Abstract
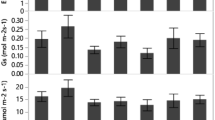
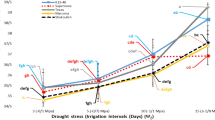
Young plane trees (Platanus orientalis L.) in urban settings contrary to the old plane trees suffer from leaf chlorosis and early leaf loss in the summer due to drought stress and heat waves as the consequences of climate change. The present study investigated the effects of Ascophyllum nodosum extract (ANE) and tree age class on mitigating drought stress in plane trees. Experimental variables included an irrigation regime with 100% field capacity (FC) (D100), 75% FC (D75); and 50% FC (D50), ANE application with 0% (control or A0), 1.5% (A1), and 3.0% (A2) (v/v); and tree age class i.e cuttings propagated from two types of trees: An old tree (OT) or a young tree (YT). This experiment was carried out using a factorial design with three replications. Results demonstrated that chlorophyll content (Chl), net assimilation rate (Pn), relative water content (RWC), leaf Fe, and Fv/Fm index declined significantly as drought stress severity rose, whereas the ANE treatment, specifically A2, increased Chl content, Pn, RWC, and leaf Fe. In addition, OT age class trees had higher photosynthetic pigments, Pn, Fe content, root volume, APX, and CAT activity than the YT age class. ANE application especially at 3% concentration with increasing antioxidant enzymes activity decreased the negative effect of stress and had a positive influence on Chl and Pn. Our findings indicate that the OT class of propagation source and ANE application was useful for inducing stress tolerance in the plane tree.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalipour H, Nikbakht A, Etemadi N (2019) Relationship between chlorosis, photosynthesis and the nutrient content of plane trees in the presence of chemical and organic fertilizers. Adv Hortic Sci 33:171–177. https://doi.org/10.13128/ahs-23326
Adbel-Mawgoud A, Tantawy AS, Hafez MM, Habib HAM (2010) Seaweed extract improves growth, yield and quality of different watermelon hybrids. Res J Agric Biol Sci 6:161–186
Agarwal S, Sairam RK, Srivastava GC, Meena RC (2005) Changes in antioxidant enzymes activity and oxidative stress by abscisic acid and salicylic acid in wheat genotypes. Biol Plant 49:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-0048-z
Alexieva V, Sergiev I, Mapelli S, Karanov E (2001) The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 24:1337–1344. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2001.00778.x
Ali J, Jan I, Ullah H, Ahmed N, Alam M, Ullah R, El-Sharnouby M, Kesba H, Shukry M, Sayed S, Nawaz T (2022) Influence of Ascophyllum nodosum extract foliar spray on the physiological and biochemical attributes of okra under drought stress. Plants 11:790. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11060790
Arunyanark A, Jogloy S, Akkasaeng C, Vorasot N, Kesmala T, Nageswara Rao RC, Wright GC, Patanothai A (2008) Chlorophyll stability is an indicator of drought tolerance in peanut. J Agron Crop Sci 194:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2008.00299.x
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.12.006
Banks JM (2018) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool to identify drought stress in Acer genotypes. Environ Exp Bot 155:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.06.022
Bates LS, Woldren RP, Teare ID (1975) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Battacharyya D, Babgohari M, Rathor P, Prithiviraj B (2015) Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci Hortic 196:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.09.012
Brunner I, Herzog C, Dawes MA, Arend M, Sperisen C (2015) How tree roots respond to drought. Front Plant Sci 6:152207. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00547
Campobenedetto C, Agliassa C, Mannino G, Vigliante I, Contartese V, Secchi F, Bertea CM (2021) A bio-stimulant based on seaweed (Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria digitata) and yeast extracts mitigates water stress effects on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Agriculture 11:557. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11060557
Carrasco-Gil S, Hernandez-Apaolaza L, Lucena JJ (2018) Effect of several commercial seaweed extracts in the mitigation of iron chlorosis of tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Growth Regul 86:401–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-018-0438-9
Cherki GH, Foursy A, Fares K (2002) Effects of salt stress on growth inorganic ions and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in five sugar beet cultivars. Environ Exp Bot 47:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-8472(01)00109-5
Choukri H, Hejjaoui K, El-Baouchi A, El Haddad N, Smouni A, Maalouf F, Thavarajah D, Kumar S (2020) Heat and drought stress impact on phenology, grain yield, and nutritional quality of lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus). Front Nutr 7:596307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.596307
Davey MW, Stals E, Panis B, Keulemans J, Swennen RL (2005) High-throughput determination of malondialdehyde in plant tissues. Anal Biochem 347:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2005.09.041
De Saeger J, Van Praet S, Vereecke D, Park J, Jacques S, Han T, Depuydt S (2020) Toward the molecular understanding of the action mechanism of Ascophyllum nodosum extracts on plants. J Appl Phycol 32:573–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01903-9
Dehkordi RA, Roghani SR, Mafakheri S, Asghari B (2021) Effect of biostimulants on morpho-physiological traits of various genotypes of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) under water deficit stress. Sci Hortic 283:110077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110077
