Abstract
Substance P (SP) is a highly conserved member of the tachykinin peptide family that is widely expressed throughout the animal kingdom. The numerous members of the tachykinin peptide family are involved in a multitude of neuronal signaling pathways, mediating sensations and emotional responses (Steinhoff et al. in Physiol Rev 94:265–301, 2014). In contrast to receptors for classical transmitters, such as glutamate (Parsons et al. in Handb Exp Pharmacol 249–303, 2005), only a minority of neurons in certain brain areas express neurokinin receptors (NKRs) (Mantyh in J Clin Psychiatry 63:6–10, 2002). SP is also expressed by a variety of non-neuronal cell types such as microglia, as well as immune cells (Mashaghi et al. in Cell Mol Life Sci 73:4249–4264, 2016). SP is an 11-amino acid neuropeptide that preferentially activates the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R). It transmits nociceptive signals via primary afferent fibers to spinal and brainstem second-order neurons (Cao et al. in Nature 392:390–394, 1998). Compounds that inhibit SP’s action are being investigated as potential drugs to relieve pain. More recently, SP and NKR have gained attention for their role in complex psychiatric processes. It is a key goal in the field of pain research to understand mechanisms involved in the transition between acute pain and chronic pain. The influence of emotional and cognitive inputs and feedbacks from different brain areas makes pain not only a perception but an experience (Zieglgänsberger et al. in CNS Spectr 10:298–308, 2005; Trenkwaldner et al. Sleep Med 31:78–85, 2017). This review focuses on functional neuronal plasticity in spinal dorsal horn neurons as a major relay for nociceptive information.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Substance P, a member of the tachykinin peptide family
History
Substance P (SP) was first isolated from equine brain and gut (v Euler and Gaddum 1931) and later from bovine hypothalamic tissue and identified as an undecapeptide (Chang and Leeman 1970; Chang et al. 1971; Pickel et al. 1977). In mammals, the three main tachykinins are SP, neurokinin A (NKA) and neurokinin B (NKB). Tachykinin family members are ubiquitously distributed in all mammalian tissues and body fluids. In the nervous system, the highest densities of SP are found in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, the substantia nigra and the amygdala (Ribeiro-da-Silva and Hökfelt 2000). The observation that SP is expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and dorsal horn but not in the ventral horn was taken as evidence in favor of its involvement in primary afferent sensory neurotransmission (Lembeck 1953; Lembeck and Holzer 1979; Lembeck 2008; Pernow 1953).
Tachykinin receptors, synthesis and release
The tachykinins derive from alternate processing of three TAC gene products that are expressed throughout the nervous and immune systems. These genes encode precursor proteins, from which the active peptide transmitter is subsequently cleaved. Neuropeptide-encoding messenger RNAs (mRNAs) can be found in neuronal processes beyond the perikaryon. SP is synthesized in small- and medium-sized neurons of DRG and stored in dense core vesicles and transported by fast axonal transport to both spinal and peripheral nerve terminals (Hoyer and Bartfai 2012). It binds to tachykinin receptors [neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R), NK2R, NK3R] that belong, like most neuropeptide receptors, to the family of seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptors. All tachykinins interact with all the three-receptor subtypes with SP preferring NK1, NKA preferring NK2 and NKB (encoded by the TAC3 gene in humans and by the tachykinin 2 (TAC2) gene in rodents) preferring NK3. This lack of specificity can be accounted for by the conformational flexibility of the short, linear peptides (Ganjiwale and Cowsik 2013). Additionally, some of the multiple subtypes and splice variants of these receptors form heterodimers with other neuropeptides and regulate, e.g., trafficking and resensitization of receptors (Pfeiffer et al. 2003). Toxins such as saporin bind to NK receptors (NKRs) and kill, e.g., dorsal horn neurons after they have been internalized following activation (Wiley et al. 2007; Iadarola et al. 2017).
Peripheral nerve injury and inflammation change the phenotype of neurons with regard to receptors and messengers (Weisshaar and Winkelstein 2014). SP released from primary afferent fibers during inflammation upregulates NK1 receptors in dorsal horn neurons. Peptidase inhibitors, which prevent SP breakdown, enhance peptidergic transmission. NKR couples to phospholipase C generating intracellular messengers whose downstream effects include depolarizing the membrane and facilitating the function of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) and NMDA receptors (see below). They, furthermore, control the expression of cytokines and chemokines as well as transcription factors such as nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB) (Bekhbat et al. 2017) and members of the nuclear hormone family PPAR (Okine et al. 2018). NF-kB is a ubiquitous transcriptional activator of inflammatory mediators that increases the synthesis of pro-inflammatory factors such as cytokines, prostaglandins and nitric oxide that contribute to the development of hyperalgesia (Petho and Reeh 2012).
Whereas NK1 receptors in the hippocampus are downregulated in rat models of pain and stress (Duric and McCarson 2005), they are upregulated in neurons of superficial laminae in the spinal cord (Bradesi et al. 2009). Inflammation and stimulation of nociceptors by capsaicin triggers NKR endocytosis in neurons in superficial laminae of the dorsal horn reflecting sustained release of SP (Kunde et al. 2013). Microglial cell activation plays a major role in the development of this nociceptive sensitization (Wieseler-Frank et al. 2004; Li et al. 2015) (see below). The half-life of the SP response is defined by the kinetics of degradation of the neuropeptide in the extracellular environment and by the dynamics of desensitization and cellular internalization followed by recycling of the receptor. Noteworthy, ligand-induced internalization of NK1 receptors into neurons in the dorsal horn can be triggered also by non-noxious somatosensory stimulation (Honor et al. 1999).
SP antagonists
Many potent and selective non-peptide, low molecular tachykinin antagonists have been developed and proven effective in preclinical studies (Carvalho et al. 2018). Early experiments showed that antagonists selectively block nociceptive responses such as the slow, prolonged, excitatory postsynaptic potential that follows intense electrical stimuli to small high-threshold multimodal nociceptors (De Koninck and Henry 1991). Unfortunately, most of the knowledge obtained from preclinical studies on nociception has not yet been translated into new therapies. This failure could be due, at least to some extent, to a misconception of what characterizes pain as a chronic disease. Both preclinical and clinical evidence support the involvement of tachykinins and NK1 and NK2 receptors in the neurobiology of depression and anxiety disorders, key features of suffering during chronic pain states (Ebner et al. 2009; Bardelli et al. 2013; Catena-Dell’Osso et al. 2013; Kormos and Gaszner 2013; Rupniak and Kramer 2017).
Neuromodulation and volume transmission
The discovery of peptidergic neurotransmission in numerous neuronal structures, where the release site and the target do not have to be in close contact, together with synaptic processes by which given neurons use more than one signaling molecule was accompanied by a considerable debate over the definition of a neurotransmitter (Hökfelt et al. 1980; Calza et al. 1998).
The terms neuromodulation and volume transmission were introduced. They describe calcium-dependent signaling at synaptic and non-synaptic sites by neuropeptides co-stored and co-released with classical transmitters. Neuropeptides like SP diffuse farther from their site of release in the intercellular space to reach mostly high-affinity receptors at more remote targets and to regulate synaptic transmission in diverse populations of neurons by volume transmission (Nakamura et al. 2013). This form of chemical communication is much less spatially distinct than classical neurotransmitter signaling and it seems unlikely that neuropeptides participate in rapid integrative functions between nerve cells (Zieglgänsberger 2009).
In a number of primary afferent fibers, SP and other members of the tachykinin family co-exist with glutamate (Hunt and Manthy 2001). Neuromodulation is often contrasted to classical fast synaptic transmission in which an axon terminal secretes neurotransmitters to a restricted target carrying fast-acting receptors and the partner neuron has high affinity reuptake mechanisms that remove the transmitter from the synaptic or extracellular space. Most peptide transmitters lack such a high-affinity reuptake process and are mainly inactivated enzymatically. Such a mechanism markedly extends the signaling capability of neurons in a neuronal network to subsequent stimuli for a period of seconds or even minutes. The actions of certain peptidases may lead to further biologically active fragments making it sometimes difficult to distinguish between extracellular synthetic processing and inactivation. Usually, the peptide that is stored in dense core vesicles and then released is considered the neurotransmitter. Since its release most often requires burst activity or higher frequencies and intensities of stimulation, the signaling of the peptide appears primarily restricted to specific circumstances, i.e., a developing inflammation. The release of fast-acting neurotransmitters, such as glutamate and neuropeptides, may thus contribute significantly to the diversified responses to external stimuli (Zieglgänsberger 2009).
Cortical and subcortical networks and descending pathways
The role of SP in cortical and subcortical networks as well as in descending pathways involved in the processing of nociceptive inputs is still largely unclear (Budai et al. 2007; Khasabov et al. 2017). Neurons with their perikarya in laminae 1 and 5 project to various sites of the rostral brain such as the caudal ventrolateral medulla, parabrachial area, periaqueductal gray and thalamus as a major relay (Ralston 2005; Todd 2002; Marshall et al. 1996). A recent study underlines the importance of topographic organization of spinofugal connections for nociceptive topognosis, i.e., the ability to localize painful stimuli. Avoidance of environmental nociceptive dangers depends on somatotopic maps arising from topographically organized point-to-point connections between the body surface and the central nervous system (CNS). Humans with an impaired topognosis experience, for example, bilateral sensation evoked by unilateral somatosensory stimulation (da Silva et al. 2018).
Functional magnetic resonance imaging studies have shown that stress exposure reduces pain responses by activation of descending pain inhibitory circuits and may be an indicator of adequate centrally mediated pain control. It has been reported that SP drives endocannabinoid-mediated disinhibition in the periaqueductal/rostral ventromedial medulla projection system, which facilitates these descending pathways to the dorsal horn by an enhancing glutamatergic receptor-mediated function (Drew et al. 2005, 2009). Stress-induced analgesia apparently involves similar sensory, affective and cognitive modulatory brain circuits as placebo analgesia or analgesia mediated by diffuse noxious inhibitory controls (DNICs). The increase in pain tolerance and pain unpleasantness correlated significantly with activation in the rostral anterior cingulate cortex (Yilmaz et al. 2010). Recently, a cingulate cortex/posterior insula pathway was identified that can induce and maintain nociceptive hypersensitivity in the absence of conditioned peripheral noxious drive (Tan et al. 2017).
