced from sustainably managed Douglas fir under different commercial production conditions. Biochar and leaf tissue were chemically analyzed by the Cornell Nutrient Analysis Laboratory following methods from the Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual created by the National Soil Survey Center (Soil Survey Staff, 2014). Five leaves of H7996 from replicate 1 were pooled for leaf tissue analysis.
Seed sterilization
For all experiments, tomato seeds were sterilized by shaking in 10% bleach for 10 minutes, and then rinsed six times in sterile double distilled water (ddH2O). Seeds were then left in sterile water overnight in a 4 °C refrigerator to imbibe. Arabidopsis thaliana seeds were prepared by allowing to stratify in sterile water in a 4 °C refrigerator for five days. Seeds were then sterilized by shaking in 1 mL 50% bleach and 1 µL Tween for five minutes and then rinsing in sterile ddH2O five times.
Tomato Growth in Biochar
A full-factorial greenhouse experiment was designed to test the effects of biochar addition on the growth response of two Solanum lycopersicum (tomato) cultivars and two wild tomato species, S. pimpinellifolium and S. pennellii. The tomato cultivars used were Hawaii7996 (H7996), known for its disease resistance55 and M82, an inbred processing tomato cultivar56. The Solanum pimpinellifolium accession used was West Virginia700 (WV), known for its susceptibility to the bacterial pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum57. The Solanum pennellii (SP) accession was LA0716, which was recently sequenced58. For simplicity, the two tomato cultivars and two wild species will be referred to as four genotypes. Two types of biochar made from the same feedstock under different production conditions were used: Premium and Ultra. A custom soilless potting mix was made that consisted of a 1:1 (volume volume−1) ratio of peat to Turface MVP (Turface Athletics, Buffalo Grove, IL, USA). Biochars were amended into the potting mix at a rate of 4% biochar (weight weight−1) and mixed by hand. All four genotypes were also grown in control pots not amended with biochar.
Sterile tomato seeds were planted into classic 300 size pots (about 2.5 L) (Nursery Supplies, Inc., Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, USA) and were grown in a light and temperature-controlled greenhouse (temperature setting 75–84 °F) that was regularly maintained for pests. Lights operated on a 16 hour on, 8 hour off long day cycle. Pots were watered two to five minutes, one to three times per day by drip irrigation to maintain adequate water status and fertilized with a solution of Peter’s Excel 15-5-15 NPK Cal-Mag Special (Hummert’s International, Earth City, Missouri, USA) at 80 ppm nitrogen (N) with every watering after plants reached first true leaf stage. Pots were organized into five randomized, complete blocks for statistical analysis. Each biochar treatment (0 or 4%) and tomato genotype combination had five replicates, and the full experiment was repeated in two independent trials. The first trial was from Dec 2014–Feb 2015 and the second from March–May 2015. In each trial, plants were harvested 8 weeks after planting and measured for shoot length and fresh weight. Days to flowering and number of open flowers were counted for the second trial only. Days to flowering was counted as number of days from germination to first open flowers.
Results were analyzed by three-way ANOVA with a general linear mixed model (PROC GLIMMIX) in SAS 9.4. Biochar treatment, genotype, and trial were included as fixed effects with all possible interactions between the three effects, and block was included as a random effect. Post-hoc tests were performed with Tukey’s honest significant differences test. No transformations were necessary to meet the homogeneity of variance and normality assumptions.
Germination in potting mix
In order to determine the effect of Premium biochar amendment on germination, individual sterile seeds of each of the four genotypes (H7996, M82, WV, and SP) were planted into pots in 36 pot flats containing either 1:1 peat/turface potting mix or 1:1 peat/turface amended with 4% Premium biochar by weight. Fifty-four seeds per treatment and genotype were planted. Days to germination was defined as the number of days to cotyledon expansion. Germination was measured once per day for 10 days. The germination experiment was fully replicated in four trials. Percent germination was calculated as follows:
Area under the germination progress curve (AUGPC) was calculated by the trapezoidal integration method (Campbell and Madden, 1990). Statistical analysis was performed in JMP12 to compare AUGPC values between Premium biochar-amended and un-amended pots within each species with a linear mixed model with biochar treatment as a fixed effect and trial as a random effect. The effect of biochar treatment was considered significantly different at p < 0.05.
