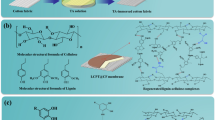
Abstract
Solar-driven seawater desalination has attracted much attention for alleviating global freshwater shortage, but the practical application is often limited by complicated fabrication processes, unsatisfactory seawater-transferring and severe salt accumulation on the photothermal membranes. To solve these problems, hydrophobic industrial-grade carbon fiber membrane (CFM) with good photoabsorption was surface-modified with polydopamine (PDA) to prepare superhydrophilic CFM@PDA for the construction of efficient hanging-model evaporators without salt accumulation. The coating of PDA on CFM is realized by simple self-polymerization of dopamine, and the as-prepared CFM@PDA exhibits high solar absorption efficiency of 96.7%, good photothermal effect and superhydrophilicity. Especially, when CFM@PDA is hanging between two water tanks (one contains seawater and the other is empty) in a flat hanging-model evaporator, it can transport seawater at a high rate (26.35 g/h) which is 3.6 times that (7.28 g/h) of commercial cotton fabric. Under simulated sunlight (1.0 kW m−2) irradiation, CFM@PDA shows a high evaporation rate of 1.79 kg m−2 h−1 with a solar evaporation efficiency of 92.6%. Even if NaCl solution with a high concentration (21.0 wt%) is used for the evaporation, the hanging CFM@PDA can retain a high evaporation rate (~ 1.80 kg m−2 h−1) without salt accumulation during the long-time test (8 h), which is significantly better than that of the tradition floating model. Therefore, this study not only demonstrates the simple preparation of superhydrophilic CFM@PDA, but also promotes the further practical applications of hanging-model evaporators for continuous salt-free desalination.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Elimelech M, Phillip WA. The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment. Science. 2011;333:712.
Xu D, Zhu ZG, Li JS. Recent progress in electrospun nanofibers for the membrane distillation of hypersaline wastewaters. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1357.
Mekonnen MM, Hoekstra AY. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci Adv. 2016;2: e1500323.
Politano A, Argurio P, Di Profio G, Sanna V, Cupolillo A, Chakraborty S, Arafat HA, Curcio E. Photothermal membrane distillation for seawater desalination. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1603504.
Jiang ZW, Karan S, Livingston AG. Water transport through ultrathin polyamide nanofilms used for reverse osmosis. Adv Mater. 2018;30:1705973.
Yao YJ, Zhang PX, Jiang C, DuChanois RM, Zhang X, Elimelech M. High performance polyester reverse osmosis desalination membrane with chlorine resistance. Nat Sustain. 2021;4:138.
Wu B, Hochstrasser F, Akhondi E, Ambauen N, Tschirren L, Burkhardt M, Fane AG, Pronk W. Optimization of gravity-driven membrane (GDM) filtration process for seawater pretreatment. Water Res. 2016;93:133.
Kim K, Kim H, Lim JH, Lee SJ. Development of a desalination membrane bioinspired by mangrove roots for spontaneous filtration of sodium ions. ACS Nano. 2016;10:11428.
Zhou KG, Vasu KS, Cherian CT, Neek-Amal M, Zhang JC, Ghorbanfekr-Kalashami H, Huang K, Marshall OP, Kravets VG, Abraham J, Su Y, Grigorenko AN, Pratt A, Geim AK, Peeters FM, Novoselov KS, Nair RR. Electrically controlled water permeation through graphene oxide membranes. Nature. 2018;559:236.
Alkhadra MA, Gao T, Conforti KM, Tian HH, Bazant MZ. Small-Scale desalination of seawater by shock electrodialysis. Desalination. 2020;476: 114219.
Gao MM, Zhu LL, Peh CK, Ho GW. Solar absorber material and system designs for photothermal water vaporization towards clean water and energy production. Energ Environ Sci. 2019;12:841.
Yu Z, Gu RN, Tian Y, Xie PF, Jin BC, Cheng SA. Enhanced interfacial solar evaporation through formation of micro-meniscuses and microdroplets to reduce evaporation enthalpy. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32:2108586.
Li CX, Cao SJ, Lutzki J, Yang J, Konegger T, Kleitz F, Thomas A. A covalent organic framework/graphene dual-region hydrogel for enhanced solar-driven water generation. J Am Chem Soc. 2022;144:3083.
Xu N, Zhang HR, Lin ZH, Li J, Liu GL, Li XQ, Zhao W, Min XZ, Yao PC, Zhou L, Song Y, Zhu B, Zhu SN, Zhu J. A scalable fish-school inspired self-assembled particle system for solar-powered water-solute separation. Natl Sci Rev. 2021;8:nwab065.