Structural and functional changes induced in dendritic spines by noxious stimulation
Experience results in long-lasting changes in dendritic spine morphology, yet how the molecular architecture of the synapse responds to plasticity remains poorly understood. SP-containing terminals of small unmyelinated fibers are localized to the dendritic shafts and spines of spinofugal projection neurons, where they form axodendritic synapses on neurons (Mantyh 2002). However, SP released from primary afferent fibers presynaptically at non-junctional sites could also reach NKR distributed over the length of the long extending dendrites of dorsal horn projection wide dynamic range (WDR) neurons with their soma in lamina 4/5 via volume transmission (see Fig. 1). SP enhances responses to locally applied glutamate in these neurons (Zieglgänsberger and Herz 1971; King et al. 1997, 2005).
Volume transmission. Sketch illustrating the release of substance P (SP) from primary afferent fibers following nociceptive input. The neuropeptide is released at synaptic and non-synaptic sites in the dorsal horn and reaches neurokinin (NK1) receptors on lamina 1 and NK1 receptors on dendrites of lamina 5 neurons
Dendritic spines are highly dynamic during development but also in adulthood. They are probably the main targets for SP/glutamate interactions. Following spinal cord injury, the dendrites of WDR neurons located in laminae 4–5 exhibit increased spine density and redistributed spines, compared with controls. Unit recordings in vivo revealed an increase in responsiveness to innocuous and noxious peripheral stimuli under these conditions. These changes were ameliorated by the inhibition of the small GTP-binding protein Rac1 that also increased pain thresholds over a 3-day period (Tan et al. 2008). It is feasible to assume that voltage-gated calcium channels (Nanou and Catterall 2018) trigger this remodeling that contributes to the development of hyperexcitability in these neurons, which is reflected in symptoms of tactile allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia.
Spine size and shape are controlled by actin dynamics
Stimulated emission depletion (STED) can visualize actin cytoskeleton rearrangements of dendritic spines in living brains. The neuronal filamentous (F)-actin network anchors postsynaptic receptors and modulates synaptic activities, e.g., through the organization of the postsynaptic density (Willig et al. 2014). More recent studies employing novel technologies revealed that the organization and plasticity of spine synapses is linked to the addition of unitary synaptic nanomodules to spines and underlines the important role of NMDA receptors in structural plasticity (Hruska et al. 2018). The calcium-dependent cysteine protease calpain cleaves structural cytoskeleton proteins involved in synaptic plasticity and interferes with memory formation and maintenance in contextual fear conditioning, a process highly relevant for the development of chronic pain states (Popik et al. 2018).
Actin polymerization/depolymerization cycles control structural cytoskeleton proteins and other targets involved in memory formation and maintenance. A murine ortholog of the putative tumor suppressor gene DRR1’s product is a unique stress-induced protein in the brain that binds to actin, promotes bundling and stabilizes actin filaments and impacts actin-dependent neurite outgrowth. Stress has been identified as a major causal factor for many mental disorders and DRR1 emerges as a protein to link stress with actin dynamics related to synaptic function and cognition. Hippocampal virus-mediated enhancement of DRR1 expression reduces spine density, diminishes the probability of synaptic glutamate release and alters cognitive performance (Schmidt et al. 2011).
Individual vulnerability factors influencing the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis contribute to the risk of the development of chronic pain states after traumatic stress exposure (Benedetti et al. 2012; Bortsov et al. 2013). The glucocorticoid receptor co-chaperone FKBP51 acts as an intracellular scaffolding protein and has been associated with depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (Matosin et al. 2018; Fries et al. 2017) and the regulation of stress responses in numerous sites, including the spinal dorsal horn. FKBP51 most likely reduces the severity of persistent pain by modulating glucocorticoid signaling, even though FKBP51 has been found to interact with multiple other proteins in a cell type-specific manner and may thereby affect a variety of biological processes independent of GR signaling (Balsevich et al. 2017a; Gassen et al. 2014). Deletion of spinal FKBP51 after the establishment of inflammation significantly improved the pain state, suggesting that FKBP51 could regulate nociception, independent of its effect on mood. Silencing of FKBP51 alleviates pain by reducing inflammatory factors through the NF-kB signaling pathway (Yu et al. 2017). Blockade of FKBP51 has been suggested as a novel strategy to treat persistent pain (Maiarù et al. 2016). The enhanced mechanical sensitivity of inflamed hind paws accompanied with corticosteroid receptor upregulation in spinal and peripheral sensory neurons was attenuated immediately after glucocorticoid receptor agonist and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist administration. This suggests acute non-genomic effects consistent with detected membrane-bound corticosteroid receptors (Li et al. 2018). Specific inhibitors of FKBP51 are now available, enabling animal models of long-term pain to be studied (Maiarù et al. 2018). Recent studies show that functional interactions between glucocorticoid signaling and the endocannabinoid system are critical for a wide array of physiological processes (Balsevich et al. 2017b).
Dorsal horn and nociception
Primary afferent sensory neurotransmission
Ablating or functionally compromising sets of primary afferent fibers has provided important insights into peripheral modality-specific wiring in the somatosensory system. Nociceptive input into the dorsal horn is not simply passively received. It is modulated by segmental interneurons and descending supraspinal pathways that provide the neuronal circuits by which cognitive and motivational aspects influence the processing of the nociceptive input at this early stage of integration (Eliava et al. 2016). The neuropeptide oxytocin (OT) has profound prosocial effects in non-vertebrate and vertebrate species, including humans (Grinevich et al. 2016). The descending modulatory system can either inhibit or facilitate transmission of nociceptive information. The hypothalamic paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic (SON) nuclei harbor parvocellular OT cells that project to the brainstem and to neurons of deep layers of the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Magnocellular OT neurons of these nuclei also innervate numerous forebrain regions and release OT into the blood from the posterior pituitary. There is evidence that the rewarding/reinforcing effects of SP develop by modulating the mesencephalic dopaminergic system, while their mnemonic effects are mediated via the mesencephalic dopaminergic and the basal forebrain cholinergic systems (Lénárd et al. 2018). SP exerts neuromodulatory effects on pain processing and central synaptic transmission in hippocampal areas important for social interaction. SP can induce a slowly developing NMDA receptor- and protein synthesis-dependent potentiation of synaptic transmission and could prime hippocampal synapses for the formation of long-lasting plasticity and associativity (Dasgupta et al. 2017).
It has been suggested that the excitability of spinal lamina 1 neurons may play an almost exclusive role in the transmission and processing of nociceptive input leading to persisting pain. However, the release of SP and glutamate lowers the pain threshold of dorsal horn projection neurons originating from lamina 5 WDR neurons and increases the size of their receptive field (Zieglgänsberger and Herz 1971; King et al. 1997; Schadrack and Zieglgänsberger 2000; Martin et al. 2004; Mantyh and Hunt 2004) (Fig. 2). In line with these results, long-term nociception following the injection of Freund’s adjuvant into, e.g., the hind paw of an animal induces the expression of NK1 receptors and transforms non-nociceptive neurons into nociceptive neurons (Almarestani et al. 2009). The enhanced spinofugal output following this alteration of neuronal properties markedly increases the development of chronic persisting pain (see below). Recent studies employing optogenetic tools in freely moving animals show that selective stimulation of non-nociceptive primary afferent Aβ fibers evokes neuropathic pain-like sensory and emotional behaviors after peripheral nerve injury. Notably, these Aβ fiber-mediated responses were observed in lamina 1 neurons and were resistant to morphine. Whole-cell recording and activity markers such as c-Fos and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (pERK) revealed excitation of lamina 1 neurons, which were normally silent and activation of central amygdaloid neurons related to aversive behavior (Tashima et al. 2018).
Substance P (SP) increases excitability of glutamate. a Microiontophoretically applied SP (80 nA) increases the excitation induced by short applications of l-glutamate (20 nA) in a WDR neuron in lamina 5 recorded extracellularly in vivo. b Microiontophoretically applied glutamate transiently increases the size of the receptive field of lamina 5 neurons. The application of GABA shrinks the receptive field (not shown). c Activation of an inhibitory interneuron by extracellularly applied glutamate (40 nA) reduces responses to nociceptive stimuli (dots) evoked in a lamina 5 neuron
Iontophoretic application of SP amplifies excitatory responses to glutamate agonists in dorsal horn neurons (Fig. 2a) (Zieglgänsberger and Tulloch 1979), an action blocked by an SP antagonist (Sharif et al. 2005). When glutamate was electrophoretically released by short applications from multibarreled glass pipettes, it elicited rapid, short-lasting increases of the discharge activity of projection neurons without markedly enhancing ongoing activity. Interneurons of the spinal dorsal horn are central to somatosensory and nociceptive processing. In an in vivo experiment, exciting segmental interneurons evoked a massive inhibition of the projecting neurons and a reduction of the response to afferent noxious stimuli (Zieglgänsberger and Herz 1971) (Fig. 2c). It has long been appreciated and translated into new therapies that a diminished synaptic inhibition via segmental interneurons in the spinal dorsal horn may be a major contributor to the development of chronic pain states (Zieglgänsberger 1986; Hunt and Mantyh 2001; Mantyh and Hunt 2004; Alles and Smith 2018). A more recent study of the intrinsic properties and the integration of these neurons into dorsal horn circuits showed that tonic firing prevailed in inhibitory interneurons of the dorsal horn. In contrast, delayed firing and single action potential firing were the single most prevalent firing pattern in neurons of the superficial and deep dorsal horn (Punnakkal et al. 2014).
