Abstract
Purpose
The present study investigates the efficacy of Photobiomodulation (PBM) and Vitamin B Complex (VBC) to relieve pain, both in separately and combined (PBM and VBC).
Methods
Rats with chronic constriction injury of the right infraorbital nerve (CCI-IoN) or Sham surgery were used. PBM was administered at a wavelength of 904 nm and energy density of 6.23 J/cm2 and VBC (containing B1, B6 and B12) subcutaneously, both separately and combined. Behavioral tests were performed to assess mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity before and after CCI and after PBM, VBC, or PBM + VBC. The expression of inflammatory proteins in the trigeminal ganglion and the immunohistochemical alterations of Periaqueductal Gray (PAG) astrocytes and microglia were examined following CCI and treatments.
Results
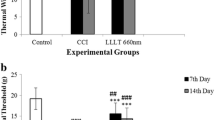
All testeds treatments reversed the painful behavior. The decrease in pain was accompanied by a decrease of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP), a specific astrocytic marker, and Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1), a marker of microglia, and decreased expression of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), Substance P, and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) induced by CCI-IoN in PAG and Trigeminal ganglion. Furthermore, both treatments showed a higher expression of Cannabinoid-type 1 (CB1) receptor in the trigeminal ganglion compared to CCI-IoN rats. Our results show that no difference was observed between groups.
Conclusion
We showed that PBM or VBC regulates neuroinflammation and reduces inflammatory protein expression. However, the combination of PBM and VBC did not enhance the effectiveness of both therapies alone.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Talbot, K., Madden, V. J., Jones, S. L., & Moseley, G. L. (2019). The sensory and affective components of pain: Are they differentially modifiable dimensions or inseparable aspects of a unitary experience? A systematic review. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 123(2), e263–e272.
Maarbjerg, S., Di Stefano, G., Bendtsen, L., & Cruccu, G. (2017). Trigeminal neuralgia—Diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia, 37(7), 648–657. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102416687280
Merrill, R. L. (2007). Central mechanisms of orofacial pain. Dental Clinics of North America, 51(1), 45–59.
Martins, D. O., Marques, D. P., Venega, R. A. G., & Chacur, M. (2020). Photobiomodulation and B vitamins administration produces antinociception in an orofacial pain model through the modulation of glial cells and cytokines expression. Brain, Behavior, & Immunity—Health. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100040
Coelho, S. C., Bastos-Pereira, A. L., Fraga, D., Chichorro, J. G., & Zampronio, A. R. (2014). Etanercept reduces thermal and mechanical orofacial hyperalgesia following inflammation and neuropathic injury. European Journal of Pain, 18(7), 957–967. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00441.x
Urano, H., Ara, T., Fujinami, Y., & Hiraoka, B. Y. (2012). Aberrant TRPV1 expression in heat hyperalgesia associated with trigeminal neuropathic pain. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 9(8), 690–697. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.4706
Shinoda, M., Kawashima, K., Ozaki, N., Asai, H., Nagamine, K., & Sugiura, Y. (2007). P2X3 receptor mediates heat hyperalgesia in a rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain. The Journal of Pain, 8(7), 588–597.
Lemos, L., Alegria, C., Oliveira, J., Machado, A., Oliveira, P., & Almeida, A. (2011). Pharmacological versus microvascular decompression approaches for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: Clinical outcomes and direct costs. Journal of Pain Research, 4, 233–244. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S20555
Lazzaroni, M., & Bianchi Porro, G. (2004). Gastrointestinal side-effects of traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and new formulations. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 20(Suppl 2), 48–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02037.x
De Toledo, I. P., Conti Réus, J., Fernandes, M., Porporatti, A. L., Peres, M. A., Takaschima, A., Linhares, M. N., Guerra, E., & De Luca Canto, G. (2016). Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review. The Journal of the American Dental Association, 147(7), 570–576.
Holland, M., Noeller, J., Buatti, J., He, W., Shivapour, E. T., & Hitchon, P. W. (2015). The cost-effectiveness of surgery for trigeminal neuralgia in surgically naïve patients: A retrospective study. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 137, 34–37.