Exogenous GA spray
To determine the effect of bioactive gibberellin (GA4) treatment on biochar-treated vs. untreated tomato plants, approximately 50 plants of each of the four genotypes were grown in +/− biochar potting mix in 36 pot flats. When plants were two weeks old, they were divided into two sets (between 12–27 individuals, depending on germination rates). Once per day for five days, one set was sprayed with 7.5 mg ml−1 GA4, while the other set was sprayed with water. Shoot length measurements were taken at the beginning (Day 1) and end of the experiment (Day 8), and shoot weights were also taken at the end (eight days after initial spray). The entire experiment was repeated four times. Shoot weight and shoot length after eight days were used for statistical analysis. Statistical analysis was performed using PROC GLIMMIX in SAS 9.4. Fixed effects included in the model were biochar treatment and GA4 treatment with their interaction, and trial was included as a random factor. Data were examined for homogeneity of variance and normality. Shoot weight and length values were square root transformed to meet the homogeneity of variance assumption. Differences in the biochar*GA4 interaction model effect were considered significant at p < 0.05.
Arabidopsis ga3ox1-3 mutant analysis
The ga3ox1-3 mutant was used for analysis38. This mutant is defective in Gibberellin 3-Oxidase 1 (At1g15550), which catalyzes the production of bioactive gibberellin GA4 during the vegetative growth stage38. ga3ox1-3 was obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (CS6943) and the homozygous mutant was confirmed using TDNA insertion PCR using primers from Mitchum et al. 2006.
Water extracts of Premium biochar were made by stirring 50 g of biochar in 1 L of ddH2O overnight at room temperature. After stirring, extract was filtered first using vacuum filtration with Whatman 42 filter paper to remove large particles, and then filter-sterilized with a 0.22 µM filter. Treated 1% agar plates were prepared by applying 2 mL of sterile ddH2O (control) or sterile biochar filtrate to the plate surface and allowing the liquid to sink into the plate. For Arabidopsis mutant growth assays on plates, approximately 30 sterile seeds each of WT (Col-0) and ga3ox1-3 were plated onto treated 1% agar plates in a single row and placed upright in a growth chamber set to 24 °C, 16-hour day and 8-hour night cycle and average of 80 μmol m−2 s−1 light. After eight days, plates were scanned and measured in ImageJ for hypocotyl length. The entire experiment was replicated twice. Statistical analysis was performed using PROC GLIMMIX in SAS 9.4. Fixed effects included in the model were biochar treatment, genotype, and trial with their interactions, and plate was included as a random factor. Hypocotyl length values were square root transformed to meet homogeneity of variance and normality assumptions.
References
Woods, W. I. & McCann, J. M. The anthropogenic origin and persistence of Amazonian dark earths. Yearb. Conf. Lat. Am. Geogr. 25, 7–14 (1999).
Marris, E. Putting the carbon back: black is the new green. Nature 442, 624–6 (2006).
Woolf, D., Amonette, J. E., Street-Perrott, F. A., Lehmann, J. & Joseph, S. Sustainable biochar to mitigate global climate change. Nat. Commun. 1, 56 (2010).
Biederman, L. A. & Harpole, W. S. Biochar and its effects on plant productivity and nutrient cycling: a meta-analysis. GCB Bioenergy 5, 202–214 (2013).
Marks, E. A. N., Alcañiz, J. M. & Domene, X. Unintended effects of biochars on short-term plant growth in a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 385, 87–105 (2014).
Sun, Z. et al. Effect of biochar on aerobic processes, enzyme activity, and crop yields in two sandy loam soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 50, 1087–1097 (2014).