SP activates NKR, which couples to phospholipase C and facilitates glutamatergic transmission by phosphorylation of subunits of the NMDA receptor. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in freshly dissociated rat dorsal horn neurons revealed a potentiation of l-glutamate-induced inward currents by SP in a majority of neurons, suggesting a postsynaptic mechanism of action of tachykinins in the rat spinal dorsal horn (Randić et al. 1990). There is evidence that signal transduction coupling between group I metabotropic glutamate receptors and NMDA receptors facilitates the activation of NMDA receptors and may play a critical role in spinal hyperexcitability and hyperalgesia. Inflammation enhanced NMDA receptor-mediated, dorsal root, stimulation-evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents and NMDA-induced currents. The increase in the frequency and amplitude of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in the presence of tetrodotoxin suggests an enhanced presynaptic glutamate release probability and postsynaptic membrane responsiveness under these conditions (Yang et al. 2011). In the lamprey, SP depolarizes spinal cord neurons by inhibiting background potassium channels (Thörn Pérez et al. 2015). In DRG neurons, the application of SP evokes a long-lasting increase of an NMDA-activated inward current (Jun et al. 2004). This modulatory effect of SP was blocked by the extracellular application of an SP antagonist (Wu et al. 2004).
The potassium chloride co-transporter KCC2
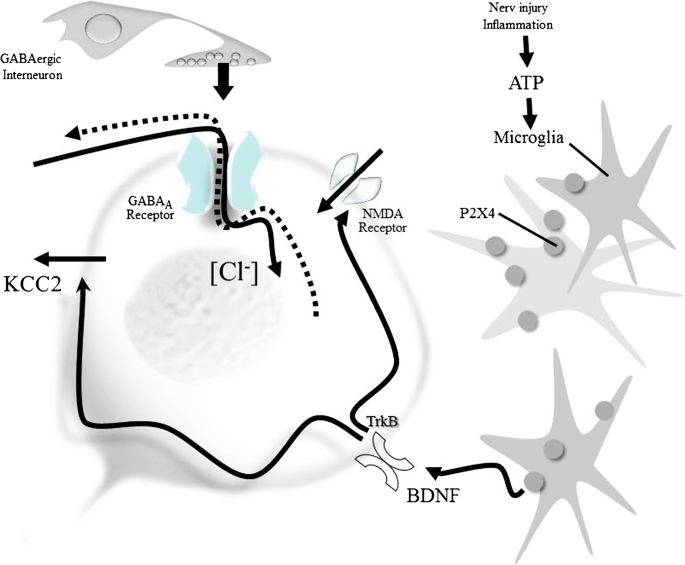
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)/glycine-induced neuronal inhibition is associated with a chloride influx that depends on the inwardly directed chloride electrochemical gradient (Fig. 3). Recent studies on loss-of-function mutations in genes encoding glycine receptors and glycine transporters underline the importance of glycinergic neurotransmission for central pain modulation in humans (Vuilleumier et al. 2018). Neuronal intracellular [Cl]− concentration influences membrane potential dynamics and neuronal inhibition in spinal neurons (Javdani et al. 2015). The perikarya and dendrites of dorsal horn neurons of rats widely express the potassium chloride co-transporter KCC2 (Agez et al. 2017), which controls the intracellular [Cl]− concentration. Nerve injury and inflammation downregulate this transporter (Modol et al. 2014). Recent results suggest that the chloride dysregulation may be transient (Castro et al. 2017). A variable density of KCC2 results in variable postsynaptic potentials evoked by GABAA and glycine receptors along the dendrites of these neurons. Most importantly, the shift in the transmembrane anion gradient evokes a loss of inhibition and can invert the inhibitory effect of GABA/glycine released from segmental spinal interneurons into a net excitation (Coull et al. 2003; Price et al. 2005, 2009). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) released from microglia following the activation of ATP-gated purinergic receptors following peripheral nerve injury or inflammation evokes a rapid trans-synaptic reduction in the expression of the KCC2 exporter (Biggs et al. 2010; Ferrini and De Koninck 2013). The intracellular [Cl]− concentration can be restored by novel chloride extrusion enhancers (Gagnon et al. 2013), KCC2 gene transfer (Li et al. 2016), or intrathecal histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor injections, suggesting an effect via epigenetic actions (Lin et al. 2017). Recent studies have shown that P2X4 receptors are upregulated in pain-processing neurons during inflammation (Lalisse et al. 2018). The downregulation of the expression of KCC2 by BDNF released from microglia during acute nociceptive stimulation can be prevented by the application of a kinase inhibitor before stimulation (Tsuruga et al. 2016). In a most recent study, it was shown that mechanical allodynia, a major symptom of neuropathic pain whereby innocuous touch evokes severe pain, cannot be evoked in animals that have peripheral sensory neurons expressing TrkB-positive neurons ablated. The study employing selective optogenetic activation identified a population of TrkB-expressing neurons both necessary and sufficient for producing pain from light touch after nerve injury in mice. The peripheral neurons that transmit pain from light touch might be a novel target for the treatment of neuropathic pain states (Dhandapani et al. 2018).
The paradoxical depolarizing action of GABA/glycine enhances glutamatergic (NMDA) responses by directly activating voltage-sensitive NMDA channels and by BDNF enhancing the phosphorylation of the GluN2B subunit via the Src family kinase Fyn (Hildebrand et al. 2016). Knockdown of KCC2 by intrathecal administration of KCC2-siRNA reduces inhibitory synaptic transmission (Lin et al. 2017). mRNA-mediated downregulation of KCC2 and vesicular GABA transporter expression in the spinal cord contribute to visceral pain in rats (Zhang et al. 2017). Dynamic changes in the mRNA profile revealed multiple regulatory mechanisms in spinofugal projection neurons (von Schack et al. 2011). Unexpectedly, not the injured but adjacent afferents showed the most robust downregulation of miRNA. In uninjured rats, BDNF reduced membrane-bound KCC2 and the inhibitory effect of the GABAA agonist muscimol. After spinal cord injury, BDNF increased KCC2 expression, which might help restore GABAergic inhibition (Huang et al. 2017).
WDR-type response properties were previously almost exclusively observed in neurons located in deeper laminae (Basbaum 1999). The shift of response properties of lamina 1 neurons to a WDR type markedly increases nociceptive signaling to rostral brain structures and enhances lasting maladaptive plasticity in neuronal circuits, e.g., in the limbic system. In monoarthritic animals, the expression of SP and its receptor is increased and the baseline activity of WDR neurons is greater than that in control animals. Disruption of inhibitory control supports long-term potentiation (LTP) in both groups of projection neurons in the dorsal horn and contributes to the development of persisting pain. Previously innocuous stimulation then evokes discharge patterns characteristic for nociceptive stimulation (Pitcher and Henry 2004; Sharif et al. 2005). A synopsis of this data suggests that KCC2 may represent an important novel target for the development of analgesics (Gu et al. 2017a, b).
Prevention of the phosphorylation of the Na-K-Cl co-transporter (NKCC1) avoids downregulation of KCC2 in central sensory pathways and reduces neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury (Mòdol et al. 2014). An upregulation of NKCC1 (Price et al. 2009; Glykys et al. 2017) during inflammation produces excessive GABAergic depolarization in primary afferents that leads to cross-excitation between low- and high-threshold afferents (Price et al. 2005). The activation of GABAA receptors on afferent fibers facilitates the development of hyperalgesia induced by inflammation (Lee et al. 2018). The voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 that is encoded by the gene SCN9A and preferentially located in nociceptors might lose its exclusive role under such conditions. Inflammatory hyperalgesia, cold pain and noxious mechanosensation have all been shown to depend also upon Nav1.8-positive sensory neurons. The voltage-gated tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels Nav1.8 and Nav1.9 (coded by SCN10A and SCN11A, respectively) are also expressed in small-diameter, unmyelinated primary afferents and are currently being investigated for novel pain treatments. Interestingly, Nav1.7 blocking spider toxins produced profound analgesia when applied in combination with an opioid agonist at subthreshold concentrations. It was suggested that a lack of Nav1.7 channels may upregulate the expression of the efficacy of antinociceptive opioid signaling mediated by the Gαi-coupled mu opioid receptors (Isensee et al. 2017).
Immune cell recruitment of SP is a critical component of a number of pathologies; e.g., SP recruits leucocytes to the peripheral terminals of nociceptors where they release neuroactive mediators that contribute to neuropathic pain (González-Ramírez et al. 2017; Sousa-Valente and Brain 2018). Human autoantibodies to contactin-associated protein-like 2 (CASPR2) are often associated with neuropathic pain disorder and CASPR2 mutations have been linked to mechanical pain-related hypersensitivity in the absence of neural injury. Mice lacking CASPR2 (Cntnap2−/−) demonstrated enhanced pain-related hypersensitivity to noxious mechanical stimuli, heat and algogens. Both primary afferent excitability and subsequent nociceptive transmission within the dorsal horn were increased in Cntnap2−/− mice. Either immune- or genetic-mediated ablation of CASPR2 enhanced the excitability of DRG neurons in a cell-autonomous fashion through regulation of Kv1 channel expression at the soma membrane. These data suggest a key role for CASPR2 in regulating cell-intrinsic DRG neuron excitability (Dawes et al. 2018).
Stimulation of unmyelinated C fibers, collaterals, or spinal ganglion cells and even central terminals in the dorsal horn initiate antidromic activity. This activity releases biologically active agents such as SP and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and possibly other sensory messengers from distal afferent terminals that evoke local inflammatory responses in the innervated organ systems (Sorkin et al. 2018). These inflammatory processes are referred to as neurogenic inflammation. Recent studies have suggested that electrical coupling via Cx36-containing gap junctions between peripheral sensory fibers containing SP and CGRP exists and that, to some degree of selectivity, electrical coupling may occur between fibers belonging to subpopulations of sensory neurons (Nagy et al. 2018).
Memory of pain
Actions elicited by SP not only transmit and integrate nociceptive signals but also control their consequences, which are anxiety and depression (Parent et al. 2012). Numerous animal and human studies suggested a role of SP and other members of the tachykinin family in the regulation of biopsychosocial stress responses and emotion processing (de Felipe et al. 1998; Ebner et al. 2009; Madaan and Wilson 2009; Han et al. 2015). A most recent study revealed a profound effect of social isolation stress on the tachykinin system. Enhancing NKB expression and release phenocopied social isolation stress in group-housed mice, promoting aggression and converting stimulus-locked defensive behaviors to persistent responses. The multiple behavioral changes evoked by brain-wide upregulation of TAC2/neurokinin B could be blocked by systemic administration of an NK3R antagonist (Zelikowsky et al. 2018).
