Abstract
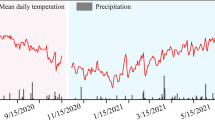
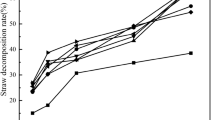
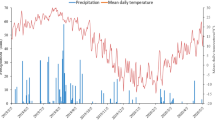
Understanding farmland ecosystem processes such as straw decomposition under nitrogen fertilization is critical for predicting carbon and nitrogen cycles. Nitrogen fertilization significantly affects soil and straw quality, which may significantly affect straw decomposition; however, comprehensive studies considering both factors are lacking. To evaluate the decomposability of crop residues under nitrogen fertilization, we conducted three subexperiments involving straw decomposition in situ, decomposition of the same straw in soils with different nitrogen fertilization regimes and decomposition of different straw types in the same soil with nitrogen fertilization and investigated the changes in soil respiration and wheat straw physicochemical properties. Nitrogen fertilization promoted straw decomposition: 180 and 360 kg N ha−1 year−1 increased the weight loss rate by 9.95% and 11.15%, respectively, but the difference between the two was not significant. The carbon emissions under 360 kg N ha−1 year−1 were significantly higher than those under 180 kg N ha−1 year−1. Straw chemical characteristics exhibited different sensitivities to nitrogen fertilization; hemicellulose responded positively to 180 kg N ha−1 year−1, while carbon and cellulose had obvious responses to only 360 kg N ha−1 year−1. The soil temperature, soil moisture, straw nitrogen content, and straw C/N ratio were the main factors affecting decomposition. Excessive nitrogen fails to promote nutrient return during straw decomposition and may also increase carbon emissions from farmland soil and aggravate the greenhouse effect. This study provides a theoretical basis for understanding nutrient cycling in farmland ecosystems under reasonable fertilization regimes and for improving farmland soil quality and nitrogen fertilization.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the figures and tables.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Allison SD, Lebauer DS, Ofrecio MR, Reyes R, Tran TM (2009) Low levels of nitrogen addition stimulate decomposition by boreal forest fungi. Soil Biol Biochem 41:293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.10.032
Angst Š, Cajthaml T, Angst G, Šimáčková H, Brus J, Frouz J (2017) Retention of dead standing plant biomass (marcescence) increases subsequent litter decomposition in the soil organic layer. Plant Soil 418:571–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3318-6
Bakht J, Shafi M, Jan MT, Shah Z (2009) Influence of crop residue management, cropping system and N fertilizer on soil N and C dynamics and sustainable wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production. Soil till Res 104:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.02.006
Banerjee S, Kirkby CA, Schmutter D, Bissett A, Kirkegaard JA, Richardson AE (2016) Network analysis reveals functional redundancy and keystone taxa amongst bacterial and fungal communities during organic matter decomposition in an arable soil. Soil Biol Biochem 97:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.03.017
Berg B, Mcclaugherty C (2013) Decomposition, Humus Formation, Carbon Sequestration. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59631-6
Bremner JM, Mulvaney C (1996) Nitrogen-total. In: Klute A, Page A, Miller R, Keeney D (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. ASA and SSSA, Madison, pp 539–579. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.3.c37
Cao Y, Sun H, Zhang J, Chen G, Zhu H (2018) Effects of wheat straw addition on dynamics and fate of nitrogen applied to paddy soils. Soil till Res 178:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.12.023
Chen H, Hou R, Gong Y, Li H, Fan M, Kuzyakov Y (2009) Effects of 11 years of conservation tillage on soil organic matter fractions in wheat monoculture in Loess Plateau of China. Soil till Res 106:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.09.009
Chen Y, Sayer EJ, Li Z, Mo Q, Li Y, Ding Y, Wang J, Lu X, Tang J, Wang F (2016) Nutrient limitation of woody debris decomposition in a tropical forest: contrasting effects of N and P addition. Funct Ecol 30:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12471
Chen Z, Wang H, Liu X, Zhao X, Lu D, Zhou J, Li C (2017) Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice–wheat cropping system. Soil till Res 165:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.07.018
Christensen BT (1985) Wheat and barley straw decomposition under field conditions: Effect of soil type and plant cover on weight loss, nitrogen and potassium content. Soil Biol Biochem 17:691–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(85)90047-1
Core Team R (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, p 2014
