Abstract
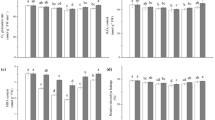
Low light reduces growth and adversely affects the antioxidant defense system. At the same time, the silica nanoparticles (SiO2 NPs) mitigate the biotic and abiotic stresses and improve plant growth. Therefore, this study investigated whether SiO2 NPs alleviates the low light stress by measuring the biomass and physiological indices of maize seedlings. A hydroponic experiment was set up with two maize varieties, Yuebaitiannuo10 and Yuebaitiannuo12, grown under two light treatments, namely normal light (NL) and low light (LL) and three SiO2 NPs foliar treatments (SiO2 NPs at doses of 0 mg L− 1 (Si0), 150 mg L− 1 (Si1), and 300 mg L− 1 (Si2)). The plant growth, antioxidant responses, nitrogen metabolism, and photosynthetic pigments in the maize seedlings were determined. The results showed that the low light treatment significantly reduced the maize seedling growth in both varieties. However, the SiO2 NPs slightly increased the biomass and altered the growth, with the highest aboveground dry weight/plant height detected in the Si1 treatment, irrespective of the maize variety and light treatment. Compared to the Si0 treatment, Si1 significantly increased the aboveground dry weight/plant height by 35.38% in Yuebaitiannuo12 at low light. Various changes in antioxidant response, photosynthesis pigments, and nitrogen metabolism were recorded in the different maize varieties and light treatments in response to the SiO2 NPs treatments. Correlation analysis suggested that the maize seedling growth parameters and biomass were related to the superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and ascorbic acid content in the root, SOD activity and malondialdehyde content in the stem, and nitrate reductase activity in the leaves (P<0.05). The results of this study provide a theoretical basis for expanding the research on the application of SiO2 NPs in maize. It also provides the relevant reference for elucidating the response mechanism of maize seedlings under fluctuating light environments to lay a foundation for improving maize yield at later growth stages.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
Code Availability
No code.
References
Agnihotri A, Seth CS (2016) Exogenously applied nitrate improves the photosynthetic performance and nitrogen metabolism in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. Cv Pusa Rohini) under arsenic (V) toxicity. Physiol Mol Biol Pla 22:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-016-0370-2
Aguirre-Becerra H, Feregrino-Perez AA, Esquivel K, Perez-Garcia CE, Vazquez-Hernandez MC, Mariana-Alvarado A (2022) Nanomaterials as an alternative to increase plant resistance to abiotic stresses. Front Plant Sci 13:1023636. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1023636
Ahanger MA, Agarwal RM, Tomar NS, Shrivastava M (2015) Potassium induces positive changes in nitrogen metabolism and antioxidant system of oat (Avena sativa L cultivar Kent). J Plant Interact 10:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2015.1056260
Ahmad S, Wang G, Muhammad I, Chi Y, Zeeshan M, Nasar J, Zhou X (2022) Interactive effects of melatonin and nitrogen improve drought tolerance of maize seedlings by regulating growth and physiochemical attributes. Antioxidants-Basel 11:359 https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020359
Al-Mokadem AZ, Sheta MH, Mancy AG, Hussein HA, Kenawy S, Sofy AR, Abu-Shahba MS, Mahdy HM, Sofy MR, Al BA, Agha MS (2023) Synergistic effects of kaolin and silicon nanoparticles for ameliorating deficit irrigation stress in maize plants by upregulating antioxidant defense systems. Plants-Basel 12:2221 https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112221
Albalawi MA, Abdelaziz AM, Attia MS, Saied E, Elganzory HH, Hashem AH (2022) Mycosynthesis of silica nanoparticles using aspergillus Niger: control of Alternaria Solani causing early blight disease, induction of innate immunity and reducing of oxidative stress in eggplant. Antioxidants-Basel 11:2323 https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122323