Gao T, Wang YD, Wu X, Wu P, Yang XF, Li Q, Zhang ZZ, Zhang DK, Owens G, Xu HL. More from less: improving solar steam generation by selectively removing a portion of evaporation surface. Sci Bull. 2022;67:1572.
Wang YD, Wu X, Wu P, Zhao JY, Yang XF, Owens G, Xu HL. Enhancing solar steam generation using a highly thermally conductive evaporator support. Sci Bull. 2021;66:2479.
Jia J, Liang WD, Sun HX, Zhu ZQ, Wang CJ, Li A. Fabrication of bilayered attapulgite for solar steam generation with high conversion efficiency. Chem Eng J. 2019;361:999.
Zhao LY, Wang L, Shi JD, Hou XY, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Bai NN, Yang JL, Zhang JM, Yu B, Guo CF. Shape-Programmable interfacial solar evaporator with salt-precipitation monitoring function. ACS Nano. 2021;15:5752.
Han J, Xing WQ, Yan J, Wen J, Liu YT, Wang YQ, Wu ZF, Tang LC, Gao JF. Stretchable and superhydrophilic polyaniline/halloysite decorated nanofiber composite evaporator for high efficiency seawater desalination. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1233.
Wang FY, Xu N, Zhao W, Zhou L, Zhu PC, Wang XY, Zhu B, Zhu J. A high-performing single-stage invert-structured solar water purifier through enhanced absorption and condensation. Joule. 2021;5:1602.
Wu P, Wu X, Wang YD, Xu HL, Owens G. Towards sustainable saline agriculture: interfacial solar evaporation for simultaneous seawater desalination and saline soil remediation. Water Res. 2022;212: 118099.
Zielinski MS, Choi JW, La Grange T, Modestino M, Hashemi SMH, Pu Y, Birkhold S, Hubbell JA, Psaltis D. Hollow mesoporous plasmonic nanoshells for enhanced solar vapor generation. Nano Lett. 2016;16:2159.
Zhang CB, Yan C, Xue ZJ, Yu W, Xie YD, Wang T. Shape-Controlled synthesis of high-quality Cu7S4 nanocrystals for efficient light-induced water evaporation. Small. 2016;12:5320.
Wang XQ, Ou G, Wang N, Wu H. Graphene-Based recyclable photo-absorbers for high-efficiency seawater desalination. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2016;8:9194.
Chala TF, Wu CM, Chou MH, Guo ZL. Melt electrospun reduced tungsten oxide/polylactic acid fiber membranes as a photothermal material for light-driven interfacial water evaporation. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2018;10:28955.
Wang J, Li YY, Deng L, Wei NN, Weng YK, Dong S, Qi DP, Qiu J, Chen XD, Wu T. High-Performance photothermal conversion of narrow-bandgap Ti2O3 nanoparticles. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1603730.
Zhao L, Yang QZ, Guo W, Liu HX, Ma TY, Qu FY. Co2.67S4-Based photothermal membrane with high mechanical properties for efficient solar water evaporation and photothermal antibacterial applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11:20820.
Shao Y, Jiang ZP, Zhang YJ, Wang TZ, Zhao P, Zhang Z, Yuan JY, Wang H. All-Poly(ionic liquid) membrane-derived porous carbon membranes: scalable synthesis and application for photothermal conversion in seawater desalination. ACS Nano. 2018;12:11704.
Zhang LB, Tang B, Wu JB, Li RY, Wang P. Hydrophobic light-to-heat conversion membranes with self-healing ability for interfacial solar heating. Adv Mater. 2015;27:4889.
Yang Y, Zhao RQ, Zhang TF, Zhao K, Xiao PS, Ma YF, Ajayan PM, Shi GQ, Chen YS. Graphene-Based standalone solar energy converter for water desalination and purification. ACS Nano. 2018;12:829.
Zhu B, Kou H, Liu ZX, Wang ZJ, Macharia DK, Zhu MF, Wu BH, Liu XG, Chen ZG. Flexible and washable CNT-embedded PAN nonwoven fabrics for solar-enabled evaporation and desalination of seawater. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2019;11:35005.
Yu ST, Zhang Y, Duan HZ, Liu YM, Quan XJ, Tao P, Shang W, Wu JB, Song CY, Deng T. The impact of surface chemistry on the performance of localized solar-driven evaporation system. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13600.