Dien DC, Mochizuki T, Yamakawa T (2019) Effect of various drought stresses and subsequent recovery on proline, total soluble sugar and starch metabolisms in rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Plant Prod Sci 22:530–545. https://doi.org/10.1080/1343943X.2019.1647787
Elansary HO, Skalicka-Woźniak K, King IW (2016) Enhancing stress growth traits as well as phytochemical and antioxidant contents of Spiraea and Pittosporum under seaweed extract treatments. Plant Physiol Biochem 105:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.024
Elansary HO, Yessoufou K, Abdel-Hamid AM, El-Esawi MA, Ali HM, Elshikh MS (2017) Seaweed extracts enhance Salam turfgrass performance during prolonged irrigation intervals and saline shock. Front Plant Sci 8:264359. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00830
Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi NSM, Fujita DBS, Basra SMA (2009) Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev 29:185–212. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2008021
Feng Y, Oh SH, Manos PS (2005) Phylogeny and historical biogeography of the genus Platanus as inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA. Syst Bot 30:786–799. https://doi.org/10.1600/036364405775097851
Franzoni G, Cocetta G, Ferrante A (2021) Effect of glutamic acid foliar applications on lettuce under water stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27:1059–1072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-00984-6
Frioni T, VanderWeide J, Palliotti A, Tombesi S, Poni S, Sabbatini P (2021) Foliar vs. soil application of Ascophyllum nodosum extracts to improve grapevine water stress tolerance. Sci Hortic 277:109807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109807
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Lotfi R (2015) The impact of salicylic acid and silicon on chlorophyll a fluorescence in mung bean under salt stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 62:611–616. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715040081
Goñi O, Quille P, O’Connell S (2018) Ascophyllum nodosum extract bio-stimulants and their role in enhancing tolerance to drought stress in tomato plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 126:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.02.024
Guo D, Xia M, Wei X, Chang W, Liu Y, Wang Z (2008) Anatomical traits associated with absorption and mycorrhizal colonization are linked to root branch order in twenty-three Chinese temperate tree species. New Phytol 180:673–683. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02573.x
Hoekstra FA, Golovina EA, Buitink J (2001) Mechanisms of plant desiccation tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:431–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(01)02052-0
Irani H, ValizadehKaji B, Naeini MR (2021) Biostimulant-induced drought tolerance in grapevine is associated with physiological and biochemical changes. Chem Biol Technol Agric 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-020-00200-9
Jannin L, Arkoun M, Etienne P, Laíné P, Goux D, Garnica M, Fuentes M, Francisco S, Baigorri R, Cruz F, Houdusse F, Garcia-Mina JM, Yvin JC, Ourry A (2013) Brassica napus growth is promoted by Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) seaweed extract: microarray analysis and physiological characterization of N, C, and S metabolisms. J Plant Growth Regul 32:31–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-012-9273-9
Kasim WA, Hamada EA, El-Din NS, Eskander S (2015) Influence of seaweed extracts on the growth, some metabolic activities and yield of wheat grown under drought stress. Int J Agron Agric Res 7:173–189
Kavi Kishor PB, Sreenivasulu N (2014) Is proline accumulation per se correlated with stress tolerance or is proline homeostasis a more critical issue? Plant Cell Environ 37:300–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12157
Khorsandy S, Nikbakht A, Sabzalian MR, Pessarakli M (2016) Effect of fungal endophytes on morphological characteristics, nutrients content and longevity of plane trees (Platanus orientalis L.). J Plant Nutr 39:1156–1166. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1109113
Krause GH, Weis E (1984) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a tool in plant physiology. Photosynth Res 5:139–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028527
Lichtenthaler HK, Babani F (2022) Contents of photosynthetic pigments and ratios of chlorophyll a/b and chlorophylls to carotenoids (a+b)/(x+c) in C4 plants as compared to C3 plants. Photosynthetica 60:3–9. https://doi.org/10.32615/ps.2021.041
Lindenmayer DB, Laurance WF (2017) The ecology, distribution, conservation and management of large old trees. Biol Revs 92:1434–1458. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12290
Lutts S, Kinet JM, Bouharmont J (1996) NaCl-induced senescence in leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Ann Bot 78:389–398. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1996.0134
MacKinnon SL, Hiltz D, Ugarte R, Craft CA (2010) Improved methods of analysis for betaines in Ascophyllum nodosum and its commercial seaweed extracts. J Appl Phycol 22:489–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-009-9483-0
Mansori M, Farouk IA, Hsissou D, El Kaoua M (2019) Seaweed extract treatment enhances vegetative growth and antioxidant parameters in water-stressed (Salvia officinalis L.). J Mater Environ Sci 10:756–766
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 39:202–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.07.012
Nair P, Kandasamy S, Zhang J, Ji X, Kirby C, Benkel B, Prithiviraj B (2012) Transcriptional and metabolomic analysis of Ascophyllum nodosum mediated freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genet 13:643. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-643