The memory of pain is built up by persistent nociceptive, aversive input and should be considered as an experience-based adaption of expectancies and conditioned fear avoidance (Zieglgänsberger et al. 2005). Neurons in the reward system and the amygdala are activated by painful stimuli. Neurons expressing CGRP in the parabrachial nucleus appear critical for relaying nociceptive signals to the central nucleus of the amygdala. After a stable threat memory has been built, a neutral stimulus would then be perceived as being aversive and painful (Han et al. 2015). These neuronal circuits evaluate the expectancy to a known condition and transduce the affective motivational aspects of nociception and thus may be pertinent for treating psychiatric comorbidities (Radat et al. 2013; Vachon et al. 2013).
Acute vs chronic pain
Pain is one of the most prevalent health conditions in the world. It is widely accepted that only acute pain has an important protective role and warns the organism of an imminent danger, whereas chronic pain usually persists beyond its biological usefulness and compromises the quality of life (Urban and Gebhart 1999; Chang et al. 2010). Most importantly, chronic pain is not simply a temporal continuum of acute pain. In the setting of persistent injury, functional and structural reorganization of neuronal circuits in the CNS leads to long-term changes in perception and behavior (Kuner and Flor 2016).
Associative memory can be inactivated and reactivated by LTP and long-term depression (LTD), respectively, supporting a causal link between these synaptic processes and memory. Although it is clear that chronicity of pain involves learning and psychosocial factors, it remains unclear how they act at the level of neuronal circuits and how the molecular architecture of the synapse responds to plasticity. Compared to the dynamic changes in synaptic connectivity through the growth and elimination of synaptic structures, large-scale organization of axonal and dendritic arbors seems to be rather stable. Rapid developments in technologies to visualize and manipulate circuits, such as infrared microscopy (Dodt et al. 2013), stimulated emission depletion (Willig et al. 2014) and optogenetics (Chen et al. 2018), have opened new avenues for attempts to detail key brain functions and to gain a mechanistic understanding of nociception and pain.
It is well established that the low-frequency afferent barrage during inflammation and trauma enhances pain sensitivity by altering synaptic efficacy (Ikeda et al. 2006) and activity-dependent gene expression in spinal neuronal circuits involved in the transmission and processing of nociceptive signals. The c-Fos immediate early gene has been used as an activation marker for neurons in the superficial dorsal horn (Schadrack et al. 1998, 1999; Schadrack and Zieglgänsberger 2000; Berthele et al. 1999). An increase in synaptic strength involves the de novo formation or elaboration of postsynaptic dendritic structures and constitutes a structural basis for learning and memory in the CNS. LTP plays a key role in the processing and transmission of nociceptive signals to rostral structures via ascending projecting pathways originating from superficial and deep dorsal horn neurons (Rygh et al. 2006). Additionally, it involves specific changes in signaling molecules and intracellular messengers in glia cells (Xanthos and Sandkühler 2014; Kronschläger et al. 2016). The increase in synaptic strength and neuronal excitability includes a cascade of alterations of ionotropic NMDA, AMPA and kainate receptors as well as metabotropic receptors for glutamate (Sheng et al. 2018). Vesicular glutamate transporters sequester glutamate into synaptic vesicles and are reliable markers for glutamatergic neurons and can be used to impair glutamatergic signaling in animal models. They change the temporal and spatial profile of a neurotransmitter and can affect the downstream effects of these neurotransmitters and hence modulate pain (Yousuf and Kerr 2016).
Since many forms of synaptic plasticity rely on glutamate, the major excitatory small synaptic vesicle transmitter, used by most, if not all, primary sensory afferents involved in pain signaling, it is not surprising that SP enhances the generation of LTP. SP has to be increased extracellularly during the induction of LTP in these projection neurons. Whereas the maintenance of spinal LTP following high-frequency peripheral nerve stimulation does not depend on increased SP release (Afrah et al. 2002). Also, the enhancement of SP signaling in the motor cortex seems to facilitate learning of a motor task preferentially in the early phase of skill acquisition (Hertler et al. 2017).
Long-term storage of memory and the perineuronal net
In adult animals, fear conditioning induces memory that appears resilient to erasure. Fear memories may actively be protected in pain-recipient neurons of the amygdala by perineuronal nets (PNNs) (Gogolla et al. 2009). Enzymatic digestion of PNNs by chondroitinase ABC lyase (chABC) in the amygdala renders subsequently acquired fear memories susceptible to erasure. It was suggested that very long-term memories may even be stored in the pattern of holes in a web-like structure of proteins such as brevican, aggrecan, neurocan and hyaluronan cross-linked by link proteins and tenascin-R (Tsien 2013). These specialized reticular extracellular matrix proteins envelop mature neurons and apparently restrict synapse formation and squelch neuronal signaling. In the cortex and other subcortical areas, PNNs preferentially surround GABAergic interneurons containing the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin. These specific cells have been recently identified as fast-spiking cells relevant for gamma-oscillations (Dine et al. 2016).
Cell surface proteins, including neurotransmitter receptors, are highly mobile in the plasma membrane due to lateral diffusion. Fast trafficking of AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) is involved in the modulation of synaptic transmission. PNNs compartmentalize the neuronal surface and may act as lateral diffusion barriers for AMPARs and limit synaptic plasticity once PNNs become upregulated (Sheng et al. 2018). Heterodimers formed by NKRs with other neuropeptide receptors control these trafficking and resensitization processes (Pfeiffer et al. 2003).
The enzymatic degradation of PNNs by chABC collapses much of the net-associated extracellular matrix (Brückner et al. 1998; Pizzorusso et al. 2002) and leads to reactivation of plasticity (Pizzorusso et al. 2002; Corvetti and Rossi 2005). chABC applied to lesion-denervated targets has been shown to enhance collateral sprouting and synapse formation by spared fibers (Tropea et al. 2003). The PNN is initially laid down at the end of the critical period in wiring of sensory inputs, a process that may have both neuronal and glial contributions. After the critical period passes, the PNN is quickly produced, which stabilizes the whole neural network, making it difficult for neurons to make new connections (Massey et al. 2006). Inhibition of HDAC can reopen critical-period neuroplasticity in adult mice. HDAC may act as an epigenetic “brake” on critical learning (Nabel and Morishita 2013). The antidepressant fluoxetine increases synaptic plasticity and helps to remodel the fear memory circuitry in the limbic system and apparently converts the fear memory circuitry to a more immature state (Karpova et al. 2011).
Nociceptive inputs create different levels of stress and anxiety depending on their nature, duration and intensity; therefore, the memory of pain can become more damaging than its initial experience. However, not all individuals develop the same level of psychopathology after stress exposure (Santarelli et al. 2017). Depending on the set and setting, chronic and repeated stress can lead to either a reduction or exacerbation of the pain state. Repeated stress can produce maladaptive neurobiological changes in pathways associated with pain processing, resulting in stress-induced hyperalgesia (Jennings et al. 2014). The influence of genetic background on this stress-induced hyperalgesia is poorly understood.
Repeated exposure to stress such as forced swimming alters endocannabinoid signaling differently in the dorsal horn and the amygdala in genetically different animals. These data implicate the endocannabinoid system in the spinal cord and amygdala in these differences (Jennings et al. 2016). It has been shown previously that the endocannabinoid system facilitates the erasure of aversive memory in the amygdala by affecting associative plasticity in inhibitory circuits (Marsicano et al. 2002; Azad et al. 2003). The endocannabinoid system is involved in neuroprotection (Marsicano et al. 2003) and controls key epileptogenic circuits in the hippocampus (Monory et al. 2006).
Relearning
Since most neuronal circuits remain plastic throughout life, it should be possible to modify dysfunctional cognition by promnesic drugs and thus increase the patient’s hope for therapeutic relief. Even a reopening of the critical period might be considered. However, superior memory could have a downside and trying to improve memory in humans may provide unintended traits. It has been shown that mice overexpressing the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B are “smarter” but more sensitive to the development of persisting pain, although they reacted like controls in acute pain tests (Tang et al. 1999). Patients often turn to medical cannabis to manage chronic pain states. We still do not have a consolidated perspective as to whether CB1 agonists are drugs of abuse or medicine. At present, there is still a lack of adequate clinical studies in this area. Cannabis is not just another analgesic; rather, it helps relieve the anxiety triggered by the fear of pain, the hallmark of the memory of pain. Recent research suggests that activating the endocannabinoid system ameliorates inflammatory, nociceptive and neuropathic pain and stress and thus may provide a novel treatment option to beneficially influence relearning by alleviating anxiety and depression, the key features of suffering during chronic pain states.
Outlook
The various members of the tachykinin family are processed differently and bind to distinctive NKR, illustrating the bewildering complexity of this peptidergic system (Hallberg 2015). Many of the fragments generated have not yet been examined in detail with regard to their potential biological activities. The multiple mechanisms involved in these processes may offer unique and important targets for the development of therapeutically relevant agonists and antagonists. SP is also expressed by a variety of non-neuronal cell types such as microglia, as well as immune cells such as T cells, tissue-resident macrophages, dendritic cells and eosinophils. SP is known to play a key role in immune cell migration and expression of chemokines and adhesion molecules (Mashaghi et al. 2016). Factors released from neuronal and non-neuronal elements have been recognized as mediators of persisting pain (Guo et al. 2007; Xanthos and Sandkühler 2014; Totsch and Sorge 2017). T cells may contribute to neuropathic pain that arises from an injury or disease of the somatosensory nervous system through pro-inflammatory interactions with microglia and by facilitating the activation of astrocytes, rather than through nociceptor activation (Grace et al. 2011, 2014). The phenotypic changes observed in transgenic animals lacking components of the neurokinin system are not as dramatic as pharmacological and morphological studies had suggested. This is possibly due to compensatory mechanisms in the tachykinin system.