Kou H, Liu ZX, Zhu B, Macharia DK, Ahmed S, Wu BH, Zhu MF, Liu XG, Chen ZG. Recyclable CNT-coupled cotton fabrics for low-cost and efficient desalination of seawater under sunlight. Desalination. 2019;462:29.
Zhang PP, Li J, Lv LX, Zhao Y, Qu LT. Vertically aligned graphene sheets membrane for highly efficient solar thermal generation of clean water. ACS Nano. 2017;11:5087.
Ghasemi H, Ni G, Marconnet AM, Loomis J, Yerci S, Miljkovic N, Chen G. Solar steam generation by heat localization. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4449.
Li T, Liu H, Zhao XP, Chen G, Dai JQ, Pastel G, Jia C, Chen CJ, Hitz E, Siddhartha D, Yang RG, Hu LB. Scalable and highly efficient mesoporous wood-based solar steam generation device: localized heat, rapid water transport. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28:1707134.
Yao W, Li XY, Zhu XD, Pei LY, Liu GL, Cheng Y, Chee MOL, Dong P, Shen JF, Ye MX. Thermal-localized and salt-resistant polyacrylonitrile/polyvinylidene fluoride aerogel for efficient solar desalination. Desalination. 2022;532: 115751.
Zhao W, Gong H, Song Y, Li B, Xu N, Min XZ, Liu GL, Zhu B, Zhou L, Zhang XX, Zhu J. Hierarchically designed salt-resistant solar evaporator based on donnan effect for stable and high-performance brine treatment. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2100025.
Liu ZX, Zhong QP, Wu NY, Zhou HZ, Wang LX, Zhu LQ, Jiang N, Zhu B, Chen ZG, Zhu MF. Vertically symmetrical evaporator based on photothermal fabrics for efficient continuous desalination through inversion strategy. Desalination. 2021;509: 115072.
Li CC, Zhu B, Liu ZX, Zhao JT, Meng RR, Zhang LS, Chen ZG. Polyelectrolyte-based photothermal hydrogel with low evaporation enthalpy for solar-driven salt-tolerant desalination. Chem Eng J. 2022;431: 134224.
Liu ZX, Wu BH, Zhu B, Chen ZG, Zhu MF, Liu XG. Continuously producing watersteam and concentrated brine from seawater by hanging photothermal fabrics under sunlight. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29:1905485.
Liu ZX, Zhou Z, Wu NY, Zhang RQ, Zhu B, Jin H, Zhang YM, Zhu MF, Chen ZG. Hierarchical photothermal fabrics with low evaporation enthalpy as heliotropic evaporators for efficient, continuous, salt-free desalination. ACS Nano. 2021;15:13007.
Jiang GY, Jiang N, Zheng N, Chen X, Mao JY, Ding GY, Li YH, Sun FG, Li YS. MOF-derived porous Co3O4-NC nanoflake arrays on carbon fiber cloth as stable hosts for dendrite-free Li metal anodes. Energy Storage Mater. 2019;23:181.
Liu SN, Cai ZY, Zhou J, Zhu MN, Pan AQ, Liang SQ. High-performance sodium-ion batteries and flexible sodium-ion capacitors based on Sb2X3 (X = O, S)/carbon fiber cloth. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5:9169.
Lu Q, Zou XH, Liao KM, Ran R, Zhou W, Ni M, Shao ZP. Direct growth of ordered N-doped carbon nanotube arrays on carbon fiber cloth as a free-standing and binder-free air electrode for flexible quasi-solid-state rechargeable Zn-Air batteries. Carbon Energy. 2020;2:461.
Wang C, Zhang JS, Wang XF, Lin CF, Zhao XS. Hollow rutile cuboid arrays grown on carbon fiber cloth as a flexible electrode for sodium-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30:2002629.
Shen XF, Zhang TY, Xu PF, Zhang LS, Liu JS, Chen ZG. Growth of C3N4 nanosheets on carbon-fiber cloth as flexible and macroscale filter-membrane-shaped photocatalyst for degrading the flowing wastewater. Appl Catal B Environ. 2017;219:425.
Wu Z, Yang JH, Shao WJ, Cheng MH, Luo XL, Zhou M, Li S, Ma T, Cheng C, Zhao CS. High-valence transition metal modified FeNiV oxides anchored on carbon fiber cloth for efficient oxygen evolution catalysis. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:774.