Nandwani D, Dennery S, Forbes V, Geiger T, Sidhu V (2015) Effect of bio-stımulants on the yield performance of organically-grown eggplant cultivars in the U. S. Virgin Islands. Conference Paper/Presentation. Proceedings Caribbean Food Crops Society (No. 539-2016-38630) 51:181–106. https://doi.org/10.22004/ag.econ.253116
Niu T, Zhang T, Qiao Y, Wen P, Zhai G, Liu E, Al-Bakre DA, Al-Harbi MS, Gao X, Yang X (2021) Glycine betaine mitigates drought stress-induced oxidative damage in pears. Plos one 16:e0251389. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0251389
Ozbay N, Demirkiran AR (2019) Enhancement of growth in ornamental pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants with application of a commercial seaweed product, stimplex®. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17:4361–4375. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1702_43614375
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis II Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd edn. ASA, SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin USA, p 1159
Peripolli M, Dornelles SH, Lopes SJ, Tabaldi LA, Trivisiol VS, Rubert J (2021) Application of biostimulants in tomato subjected to water deficit: physiological, enzymatic and production responses1. Rev Bras Eng Agric Ambient 25:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v25n2p90-95
Raj A, Sailo L, Husaini A (2021) Evidence of proteoid roots in Chinar (Platanus orientalis L.): taxonomic implications. Curr Sci 120:757–758
Rasul F, Gupta S, Olas JJ, Gechev T, Sujeeth N, Mueller-Roeber B (2021) Priming with a seaweed extract strongly improves drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 22:1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031469
Rose R, Haase DL, Kroiher F, Sabin T (1997) Root volume and growth of ponderosa pine and Douglas-fir trees: a summary of eight growing seasons. West J Appl for 12:69–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/wjaf/12.3.69
Sadeghi F, Samsampour D, Seyahooei MA, Bagheri A, Soltani J (2020) Fungal endophytes alleviate drought-induced oxidative stress in mandarin (Citrus reticulata L.): toward regulating the ascorbate–glutathione cycle. Sci Hortic 261:108991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108991
Salvi L, Brunetti C, Cataldo E, Niccolai A, Centritto M, Ferrini F, Mattii GB (2019) Effects of Ascophyllum nodosum extract on Vitis vinifera: consequences on plant physiology, grape quality and secondary metabolism. Plant Physiol Biochem 139:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.03.002
Santaniello A, Scartazza A, Gresta F, Loreti E, Biasone A, Di Tommaso D, Perata P (2017) Ascophyllum nodosum seaweed extract alleviates drought stress in Arabidopsis by affecting photosynthetic performance and related gene expression. Front Plant Sci 8:275332. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01362
Schlegel HQ (1956) Die Verwertung organischer Säuren durch Chlorella im Licht. Planta 47:510–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01935418
Sikder S, Paul NK (2010) Evaluation of heat tolerance of wheat cultivars through physiological approaches. Thai J Agric Sci 43:251–258
Spann TM, Little HA (2011) Applications of a commercial extract of the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum increases drought tolerance in container-grown ‘Hamlin’sweet orange nursery trees. HortScience 46:577–582. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.46.4.577
Tadayyon A, Nikneshan P, Pessarakli M (2018) Effects of drought stress on concentration of macro-and micro-nutrients in Castor (Ricinus communis L.) plant. J Plant Nutr 41:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2017.1381126
Turfan N, Alay M, Sariyildiz T (2018) Effect of tree age on chemical compounds of ancient Anatolian black pine (Pinus nigra subsp. pallasiana) needles in Northwest Turkey. IForest 11:406–410 (http://www.sisef.it/iforest/contents/?id=ifor2665-011)
Verma SK, Sahu PK, Kumar K, Pal G, Gond SK, Kharwar RN, White JF (2021) Endophyte roles in nutrient acquisition, root system architecture development and oxidative stress tolerance. J Appl Microbiol 131:2161–2177. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.15111
Whapham CA, Blunden TJ, Jenkins T, Hankins SD (1993) Significance of betaines in the increased chlorophyll content of plants treated with seaweed extract. J Appl Phycol 5:231–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00004023
Zargar SM, Gupta N, Nazir M, Mahajan R, Malik FA, Sofi NR, Salgotra RK (2017) Impact of drought on photosynthesis: molecular perspective. Plant Gene 11:154–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2017.04.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G. Akhbarfar performing project, data collection, software, data analysis, and original draft writing. A. Nikbakht conception and design of the study, supervision, data analysis, investigation, writing, and editing. N. Etemadi design of the study, investigation, writing, and editing. O. Gailing data analysis, investigation, writing, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declarations
We also declare that none of the authors listed in the manuscript is employed by a government agency that has a primary function other than research and/or education. Moreover, the authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. We do not have any prior discussions with a Scientific Reports Editorial Board Member about the work described in our manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akhbarfar, G., Nikbakht, A., Etemadi, N. et al. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Plantain Trees (Platanus orientalis L.) Derived from Different Ages to Drought Stress and Ascophyllum nodosum L. Extract. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 5945–5961 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01452-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01452-8