Abstract
Background
Norcantharidin, a modified pure compound from blister beetles, was previously demonstrated to induce apoptosis of cancer cells. This study investigated its anti-cancer activity in prostate cancer cells and the mechanisms involved.
Methods
Two human prostate cancer cell lines, 22Rv1 and Du145, were treated with norcantharidin at concentrations ranging from 3 to 30 μg/ml. Cytotoxic effect of norcantharidin was determined by use of the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-yl)-diphenyl tetrazoliumbromide (MTT) assay. The effects of apoptosis were evaluated by cell death assay, Caspase-3, -8, -9 activity and cytochrome c release. The apoptotic related protein expressions (Bcl-2 family and inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) were determined using western blotting.
Results
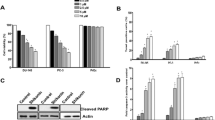
An MTT assay revealed that norcantharidin induced cytotoxicity against both prostate cancer cells in dose- and time-dependent manners. Treatment with norcantharidin at 3 μg/ml or higher significantly increased oligonucleosomal formation with concomitant appearance of PARP cleavage, implicating the induction of apoptosis. Norcantharidin intrinsically elevated cytosolic cytochrome c levels and activated caspase-3, -8, and -9. Extrinsically, it upregulated the expression of not only the death receptors Fas and DR5 in 22Rv1 cells, but also of RIP and TRADD adaptor proteins in Du145 cells. Mechanistically, norcantharidin increased ratios of pro-/anti-apoptotic proteins and decreased expression of IAP family member proteins, including cIAP1 and survivin, regardless of the distinct status of androgen receptor expression in both cells.
Conclusions
Norcantharidin exhibited cytotoxicity against 22Rv1 and Du145 prostate cancer cells by inducing both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways and could thus potentially be a remedy for prostate cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 2014;64:9–29.
Ganju A, Yallapu MM, Khan S, Behrman SW, Chauhan SC, Jaggi M. Nanoways to overcome docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer. Drug Resist Updat 2014; 17: 13–23.
Wang GS. Medical uses of mylabris in ancient China and recent studies. J Ethnopharmacol 1989;26:147–62.
Kok SH, Hong CY, Kuo MY, Lee CH, Lee JJ, Lou IU, et al. Comparisons of norcantharidin cytotoxic effects on oral cancer cells and normal buccal keratinocytes. Oral Oncol 2003;39:19–26.
Yang EB, Tang WY, Zhang K, Cheng LY, Mack PO. Norcantharidin inhibits growth of human HepG2 cell-transplanted tumor in nude mice and prolongs host survival. Cancer Lett 1997;117:93–8.
Chen YN, Chen JC, Yin SC, Wang GS, Tsauer W, Hsu SF, et al. Effector mechanisms of norcantharidin-induced mitotic arrest and apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. Int J Cancer 2002;100:158–65.
Yeh CH, Yang YY, Huang YF, Chow KC, Chen MF. Induction of apoptosis in human Hep3B hepatoma cells by norcantharidin through a p53 independent pathway via TRAIL/DR5 signal transduction. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:676–82.
Zhang S, Li G, Ma X, Wang Y, Liu G, Feng L, et al. Norcantharidin enhances ABT-737-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by transcriptional repression of Mcl-1. Cell Signal 2012;24:1803–9.
Liao HF, Chen YJ, Chou CH, Wang FW, Kuo CD. Norcantharidin induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits progression of human leukemic Jurkat T cells through mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated regulation of interleukin-2 production. Toxicol In Vitro 2011;25:206–12.
Peng F, Wei YQ, Tian L, Yang L, Zhao X, Lu Y, et al. Induction of apoptosis by norcantharidin in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines: involvement of the CD95 receptor/ligand. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2002;128:223–30.
Chen YJ, Kuo CD, Tsai YM, Yu CC, Wang GS, Liao HF. Norcantharidin induces anoikis through Jun-N-terminal kinase activation in CT26 colorectal cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 2008;19:55–64.
Yang PY, Chen MF, Tsai CH, Hu DN, Chang FR, Wu YC. Involvement of caspase and MAPK activities in norcantharidin-induced colorectal cancer cell apoptosis. Toxicol In Vitro 2010;24:766–75.
An WW, Wang MW, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T. Norcantharidin induces human melanoma A375-S2 cell apoptosis through mitochondrial and caspase pathways. J Korean Med Sci 2004;19:560–6.
An WW, Wang WM, Tashiro SI, Onodera S, Ikejima T. Mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent apoptosis in norcan-tharidin-treated A375-S2 cells is proceeded by the activation of protein kinase C. Chin Med J 2005;118:198–203.
Hong CY, Huang SC, Lin SK, Lee JJ, Chueh LL, Lee CH, et al. Norcantharidin-induced post-G(2)/M apoptosis is dependent on wild-type p53 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000;276:278–85.
Fan YZ, Zhao ZM, Fu JY, Chen CQ, Sun W. Norcantharidin inhibits growth of human gallbladder carcinoma xenografted tumors in nude mice by inducing apoptosis and blocking the cell cycle in vivo. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2010;9:414–22.
Chen S, Wan P, Ding W, Li F, He C, Chen P, et al. Norcantharidin inhibits DNA replication and induces mitotic catastrophe by degrading initiation protein Cdc6. Int J Mol Med 2013;32:43–50.
Shen B, He PJ, Shao CL. Norcantharidin induced DU145 cell apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and energy depletion. PLoS One 2013;8:e84610.
Xiao W, Dai B, Zhu Y, Ye D. Norcantharidin induces autophagy-related prostate cancer cell death through Beclin-1 upregulation by miR-129-5p suppression. Tumour Biol 2015;36:1–6.
