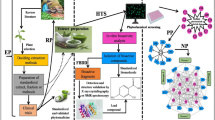
Abstract
Rhizoma Coptidis is an alkaloid-rich herbal drug used in Chinese herbal medicine. Currently, conventional methods for screening and isolating alkaloids are labor-intensive and time-consuming. In the present study, ultrafiltration liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ultrafiltration liquid chromatography-photodiode array detector-electrospary ionization mass spectrometry (LC-PDA-ESI/MS)) were applied to screen and identify α-glucosidase inhibitors in R. Coptidis. High-speed countercurrent chromatography and reverse-phase medium-pressure liquid chromatography were applied to separate and isolate the active constituents. As a result, five major compounds in R. Coptidis were screened and identified as α-glucosidase inhibitors by ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI/MS. Five ligands, jatrorrhizine, epiberberine, coptisine, palmatine, and berberine, were isolated by reverse-phase medium-pressure liquid chromatography and high-speed countercurrent chromatography. The purities of the five compounds as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography were 76.20, 75.13, 82.24, 93.78, and 92.01%, respectively. The results indicate that systematic isolation of bioactive components in R. Coptidis guided by ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI/MS is a feasible and efficient technique that could be extended to separation of other enzyme inhibitors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang LC, Sun SW (2006) Micellar electrokinetic chromatography for separation of a mixture of coptis alkaloids, scute flavonoids, and rhubarb anthraquinones and bianthrones. J Pharm Biomed Anal 40:62–67
Chen JH, Zhao HQ, Wang XR, Lee FS, Yang HH, Zheng L (2008) Analysis of major alkaloids in Rhizoma coptidis by capillary electrophoresis-electrospray-time of flight mass spectrometry with different background electrolytes. Electrophoresis 29:2135–2147
Delavenne X, Montbel A, Hodin S, Zufferey P, Basset T (2014) Quantification of total and unbound tranexamic acid in human plasma by ultrafiltration liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: Application to pharmacokinetic analysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 91:32–36
Derosa G, Maffioli P (2012) α-Glucosidase inhibitors and their use in clinical practice. Arch Med Sci 8:899–906
Hussain RA, Kim J, Beecher CW, Kinghorn AD (1989) Unambiguous carbon-13 NMR assignments of some biologically active protoberberine alkaloids. Heterocycles 29:2257–2260
Ito Y (2005) Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1065:145–168
Jung HA, Yoon NY, Bae HJ, Min BS, Choi JS (2008) Inhibitory activities of the alkaloids from Coptidis Rhizoma against aldose reductase. Arch Pharm Res 31:1405–1412
Lee WC, Kim JK, Kang JW, Oh WY, Jung JY, Kim YS, Jung HA, Choi JS, Lee SM (2010) Palmatine attenuates D-galactosamine/ lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 48:222–228
Li HL, Song FR, Xing JP, Tsao R, Liu ZQ, Liu SY (2009) Screening and structural characterization of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from hawthorn leaf flavonoids extract by ultrafiltration lc-dad-ms(n) and sori-cid fticr ms. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 20:1496–1503
Li YB, Zhang TJ, Zhang XL, Xu HY, Liu CX (2010) Chemical fingerprint analysis of Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex by ultra performance LC/Q-TOF-MS methods combined with chemometrics. J Sep Sci 33:3347–3353
Luo XB, Chen B, Yao SZ (2005) Simultaneous analysis of protoberberine, indolequinoline and quinolone alkaloids in coptis-evodia herb couple and the chinese herbal preparations by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. Talanta 66:103–110
Qian P, Yang XW (2014) Five new alkaloids from Coptidis Rhizoma-Euodiae Fructus couple and their cytotoxic activities against gastrointestinal cancer cells. Fitoterapia 93:74–80
Ren LL, Xue XY, Zhang FF, Xu Q, Liang XM (2007) High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of protoberberine alkaloids in medicine herbs. J Sep Sci 30:833–842
Shi SY, Huang KL, Zhang YP, Zhao Y, Du QZ (2007) Purification and identification of antiviral components from Laggera pterodonta by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr B 859(1):119–124
Tong SQ, Yan JZ (2007) Large-scale separation of hydroxyanthraquinones from rheum palmatum L. by ph-zone-refining counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1176:163–168
Wang DW, Liu ZQ, Guo MQ, Liu SY (2004) Structural elucidation and identification of alkaloids in Rhizoma Coptidis by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 39:1356–1365
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27:1047–1053
Xie Z, Sun Y, Lam S, Zhao M, Liang Z, Yu X, Yang D, Xu X (2014) Extraction and isolation of flavonoid glycosides from Flos Sophorae Immaturus using ultrasonic-assisted extraction followed by high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J Sep Sci 37:957–965
Yan R, Mu Q, Wang Y, Liu Y, Di X (2012) Relative determination approach to the metabolites of protoberberine alkaloids in Rat urine by liquid chromatography Tandem mass spectrometry for the comparative studies on Rhizome coptidis and Zuojinwan preparation. Iran J Pharm Res 11:1265–1273
Zhang YC, Liu CM, Zhang ZK, Wang J, Wu GM, Li SN (2010) Comprehensive separation and identification of chemical constituents from Apocynum venetum leaves by high-performance counter-current chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 878:3149–3155
Zou JG, Liu F, Xiao-Long XU, Liu YY, Peng HL, Wang HP (2010) Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of total alkaloids from semen strychni. Food Sci 31:116–119
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31170326, 31370374), the team project of Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department (No. 20130413043GH), the Academic Innovation Foundation of Changchun Normal University (cscxy2015003), the project of Jilin Provincial Education Department ([2013] 253), and the Natural Science Foundation of Changchun Normal University (No. [2013] 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Li, S., Li, S. et al. Screening and isolating potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from Rhizoma Coptidis by ultrafiltration LC-PDA-ESI/MS combined with high-speed countercurrent chromatography and reverse-phase medium-pressure liquid chromatography. Med Chem Res 26, 3384–3394 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2031-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2031-6