Martins, D. O., Santos, F. M., Britto, L. R., Lemos, J. B., & Chacur, M. (2017). Neurochemical effects of photobiostimulation in the trigeminal ganglion after inferior alveolar nerve injury. Journal of biological regulators and homeostatic agents, 31(1), 147–152.
Wu, S., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, W., Shao, S., Shen, H., Zhu, L., Ye, P., Svensson, P., & Wang, K. (2018). Effect of low-level laser therapy on tooth-related pain and somatosensory function evoked by orthodontic treatment. International Journal of Oral Science, 10(3), 018–0023.
de Freitas Rodrigues, A., de Oliveira Martins, D., Chacur, M., & Luz, J. G. C. (2020). The effectiveness of photobiomodulation in the management of temporomandibular pain sensitivity in rats: Behavioral and neurochemical effects. Lasers in Medical Science, 35(2), 447–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-019-02842-0
Mazuqueli Pereira, E. S. B., Basting, R. T., Abdalla, H. B., Garcez, A. S., Napimoga, M. H., & Clemente-Napimoga, J. T. (2021). Photobiomodulation inhibits inflammation in the temporomandibular joint of rats. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 222(112281), 5.
Kalhori, K. A. M., Vahdatinia, F., Jamalpour, M. R., Vescovi, P., Fornaini, C., Merigo, E., & Fekrazad, R. (2019). Photobiomodulation in oral medicine. Photobiomodulation, Photomedicine, and Laser Surgery, 37(12), 837–861.
Han, D. S., Lee, C. H., Shieh, Y. D., & Chen, C. C. (2019). Involvement of substance P in the analgesic effect of low-level laser therapy in a mouse model of chronic widespread muscle pain. Pain Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pnz056
de Oliveira Martins, D., Martinez dos Santos, F., Evany de Oliveira, M., de Britto, L. R., Benedito Dias Lemos, J., & Chacur, M. (2013). Laser therapy and pain-related behavior after injury of the inferior alveolar nerve: Possible involvement of neurotrophins. Journal of Neurotrauma, 30(6), 480–486. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2012.2603
Martins, D. O., Dos Santos, F. M., Ciena, A. P., Watanabe, I. S., de Britto, L. R., Lemos, J. B., & Chacur, M. (2017). Neuropeptide expression and morphometric differences in crushed alveolar inferior nerve of rats: Effects of photobiomodulation. Lasers in Medical Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2181-2
Kopruszinski, C. M., Reis, R. C., & Chichorro, J. G. (2012). B vitamins relieve neuropathic pain behaviors induced by infraorbital nerve constriction in rats. Life Sciences, 91(23–24), 1187–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2012.08.025
Yu, C. Z., Liu, Y. P., Liu, S., Yan, M., Hu, S. J., & Song, X. J. (2014). Systematic administration of B vitamins attenuates neuropathic hyperalgesia and reduces spinal neuron injury following temporary spinal cord ischaemia in rats. European Journal of Pain, 18(1), 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00390.x
Caram-Salas, N. L., Reyes-Garcia, G., Medina-Santillan, R., & Granados-Soto, V. (2006). Thiamine and cyanocobalamin relieve neuropathic pain in rats: Synergy with dexamethasone. Pharmacology, 77(2), 53–62. https://doi.org/10.1159/000092643
Zeng, X., Zhang, L., Sun, L., Zhang, D., Zhao, H., Jia, J., & Wang, W. (2013). Recovery from rat sciatic nerve injury in vivo through the use of differentiated MDSCs in vitro. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 5(1), 193–196. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2012.785
Levin, O. S., & Moseikin, I. A. (2009). Vitamin B complex (milgamma) in the treatment of vertebrogenic lumbosacral radiculopathy. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S. Korsakova, 109(10), 30–35.
Buljubašić, R., Vucicevic Boras, V., A. L., T, K., A, K., Vidović Juras, D., & V. Brailo. (2018). The effectiveness of low level laser therapy and vitamin B injections in patients with mental paraesthesia after third molar surgery.