We witnessed a large drive to identify molecular mediators of pain-related functional plasticity leading to chronicity. Chronic pain is no longer considered an extension of acute pain: it is the result of the memory of pain experienced over time and should be considered as a disease state of the nervous system. Currently, the treatment of chronic pain is inadequate and compromised by debilitating CNS side effects. It is the set and setting of the experience of nociceptive stimuli, rather than their intensity, which makes them memorable. The influence of emotional and cognitive input and feedback from different brain areas makes nociception not only a perception but also an experience. Maladaptive experience-based adaption of expectancies contributes to contextual fear conditioning. The limbic system stores memories of aversive stimuli with no simple mechanism for erasing them. The memory of pain is best countered by overlaying it with positive new associations. Numerous therapeutic algorithms and pharmacological agents have been described to block the generation of nociceptive hypersensitivity in animal models. These steps clearly indicate major progress. However, despite these important advances, their clinical translation remains stunted. Nevertheless, we begin to piece together intricate pathways in the neurobiology of nociception and mechanisms of cell-to-cell communication in modulating nociception leading to pain and suffering.
References
Afrah AW, Fiskå A, Gjerstad J, Gustafsson H, Tjølsen A, Olgart L, Stiller CO, Hole K, Brodin E (2002) Spinal substance P release in vivo during the induction of long-term potentiation in dorsal horn neurons. Pain 96(1–2):49–55
Agez M, Schultz P, Medina I, Baker DJ, Burnham MP, Cardarelli RA, Conway LC, Garnier K, Geschwindner S, Gunnarsson A, McCall EJ, Frechard A, Audebert S, Deeb TZ, Moss SJ, Brandon NJ, Wang Q, Dekker N, Jawhari A (2017) Molecular architecture of potassium chloride co-transporter KCC2. Sci Rep 7(1):16452
Alles Sascha RA, Smith PA (2018) Etiology and pharmacology of neuropathic pain. Pharmacological Reviews 70(2):315–347
Almarestani L, Waters SM, Krause JE, Bennett GJ, Ribeiro-da-Silva A (2009) De novo expression of the neurokinin 1 receptor in spinal lamina I pyramidal neurons in polyarthritis. J Comp Neurol 514(3):284–295
Azad SC, Eder M, Marsicano G, Lutz B, Zieglgänsberger W, Rammes G (2003) Activation of the cannabinoid receptor type 1 decreases glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission in the lateral amygdala of the mouse. Learn Mem 10(2):116–128
Balsevich G, Häusl AS, Meyer CW, Karamihalev S, Feng X, Pöhlmann ML, Dournes C, Uribe-Marino A, Santarelli S, Labermaier C, Hafner K, Mao T, Breitsamer M, Theodoropoulou M, Namendorf C, Uhr M, Paez-Pereda M, Winter G, Hausch F, Chen A, Tschöp MH, Rein T, Gassen NC, Schmidt MV (2017a) Stress-responsive FKBP51 regulates AKT2-AS160 signaling and metabolic function. Nat Commun 8(1):1725
Balsevich G, Petrie GN, Hill MN (2017b) Endocannabinoids: effectors of glucocorticoid signaling. Front Neuroendocrinol 47:86–108
Bardelli C, Amoruso A, Manzetti E, Fresu LG, Valsesia R, Zeppegno P, Brunelleschi S (2013) Recurrent major depressive disorder: imbalance of neurokinin (NK)-1 and NK-2 receptor expression in monocytes. Pharmacol Res 68(1):24–30
Basbaum AI (1999) Distinct neurochemical features of acute and persistent pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(14):7739–7743
Bekhbat M, Rowson SA, Neigh GN (2017) Checks and balances: the glucocorticoid receptor and NFĸB in good times and bad. Front Neuroendocrinol 46:15–31
Benedetti M, Merino R, Kusuda R, Ravanelli MI, Cadetti F, dos Santos P, Zanon S, Lucas G (2012) Plasma corticosterone levels in mouse models of pain. Eur J Pain 16(6):803–815
Berthele A, Boxall SJ, Urban A, Anneser JM, Zieglgänsberger W, Urban L, Tölle TR (1999) Distribution and developmental changes in metabotropic glutamate receptor messenger RNA expression in the rat lumbar spinal cord. Dev Brain Res 112:39–53
Biggs JE, Lu VB, Stebbing MJ, Balasubramanyan S, Smith PA (2010) Is BDNF sufficient for information transfer between microglia and dorsal horn neurons during the onset of central sensitization? Mol Pain 6:44
Bortsov AV, Smith JE, Diatchenko L, Soward AC, Ulirsch JC, Rossi C, Swor RA, Hauda WE, Peak DA, Jones JS, Holbrook D, Rathlev NK, Foley KA, Lee DC, Collette R, Domeier RM, Hendry PL, McLean SA (2013) Polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid receptor co-chaperone FKBP5 predict persistent musculoskeletal pain after traumatic stress exposure. Pain 154(8):1419–1426
Bradesi S, Svensson CI, Steinauer J, Pothoulakis C, Yaksh TL, Mayer EA (2009) Role of spinal microglia in visceral hyperalgesia and NK1R up-regulation in a rat model of chronic stress. Gastroenterology 136(4):1339–1348
Brückner G, Härtig W, Seeger J, Rübsamen R, Reimer K, Brauer K (1998) Cortical perineuronal nets in the gray short-tailed opossum (Monodelphis domestica): a distribution pattern contrasting with that shown in placental mammals. Anat Embryol (Berl) 197(4):249–262
Budai D, Khasabov SG, Mantyh PW, Simone DA (2007) NK-1 receptors modulate the excitability of ON cells in the rostral ventromedial medulla. J Neurophysiol 97(2):1388–1395
Calzà L, Pozza M, Zanni M, Manzini CU, Manzini E, Hökfelt T (1998) Peptide plasticity in primary sensory neurons and spinal cord during adjuvant-induced arthritis in the rat: an immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience 82(2):575–589
Cao YQ, Mantyh PW, Carlson EJ, Gillespie AM, Epstein CJ, Basbaum AI (1998) Primary afferent tachykinins are required to experience moderate to intense pain. Nature 392(6674):390–394
Carvalho MC, Veloni AC, Genaro K, Brandão ML (2018) Behavioral sensitization induced by dorsal periaqueductal gray electrical stimulation is counteracted by NK1 receptor antagonism in the ventral hippocampus and central nucleus of the amygdala. Neurobiol Learn Mem 148:60–68
Castro A, Li Y, Raver C, Chandra R, Masri R, Lobo MK, Keller A (2017) Neuropathic pain after chronic nerve constriction may not correlate with chloride dysregulation in mouse trigeminal nucleus caudalis neurons. Pain 158(7):1366–1372
Catena-Dell’Osso M, Fagiolini A, Marazziti D, Baroni S, Bellantuono C (2013) Non-monoaminergic targets for the development of antidepressants: focus on neuropeptides. Mini Rev Med Chem 13(1):2–10
Chang MM, Leeman SE, Niall HD (1971) Amino-acid sequence of substance P. Nat New Biol 232(29):86–87
Chang MM, Leeman SE (1970) Isolation of a sialogogic peptide from bovine hypothalamic tissue and its characterization as substance P. J Biol Chem 245(18):4784–4790
Chang YW, Tan A, Saab C, Waxman S (2010) Unilateral focal burn injury is followed by long-lasting bilateral allodynia and neuronal hyperexcitability in spinal cord dorsal horn. J Pain 11(2):119–130
Chen IW, Papagiakoumou E, Emiliani V (2018) Towards circuit optogenetics. Curr Opin Neurobiol 50:179–189
Corvetti L, Rossi F (2005) Degradation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans induces sprouting of intact purkinje axons in the cerebellum of the adult rat. J Neurosci 25(31):7150–7158
Coull JA, Boudreau D, Bachand K, Prescott SA, Nault F, Sík A, De Koninck P, De Koninck Y (2003) Trans-synaptic shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism of neuropathic pain. Nature 424(6951):938–942
da Silva RV, Johannssen HC, Wyss MT, Roome RB, Bourojeni FB, Stifani N, Marsh APL, Ryan MM, Lockhart PJ, Leventer RJ, Richards LJ, Rosenblatt B, Srour M, Weber B, Zeilhofer HU, Kania A (2018) DCC is required for the development of nociceptive topognosis in mice and humans. Cell Rep 22(5):1105–1114
Dasgupta A, Baby N, Krishna K, Hakim M, Wong YP, Behnisch T, Soong TW, Sajikumar S (2017) Substance P induces plasticity and synaptic tagging/capture in rat hippocampal area CA2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(41)
Dawes JM, Weir GA, Middleton SJ, Patel R, Chisholm KI, Pettingill P, Peck LJ, Sheridan J, Shakir A, Jacobson L, Gutierrez-Mecinas M, Galino J, Walcher J, Kühnemund J, Kuehn H, Sanna MD, Lang B, Clark AJ, Themistocleous AC, Iwagaki N, West SJ, Werynska K, Carroll L, Trendafilova T, Menassa DA, Giannoccaro MP, Coutinho E, Cervellini I, Tewari D, Buckley C, Leite MI, Wildner H, Zeilhofer HU, Peles E, Todd AJ, McMahon SB, Dickenson AH, Lewin GR, Vincent A, Bennett DL (2018) Immune or genetic-mediated disruption of CASPR2 causes pain hypersensitivity due to enhanced primary afferent excitability. Neuron 97(4):806–822
De Felipe C, Herrero JF, O’Brien JA, Palmer JA, Doyle CA, Smith AJ, Laird JM, Belmonte C, Cervero F, Hunt SP (1998) Altered nociception, analgesia and aggression in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature 392(6674):394
De Koninck Y, Henry JL (1991) Substance P-mediated slow excitatory postsynaptic potential elicited in dorsal horn neurons in vivo by noxious stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(24):11344–11348
Dhandapani R, Arokiaraj CM, Taberner FJ, Pacifico P, Raja S, Nocchi L, Portulano C, Franciosa F, Maffei M, Hussain AF, de Castro Reis F, Reymond L, Perlas E, Garcovich S, Barth S, Johnsson K, Lechner SG, Heppenstall PA (2018) Control of mechanical pain hypersensitivity in mice through ligand-targeted photoablation of TrkB-positive sensory neurons. Nat Commun 9(1):1640
