Abstract
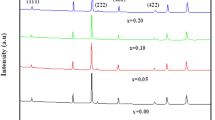
In this communication, the synthesis (solid-state reaction) and characterization (XRD, SEM, EDX, and IS) of the (1 − x)BiFeO3 − x(BiNaKTiMnO3), (x = 0.05 and 0.1) ceramics were reported. The structural analysis suggests a rhombohedral crystal symmetry (#R3c) with an average crystallite size of 39.6 nm and micro-lattice strain of 0.000401 in x = 0.05 sample, whereas average crystallite size of 46.6 nm and lattice strain of 0.00133 in x = 0.1 sample, respectively. The growth and distribution of the grains and the position of grain boundaries were studied from a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The purity and compositional analysis of the prepared samples were checked from an energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) image. The study of the Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectrum suggests the presence of a stretching band of the constituent elements in the modified bismuth ferrite. The presence of the Maxwell–Wanger type of dispersion was confirmed by a dielectric study. The investigation of impedance as a function of temperature and frequency reveals the existence of a negative temperature coefficient of resistance (NTCR). A non-Debye kind of relaxation mechanism is revealed by electric modulus analysis; however, a thermally induced relaxation process is confirmed by an ac conductivity study. The semi-circular arcs in the Nyquist and Cole–Cole plots indicate that the sample is semiconducting. BNKTM 5% has an energy bandgap of 2.9 eV, while BNKTM 10% has an energy bandgap of 2.7 eV, according to UV–visible spectra. The field-dependent hysteresis loop is analogous to the onset of ferroelectricity.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
J.L. Rosas, J.M. Cervantes, J. Leon-Flores, E. Carvajal, J.A. Arenas, M. Romero, R. Escamilla, DFT study on the electronic and magnetic properties of the Sr2FeNbO6 compound. Mater. Today Commun. 23, 100844–100853 (2020)
S.M. Borchani, W.C.-R. Koubaa, M. Megdiche, Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of a new double-perovskite LaNaMnMoO6 material. R. Soc. Open Sci. 4, 170920–170926 (2017)
H. Zheng, Y.L. Dong, X. Wang, W.J. Weng, G.R. Han, N. Ma, P.Y. Du, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 48, 8927–8930 (2009)
M. Gajek, S. Fusil, K. Bouzehouane, J. Fontcuberta, A. Barthelemy, A. Fert et al., Nat. Mater. 6, 296–302 (2007)
M. Bibes, A. Barthélémy, Nat Mater. 7, 425–426 (2008)
K.K. Shung, J.M. Cannata, Q.F. Zhou, Piezoelectric materials for high-frequency medical imaging applications: a review. J. Electroceram. 19, 139–145 (2007)
G.A. Smolenskii, A.I. Agranovskaya, N.N. Krainic, New ferroelectrics of complex composition IV. Sov. Phys. Solid State 2, 2651–2654 (1961)
T. Takenaka, K. Sakata, Dielectric, piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties of (BiNa)1/2TiO3-based ceramics. Ferroelectrics 95, 153–156 (1989)
S. Said, J.P. Mercurio, Relaxor behavior of low lead and lead-free ferroelectric ceramics of the Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–PbTiO3 and Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 systems. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1333–1336 (2001)
R.K. Parida, B.N. Parida, R.K. Bhuyan, S.K. Parida, Structural, mechanical and electric properties of La doped BNT-BFO perovskite ceramics. Ferroelectrics 571, 162–174 (2021)
F. Aziz, N. Gupta, G.G. Soni, K.K. Kushwah, Contrasting effects of mismatch strain on the magnetic behavior of undoped and doped BaFeO3-δ thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 517, 167338 (2021)
S.K. Parida, P. Kumar Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural and electrical characterization of SrMn0.97Ce0.03O3 ceramics. Integr. Ferroelectr. 221, 215–230 (2021)
T. Zhao, A. Scholl, F. Zavaliche et al., Electrical control of antiferromagnetic domains in multiferroic BiFeO 3 films at room temperature. Nat. Mater. 5(10), 823–829 (2006)
Y.H. Chu, L.W. Martin, M.B. Holcomb, Electric-field control of local ferromagnetism using a magnetoelectric multiferroic. Nat. Mater. 7, 478–482 (2008)
S. Lee, W. Ratcliff, S.W. Cheong, V. Kiryukhin, Electric field control of the magnetic state in BiFeO3 single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 192906–192907 (2008)