Smider, B. & Singh, B. Agronomic performance of a high ash biochar in two contrasting soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 191, 99–107 (2014).
Borchard, N., Siemens, J., Ladd, B., Möller, A. & Amelung, W. Application of biochars to sandy and silty soil failed to increase maize yield under common agricultural practice. Soil Tillage Res. 144, 184–194 (2014).
Haider, G., Steffens, D., Moser, G., Müller, C. & Kammann, C. I. Biochar reduced nitrate leaching and improved soil moisture content without yield improvements in a four-year field study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 237, 80–94 (2015).
Nelissen, V. et al. Impact of a woody biochar on properties of a sandy loam soil and spring barley during a two-year field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 62, 65–78 (2015).
Butnan, S., Deenik, J. L., Toomsan, B., Antal, M. J. & Vityakon, P. Biochar characteristics and application rates affecting corn growth and properties of soils contrasting in texture and mineralogy. Geoderma 237–238, 105–116 (2015).
Carvalho, M. T. M. et al. Properties of a clay soil from 1.5 to 3.5 years after biochar application and the impact on rice yield. Geoderma 276, 7–18 (2016).
Egamberdieva, D., Wirth, S., Behrendt, U., Abd_Allah, E. F. & Berg, G. Biochar treatment resulted in a combined effect on soybean growth promotion and a shift in plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 7, 1–11 (2016).
Spokas, K. A. et al. Biochar: a synthesis of its agronomic impact beyond carbon sequestration. J. Environ. Qual. 41, 973–89 (2012).
Lehmann, J. et al. Biochar effects on soil biota – A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 1812–1836 (2011).
Elad, Y., Cytryn, E., Harel, Y. M., Lew, B. & Graber, E. R. The Biochar Effect: plant resistance to biotic stresses. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 50, 335–349 (2011).
Graber, E. R., Frenkel, O., Jaiswal, A. K. & Elad, Y. How may biochar influence severity of diseases caused by soilborne pathogens? Carbon Manag. 5, 169–183 (2014).
Shoaf, N., Hoagland, L. & Egel, D. S. Suppression of phytophthora blight in sweet pepper depends on biochar amendment and soil type. HortScience 51, 518–524 (2016).
Ebrahimi, N. et al. Traditional and new soil amendments reduce survival and reproduction of potato cyst nematodes, except for biochar. Appl. Soil Ecol. 107, 191–204 (2016).
Copley, T. R., Aliferis, K. A. & Jabaji, S. Maple bark biochar affects Rhizoctonia solani metabolism and increases damping-off severity. Phytopathology 105, 1334–1346 (2015).
Copley, T., Bayen, S. & Jabaji, S. Biochar amendment modifies expression of soybean and Rhizoctonia solani genes leading to increased severity of Rhizoctonia Foliar Blight. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 1–15 (2017).
Major, J., Rondon, M., Molina, D., Riha, S. J. & Lehmann, J. Maize yield and nutrition during 4 years after biochar application to a Colombian savanna oxisol. Plant Soil 333, 117–128 (2010).
Zhang, A. et al. Effects of biochar amendment on soil quality, crop yield and greenhouse gas emission in a Chinese rice paddy: A field study of 2 consecutive rice growing cycles. F. Crop. Res. 127, 153–160 (2012).
Dong, D. et al. Effects of biochar amendment on rice growth and nitrogen retention in a waterlogged paddy field. J. Soils Sediments 15, 153–162 (2014).
Olmo, M. et al. Wheat growth and yield responses to biochar addition under Mediterranean climate conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 50, 1177–1187 (2014).
Zhao, X., Wang, J., Wang, S. & Xing, G. Successive straw biochar application as a strategy to sequester carbon and improve fertility: A pot experiment with two rice/wheat rotations in paddy soil. Plant Soil 378, 279–294 (2014).