Dijkstra FA, Hobbie SE, Knops JM, Reich H, PB, (2004) Nitrogen deposition and plant species interact to influence soil carbon stabilization. Ecol Lett 7:1192–1198. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00679.x
Dukes JS, Field CB (2010) Diverse mechanisms for CO2 effects on grassland litter decomposition. Global Change Biol 6:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.00292.x
Gao H, Chen X, Wei J, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Chang J, Thompson ML (2016) Decomposition Dynamics and changes in chemical composition of wheat straw residue under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. PLoS ONE 11:158–172. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158172
García-Palacios P, Mckie BG, Handa IT, Frainer A, Hättenschwiler S (2016) The importance of litter traits and decomposers for litter decomposition: a comparison of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems within and across biomes. Funct Ecol 30:819–829. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12589
Green CJ, Blackmer AM, Horton R (1995) Nitrogen effects on conservation of carbon during corn residue decomposition in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:453–459. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1995.03615995005900020026x
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451:293–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06592
Hamer U, Marschner B (2005) Priming effects in different soil types induced by fructose, alanine, oxalic acid and catechol additions. Soil Biol Biochem 37:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.037
Hattenschwiler S, Jorgensen HB (2010) Carbon quality rather than stoichiometry controls litter decomposition in a tropical rain forest. J Ecol 98(4):754–763. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2010.01671.x
Hobbie SE (1999) Early stages of root and leaf decomposition in Hawaiian forests: effects of nutrient availability. Oecologia 121:564–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420050963
Hobbie SE (2005) Contrasting effects of substrate and fertilizer nitrogen on the early stages of litter decomposition. Ecosystems 8:644–656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-003-0110-7
Hogervorst RF, Dijkhuis MAJ, Schaar MAVD, Berg MP, Verhoef HA (2003) Indications for the tracking of elevated nitrogen levels through the fungal route in a soil food web. Environ Pollut 126:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00186-6
Jiang X, Cao L, Zhang R, Yan L, Mao Y, Yang Y (2014) Effects of nitrogen addition and litter properties on litter decomposition and enzyme activities of individual fungi. Appl Soil Ecol 80:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.04.002
Jani A, Grossman JM, Smyth TJ, Hu S (2015) Influence of soil inorganic nitrogen and root diameter size on legume cover crop root decomposition and nitrogen release. Plant Soil 393:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2473-x
Jing H, Li J, Yan B, Wei F, Liu G (2021) The effects of nitrogen addition on soil organic carbon decomposition and microbial C-degradation functional genes abundance in a Pinus tabulaeformis forest. Forest Ecol Manag 489:119098. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FORECO.2021.119098
Jing H, Wang G (2020) Temporal dynamics of Pinus tabulaeformis litter decomposition under nitrogen addition on the Loess Plateau of China. Forest Ecol Manag 476:118465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118465
Jing H, Zhang P, Li J, Yao X, Liu G, Wang G (2019) Effect of nitrogen addition on the decomposition and release of compounds from fine roots with different diameters: the importance of initial substrate chemistry. Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04017-w
Johannes R, Erland B (2007) Fungal and bacterial growth in soil with plant materials of different C/N ratios. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00398.x
Kai Y, Changhui P, Wanqin Y, Peng Y, Zhang C, Huang C, Wu F (2016) Degradation of lignin and cellulose during foliar litter decomposition in an alpine forest river. Ecosphere 7. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.1523
Knorr M, Frey SD, Curtis PS (2005) Nitrogen additions and litter decomposition: a meta-analysis. Ecology 86:3252–3257. https://doi.org/10.1890/05-0150
Kumar K, Goh KM (1999) Crop residues and management practices: Effects on soil quality, soil nitrogen dynamics, crop yield, and nitrogen recovery. Adv Agron 68:197–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(08)60846-9
Kumar K, Goh KM (2002) Management practices of antecedent leguminous and non-leguminous crop residues in relation to winter wheat yields, nitrogen uptake, soil nitrogen mineralization and simple nitrogen balance. Eur J Agron 16:295–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(01)00133-2