G. Catalan, J.F. Scott, Physics and applications of bismuth ferrite. Adv. Mater. 21, 2463–2485 (2009)
M. Załȩski, Thermally stimulated processes related to photochromism of scandium doped sillenites. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 4279–4284 (2000)
E. Nippolainen, A.A. Kamshilin, V.V. Prokofiev, T. Jaaskelainen, Combined formation of a self-pumped phase-conjugate mirror and spatial subharmonics in photorefractive sillenites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 859–861 (2001)
P.H. Borse, U.A. Joshi, S.M. Ji, J.S. Jang, J.S. Lee, E.D. Jeong, H.G. Kim, Band gap tuning of lead-substituted BaSnO3 for visible light photocatalysis. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 034103 (2007)
L.M. Campos, A. Tontcheva, S. Günes, G. Sonmez, H. Neugebauer, N.S. Sariciftci, F. Wudl, Extended photocurrent spectrum of a low band gap polymer in a bulk heterojunction solar cell. Chem. Mater. 17, 4031–4033 (2005)
C. Michel, J.M. Moreau, G.D. Achenbechi, R. Gerson, W.J. James, Solid State Commun. 7, 701 (1969)
F. Kubel, H. Schmid, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B: Struct. Sci. B46, 698 (1990)
A. Maqbool, A. Hussain, J.U. Rahman, J.K. Park, T.G. Park, J.S. Song, M.H. Kim, Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of SrZrO3-modified Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 lead-free ceramics. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24, s146–s151 (2014)
J.R. Chen, W.L. Wang, J.-B. Li, G.H. Rao, X-ray diffraction analysis and specific heat capacity of (Bi1−xLax)FeO3 perovskites. J. Alloy. Compd. 459, 66–70 (2008)
T.-J. Park, G.C. Papaefthymiou, A.J. Viescas, A.R. Moodenbaugh, S.S. Wong, Size-dependent magnetic properties of single-crystalline multiferroic BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 7, 766–772 (2007)
T. Zheng, C. Zhao, J. Wu, K. Wang, J.-F. Li, Large strain of lead-free bismuth ferrite ternary ceramics at elevated temperature. Scripta Mater. 155, 11–15 (2018)
C. Ederer, N.A. Spaldin, Influence of strain and oxygen vacancies on the magnetoelectric properties of multiferroic bismuth ferrite. Phys. Rev. B. 71, 224103 (2005)
B.M. Al Maswari, J. Ahmed, N. Alzaqri, T. Ahamad, Y. Mao, A. Hezam, B.M. Venkatesha, Synthesis of perovskite bismuth ferrite embedded nitrogen-doped carbon (BiFeO3-NC) nanocomposite for energy storage application. J. Energy Storage 44, 103515 (2021)
R. Palai, R.S. Katiyar, H. Schmid, P. Tissot, S.J. Clark, J. Robertson, S.A.T. Redfern, G. Catalan, J.F. Scott, The beta phase of multiferroic bismuth ferrite and its beta-gamma metal-insulator transition. Phys. Rev. B 77, 014110 (2008)
X. Zhu, Q. Hang, Z. Xing, Y. Yang, J. Zhu, Z. Liu, N. Ming, P. Zhou, Y.E. Song, Z. Li, T. Yu, Z. Zou, Microwave hydrothermal synthesis, structural characterization, and visible-light photocatalytic activities of single-crystalline bismuth ferric nanocrystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 2688–2693 (2011)
S.K. Parida, Influence of cerium substitution on structural and dielectric properties of the modified BiFeO3-PbTiO3 ceramics. Ferroelectric 583, 19–32 (2021)
V.D. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B.N. Dole, Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particle. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 6, 1–8 (2012)
C.-T. Xia, V.M. Fuenzalida, R.A. Zarate, Electrochemical preparation of crystallized Ba1-xSrxMoO4 solid-solution films at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 316, 250–255 (2001)
S. Mishra, R.N.P. Choudhary, S.K. Parida, Structural, dielectric, electrical and optical properties of a double perovskite: BaNaFeWO6 for some device applications. J. Mol. Struct. 1265, 133353–133367 (2022)
S.K. Parida, Studies on structural, dielectric, and optical properties of Cu/W double substituted calcium manganite for solar cells and thermistor applications. Phase Transit. 94, 1033–1052 (2021)
M.R. Islam, M.S. Islam, M.A. Zubair, H.M. Usama, M.S. Azam, A. Sharif, Evidence of super-paramagnetism and improved electrical properties in Ba and Ta co-doped BiFeO3 ceramics. Alloys Compd. 735, 2584–2596 (2018)
J. Liu, C.G. Duan, W.N. Mei, R.W. Smith, J.R. Hardy, Dielectric properties and Maxwell-Wagner relaxation of compounds ACu3Ti4O12(A=Ca, Bi2/3, Y2/3, La2/3). J. Appl. Phys. 98, 1–6 (2005)