Dine J, Genewsky A, Hladky F, Wotjak CT, Deussing JM, Zieglgänsberger W, Chen A, Eder M (2016) Local optogenetic induction of fast (20-40 Hz) pyramidal-interneuron network oscillations in the in vitro and in vivo CA1 hippocampus: modulation by CRF and enforcement of perirhinal theta activity. Front Cell Neurosci 10:108
Dodt HU, Becker K, Zieglgänsberger W (2013) Infrared video microscopy for visualizing neurons and neuronal excitation in brain slices. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2013(12):1149–1152
Drew GM, Lau BK, Vaughan CW (2009) Substance P drives endocannabinoid-mediated disinhibition in a midbrain descending analgesic pathway. J Neurosci 29(22):7220–7229
Drew GM, Mitchell VA, Vaughan CW (2005) Postsynaptic actions of substance P on rat periaqueductal grey neurons in vitro. Neuropharmacology 49(5):587–595
Duric V, McCarson KE (2005) Hippocampal neurokinin-1 receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression is decreased in rat models of pain and stress. Neuroscience 133(4):999–1006
Ebner K, Sartori SB, Singewald N (2009) Tachykinin receptors as therapeutic targets in stress-related disorders. Curr Pharm Des 15(14):1647–1674
Eliava M, Melchior M, Knobloch-Bollmann HS, Wahis J, da Silva GM, Tang Y, Ciobanu AC, Triana Del Rio R, Roth LC, Althammer F, Chavant V, Goumon Y, Gruber T, Petit-Demoulière N, Busnelli M, Chini B, Tan LL, Mitre M, Froemke RC, Chao MV, Giese G, Sprengel R, Kuner R, Poisbeau P, Seeburg PH, Stoop R, Charlet A, Grinevich V (2016) A new population of parvocellular oxytocin neurons controlling magnocellular neuron activity and inflammatory pain processing. Neuron 89(6):1291–1304
Ferrini F, De Koninck Y. Microglia control neuronal network excitability via BDNF signalling. Neural Plast 2013; 429815
Fries GR, Gassen NC, Rein T. The FKBP51 glucocorticoid receptor co-chaperone: regulation, function, and implications in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 2017; 18(12)
Gagnon M, Bergeron MJ, Lavertu G, Castonguay A, Tripathy S, Bonin RP, Perez-Sanchez J, Boudreau D, Wang B, Dumas L, Valade I, Bachand K, Jacob-Wagner M, Tardif C, Kianicka I, Isenring P, Attardo G, Coull JA, De Koninck Y (2013) Chloride extrusion enhancers as novel therapeutics for neurological diseases. Nat Med 19(11):1524–1528
Ganjiwale A, Cowsik SM (2013) Molecular recognition of tachykinin receptor selective agonists: insights from structural studies. Mini Rev Med Chem 13(14):2036–2046
Gassen NC, Hartmann J, Zschocke J, Stepan J, Hafner K, Zellner A, Kirmeier T, Kollmannsberger L, Wagner KV, Dedic N, Balsevich G, Deussing JM, Kloiber S, Lucae S, Holsboer F, Eder M, Uhr M, Ising M, Schmidt MV, Rein T (2014) Association of FKBP51 with priming of autophagy pathways and mediation of antidepressant treatment response: evidence in cells, mice, and humans. PLoS Med 11(11):e1001755
Glykys J, Dzhala V, Egawa K, Kahle KT, Delpire E, Staley K (2017) Chloride dysregulation, seizures, and cerebral edema: a relationship with therapeutic potential. Trends Neurosci
Gogolla N, Caroni P, Lüthi A, Herry C (2009) Perineuronal nets protect fear memories from erasure. Science 325(5945):1258–1261
González-Ramírez R, Chen Y, Liedtke WB, Morales-Lázaro SL (2017) TRP channels and pain. In: Emir TLR (ed) Neurobiology of TRP channels, 2nd edn. CRC/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Grace PM, Hutchinson MR, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2014) Pathological pain and the neuroimmune interface. Nat Rev Immunol 14(4):217–231
Grace PM, Rolan PE, Hutchinson MR (2011) Peripheral immune contributions to the maintenance of central glial activation underlying neuropathic pain. Brain Behav Immun 25(7):1322–1332
Grinevich V, Knobloch-Bollmann HS, Eliava M, Busnelli M, Chini B (2016) Assembling the puzzle: pathways of oxytocin signaling in the brain. Biol Psychiatry 79(3):155–164
Gu W, Zhang W, Lei Y, Cui Y, Chu S, Gu X, Ma Z (2017a) Activation of spinal alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor shortens the duration of remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia by upregulating KCC2 in the spinal dorsal horn in rats. Mol Pain 13:1744806917704769
Gu W, Zhang W, Lei Y, Cui Y, Chu S, Gu X, Ma Z (2017b) Activation of spinal alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor shortens the duration of remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia by upregulating KCC2 in the spinal dorsal horn in rats. Mol Pain 13:1744806917704769
Guo W, Wang H, Watanabe M, Shimizu K, Zou S, LaGraize SC, Wei F, Dubner R, Ren K (2007) Glial-cytokine-neuronal interactions underlying the mechanisms of persistent pain. J Neurosci 27(22):6006–6018
Hallberg M (2015) Neuropeptides: metabolism to bioactive fragments and the pharmacology of their receptors. Med Res Rev 35(3):464–519
Han S, Soleiman MT, Soden ME, Zweifel LS, Palmiter RD (2015) Elucidating an affective pain circuit that creates a threat memory. Cell 162(2):363–374
Hertler B, Hosp JA, Blanco MB, Luft AR. Substance P signalling in primary motor cortex facilitates motor learning in rats. PLoS One 2017; 12(12)
Hildebrand ME, Xu J, Dedek A, Li Y, Sengar AS, Beggs S, Lombroso PJ, Salter MW (2016) Potentiation of synaptic GluN2B NMDAR currents by fyn kinase is gated through BDNF-mediated disinhibition in spinal pain processing. Cell Rep 17(10):2753–2765
Hökfelt T, Johansson O, Ljungdahl A, Lundberg JM, Schultzberg M (1980) Peptidergic neurones. Nature 284(5756):515–521
Honor P, Menning PM, Rogers SD, Nichols ML, Basbaum AI, Besson JM, Mantyh PW (1999) Spinal substance P receptor expression and internalization in acute, short-term, and long-term inflammatory pain states. J Neurosci 19(17):7670–7678
Hoyer D, Bartfai T (2012) Neuropeptides and neuropeptide receptors: drug targets, and peptide and non-peptide ligands: a tribute to Prof. Dieter Seebach. Chem Biodivers 9(11):2367–2387
Hruska M, Henderson N, Le Marchand SJ, Jafri H, Dalva MB (2018) Synaptic nanomodules underlie the organization and plasticity of spine synapses. Nat Neurosci 21(5):671–682
Huang YJ, Lee KH, Grau JW (2017) Complete spinal cord injury (SCI) transforms how brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) affects nociceptive sensitization. Exp Neurol 288:38–50
Hunt SP, Mantyh PW (2001) The molecular dynamics of pain control. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(2):83–91
Iadarola MJ, Sapio MR, Wang X, Carrero H, Virata-Theimer ML, Sarnovsky R, Mannes AJ, FitzGerald DJ (2017) Analgesia by deletion of spinal neurokinin 1 receptor expressing neurons using a bioengineered substance P-Pseudomonas exotoxin conjugate. Mol Pain 13:1744806917727657
Ikeda H, Stark J, Fischer H, Wagner M, Drdla R, Jäger T, Sandkühler J (2006) Synaptic amplifier of inflammatory pain in the spinal dorsal horn. Science 312(5780):1659–1662
Isensee J, Krahé L, Moeller K, Pereira V, Sexton JE, Sun X, Emery E, Wood JN, Hucho F Synergistic regulation of serotonin and opioid signaling contributes to pain insensitivity in Nav1.7 knockout mice. Sci Signal 2017; 10(461)
Javdani F, Holló K, Hegedűs K, Kis G, Hegyi Z, Dócs K, Kasugai Y, Fukazawa Y, Shigemoto R, Antal M (2015) Differential expression patterns of K(+) /Cl(-) cotransporter 2 in neurons within the superficial spinal dorsal horn of rats. J Comp Neurol 523(13):1967–1983
Jennings EM, Okine BN, Olango WM, Roche M, Finn DP (2016) Repeated forced swim stress differentially affects formalin-evoked nociceptive behavior and the endocannabinoid system in stress normo-responsive and stress hyper-responsive rat strains. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 64:181–189
Jennings EM, Okine BN, Roche M, Finn DP (2014) Stress-induced hyperalgesia. Prog Neurobiol 121:1–18
Jun JY, Choi S, Yeum CH, Chang IY, You HJ, Park CK, Kim MY, Kong ID, Kim MJ, Lee KP, So I, Kim KW (2004) Substance P induces inward current and regulates pacemaker currents through tachykinin NK1 receptor in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal of murine small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol 495(1):35–42
Karpova NN, Pickenhagen A, Lindholm J, Tiraboschi E, Kulesskaya N, Agústsdóttir A, Antila H, Popova D, Akamine Y, Bahi A, Sullivan R, Hen R, Drew LJ, Castrén E (2011) Fear erasure in mice requires synergy between antidepressant drugs and extinction training. Science 334(6063):1731–1734
Khasabov SG, Malecha P, Noack J, Tabakov J, Giesler GJ Jr, Simone DA (2017) Hyperalgesia and sensitization of dorsal horn neurons following activation of NK-1 receptors in the rostral ventromedial medulla. J Neurophysiol 118(5):2727–2744
King AE, Ackley MA, Slack JR (1997) Profile of neuronal excitation following selective activation of the neurokinin-1 receptor in rat deep dorsal horn in vitro. Brain Res 767(1):55–63
King T, Gardell LR, Wang R, Vardanyan A, Ossipov MH, Malan TP Jr, Vanderah TW, Hunt SP, Hruby VJ, Lai J, Porreca F (2005) Role of NK-1 neurotransmission in opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Pain 116(3):276–288
Kormos V, Gaszner B (2013) Role of neuropeptides in anxiety, stress, and depression: from animals to humans. Neuropeptides 47(6):401–419