Kumar K, Goh KM (2003) Nitrogen release from crop residues and organic amendments as affected by biochemical composition. Commun Soil Sci Plan 34:2441–2460. https://doi.org/10.1081/CSS-120024778
Liu C, Lu M, Cui J, Li B, Fang C (2014) Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis. Global Change Biol 20:1366–1381. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12517
Liu P, Huang J, Han X, Sun OJ, Zhou Z (2005) Differential responses of litter decomposition to increased soil nutrients and water between two contrasting grassland plant species of Inner Mongolia. China Appl Soil Ecol 34:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.12.009
Magill AH, Aber JD (1998) Long-term effects of experimental nitrogen additions on foliar litter decay and humus formation in forest ecosystems. Plant Soil 203:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004367000041
Mastny J, Kaštovská E, Bárta J, Chroňáková A, Borovec J, Šantrůčková H, Urbanová Z, Edwardsa RK, Picek T (2018) Quality of DOC produced during litter decomposition of peatland plant dominants. Soil Biol Biochem 121:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.03.018
Megonigal JP, Hines ME, Visscher PT (2014) Anaerobic metabolism: linkages to trace gases and aerobic processes. Geochemistry 8:317–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-095975-7.00808-1
Moyano FE, Manzoni S, Chenu C (2013) Responses of soil heterotrophic respiration to moisture availability: An exploration of processes and models. Soil Biol Biochem 59:72–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.01.002
Mtb A, Dc A, Ans B, Gs C, Vh C, Nrs B, Tn A (2019) Why does nitrogen addition to forest soils inhibit decomposition? Soil Biol Biochem 137:107570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107570
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1983) Total carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL et al (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Agron Mongr 9.2, 2nd edn. ASA and SSSA, Madison, pp 539–579. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed.c29
Nottingham AT, Hicks LC, Ccahuana AJQ, Salinas N, Baath E, Meir P (2018) Nutrient limitations to bacterial and fungal growth during cellulose decomposition in tropical forest soils. Biol Fert Soils 54:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1247-4
Olson JS (1963) Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 44:322–331. https://doi.org/10.2307/1932179
Roper MM (1985) Straw decomposition and nitrogenase activity (C2H2 reduction): Effects of soil moisture and temperature. Soil Biol Biochem 23:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(91)90064-Q
Rubenstein MA, Crowther TW, Maynard DS, Schilling JS, Bradford MA (2017) Decoupling direct and indirect effects of temperature on decomposition. Soil Biol Biochem 112:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.05.005
Sakala WD, Cadisch G, Giller KE (2000) Interactions between residues of maize and pigeonpea and mineral N fertilizers during decomposition and N mineralization. Soil Biol Biochem 32:679–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00204-7
Schreiber JD (1985) Leaching of nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic carbon from wheat straw residues: II. Loading Rate1. J Environ Qual 14:256–260. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1985.00472425001400020020x
Shah Z, Shah SH, Peoples MB, Schwenke GD, Herridge DF (2003) Crop residue and fertiliser N effects on nitrogen fixation and yields of legume-cereal rotations and soil organic fertility. Field Crop Res 83:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00005-4
Shahryari Z, Fazaelipoor MH, Setoodeh P, Nair RB, Taherzadeh MJ, Ghasemi Y (2018) Utilization of wheat straw for fungal phytase production. Int J Recyc Org Waste Agric 7:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-018-0220-z
Shu L, Yang W, Yu T, Peng Y, Li J, Tan B, Wu F, Liang W (2015) Soil fauna affects dissolved carbon and nitrogen in foliar litter in alpine forest and alpine meadow. PLoS ONE 10:e0139099. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139099
Soest PJV, Wine RH (1967) Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds. 4. Determination of plant cell-wall constituents. J. A.O.A.C 50(50):55. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/50.1.50Stephan
Sun L, Jing H, Wang G, Liu G (2018) Nitrogen addition increases the contents of glomalin-related soil protein and soil organic carbon but retains aggregate stability in a Pinus tabulaeformis forest. Peer j 6:e5039. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5039
Swift MJ, Heal OW, Anderson JM (1979) Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. University of California Press, California
Tardy V, Spor E, Mathieu O, Eque JLE, Maron PA (2015) Shifts in microbial diversity through land use intensity as drivers of carbon mineralization in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 90:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.010