M. Atif, M. Idrees, M. Nadeem, M. Siddique, M.W. Ashraf, Investigation on the structural, dielectric and impedance analysis of manganese substituted cobalt ferrite i.e. Co1– xMnxFe2O4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.4). RSC Adv. 6, 20876–20885 (2016)
S. Mishra, R.N.P. Choudhary, S.K. Parida, Structural, dielectric, electrical and optical properties of Li/Fe modified barium tungstate double perovskite for electronic devices. Ceram. Int. 48, 17020–17033 (2022)
M. Lal, M. Chandrasekhar, R. Rai, P. Kumar, Structural, dielectric and impedance studies of KNNS–BKT ceramics. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 7, 25–34 (2017)
P.G.R. Achary, A.A. Nayak, R.K. Bhuyan, R.N.P. Choudhary, S.K. Parida, Effect of cerium dopant on the structural and electrical properties of SrMnO3 single perovskite. J. Mol. Struct. 1226, 129391–129399 (2021)
S.K. Parida, R.N.P. Choudhary, Preparation method and cerium dopant effects on the properties of BaMnO3 single perovskite. Phase Transit. 93, 981–991 (2020)
A.K. Pradhan, K. Zhang, D. Hunter, J.B. Dadson, G.B. Loiutts, P. Bhattacharya, R. Katiyar, J. Zhang, D.J. Sellmyer, U.N. Roy, Y. Cui, A. Burger, Magnetic and electrical properties of single-phase multiferroic BiFeO3. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 3–6 (2005)
R. Ranjan, R. Kumar, N. Kumar, B. Behera, R.N.P. Choudhary, Impedance and electric modulus analysis of Sm-modified Pb(Zr0.55Ti0.45)1x/4O3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6388–6394 (2011)
M. Hanief Najar, K. Majid, Investigation of the transport properties of PPy/[Co (EDTA) NH 3 Cl] $ H2O nanocomposite prepared by chemical oxidation method. RSC Adv. 6, 25449–25459 (2016)
E.V. Gopalan, K.A. Malini, S. Saravanan, D.S. Kumar, Y. Yoshida, M.R. Anantharaman, Evidence for polaron conduction in nanostructured manganese ferrite. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 185005–185013 (2008)
S. Sahoo, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, M.L. Nandagoswamy, Dielectric and impedance spectroscopy of (Ba, Sm)(Ti, Fe)O3 system in the low-medium frequency range. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 6572–6584 (2015)
B. Senthilkumar, R. Kalai Selvan, P. Vinothbabu, I. Perelshtein, A. Gedanken, Structural, magnetic, electrical and electrochemical properties of NiFe2O4 synthesized by the molten salt technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 285–292 (2011)
L. D’Amario, J. Föhlinger, G. Boschloo, L. Hammarström, Unveiling hole trapping and surface dynamics of NiO nanoparticles. Chem. Sci. 9, 223–230 (2018)
H. Dixit, R. Saniz, D. Lamoen, B. Partoens, The quasiparticle band structure of zincblende and rocksalt ZnO. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22, 125505 (2010)
V. Kumar, J.K. Singh, Model for calculating the refractive index of different materials. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 48, 571–574 (2010)
U.K. Panigrahi, B. Sahu, H.G. Behuria, S.K. Sahu, S.P. Dhal, S. Hussain, P. Mallick, Synthesis, characterization and bioactivity of thio-acetamide modified ZnO nanoparticles embedded in zinc acetate matrix. Nano Express 2, 010012 (2021)
S. Sumathi, V. Lakshmipriya, Structural, magnetic, electrical and catalytic activity of copper and bismuth co-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 2795–2802 (2017)
S.K. Parida, Structural, electrical and optical properties of zinc and tungsten modified lead titanate ceramics. SPIN 11, 2150018–2150114 (2021)
A. Kumar, K.C. James Raju, J. Ryu, A.R. James, Composition dependent ferro-piezo hysteresis loops and energy density properties of mechanically activated (Pb1−xLax) (Zr0.60Ti0.40)O3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 126, 1–10 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their heartfelt gratitude to Siksha O Anusandhan Deemed to be University, Bhubaneswar, for providing experimental facilities. We would also like to thank Bandana, Preeti, and Sagarika for their encouragement and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sourav, S.K., Parida, S.K., Choudhary, R.N.P. et al. Structural, microstructural, dielectric, transport, and optical properties of modified bismuth ferrite. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 60, 687–701 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00294-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00294-5