Chen YJ, Shieh CJ, Tsai TH, Kuo CD, Ho LT, Liu TY, et al. Inhibitory effect of norcantharidin, a derivative compound from blister beetles, on tumor invasion and metastasis in CT26 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs 2005;16:293–9.
Cimmino F, Scoppettuolo MN, Carotenuto M, De Antonellis P, Dato VD, De Vita G, et al. Norcantharidin impairs medulloblastoma growth by inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Neurooncol 2011;106:59–70.
Chen YJ, Tsai YM, Kuo CD, Ku KL, Shie HS, Liao HF. Norcantharidin is a small-molecule synthetic compound with anti-angiogenesis effect. Life Sci 2009;85:642–51.
An WW, Gong XF, Wang MW, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T. Norcantharidin induces apoptosis in HeLa cells through caspase, MAPK, and mitochondrial pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2004;25:1502–8.
Chen YJ, Chang WM, Liu YW, Lee CY, Jang YH, Kuo CD, et al. A small-molecule metastasis inhibitor, norcantharidin, downregulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by inhibiting Sp1 transcriptional activity in colorectal cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact 2009;181(3):440–6.
Yang PY, Chen MF, Kao YH, Hu DN, Chang FR, Wu YC. Norcantharidin induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells: involvement of activities of mitogen activated protein kinases and signal transducers and activators of transcription. Toxicol In Vitro 2011;25:699–707.
Chen YJ, Kuo CD, Chen SH, Chen WJ, Huang WC, Chao KS, et al. Small-molecule synthetic compound norcantharidin reverses multi-drug resistance by regulating Sonic hedgehog signaling in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One 2012;7:e37006.
Zhu ML, Horbinski CM, Garzotto M, Qian DZ, Beer TM, Kyprianou N. Tubulintargeting chemotherapy impairs androgen receptor activity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2010;70:7992–8002.
Shankar S, Chen Q, Sarva K, Siddiqui I, Srivastava RK. Curcumin enhances the apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL in prostate cancer cells: molecular mechanisms of apoptosis, migration and angiogenesis. J Mol Signal 2007;2:10.
Hahm ER, Arlotti JA, Marynowski SW, Singh SV. Honokiol, a constituent of oriental medicinal herb magnolia officinalis, inhibits growth of PC-3 xenografts in vivo in association with apoptosis induction. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1248–57.
Liao HF, Su SL, Chen YJ, Chou CH, Kuo CD. Norcantharidin preferentially induces apoptosis in human leukemic Jurkat cells without affecting viability of normal blood mononuclear cells. Food Chem Toxicol 2007;45:1678–87.
Chen YN, Cheng CC, Chen JC, Tsauer W, Hsu SL. Norcantharidin-induced apoptosis is via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase signaling pathways in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Br J Pharmacol 2003;140:461–70.
Lv H, Li Y, Du H, Fang J, Song X, Zhang J. The synthetic compound norcantharidin induced apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma in Vivo and in vitro through the PI3K-Akt-NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013;2013:461487.
Yu CC, Ko FY, Yu CS, Lin CC, Huang YP, Yang JS, et al. Norcantharidin triggers cell death and DNA damage through S-phase arrest and ROS-modulated apoptotic pathways in TSGH 8301 human urinary bladder carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 2012;41:1050–60.
Haupt S, Berger M, Goldberg Z, Haupt Y. Apoptosis — the p53 network. J Cell Sci 2003;116:4077–85.
Sun SY, Yue P, Shroot B, Hong WK, Lotan R. Implication of c-Myc in apoptosis induced by the retinoid CD437 in human lung carcinoma cells. Oncogene 1999;18:3894–901.
Sun SY, Yue P, Hong WK, Lotan R. Induction of Fas expression and augmentation of Fas/Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis by the synthetic retinoid CD437 in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2000;60:6537–43.
Sun SY, Yue P, Chen X, Hong WK, Lotan R. The synthetic retinoid CD437 selectively induces apoptosis in human lung cancer cells while sparing normal human lung epithelial cells. Cancer Res 2002;62:2430–6.
Kok SH, Cheng SJ, Hong CY, Lee JJ, Lin SK, Kuo YS, et al. Norcantharidin-induced apoptosis in oral cancer cells is associated with an increase of proapoptotic to antiapoptotic protein ratio. Cancer Lett 2005;217:43–52.
Huang Y, Liu Q, Liu K, Yagasaki K, Zhang G. Suppression of growth of highly-metastatic human breast cancer cells by norcantharidin and its mechanisms of action. Cytotechnology 2009.
Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD. IAPs: what’s in a name. Mol Cell 2008;30:123–35.
Kelly RJ, Lopez-Chavez A, Citrin D, Janik JE, Morris JC. Impacting tumor cell-fate by targeting the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin. Mol Cancer 2011;10:35.
Fan YZ, Fu JY, Zhao ZM, Chen CQ. Inhibitory effect of norcantharidin on the growth of human gallbladder carcinoma GBC-SD cells in vitro. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2007;6:72–80.
Conte D, Holcik M, Lefebvre CA, Lacasse E, Picketts DJ, Wright KE, et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis protein cIAP2 is essential for lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage survival. Mol Cell Biol 2006;26:699–708.
Tse BW, Jovanovic L, Nelson CC, de Souza P, Power CA, Russell PJ. From bench to bedside: immunotherapy for prostate cancer. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:981434. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/981434.
Hsieh CH, Chao KS, Liao HF, Chen YJ. Norcantharidin, derivative of cantharidin, for cancer stem cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013;2013:838651. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/838651.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, PY., Hu, DN., Kao, YH. et al. Norcantharidin induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Pharmacol. Rep 68, 874–880 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2016.04.010
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2016.04.010