Treseder KK (2010) Nitrogen additions and microbial biomass: a meta-analysis of ecosystem studies. Ecol Lett 11:1111–1120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01230.x
Tu LH, PengY CG, Hu HL, Xiao YL, Hu TX, Liu L, Tang Y (2015) Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen additions on fine root decomposition in a subtropical bamboo forest. Plant Soil 389:273–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2353-9
Vivanco L, Austin AT (2011) Nitrogen addition stimulates forest litter decomposition and disrupts species interactions in Patagonia. Argentina Global Change Biol 17:1963–1974. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02344.x
Xia L, Lam SK, Wolf B, Kiese R, Chen D, Butterbach-Bahl K (2018) Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems. Global Change Biol 24:5919–5932. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14466
Xu Y, Chen Z, Ding W, Fan J (2017). Responses of manure decomposition to nitrogen addition: Role of chemical composition. Sci Total Environ s587–588:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.033
Yan W, Zhong Y, Liu J, Shangguan Z (2021) Response of soil respiration to nitrogen fertilization: Evidence from a 6-year field study of croplands. Geoderma 384:114829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114829
Yan W, Zhong Y, Zhu G, Liu W, Shangguan Z (2020) Nutrient limitation of litter decomposition with long-term secondary succession: evidence from controlled laboratory experiments. J Soil Sediment 20(4):1858–1868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02523-z
Zhang J, Ai Z, Liang C, Wang G, Xue S (2017) Response of soil microbial communities and nitrogen thresholds of Bothriochloa ischaemum to short-term nitrogen addition on the Loess Plateau. Geoderma 308:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.08.034
Zhang Q, Lei H, Yang DW (2013) Seasonal variations in soil respiration, heterotrophic respiration and autotrophic respiration of a wheat and maize rotation cropland in the North China Plain. Agr Forest Meteorol 180:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2013.04.028
Zhang W, Wang S (2012) Effects of NH4+ and NO3- on litter and soil organic carbon decomposition in a Chinese fir plantation forest in South China. Soil Biol Biochem 47:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.12.004
Zhao S, Qiu S, Xu X, Ciampitti IA, Zhang S, He P (2019) Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils. Appl Soil Ecol 138:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.02.018
Zhong Y, Liu J, Jia X, Shangguan Z, Wang R, Yan W (2020) Microbial community assembly and metabolic function during wheat straw decomposition under different nitrogen fertilization treatments. Biol Fert Soils 56:697–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01438-z
Zhong Y, Yan W, Shangguan Z (2015) Impact of long-term N additions upon coupling between soil microbial community structure and activity, and nutrient-use efficiencies. Soil Biol Biochem 91:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.030
Zhong Y, Yan W, Wang R, Shangguan Z (2017) Differential responses of litter decomposition to nutrient addition and soil water availability with long-term vegetation recovery. Biol Fert Soils 53:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1242-9
Zhou L, Zhou X, Shao J, Nie Y, He Y, Jiang L, Wu Z, Bai SH (2016) Interactive effects of global change factors on soil respiration and its components: a meta-analysis. Global Change Biol 22(9):3157–3169. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13253
Zhu Y, Jin M, Ma C, Guang M, Gao M, Gao H (2019) Impacts of exogenous nitrogen and effective microorganism on the decomposition of wheat straw residues. Ecol. Environ. Sci 28:188–195. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.03.023
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Science Foundation of China (41701336 and 41807323) and the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX201700200 and BX201700198).
Funding
This study was funded by the National Science Foundation of China (41701336 and 41807323) and the National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX201700200 and BX201700198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Statements are not mandatory.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Appropriate approval was obtained.
Consent to Participate
All authors consent to participate.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to publication.
Conflicts of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhong, Y., Jia, X. et al. Wheat Straw Decomposition Patterns and Control Factors Under Nitrogen Fertilization. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 3110–3121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00592-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00592-z