Liu HC, Huang GC, Wang R, Huang L, Wang HZ, Hu YZ, Cong GT, Bao F, Xu M, Zhu CZ, Xu J, Ji MW. Carbon nanotubes grown on the carbon fibers to enhance the photothermal conversion toward solar-driven applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2022;14:32404.
Wang J, Shi QQ, Li CJ, Zhang YZ, Du SY, Mao JF, Wang J. Pistia-Inspired photothermal fabric based on waste carbon fiber for low-cost vapor generation: an industrialization route. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32:2201922.
Li S, Li YG, Shao YL, Wang HZ. Emerging two-dimensional materials constructed nanofluidic fiber: Properties, preparation and applications. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:129.
Bao QL, Loh KP. Graphene photonics, plasmonics, and broadband optoelectronic devices. ACS Nano. 2012;6:3677.
Wu HY, Chen RT, Shao YW, Qi XD, Yang JH, Wang Y. Novel flexible phase change materials with mussel-inspired modification of melamine foam for simultaneous light-actuated shape memory and light-to-thermal energy storage capability. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7:13532.
Lee H, Dellatore SM, Miller WM, Messersmith PB. Mussel-Inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science. 2007;318:426.
Zhang HZ, Liu QY, Fang YB, Teng CL, Liu XQ, Fang PP, Tong YX, Lu XH. Boosting Zn-ion energy storage capability of hierarchically porous carbon by promoting chemical adsorption. Adv Mater. 2019;31:1904948.
Huang C, Hu AP, Li YH, Zhou HF, Xu YL, Zhang Y, Zhou SP, Tang QL, Chen CS, Chen XH. Room temperature ultrafast synthesis of N- and O-rich graphene films with an expanded interlayer distance for high volumetric capacitance supercapacitors. Nanoscale. 2019;11:16515.
Wu Q, Wan QQ, Yang X, Wang F, Zhu JF. Effects of chain length of polyether amine on interfacial adhesion of carbon fiber/epoxy composite in the absence or presence of polydopamine bridging platform. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;547: 149162.
Gu B, Pu GH, Ding BN, Zhang K, He R, Fan JH, Xing T, Wu JY, Yang WB. Improved interfacial bonding strength of silicone rubber/carbon fiber modified by dopamine. Polym Composite. 2022;43:6975.
Liu Y, Fang YC, Liu XL, Wang XL, Yang B. Mussel-inspired modification of carbon fiber via polyethyleneimine/polydopamine co-deposition for the improved interfacial adhesion. Compos Sci Technol. 2017;151:164.
Huang C, Zhao X, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Yang YJ, Hu AP, Tang QL, Song XY, Jiang CZ, Chen XH. Sewable and cuttable flexible zinc-ion hybrid supercapacitor using a polydopamine/carbon cloth-based cathode. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2020;8:16028.
Liu TY, Kim KC, Lee B, Chen ZM, Noda S, Jang SS, Lee SW. Self-polymerized dopamine as an organic cathode for Li- and Na-ion batteries. Energ Environ Sci. 2017;10:205.
Liu YM, Yu ST, Feng R, Bernard A, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Duan H, Shang W, Tao P, Song CQ, Deng T. A bioinspired, reusable, paper-based system for high-performance large-scale evaporation. Adv Mater. 2015;27:2768.
Wang G, Fu Y, Ma XF, Pi WB, Liu DW, Wang XB. Reusable reduced graphene oxide based double-layer system modified by polyethylenimine for solar steam generation. Carbon. 2017;114:117.
Xu N, Li JL, Wang Y, Fang C, Li XQ, Wang YX, Zhou L, Zhu B, Wu Z, Zhu SN, Zhu J. A water lily-inspired hierarchical design for stable and efficient solar evaporation of high-salinity brine. Sci Adv. 2019;5:eaaw7013.
Organization WH. Safe drinking-water from desalination. WHO Press. 2017.https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549950. Accessed 24 Apr 2017.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFB3804902, 2022YFB3804900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52161145406, 51972056), Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader (20XD1420200), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (21ZR1402500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WC: conceptualization, investigation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing. RM: investigation, validation, writing-original draft. ZL: investigation. QL: data curation. JH: validation. BZ: investigation. DKM: investigation. ZC: supervision, project administration, writing-review and editing. LZ: supervision, project administration, writing-review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 16816 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 2042 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, W., Meng, R., Liu, Z. et al. Superhydrophilic Polydopamine-Modified Carbon-Fiber Membrane with Rapid Seawater-Transferring Ability for Constructing Efficient Hanging-Model Evaporator. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5, 1063–1075 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00276-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00276-6