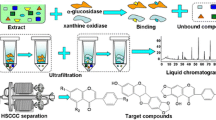
Abstract
Size-exclusion chromatography, in conjunction with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, exemplifies a screening methodology to identify α-glucosidase inhibitors from natural extracts. This approach could be used to speed the time of targeting active principles from complex matrices, as a substitute for the established in vitro enzymatic assays which depend on spectrophotometric methods where disadvantages including sensitivity to turbidity and substance interferences—extract pigmentation, or absorption in the visible light region of tested samples—represent factors that affect the chromogenic screenings. Gel permeation through a spin size-exclusion column allowed separating high-affinity molecules bounded to α-glucosidase in solution. After acid hydrolysis of the enzyme-ligand complex, electrospray ionization mass spectrometry was used as a direct detector for the ligand. This affinity-directed fractionation was illustrated by using a crude extract, semi-purified fractions, and pure active glycolipids from moon vine seeds, Ipomoea alba L., Convolvulaceae, in addition to acarbose (positive control), which led to the identification of albinosides VI (ESI-MS m/z 991 [M + Na]+) and VII (ESI-MS m/z 975 [M + Na]+), two tracked high-affinity glycolipids, which demonstrated an in vitro inhibitory potential of α-glucosidases from yeast and rat intestine. Molecular docking predicted that these inhibitors bind to the enzyme catalytic site as acarbose.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam F, Shafique Z, Amjad ST, Bin Asad MHH (2019) Enzymes inhibitors from natural sources with antidiabetic activity: a review. Phytother Res 33:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6211
Alanzi AR, Demessie AA, Mahmud T (2018) Biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of pseudo-oligosaccharides. Emerg Top Life Sci 2:405–417. https://doi.org/10.1042/ETLS20180010
Annis A, Chuang CC, Nazef N (2007) ALIS: an affinity selection–mass spectrometry system for the discovery and characterization of protein–ligand interactions. In: Wanner KT, Höfner G (eds) Mass spectrometry in medicinal chemistry: applications in drug discovery. Weinheim, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, KGaA, pp 121–156. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527610907.ch3
Assefa ST, Yang EY, Chae SY, Song M, Lee J, Cho MC, Jang S (2020) Alpha glucosidase inhibitory activities of plants with focus on common vegetables. Plants (Basel) 9:2. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010002
Atta-ur-Rahman M, Choudhar MI, Thomsen WJ (2001) Bioassay techniques for drug development. Harwood Academic, Amsterdam
Baell JB (2016) Feeling nature’s PAINS: natural products, natural product drugs, and pan assay interference compounds (PAINS). J Nat Prod 79:616–628. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00947
Castañeda-Gómez J, Rosas-Ramírez D, Cruz-Morales S, Fragoso-Serrano M, Pereda-Miranda R (2017) HPLC-MS profiling of the multidrug-resistance modifying resin glycoside content of Ipomoea alba seeds. Rev Bras Farmacogn 27:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2017.05.003
Cruz-Morales S, Castañeda-Gómez J, Rosas-Ramírez D, Fragoso-Serrano M, Figueroa-González G, Lorence A, Pereda-Miranda R (2016) Resin glycosides from Ipomoea alba seeds as potential chemosensitizers in breast carcinoma cells. J Nat Prod 79:3093–3104. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00782
Demarque DP, Crotti AE, Vessecchi R, Lopes JL, Lopes NP (2016) Fragmentation reactions using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: an important tool for the structural elucidation and characterization of synthetic and natural products. Nat Prod Rep 33:432–455. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5np00073d
Derosa G, Maffioli P (2012) α-Glucosidase inhibitors and their use in clinical practice. Arch Med Sci 8:899–906. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2012.31621
Fan M, Chen G, Sun B, Wu J, Li N, Sarker SD, Nahar L, Guo M (2019) Screening for natural inhibitors of human topoisomerases from medicinal plants with bio-affinity ultrafiltration and LC–MS. Phytochem Rev:1–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-019-09635-x
Hedrington MS, Davis SN (2019) Considerations when using alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Pharmacother 20:2229–2235. https://doi.org/10.1080/14656566.2019.1672660
Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS (2007) A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J Comput Chem 28:1145–1652. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20634
Jonker N, Kool J, Irth H, Niessen WM (2011) Recent developments in protein–ligand affinity mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:2669–2681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4350-z
Khan H, Amin S, Tewari D, Nabavi SM, Atanasov AG (2019) Plant-derived glycosides with α-glucosidase inhibitory activity: current standing and future prospects. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 19:391–401. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530319666181128104831
Kudva YC, Nair KS (2020) Diabetes Mellitus: A Perspective on the Post-Insulin Era. Mayo Clin Proc 95:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.11.016