Liang, F., Li, G., Lin, Q. & Zhao, X. Crop yield and soil properties in the first 3 years after biochar application to a calcareous soil. J. Integr. Agric. 13, 525–532 (2014).
Rogovska, N., Laird, D. A., Rathke, S. J. & Karlen, D. L. Biochar impact on Midwestern Mollisols and maize nutrient availability. Geoderma 230–231, 340–347 (2014).
Martinsen, V. et al. Farmer-led maize biochar trials: Effect on crop yield and soil nutrients under conservation farming. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 177, 681–695 (2014).
Prendergast-Miller, M. T., Duvall, M. & Sohi, S. P. Biochar-root interactions are mediated by biochar nutrient content and impacts on soil nutrient availability. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 65, 173–185 (2014).
Solaiman, Z. M., Murphy, D. V. & Abbott, L. K. Biochars influence seed germination and early growth of seedlings. Plant Soil 353, 273–287 (2012).
Gascó, G., Cely, P., Plaza, C. & Méndez, A. Relation between biochar properties and effects on seed germination and plant development. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 32, 237–247 (2017).
Olmo, M., Villar, R., Salazar, P. & Alburquerque, J. A. Changes in soil nutrient availability explain biochar’s impact on wheat root development. Plant Soil 399, 333–343 (2016).
Abiven, S., Hund, A., Martinsen, V. & Cornelissen, G. Biochar amendment increases maize root surface areas and branching: a shovelomics study in Zambia. Plant Soil 395, 45–55 (2015).
Viger, M., Hancock, R. D., Miglietta, F. & Taylor, G. More plant growth but less plant defence? First global gene expression data for plants grown in soil amended with biochar. GCB Bioenergy 7, 658–672 (2014).
Kochanek, J., Long, R. L., Lisle, A. T. & Flematti, G. R. Karrikins identified in biochars indicate post-fire chemical cues can influence community diversity and plant development. PLoS One 11, e0161234 (2016).
Nelson, D. C. et al. Karrikins discovered in smoke trigger Arabidopsis seed germination by a mechanism requiring gibberellic acid synthesis and light. Plant Physiol. 149, 863–873 (2009).
Mitchum, M. G. et al. Distinct and overlapping roles of two gibberellin 3-oxidases in Arabidopsis development. Plant J. 45, 804–818 (2006).
Meller Harel, Y. et al. Biochar mediates systemic response of strawberry to foliar fungal pathogens. Plant Soil 357, 245–257 (2012).
Jaiswal, A. K., Elad, Y., Graber, E. R. & Frenkel, O. Rhizoctonia solani suppression and plant growth promotion in cucumber as affected by biochar pyrolysis temperature, feedstock and concentration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 69, 110–118 (2014).
Jaiswal, A. K., Frenkel, O., Elad, Y., Lew, B. & Graber, E. R. Non-monotonic influence of biochar dose on bean seedling growth and susceptibility to Rhizoctonia solani: the ‘Shifted Rmax-Effect’. Plant Soil 395, 125–140 (2015).
Backer, R. G. M., Schwinghamer, T. D., Whalen, J. K., Seguin, P. & Smith, D. L. Crop yield and SOC responses to biochar application were dependent on soil texture and crop type in southern Quebec, Canada. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 179, 399–408 (2016).
Zwart, D. C. & Kim, S. H. Biochar amendment increases resistance to stem lesions caused by Phytophthora spp. in tree seedlings. HortScience 47, 1736–1740 (2012).
Free, H. F., McGill, C. R., Rowarth, J. S. & Hedley, M. J. The effect of biochars on maize (Zea mays) germination. New Zeal. J. Agric. Res. 53, 1–4 (2017).
Gravel, V., Dorais, M. & Ménard, C. Organic potted plants amended with biochar: its effect on growth and Pythium colonization. Can. J. Plant Sci. 93, 1217–1227 (2013).
Bargmann, I., Rillig, M. C., Buss, W., Kruse, A. & Kuecke, M. Hydrochar and Biochar Effects on Germination of Spring Barley. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 199, 360–373 (2013).