Abdel-Alim, H. M., Abdel-Dayem, H., Mustafa, Z. A., Bayoumi, A., Jan, A., & Jadu, F. (2015). A comparative study of the effectiveness of immediate versus delayed photobiomodulation therapy in reducing the severity of postoperative inflammatory complications. Photomedicine and Laser Surgery, 33(9), 447–451.
Leung, Y. Y. (2019). Management and prevention of third molar surgery-related trigeminal nerve injury: Time for a rethink. Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, 45(5), 233–240.
Zimmermann, M. (1983). Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain, 16(2), 109–110.
Chichorro, J. G., Zampronio, A. R., Souza, G. E., & Rae, G. A. (2006). Orofacial cold hyperalgesia due to infraorbital nerve constriction injury in rats: Reversal by endothelin receptor antagonists but not non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Pain, 123(1–2), 64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2006.02.010
Reinagel, P. (2018). Training rats using water rewards without water restriction. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00084
Neubert, J. K., Widmer, C. G., Malphurs, W., Rossi, H. L., Vierck, C. J., Jr., & Caudle, R. M. (2005). Use of a novel thermal operant behavioral assay for characterization of orofacial pain sensitivity. Pain, 116(3), 386–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2005.05.011
Cha, M., Kohan, K. J., Zuo, X., Ling, J. X., & Gu, J. G. (2012). Assessment of chronic trigeminal neuropathic pain by the orofacial operant test in rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 234(1), 82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.06.020
Bai, S. S., Mo, S. Y., Xu, X. X., Liu, Y., Xie, Q. F., & Cao, Y. (2020). Characteristics of orofacial operant test for orofacial pain sensitivity caused by occlusal interference in rats. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 52(1), 51–57.
Ang, C. D., Alviar, M. J., Dans, A. L., Bautista-Velez, G. G., Villaruz-Sulit, M. V., Tan, J. J., Co, H. U., Bautista, M. R., & Roxas, A. A. (2008). Vitamin B for treating peripheral neuropathy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004573.pub3
Wang, Z. B., Gan, Q., Rupert, R. L., Zeng, Y. M., & Song, X. J. (2005). Thiamine, pyridoxine, cyanocobalamin and their combination inhibit thermal, but not mechanical hyperalgesia in rats with primary sensory neuron injury. Pain, 114(1–2), 266–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2004.12.027
Jolivalt, C. G., Mizisin, L. M., Nelson, A., Cunha, J. M., Ramos, K. M., Bonke, D., & Calcutt, N. A. (2009). B vitamins alleviate indices of neuropathic pain in diabetic rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 612(1–3), 41–47.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Paxinos, G. A., & Watson, C. (2013). The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates (7th ed., p. 472). Academic Press.
Snedecor, G. W., Sokal, R. R., & Rohlf, F. J. (1946) Statistical methods biometry, 4 edn. In: Ames, (ed.). W.H. Freeman & Co., Owa State University Pres.
Porreca, F., & Navratilova, E. (2017). Reward, motivation, and emotion of pain and its relief. Pain, 158(Suppl 1), S43–S49. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000798
Matsuka, Y., Ono, T., Iwase, H., Mitrirattanakul, S., Omoto, K. S., Cho, T., Lam, Y. Y., Snyder, B., & Spigelman, I. (2008). Altered ATP release and metabolism in dorsal root ganglia of neuropathic rats. Molecular Pain, 4, 66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-4-66
Sacerdote, P., Franchi, S., Trovato, A. E., Valsecchi, A. E., Panerai, A. E., & Colleoni, M. (2008). Transient early expression of TNF-α in sciatic nerve and dorsal root ganglia in a mouse model of painful peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience Letters, 436(2), 210–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2008.03.023
González-Ramírez, R., Chen, Y., Liedtke, W. B., & Morales-Lázaro, S. L. (2017). TRP channels and pain. In T. L. R. Emir (Ed.), Neurobiology of TRP channels (2nd ed.). CRC Press/Taylor & Francis.