Ali M, Afzal S, Parveen A, Kamran M, Javed MR, Abbasi GH, Malik Z, Riaz M, Ahmad S, Chattha MS, Ali M, Ali Q, Uddin MZ, Rizwan M, Ali S (2021) Silicon mediated improvement in the growth and ion homeostasis by decreasing Na+ uptake in maize (Zea mays L.) cultivars exposed to salinity stress. Plant Physiol Bioch 158:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.10.040
Altaf MA, Sharma N, Srivastava D, Mandal S, Adavi S, Jena R, Bairwa RK, Gopalakrishnan AV, Kumar A, Dey A, Lal MK, Tiwari RK, Kumar R, Ahmed P (2023) Deciphering the melatonin-mediated response and signalling in the regulation of heavy metal stress in plants. Planta 25:115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04146-8
Amos B, Walters DT (2006) Maize root biomass and net rhizodeposited carbon: an analysis of the literature. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1489–1503. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0216
Awan TH, Chauhan BS, Cruz PCS (2014) Physiological and morphological responses of Ischaemum rugosum Salisb. (wrinkled grass) to different nitrogen rates and rice seeding rates. PLoS ONE 9:e98255. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098255
Babu S, Singh R, Yadav D, Rathore SS, Raj R, Avasthe R, Yadav SK, Das A, Yadav V, Yadav B, Shekhawat K, Upadhyay PK, Yadav DK, Singh VK (2022) Nanofertilizers for agricultural and environmental sustainability. Chemosphere 292:133451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133451
Behboudi F, Sarvestani ZT, Kassaee MZ, Sanavi SAMM, Sorooshzadeh A (2018) Improving growth and yield of wheat under drought stress via application of SiO2 nanoparticles. J Agr Sci Tech-Iran 20:1479–1492
Bellasio C, Griffiths H (2014) Acclimation of C4 metabolism to low light in mature maize leaves could limit energetic losses during progressive shading in a crop canopy. J Exp Bot 65:3725–3736. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru052
Bhattacharjee S (2005) Reactive oxygen species and oxidative burst: roles in stress, senescence and signal transduction in plants. Curr Sci India 89:1113–1121
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot-London 91:179–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcf118
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Chen W, Liao G, Sun F, Ma Y, Chen Z, Chen H, Tang X, Mo Z (2023) Foliar spray of La2O3 nanoparticles regulates the growth, antioxidant parameters, and nitrogen metabolism of fragrant rice seedlings in wet and dry nurseries. Environ Sci Pollut R 30:80349–80363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27892-4
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90:856–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13299
Cui J, Li Y, Jin Q, Li F (2020) Silica nanoparticles inhibit arsenic uptake into rice suspension cells via improving pectin synthesis and the mechanical force of the cell wall. Environ Sci-Nano 7:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en01035a
Deng H, Wang X, Deng S, Zhang L, Ashraf U, Imran M, Tian H, Tang X, Mo Z (2023) Silicon (Si) application improved the antioxidant response and grain yield formation in rice under high temperature conditions. Silicon-Neth 15:4387–4389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02392-9
Dvorak P, Krasylenko Y, Zeiner A, Samaj J, Takac T (2020) Signaling toward reactive oxygen species-scavenging enzymes in plants. Front Plant Sci 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.618835
Elisa D, Marcela G, Alejandra GJ, Elena DM (2022) The nutraceutical value of maize (Zea mays L.) Landraces and the determinants of its variability: a review. J Cereal Sci 103:103399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2021.103399
Epstein E (2009) Silicon: its manifold roles in plants. Ann Appl Biol 155:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00343.x
Farooq MA, Dietz K (2015) Silicon as versatile player in plant and human biology: overlooked and poorly understood. Front Plant Sci 6:994. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00994
Fu J, Li L, Wang S, Yu N, Shan H, Shi Z, Li F, Zhong X (2023) Effect of gibberellic acid on photosynthesis and oxidative stress response in maize under weak light conditions. Front Plant Sci 14:1128780. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1128780
Gao J, Zhao B, Dong S, Liu P, Ren B, Zhang J (2017) Response of summer maize photosynthate accumulation and distribution to shading stress assessed by using 13CO2 stable isotope tracer in the field. Front Plant Sci 8:1821. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01821