Kronschläger MT, Drdla-Schutting R, Gassner M, Honsek SD, Teuchmann HL, Sandkühler J (2016) Gliogenic LTP spreads widely in nociceptive pathways. Science 354(6316):1144–1148
Kunde DA, Crawford A, Geraghty DP (2013) Tachykinin (NK1, NK2 and NK3) receptor, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and early transcription factor, cFOS, mRNA expression in rat tissues following systemic capsaicin treatment. Regul Pept 183:35–41
Kuner R, Flor H (2016) Structural plasticity and reorganisation in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(1):20–30
Lalisse S, Hua J, Lenoir M, Linck N, Rassendren F, Ulmann L (2018) Sensory neuronal P2RX4 receptors controls BDNF signaling in inflammatory pain. Sci Rep 8(1):964
Lee PR, Yoon SY, Kim HW, Yeo JH, Kim YH, Oh SB (2018) Peripheral GABAA receptor-mediated signaling facilitates persistent inflammatory hypersensitivity. Neuropharmacology 135:572–580
Lembeck F, Holzer P (1979) Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 310(2):175–173
Lembeck F (2008) The archeology of substance P. Neuropeptides 42(4):444–453
Lembeck (1953) Zur Frage der zentralen Übertragung afferenter Impulse. III. Mitteilung. Das Vorkommen und die Bedeutung der Substanz P in den dorsalen Wurzeln des Rückenmarks. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 219:S197–S213
Lénárd L, László K, Kertes E, Ollmann T, Péczely L, Kovács A, Kállai V, Zagorácz O, Gálosi R, Karádi Z (2018) Substance P and neurotensin in the limbic system: their roles in reinforcement and memory consolidation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 85:1–20
Li L, Chen SR, Chen H, Wen L, Hittelman WN, Xie JD, Pan HL (2016) Chloride homeostasis critically regulates synaptic NMDA receptor activity in neuropathic pain. Cell Rep 15(7):1376–1383
Li WW, Guo TZ, Shi X, Sun Y, Wei T, Clark DJ, Kingery WS (2015) Substance P spinal signaling induces glial activation and nociceptive sensitization after fracture. Neuroscience 310:73–90
Li X, Shaqura M, Mohamed D, Beyer A, Yamada S, Mousa SA, Schäfer M (2018) Pro- versus antinociceptive nongenomic effects of neuronal mineralocorticoid versus glucocorticoid receptors during rat hind paw inflammation. Anesthesiology 128(4):796–809
Lin CR, Cheng JK, Wu CH, Chen KH, Liu CK (2017) Epigenetic suppression of potassium-chloride co-transporter 2 expression in inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA). Eur J Pain 21(2):309–321
Madaan V, Wilson DR (2009) Neuropeptides: relevance in treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. Drug News Perspect 22(6):319–324
Maiarù M, Morgan OB, Mao T, Breitsamer M, Bamber H, Pöhlmann M, Schmidt MV, Winter G, Hausch F, Géranton SM.The stress regulator Fkbp51: a novel and promising druggable target for the treatment of persistent pain states across sexes. Pain 2018. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001204.
Maiarù M, Tochiki KK, Cox MB, Annan LV, Bell CG, Feng X, Hausch F, Géranton SM (2016) The stress regulator FKBP51 drives chronic pain by modulating spinal glucocorticoid signaling. Sci Transl Med 8(325):325
Mantyh PW (2002) Neurobiology of substance P and the NK1 receptor. J Clin Psychiatry 63(Suppl 11):6–10
Mantyh PW, Hunt SP (2004) Setting the tone: superficial dorsal horn projection neurons regulate pain sensitivity. Trends Neurosci 27(10):582–584
Marshall GE, Shehab SA, Spike RC, Todd AJ (1996) Neurokinin-1 receptors on lumbar spinothalamic neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 72(1):255–263
Marsicano G, Goodenough S, Monory K, Hermann H, Eder M, Cannich A, Azad SC, Cascio MG, Gutiérrez SO, van der Stelt M, López-Rodriguez ML, Casanova E, Schütz G, Zieglgänsberger W, Di Marzo V, Behl C, Lutz B (2003) CB1 cannabinoid receptors and on-demand defense against excitotoxicity. Science 302(5642):84–88
Marsicano G, Wotjak CT, Azad SC, Bisogno T, Rammes G, Cascio MG, Hermann H, Tang J, Hofmann C, Zieglgänsberger W, Di Marzo V, Lutz B (2002) The endogenous cannabinoid system controls extinction of aversive memories. Nature 418(6897):530–534
Martin WJ, Cao Y, Basbaum AI (2004) Characterization of wide dynamic range neurons in the deep dorsal horn of the spinal cord in preprotachykinin—a null mice in vivo. J Neurophysiol 91(5):1945–1954
Mashaghi A, Marmalidou A, Tehrani M, Grace PM, Pothoulakis C, Dana R (2016) Neuropeptide substance P and the immune response. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(22):4249–4264
Massey JM, Hubscher CH, Wagoner MR, Decker JA, Amps J, Silver J, Onifer SM (2006) Chondroitinase ABC digestion of the perineuronal net promotes functional collateral sprouting in the cuneate nucleus after cervical spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 26(16):4406–4414
Matosin N, Halldorsdottir T, Binder EB (2018) Understanding the molecular mechanisms underpinning gene by environment interactions in psychiatric disorders: the FKBP5 model. Biol Psychiatry 83(10):821–830
Mòdol L, Cobianchi S, Navarro X (2014) Prevention of NKCC1 phosphorylation avoids downregulation of KCC2 in central sensory pathways and reduces neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. Pain 155(8):1577–1590
Monory K, Massa F, Egertová M, Eder M, Blaudzun H, Westenbroek R, Kelsch W, Jacob W, Marsch R, Ekker M, Long J, Rubenstein JL, Goebbels S, Nave KA, During M, Klugmann M, Wölfel B, Dodt HU, Zieglgänsberger W, Wotjak CT, Mackie K, Elphick MR, Marsicano G, Lutz B (2006) The endocannabinoid system controls key epileptogenic circuits in the hippocampus. Neuron 51(4):455–466
Nabel EM, Morishita H (2013) Regulating critical period plasticity: insight from the visual system to fear circuitry for therapeutic interventions. Front Psychiatry 4:146
Nagy JI, Lynn BD, Senecal JMM, Stecina K. Connexin36 expression in primary afferent neurons in relation to the axon reflex and modality coding of somatic sensation. Neuroscience. 2018
Nakamura Y, Izumi H, Shimizu T, Hisaoka-Nakashima K, Morioka N, Nakata Y (2013) Volume transmission of substance P in striatum induced by intraplantar formalin injection attenuates nociceptive responses via activation of the neurokinin 1 receptor. J Pharmacol Sci 121(4):257–271
Nanou E, Catterall WA (2018) Calcium channels, synaptic plasticity, and neuropsychiatric disease. Neuron 98(3):466–481
Okine BN, Gaspar JC, Finn DP (2018) PPARs and pain. Br J Pharmacol
Parent AJ, Beaudet N, Beaudry H, Bergeron J, Bérubé P, Drolet G, Sarret P, Gendron L (2012) Increased anxiety-like behaviors in rats experiencing chronic inflammatory pain. Behav Brain Res 229(1):160–167
Parsons CG, Danysz W, Zieglgänsberger W (2005) Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission. Handb Exp Pharmacol (169):249–303
Pernow B (1953) Distribution of substance P in the central and peripheral nervous system. Nature 171(4356):746
Petho G, Reeh PW (2012) Sensory and signaling mechanisms of bradykinin, eicosanoids, platelet-activating factor, and nitric oxide in peripheral nociceptors. Physiol Rev 92(4):1699–1775
Pfeiffer M, Kirscht S, Stumm R, Koch T, Wu D, Laugsch M, Schröder H, Höllt V, Schulz S (2003) Heterodimerization of substance P and mμ-opioid receptors regulates receptor trafficking and resensitization. J Biol Chem 278(51):51630–51637
Pickel VM, Reis DJ, Leeman SE (1977) Ultrastructural localization of substance P in neurons of rat spinal cord. Brain Res 122(3):534–540
Pitcher GM, Henry JL (2004) Nociceptive response to innocuous mechanical stimulation is mediated via myelinated afferents and NK-1 receptor activation in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol 186(2):173–197
Pizzorusso T, Medini P, Berardi N, Chierzi S, Fawcett JW, Maffei L (2002) Reactivation of ocular dominance plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science 298(5596):1248–1251
Popik B, Crestani AP, Silva MO, Quillfeldt JA, de Oliveira Alvares L (2018) Calpain modulates fear memory consolidation, retrieval and reconsolidation in the hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 151:53–58
Price TJ, Cervero F, de Koninck Y (2005) Role of cation-chloride-cotransporters (CCC) in pain and hyperalgesia. Curr Top Med Chem 5(6):547–555
Price TJ, Cervero F, Gold MS, Hammond DL, Prescott SA (2009) Chloride regulation in the pain pathway. Brain Res Rev 60(1):149–170
Punnakkal P, von Schoultz C, Haenraets K, Wildner H, Zeilhofer HU (2014) Morphological, biophysical and synaptic properties of glutamatergic neurons of the mouse spinal dorsal horn. J Physiol 592(4):759–776
Radat F, Margot-Duclot A, Attal N (2013) Psychiatric co-morbidities in patients with chronic peripheral neuropathic pain: a multicentre cohort study. Eur J Pain 17(10):1547–1557
Ralston HJ 3rd (2005) Pain and the primate thalamus. Prog Brain Res 149:1–10
Randić M, Hećimović H, Ryu PD (1990) Substance P modulates glutamate-induced currents in acutely isolated rat spinal dorsal horn neurones. Neurosci Lett 117(1–2):74–80
Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Hökfelt T (2000) Neuroanatomical localisation of substance P in the CNS and sensory neurons. Neuropeptides 34(5):256–271
Rupniak NMJ, Kramer MS (2017) NK1 receptor antagonists for depression: why a validated concept was abandoned. J Affect Disord 223:121–125
