Abstract
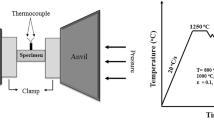
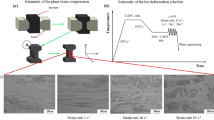
The compressive deformation behaviors of 300M high strength steel were investigated over a wide range of temperatures (850–1200 °C) and strain rates (0.001–10 s−1) on a Gleeble-3800 thermo-mechanical simulator. The measured flow stress was modified by the corrections of the friction and the temperature compensations, which nicely reflect negative effects of the friction and temperature on the flow stress. The corrected stress-strain curves were the dynamic recrystallization type on the conditions of higher deformation temperature and lower strain rate. Flow stress increases with the increase of strain rate at the same deformation temperature and strain. By contrast, flow stress decreases with the increase of temperature at the same strain rate and strain. Dependence of the peak stress on temperature and strain rate for 300M steel is described by means of the conventional hyperbolic sine equation. By regression analysis, the activation energy (Q) in the whole range of deformation temperature is determined to be 367.562 kJ/mol. The effects of the temperature and the strain rate on microstructural evolution are obvious. With the increase of the deformation temperature and the decrease of the strain rate, the original austenite grain sizes of 300M steel increase. At the same time, the corrected flow stress curves more accurately determine the evolution of the microstructure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Malakondaiah, M. Srinivas, P. Rama Rao, Prog. Mater. Sci. 42 (1997) 209–242.
J. L. Youngblood, M. Raghavan, Metall. Trans. A 8 (1977) 1439–1448.
S. S. Zhang, M. Q. Li, Y. G. Liu, J. Luo, T. Q. Liu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528 (2011) 4967–4972.
M. Sun, K. Xiao, C. F. Dong, X. G. Li, Acta Metall. Sin. 23 (2010) 301–311.
J. Y. Zhong, M. Sun, D. B. Liu, X. G. Li, T. Q. Liu, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 17 (2010) 282–289.
T. E. Pistochini, M. R. Hill, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 34 (2011) 521–533.
G. D. Zhang, X. Q. Yang, X. L. He, J. W. Li, H. C. Hu, Mater. Des. 45 (2013) 56–66.
T. Skiba, B. Baufeld, O. Van der Biest, P. I. Mech. Eng. B-J. Eng. 225 (2011) 831–839.
U. S. Dixit, S. N. Joshi, J. P. Davim, Mater. Des. 32 (2011) 3665–3670.
Y. C. Lin, Y. C. Xia, X. M. Chen, M. S. Chen, Comp. Mater. Sci. 50 (2010) 227–233.
R. W. Evans, P. J. Scharning, Mater. Sci. Technol. 17 (2001) 995–1004.
B. Roebuck, J. D. Lord, M. Brooks, M. S. Loveday, C. M. Sellers, R. W. Ewans, Mater. High Temp. 23 (2006) 59–83.
R. Ebrahimi, A. Najafizadeh, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 152 (2004) 136–143.
L. Li, J. Zhou, J. Duszczyk, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 172 (2006) 372–380.
R. L. Goetz, S. L. Semiatin, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 10 (2001) 710–717.
P. Dadras, J. F. Thomas Jr., Metall. Trans. A 12 (1981) 1867–1876.
C. M. Sellars, W. J. McTegart, Acta Metall. 14 (1966) 1136–1138.
C. Zener, J. H. Hollomon, J. Appl. Phys. 15 (1944) 22–32.
B. F. Guo, H. P. Ji, X. G. Liu, L. Gao, R. M. Dong, M. Jin, Q. H. Zhang, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 21 (2012) 1455–1461.
L. M. Wang, H. Zhang, N. Liu, Z. D. Liu, G. Yang, L. Lu, Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 33 (2012) 44–49.
A. Sanrutsadskorn, V. Uthaisangsuk, S. Suranuntchai, B. Thos-satheppitak, Appl. Mech. Mater. 249–250 (2013) 863–869.
S. Z. Huang, Y. Li, C. X. Wang, X. M. Liu, Hot Working Technol. 39 (2010) 25–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by Technology Major Projects of “High-end CNC Machine Tools and Basic Manufacturing Equipment” (2012ZX04010081); Natural Science Research Foundation Program for Distinguished Young Scholars in Higher Education Institutions of Hebei Province of China (Y2012034)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Rs., Guo, Bf., Liu, Xg. et al. Flow Stress Behaviors and Microstructure Evolution of 300M High Strength Steel Under Isothermal Compression. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21, 1116–1123 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60192-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60192-8