Gao J, Liu Z, Zhao B, Dong S, Liu P, Zhang J (2020) Shade stress decreased maize grain yield, dry matter, and nitrogen accumulation. Agron J 112:2768–2776. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20140
Ghorbanpour M, Mohammadi H, Kariman K (2020) Nanosilicon-based recovery of barley (Hordeum vulgare) plants subjected to drought stress. Environ Sci-Nano 7:443–461. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en00973f
Gu Y, Li G, Sun Y, Luo W, Liu X, Zhang W, Qi C, Zhao Y, Tang K, Zhang Y, Shao L, Xiong Y, Si C, Zhao C (2017) The effects of global dimming on the wheat crop grown in the Yangtze Basin of China simulated by SUCROS_LL, a process-based model. Ecol Model 350:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.02.009
Gui R, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Li L, Wang Z, Pan S, Zhang M, Tang X, Mo Z (2022) Deep placement of liquid fertilizer at tillering stage influences grain quality, 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline synthesis, and antioxidant response of fragrant rice. Field Crop Res 289:108716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2022.108716
Guo X, Yang Y, Liu H, Liu G, Liu W, Wang Y, Zhao R, Ming B, Xie R, Wang K, Hou P, Xiao C, Li S (2021) Effects of solar radiation on root and shoot growth of maize and the quantitative relationship between them. Crop Sci 61:1414–1425. https://doi.org/10.1002/csc2.20416
Hajizadeh HS, Azizi S, Rasouli F, Okatan V (2022) Modulation of physiological and biochemical traits of two genotypes of Rosa Damascena Mill. By SiO2-NPs under in vitro drought stress. Bmc Plant Biol 22:538. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03915-z
Hong W, Chen Y, Huang S, Li Y, Wang Z, Tang X, Pan S, Tian H, Mo Z (2022) Optimization of nitrogen-silicon (N-Si) fertilization for grain yield and lodging resistance of early-season indica fragrant rice under different planting methods. Eur J Agron 136:126508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2022.126508
Hu Y, Zhang P, Zhang X, Liu Y, Feng S, Guo D, Nadezhda T, Song Z, Dang X (2021) Multi-wall carbon nanotubes promote the growth of maize (Zea mays) by regulating carbon and nitrogen metabolism in leaves. J Agr Food Chem 69:4981–4991. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c00733
Jedrzejuk A, Rabiza-Swider J, Skutnik E, Lukaszewska A (2018) Growing conditions and preservatives affect longevity, soluble protein, H2O2 and MDA contents, activity of antioxidant enzymes and DNA degradation in cut lilacs. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 228:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.10.026
Jeelani PG, Mulay P, Venkat R, Ramalingam C (2020) Multifaceted application of silica nanoparticles. A review. Silicon-Neth 12:1337–1354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00229-y
Kaiser E, Morales A, Harbinson J, Kromdijk J, Heuvelink E, Marcelis LF (2015) Dynamic photosynthesis in different environmental conditions. J Exp Bot 66:2415–2426. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru406
Kaur G, Asthir B (2015) Proline: a key player in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Biol Plant 59:609–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-015-0549-3
Keeping MG, Reynolds OL (2009) Silicon in agriculture: new insights, new significance and growing application. Ann Appl Biol 155:153–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00358.x
Li W, Liu J, Ashraf U, Li G, Li Y, Lu W, Gao L, Han F, Hu J (2016) Exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) application improved early growth, net photosynthesis, and associated physio-biochemical events in maize. Front Plant Sci 7:919. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00919
Li Z, Song Z, Yan Z, Hao Q, Song A, Liu L, Yang X, Xia S, Liang Y (2018) Silicon enhancement of estimated plant biomass carbon accumulation under abiotic and biotic stresses. A meta-analysis. Agron Sustain Dev 38:26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-018-0496-4
Li J, Zhou X, Wei B, Cheng S, Zhou Q, Ji S (2019) GABA application improves the mitochondrial antioxidant system and reduces peel browning in ‘Nanguo’ pears after removal from cold storage. Food Chem 297:124903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.177