Jones, D. L., Rousk, J., Edwards-Jones, G., DeLuca, T. H. & Murphy, D. V. Biochar-mediated changes in soil quality and plant growth in a three year field trial. Soil Biol. Biochem. 45, 113–124 (2012).
De Tender, C. A. et al. Biological, physicochemical and plant health responses in lettuce and strawberry in soil or peat amended with biochar. Appl. Soil Ecol. 107, 1–12 (2016).
Lin, Y., Munroe, P., Joseph, S., Henderson, R. & Ziolkowski, A. Water extractable organic carbon in untreated and chemical treated biochars. Chemosphere 87, 151–157 (2012).
Graber, E. R., Tsechansky, L., Mayzlish-Gati, E., Shema, R. & Koltai, H. A humic substances product extracted from biochar reduces Arabidopsis root hair density and length under P-sufficient and P-starvation conditions. Plant Soil 395, 21–30 (2015).
Nardi, S. et al. A low molecular weight humic fraction on nitrate uptake and protein synthesis in maize seedlings. Soil Biol. Biochem. 32, 415–419 (2000).
Kolton, M. et al. Impact of biochar application to soil on the root-associated bacterial community structure of fully developed greenhouse pepper plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 4924–30 (2011).
Kolton, M., Graber, E. R., Tsehansky, L., Elad, Y. & Cytryn, E. Biochar-stimulated plant performance is strongly linked to microbial diversity and metabolic potential in the rhizosphere. New Phytol. 213, 1393–1404 (2016).
Fox, A. et al. Miscanthus biochar promotes growth of spring barley and shifts bacterial community structures including phosphorus and sulfur mobilizing bacteria. Pedobiologia (Jena). 59, 195–202 (2016).
Kim, B.-S., French, E. A., Caldwell, D., Harrington, E. J. & Iyer-Pascuzzi, A. S. Bacterial wilt disease: host resistance and pathogen virulence mechanisms. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2016.02.007 (2016).
Eshed, Y. & Zamir, D. An introgression line population of Lycopersicon pennellii in the cultivated tomato enables the identification and fine mapping of yield- associated QTL. Genetics 141, 1147–1162 (1995).
Thoquet, P. et al. Quantitative trait loci determining resistance to bacterial wilt in tomato cultivar Hawaii7996. Molecular plant-microbe interactions: MPMI 9, 826–836 (1996).
Bolger, A. et al. The genome of the stress-tolerant wild tomato species Solanum pennellii. Nat. Genet. 46, 1034–1038 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We thank Deb Lubelski, Ron Steiner, and Rob Eddy for their greenhouse growing expertise, Connie Bonham and Karl Wood for help with karrikin identification, Purdue Genomics Core, Pete Pascuzzi, and members of the Iyer-Pascuzzi Lab for their invaluable comments on this work. This work was funded by Purdue University and a NSF Graduate Student Fellowship DGE-1333468 to E.F.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.F. and A.I.P. designed experiments and wrote the paper, E.F. performed experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
French, E., Iyer-Pascuzzi, A.S. A role for the gibberellin pathway in biochar-mediated growth promotion. Sci Rep 8, 5389 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23677-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23677-9
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Mitigation of cadmium-induced stress in maize via synergistic application of biochar and gibberellic acid to enhance morpho-physiological and biochemical traits
BMC Plant Biology (2024)
-
Exploring the recuperative potential of brassinosteroids and nano-biochar on growth, physiology, and yield of wheat under drought stress
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Synergistic effect of biochar-based compounds from vegetable wastes and gibberellic acid on wheat growth under salinity stress
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Biochar from grape pomace, a waste of vitivinicultural origin, is effective for root-knot nematode control
Biochar (2023)
-
Interactive Effects of Soil and Foliar-Applied Nanobiochar on Growth, Metabolites, and Nutrient Composition in Daucus carota
Journal of Plant Growth Regulation (2023)