Lankatillake C, Huynh T, Dias DA (2019) Understanding glycaemic control and current approaches for screening antidiabetic natural products from evidence-based medicinal plants. Plant Methods 15:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0487-8
Lira-Ricárdez J, Pereda-Miranda R (2019) Reversal of multidrug resistance by amphiphilic morning glory resin glycosides in bacterial pathogens and human cancer cells. Phytochem Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-019-09631-1
Mohiuddin GS, Palaian S, Shankar PR, Sam KG, Kumar M (2019) Uncommon side effects of commonly used anti-diabetics: time to monitor them. Int J Pharm Sci Res 10:4145–4148. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.10(9).4145-48
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19:14%3C1639::AID-JCC10%3E3.0.CO;2-B
Orhan N, Ekin HN, Şüküroğlu M, Aslan M (2019) In vitro antidiabetic effect, quantitative studies and UPLC-TOF-MS analysis of black tea samples from Turkish market. J Res Pharm 23:484–497. https://doi.org/10.12991/jrp.2019.155
Pereda-Miranda R, Rosas-Ramírez D, Castañeda-Gómez J (2010) Resin glycosides from the morning glory family. In: Kinghorn AD, Falk H, Kobayashi J (eds) Progress in the chemistry of organic natural products. Springer Verlag, Wien, pp 77–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-99661-4_2
Potterat O, Hamburger M (2013) Concepts and technologies for tracking bioactive compounds in natural product extracts: generation of libraries, and hyphenation of analytical processes with bioassays. Nat Prod Rep 30:546–564. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3np20094a
Proença C, Freitas M, Ribeiro D, Oliveira EF, Sousa JL, Tomé SM, Ramos MJ, Silva AM, Fernandes PA, Fernandes E (2017) α-Glucosidase inhibition by flavonoids: an in vitro and in silico structure–activity relationship study. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 32:1216–1228. https://doi.org/10.1080/2F14756366.2017.1368503
Promyos N, Temviriyanukul P, Suttisansanee U (2017) Evaluation of α-glucosidase inhibitory assay using different sub-classes of flavonoids. Curr Appl Sci Technol 17:172–180
Rosas-Ramírez D, Escandón-Rivera S, Pereda-Miranda R (2018) Morning glory resin glycosides as α-glucosidase inhibitors: in vitro and in silico analysis. Phytochem 148:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.01.012
Siegel MM (2007) Drug screening using gel permeation chromatography spin columns coupled with ESI-MS. In: Wanner KT, Höfner G (eds) Mass spectrometry in medicinal chemistry: applications in drug discovery. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, KGaA, Weinheim, pp 65–120. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527610907.ch2
Sindhi V, Gupta V, Sharma K, Bhatnagar S, Kumari R, Dhaka N (2013) Potential applications of antioxidants - a review. J Pharm Res 7:828–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jopr.2013.10.001
Unnikrishnan MK, Veerapur V, Nayak Y, Mudgal PP, Mathew G (2014) Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of the flavonoids. In: Polyphenols in human health and disease. Elseivier Inc, pp 143–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398456-2.00013-X
Van Middlesworth F, Cannell RJP (1998) Dereplication and partial identification of natural products. In: RJP C (ed) Natural products isolation. Methods in biotechnology. Humana press, pp 279–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59259-256-2_10
Walker JM, Winder JS, Kellam SJ (1993) High-throughput microtiter plate-based chromogenic assays for glycosidase inhibitors. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 38:141–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02916417
Acknowledgments
D.R.-R. is grateful to Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología for his postdoctoral scholarship (CONACyT-Retenciones 2019-1, 205045). We thank Dr. Mabel Fragoso-Serrano (Facultad de Química) for assistance during the purification of the test compounds, M.Sc. Lucía del Carmen Márquez Alonso for support during the recording of mass spectra (Instituto de Química), and M.Sc. Cristian Fabián Salinas-Manzo for assistance during the gel permeation chromatography processes.
Funding
Funding was provided by Dirección General de Asuntos del Personal Académico, Programa de Apoyo a Proyectos de Investigación e Innovación Tecnológica, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (grants IN208019 and IG20021), and Dirección General de Servicios de Cómputo Académico (LANCAD-UNAM-DGTIC-204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DRR designed the study and performed and supervised the SEC-EM experiments, in vitro inhibitory enzymatic assays, and molecular docking, as well as elaborated the first draft of the manuscript. RPM guided the chemical analysis, contributed to the interpretation of all the results, and provided critical reading and insightful recommendations for the final manuscript. SER supervised the bioassays and molecular docking. RAE provided laboratory instrumentation and supplies. All of the authors have read the final manuscript and approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosas-Ramírez, D., Pereda-Miranda, R., Escandón-Rivera, S. et al. Identification of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Ipomoea alba by Affinity-Directed Fractionation-Mass Spectrometry. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 30, 336–345 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-020-00068-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-020-00068-8