Li L, Tian H, Zhang M, Fan P, Ashraf U, Liu H, Chen X, Duan M, Tang X, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Pan S (2021a) Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer increases rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency with fewer greenhouse gas emissions in a mechanical direct-seeded cropping system. Crop J 9:1386–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2020.12.011
Li Y, Liang L, Li W, Ashraf U, Ma L, Tang X, Pan S, Tian H, Mo Z (2021b) ZnO nanoparticle-based seed priming modulates early growth and enhances physio-biochemical and metabolic profiles of fragrant rice against cadmium toxicity. J Nanobiotechnol 19:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-00820-9
Li Z, Li C, Zhang R, Duan M, Tian H, Yi H, Xu L, Wang F, Shi Z, Wang X, Wang J, Su A, Wang S, Sun X, Zhao Y, Wang S, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Song W, Zhao J (2023) Genomic analysis of a new heterotic maize group reveals key loci for pedigree breeding. Front Plant Sci 14:1213675. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1213675
Lin BS, Diao SQ, Li CH, Fang LJ, Qiao SC, Yu M (2004) Effect of TMS (nanostructured silicon dioxide) on growth of Changbai larch seedlings. J Res 15:138–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02856749
Ma JY (2011) Characterization of long-term changes in surface solar radiation and short-term forecasting methods in China. Nanjing University of Information Engineering, Nanjing. https://doi.org/10.7666/d.y1891594(in Chinese)
Mo Z, Li W, Pan S, Fitzgerald TL, Xiao F, Tang Y, Wang Y, Duan M, Tian H, Tang X (2015) Shading during the grain filling period increases 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline content in fragrant rice. Rice 8:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-015-0040-y
Mo Z, Lei S, Ashraf U, Khan I, Li Y, Pan S, Duan M, Tian H, Tang X (2017) Silicon fertilization modulates 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline content, yield formation and grain quality of aromatic rice. J Cereal Sci 75:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2017.03.014
Mo Z, Li Y, Nie J, He L, Pan S, Duan M, Tian H, Xiao L, Zhong K, Tang X (2019) Nitrogen application and different water regimes at booting stage improved yield and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP) formation in fragrant rice. Rice 12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-019-0335-5
Mostofa MG, Rahman MM, Siddiqui MN, Fujita M, Tran L (2020) Salicylic acid antagonizes selenium phytotoxicity in rice: selenium homeostasis, oxidative stress metabolism and methylglyoxal detoxification. J Hazard Mater 394:122572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122572
Najeeb U, Bange MP, Atwell BJ, Tan DKY (2016) Low incident light combined with partial waterlogging impairs photosynthesis and imposes a yield penalty in cotton. J Agron Crop Sci 202:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12164
Parihar CM, Nayak HS, Rai VK, Jat SL, Parihar N, Aggarwal P, Mishra AK (2019) Soil water dynamics, water productivity and radiation use efficiency of maize under multi-year conservation agriculture during contrasting rainfall events. Field Crop Res 241:107570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.107570
Rastogi A, Tripathi DK, Yadav S, Chauhan DK, Zivcak M, Ghorbanpour M, El-Sheery NI, Brestic M (2019) Application of silicon nanoparticles in agriculture. 3 Biotech 9:90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1626-7
Raven JA (2003) Cycling silicon-the role of accumulation in plan. New Phytol 158:419–421. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00778.x
Ray DK, Mueller ND, West PC, Foley JA (2013) Yield trends are insufficient to double global crop production by 2050. PLoS ONE 8:e66428. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066428
Raza MA, Khalid MHB, Zhang X, Feng LY, Khan I, Hassan MJ, Ahmed M, Ansar M, Chen YK, Fan YF, Yang F, Yang W (2019) Effect of planting patterns on yield, nutrient accumulation and distribution in maize and soybean under relay intercropping systems. Sci Rep 9:4947. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41364-1