Zieglgänsberger, W. (2019). Substance P and pain chronicity. Cell and Tissue Research, 375(1), 227–241.
Zhang, H., Cang, C. L., Kawasaki, Y., Liang, L. L., Zhang, Y. Q., Ji, R. R., & Zhao, Z. Q. (2007). Neurokinin-1 receptor enhances TRPV1 activity in primary sensory neurons via PKCepsilon: A novel pathway for heat hyperalgesia. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(44), 12067–12077. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0496-07.2007
Bridges, D., Ahmad, K., & Rice, A. S. (2001). The synthetic cannabinoid WIN55,212–2 attenuates hyperalgesia and allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. British Journal of Pharmacology, 133(4), 586–594.
Tsou, K., Brown, S., Sañudo-Peña, M. C., Mackie, K., & Walker, J. M. (1998). Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience, 83(2), 393–411.
Ahluwalia, J., Urban, L., Bevan, S., & Nagy, I. (2003). Anandamide regulates neuropeptide release from capsaicin-sensitive primary sensory neurons by activating both the cannabinoid 1 receptor and the vanilloid receptor 1 in vitro. European Journal of Neuroscience, 17(12), 2611–2618.
Németh, J., Helyes, Z., Thán, M., Jakab, B., Pintér, E., & Szolcsányi, J. (2003). Concentration-dependent dual effect of anandamide on sensory neuropeptide release from isolated rat tracheae. Neuroscience Letters, 336(2), 89–92.
Linley, J. E., Ooi, L., Pettinger, L., Kirton, H., Boyle, J. P., Peers, C., & Gamper, N. (2012). Reactive oxygen species are second messengers of neurokinin signaling in peripheral sensory neurons. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(24), E1578–E1586. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1201544109
Volterra, A., & Meldolesi, J. (2005). Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: The revolution continues. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 6(8), 626–640. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1722
Mayer, D. J., & Liebeskind, J. C. (1974). Pain reduction by focal electrical stimulation of the brain: An anatomical and behavioral analysis. Brain Research, 68(1), 73–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(74)90534-4
Basbaum, A. I., & Fields, H. L. (1978). Endogenous pain control mechanisms: Review and hypothesis. Annals of Neurology, 4(5), 451–462. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410040511
Giardini, A. C., Dos Santos, F. M., da Silva, J. T., de Oliveira, M. E., Martins, D. O., & Chacur, M. (2017). Neural Mobilization treatment decreases glial cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the central nervous system in rats with neuropathic pain induced by CCI in rats. Pain Research & Management, 2017, 7429761. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7429761
Dubovy, P., Klusakova, I., Hradilova-Svizenska, I., Joukal, M., & Boadas-Vaello, P. (2018). Activation of astrocytes and microglial cells and CCL2/CCR2 upregulation in the dorsolateral and ventrolateral nuclei of periaqueductal gray and rostral ventromedial medulla following different types of sciatic nerve injury. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 12, 40. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00040
Becker, S., Gandhi, W., & Schweinhardt, P. (2012). Cerebral interactions of pain and reward and their relevance for chronic pain. Neuroscience Letters, 520(2), 182–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2012.03.013
Navratilova, E., Morimura, K., Xie, J. Y., Atcherley, C. W., Ossipov, M. H., & Porreca, F. (2016). Positive emotions and brain reward circuits in chronic pain. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 524(8), 1646–1652. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23968
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Brazilian funding agency, Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Grant number—2015/24256-0; 2014/24533-0; 2017/05218-5, by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Grant number—157284/2017-4; 405853/2018-1, and by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Grant number—2021/02897-4. The funding agencies play no role in the design of the study, data collection, analysis, interpretation of the data, or in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Marques, D.P., Chacur, M. & Martins, D.O. Photobiomodulation and vitamin B treatment alleviate both thermal and mechanical orofacial pain in rats. Photochem Photobiol Sci 22, 2315–2327 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-023-00452-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43630-023-00452-y