Rygh LJ, Suzuki R, Rahman W, Wong Y, Vonsy JL, Sandhu H, Webber M, Hunt S, Dickenson AH (2006) Local and descending circuits regulate long-term potentiation and zif268 expression in spinal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 24(3):761–772
Santarelli S, Zimmermann C, Kalideris G, Lesuis SL, Arloth J, Uribe A, Dournes C, Balsevich G, Hartmann J, Masana M, Binder EB, Spengler D, Schmidt MV (2017) An adverse early life environment can enhance stress resilience in adulthood. Psychoneuroendocrinology 78:213–221
Schadrack J, Castro-Lopes JM, Avelino A, Zieglgänsberger W, Tölle TR.Modulated expression of c-Fos in the spinal cord following noxious thermal stimulation of monoarthritic rats. J Neurosci Res 1998
Schadrack J, Neto FL, Ableitner A, Castro-Lopes JM, Willoch F, Bartenstein P, Zieglgänsberger W, Tölle TR (1999) Metabolic activity changes in the rat spinal cord during adjuvant monoarthritis. Neuroscience 94(2):595–605
Schadrack J, Zieglgänsberger W (2000) Activity-dependent changes in the pain matrix. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 113:19–23
Schmidt MV, Schülke JP, Liebl C, Stiess M, Avrabos C, Bock J, Wochnik GM, Davies HA, Zimmermann N, Scharf SH, Trümbach D, Wurst W, Zieglgänsberger W, Turck C, Holsboer F, Stewart MG, Bradke F, Eder M, Müller MB, Rein T (2011) Tumor suppressor down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma 1 (DRR1) is a stress-induced actin bundling factor that modulates synaptic efficacy and cognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(41):17213–17218
Sharif Naeini R, Cahill CM, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Ménard HA, Henry JL (2005) Remodelling of spinal nociceptive mechanisms in an animal model of monoarthritis. Eur J Neurosci 22(8):2005–2015
Sheng N, Bemben MA, Díaz-Alonso J, Tao W, Shi YS, Nicoll RA (2018) LTP requires postsynaptic PDZ-domain interactions with glutamate receptor/auxiliary protein complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(15):3948–3953
Sorkin LS, Eddinger KA, Woller SA, Yaksh TL. Origins of antidromic activity in sensory afferent fibers and neurogenic inflammation. Semin Immunopathol. 2018
Sousa-Valente J, Brain SD A historical perspective on the role of sensory nerves in neurogenic inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 2018. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-018-0673-1
Steinhoff MS, von Mentzer B, Geppetti P, Pothoulakis C, Bunnett NW (2014) Tachykinins and their receptors: contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol Rev 94(1):265–301
Tan AM, Stamboulian S, Chang YW, Zhao P, Hains AB, Waxman SG, Hains BC (2008) Neuropathic pain memory is maintained by Rac1-regulated dendritic spine remodeling after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 28(49):13173–13183
Tan LL, Pelzer P, Heinl C, Tang W, Gangadharan V, Flor H, Sprengel R, Kuner T, Kuner R (2017) A pathway from midcingulate cortex to posterior insula gates nociceptive hypersensitivity. Nat Neurosci 20(11):1591–1601
Tang YP, Shimizu E, Dube GR, Rampon C, Kerchner GA, Zhuo M, Liu G, Tsien JZ (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401(6748):63–69
Tashima R, Koga K, Sekine M, Kanehisa K, Kohro Y, Tominaga K, Matsushita K, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Fukazawa Inoue K, Yawo H, Furue H, Tsuda M. Optogenetic activation of non-nociceptive Aβ fibers induces neuropathic pain-like sensory and emotional behaviors after nerve injury in rats. eNeuro 2018; 5(1)
Thörn Pérez C, Hill RH, Grillner S (2015) Substance P depolarizes lamprey spinal cord neurons by inhibiting background potassium channels. PLoS One 10(7):e0133136
Todd AJ (2002) Anatomy of primary afferents and projection neurones in the rat spinal dorsal horn with particular emphasis on substance P and the neurokinin 1 receptor. Exp Physiol 87(2):245–249
Totsch SK, Sorge RE. Immune system involvement in specific pain conditions. Mol Pain. 2017
Trenkwalder C, Zieglgänsberger W, Ahmedzai SH, Högl B (2017) Pain, opioids, and sleep: implications for restless legs syndrome treatment. Sleep Med 31:78–85
Tropea D, Caleo M, Maffei L (2003) Synergistic effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and chondroitinase ABC on retinal fiber sprouting after denervation of the superior colliculus in adult rats. J Neurosci 23(18):7034–7044
Tsien RY (2013) Very long-term memories may be stored in the pattern of holes in the perineuronal net. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(30):12456–12461
Tsuruga K, Hashimoto T, Kato R, Kato R, Uchida Y, Hase T, Morimoto Y (2016) Plantar injection of formalin in rats reduces the expression of a potassium chloride cotransporter KCC2 in the spinal cord and a kinase inhibitor suppresses this reduction. Biomed Res 37(4):243–249
Urban MO, Gebhart GF (1999) Central mechanisms in pain. Med Clin North Am 83(3):585–596
V Euler US, Gaddum JH (1931) An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol 72(1):74–87
Vachon P, Millecamps M, Low L, Thompsosn SJ, Pailleux F, Beaudry F, Bushnell CM, Stone LS (2013) Alleviation of chronic neuropathic pain by environmental enrichment in mice well after the establishment of chronic pain. Behav Brain Funct 9:22
von Schack D, Agostino MJ, Murray BS, Li Y, Reddy PS, Chen J, Choe SE, Strassle BW, Li C, Bates B, Zhang L, Hu H, Kotnis S, Bingham B, Liu W, Whiteside GT, Samad TA, Kennedy JD, Ajit SK. Dynamic changes in the microRNA expression profile reveal multiple regulatory mechanisms in the spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain. PLoS One 2011; 6(3)
Vuilleumier PH, Fritsche R, Schliessbach J, Schmitt B, Arendt-Nielsen L, Zeilhofer HU, Curatolo M (2018) Mutations affecting glycinergic neurotransmission in hyperekplexia increase pain sensitivity. Brain 141(1):63–71
Weisshaar CL, Winkelstein BA (2014) Ablating spinal NK1-bearing neurons eliminates the development of pain and reduces spinal neuronal hyperexcitability and inflammation from mechanical joint injury in the rat. J Pain 15(4):378–386
Wieseler-Frank J, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2004) Glial activation and pathological pain. Neurochem Int 45(2–3):389–395
Wiley RG, Kline RH 4th, Vierck CJ Jr (2007) Anti-nociceptive effects of selectively destroying substance P receptor-expressing dorsal horn neurons using [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-substance P-saporin: behavioral and anatomical analyses. Neuroscience 146(3):1333–1345
Willig KI, Steffens H, Gregor C, Herholt A, Rossner MJ, Hell SW (2014) Nanoscopy of filamentous actin in cortical dendrites of a living mouse. Biophys J 106(1):L01–L03
Wu ZZ, Guan BC, Li ZW, Yang Q, Liu CJ, Chen JG (2004) Sustained potentiation by substance P of NMDA-activated current in rat primary sensory neurons. Brain Res 1010(1–2):117–126
Xanthos DN, Sandkühler J (2014) Neurogenic neuroinflammation: inflammatory CNS reactions in response to neuronal activity. Nat Rev Neurosci 15(1):43
Yang K, Takeuchi K, Wei F, Dubner R, Ren K (2011) Activation of group I mGlu receptors contributes to facilitation of NMDA receptor membrane current in spinal dorsal horn neurons after hind paw inflammation in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 670(2–3):509–518
Yilmaz P, Diers M, Diener S, Rance M, Wessa M, Flor H (2010) Brain correlates of stress-induced analgesia. Pain 151(2):522–529
Yousuf MS, Kerr BJ (2016) The role of regulatory transporters in neuropathic pain. Adv Pharmacol 75:245–271
Yu HM, Wang Q, Sun WB (2017) Silencing of FKBP51 alleviates the mechanical pain threshold, inhibits DRG inflammatory factors and pain mediators through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Gene 627:169–175
Zelikowsky M, Hui M, Karigo T, Choe A, Yang B, Blanco MR, Beadle K, Gradinaru V, Deverman BE, Anderson DJ (2018) The neuropeptide Tac2 controls a distributed brain state induced by chronic social isolation stress. Cell 173(5):1265–1279
Zhang J, Yu J, Kannampalli P, Nie L, Meng H, Medda BK, Shaker R, Sengupta JN, Banerjee B (2017) MicroRNA-mediated downregulation of potassium-chloride-cotransporter and vesicular γ-aminobutyric acid transporter expression in spinal cord contributes to neonatal cystitis-induced visceral pain in rats. Pain 158(12):2461–2474
Zieglgänsberger W, Berthele A, Tölle TR (2005) Understanding neuropathic pain. CNS Spectr 10(4):298–308
Zieglgänsberger W, Herz A (1971) Changes of cutaneous receptive fields of spino-cervical-tract neurones and other dorsal horn neurones by microelectrophoretically administered amino acids. Exp Brain Res 13(2):111–126
Zieglgänsberger W, Tulloch IF (1979) Effects of substance P on neurones in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord of the cat. Brain Res 166(2):273–282
Zieglgänsberger W (1986) Central control of nociception. In: Mountcastle VB, Bloom FE, Geiger SR (eds) Handbook of physiology—the nervous system, 4th edn. Williams & Wilkins Comp, Baltimore, pp 581–645
Zieglgänsberger W (2009) Neuropeptides: electrophysiology. In: Squire LR (ed) Encyclopedia of neuroscience. Academic, Oxford, pp 885–890
Funding
Open access funding provided by Max Planck Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Zieglgänsberger, W. Substance P and pain chronicity. Cell Tissue Res 375, 227–241 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2922-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2922-y