Ren B, Cui H, Camberato JJ, Dong S, Liu P, Zhao B, Zhang J (2016) Effects of shading on the photosynthetic characteristics and mesophyll cell ultrastructure of summer maize. Sci Nat-Heidelberg 103:67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-016-1392-x
Rizwan M, Imtiaz M, Dai Z, Mehmood S, Adeel M, Liu J, Tu S (2017) Nickel stressed responses of rice in Ni subcellular distribution, antioxidant production, and osmolyte accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:20587–20598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9665-2
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034
Shao L, Liu Z, Li H, Zhang Y, Dong M, Guo X, Zhang H, Huang B, Ni R, Li G, Cai C, Chen W, Luo W, Yin X (2021) The impact of global dimming on crop yields is determined by the source - sink imbalance of carbon during grain filling. Global Change Biol 27:689–708. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15453
Sharf-Eldin AA, Alwutayd KM, El-Yazied AA, El-Beltagi HS, Alharbi BM, Eisa MAM, Alqurashi M, Sharaf M, Al-Harbi NA, Al-Qahtani SM, Ibrahim MFM (2023) Response of maize seedlings to silicon dioxide nanoparticles (SiO2 NPs) under drought stress. Plants-Basel 12:2592 https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12142592
Sharma P, Bhatt D, Zaidi MGH, Saradhi PP, Khanna PK, Arora S (2012) Silver nanoparticle-mediated enhancement in growth and antioxidant status of Brassica juncea. Appl Biochem Biotech 167:2225–2233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9759-8
Shi DY, Li YH, Zhang JW, Liu P, Zhao B, Dong ST (2016) Increased plant density and reduced n rate lead to more grain yield and higher resource utilization in summer maize. J Integr Agr 15:2515–2528. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61355-2
Shi K, Gu X, Lu W, Lu D (2018) Effects of weak-light stress during grain filling on the physicochemical properties of normal maize starch. Carbohyd Polym 202:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.114
Siddiqui MH, Al-Whaibi MH (2014) Role of nano-SiO2 in germination of tomato (Lycopersicum Esculentum seeds Mill). Saudi J Biol Sci 21:13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.04.005
Siddiqui MH, Alamri S, Khan MN, Corpas FJ, Al-Amri AA, Alsubaie QD, Ali HM, Kalaji HM, Ahmad P (2020) Melatonin and calcium function synergistically to promote the resilience through ROS metabolism under arsenic-induced stress. J Hazard Mater 398:122882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122882
Slattery RA, Walker BJ, Weber APM, Ort DR (2018) The impacts of fluctuating light on crop performance. Plant Physiol 176:990–1003. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01234
Slewinski TL, Braun DM (2010) Current perspectives on the regulation of whole-plant carbohydrate partitioning. Plant Sci 178:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.01.010
Sun F, Chen W, Ren Y, Cheng S, Ashraf U, Zheng J, Lin L, Ma Y, Tang X, Mo Z (2023) Nano-priming with La2O3 improves early growth and regulates physio-biochemical mechanisms in fragrant rice against cadmium toxicity. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 23:4004–4020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01318-z
Tripathi DK, Singh S, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Dubey NK, Chauhan DK (2017) Silicon nanoparticles more effectively alleviated UV-B stress than silicon in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. Plant Physiol Bioch 110:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.06.026
Ulhassan Z, Yang S, Di He, Khan AR, Salam A, Azhar W, Muhammad S, Ali S, Hamid Y, Khan I, Sheteiwy MS, Zhou W (2023) Seed priming with nano-silica effectively ameliorates chromium toxicity in Brassica napus. J Hazard Mater 458:131906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131906
Wang L, Deng F, Ren W (2015) Shading tolerance in rice is related to better light harvesting and use efficiency and grain filling rate during grain filling period. Field Crop Res 180:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.05.010
Wang J, Shi K, Lu W, Lu D (2020) Post-silking shading stress affects leaf nitrogen metabolism of spring maize in Southern China. Plants-Basel 9:210. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020210
Xia X, Zhou Y, Shi K, Zhou J, Foyer CH, Yu J (2015) Interplay between reactive oxygen species and hormones in the control of plant development and stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 66:2839–2856. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv089
Xu H, Zhang LJ, Zhao YX, Jiang LQ (2014) Risk zoning of continuous overcast rain disaster of summer maize during florescence in Huang-Huai-Hai region. J Nat Disasters 23:263–272. https://doi.org/10.13577/j.jnd.2014.0534(in Chinese)
Yang YS, Guo XX, Liu HF, Liu GZ, Liu WM, Ming B, Xie RZ, Wang KR, Hou P, Li SK (2021) The effect of solar radiation change on the maize yield gap from the perspectives of dry matter accumulation and distribution. J Integr Agr 20:482–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63581-X
Yang W, Xu D, Li S, Tang X, Pan S, Chen X, Mo Z (2022) Emergence and seedling establishment of rice varieties at different sowing depths. J Plant Growth Regul 41:1672–1686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10408-0
Yao Y, Le Yue, Cao X, Chen F, Li J, Cheng B, Wang C, Wang Z (2023) Carbon dots embedded in nanoporous SiO2 nanoparticles for enhancing photosynthesis in agricultural crops. Acs Appl Nano Mater 6:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c03843
Yuan F, Guan D, Wang A, Wu J, Jin C (2012) Effects of long-term shade on maize (Zea mays L.) growth and yield in west of Liaoning Province, Northeastern China. J Food Agric Enviro 10:357–361
Yuan L, Liu J, Cai Z, Wang H, Fu J, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhu S, Wu W, Yan H, Zhang H, Li T, Zhang L, Yuan M (2022) Shade stress on maize seedlings biomass production and photosynthetic traits. Cienc Rural 52:e20201022. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20201022
Zhang X, Zhao X, Wang Z, Shen W, Xu X (2015) Protective effects of hydrogen-rich water on the photosynthetic apparatus of maize seedlings (Zea mays L.) as a result of an increase in antioxidant enzyme activities under high light stress. Plant Growth Regul 77:43–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0033-2
Zhong XM, Shi ZS, Li FH, Huang HJ (2014) Photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of infertile and fertile stalks of paired near-isogenic lines in maize (Zea mays L.) under shade conditions. Photosynthetica 52:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-014-0071-4
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Key R & D projects in Guangzhou (202206010172), Guangdong provincial rural revitalization strategy special funds seed industry revitalization project (Guangdong Finance and agriculture [2022]184); Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Project (2021A0505040002); China Seed Corporation Horizontal Technology Project (ZWS-KYSR2022061); Institute of Crop Research, Guangdong Academy of agricultural sciences, “Reward system” free exploration special (Guangdong agricultural crops [2022]63).
Funding
This study was supported by the Key R & D projects in Guangzhou (202206010172), Guangdong provincial rural revitalization strategy special funds seed industry revitalization project (Guangdong Finance and agriculture [2022]184); Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Project (2021A0505040002); China Seed Corporation Horizontal Technology Project (ZWS-KYSR2022061); Institute of Crop Research, Guangdong Academy of agricultural sciences, “Reward system” free exploration special (Guangdong agricultural crops [2022]63).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wu Li and Zhaowen Mo designed the experiments; Guangyu Li, Ziwei Ma, Meng Li, and Nan Zhang investigated the traits; Guangyu Li, Ziwei Ma, Meng Li, and Nan Zhang analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; Wu Li and Zhaowen Mo revised and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
The authors permitted that this article can be published in Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Ma, Z., Zhang, N. et al. Foliar Application of Silica Nanoparticles Positively Influences the Early Growth Stage and Antioxidant Defense of Maize Under Low Light Stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01789-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-024-01789-8