Abstract
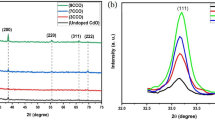
A cost-effective spray pyrolysis technique was used to deposit CuO thin films on a variety of precleaned substrates. Films were air-annealed for 1 h at 400 °C, 450 °C, and 500 °C. XRD, Raman analysis, XPS, FTIR, SEM, EDS, UV–VIS-NIR spectrophotometry, and Hall effect studies were used to analyze the structural, morphological, compositional, optical, and electrical properties of films. XPS analysis reveals the presence of Cu and O without impurities. The presence of Cu–O stretching bonds was confirmed using FTIR. The Raman spectrum reveals monoclinic structure confirming XRD results, along with the presence of micro stress in films. The elemental composition of synthesized films is analyzed using EDX spectroscopy. The optical study depicts how air annealing can easily change the porosity and dielectric constant of films. As per the Hall effect study, p-to-n type conversion occurs at 450 °C. The gas selectivity of an as-deposited CuO-based MOM (Metal-Oxide-Metal) sensor was studied at 100 °C with four different test gases: acetone, ammonia, ethanol, and nitrogen dioxide. Sensors were found to possess the highest selectivity for ethanol. The optimal operating temperature for the fabricated sensors for ethanol test gas is found to be 200 °C. The estimated recovery and response time are both short, and the sensor is stable over the entire operating temperature range. The fabricated, low-cost MOM ethanol gas sensor could be used in medical and industrial fields.
Graphical Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data underlying the results is available as part of the article and no additional resource data is required.
References
L. Van Nang, C.M. Hung, C.T. Xuan, N. Van Duy, N.D. Hoa, Preparation and gas sensing properties of rGO/CuO nanocomposites. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 11(3), 035009 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac5c7f
J. Zhang, S. Ma, B. Wang, S. Pei, Hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2-CuO composite nanoparticles as a fast-response ethanol gas sensor. J. Alloy. Compd. 886, 161299 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161299
I.S. Yahia, A.A.M. Farag, S. El-Faify, F. Yakuphanoglu, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, Synthesis, optical constants, optical dispersion parameters of CuO nanorods. Optik 127(3), 1429–1433 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.10.021
C.C. Hsu, C.H. Wu, S.Y. Wang, Low power deposition of the polycrystalline CuxO film with a high mobility and a low hole concentration by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering of a Cu2O target. J. Alloy. Compd. 663, 262–269 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.112
S. Baturay, A. Tombak, D. Kaya, Y.S. Ocak, M. Tokus, M. Aydemir, T. Kilicoglu, Modification of electrical and optical properties of CuO thin films by Ni doping. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 78, 422–429 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3953-4
T. Maruyama, Copper oxide thin films prepared by chemical vapor deposition from copper dipivaloylmethanate. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 56(1), 85–92 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(98)00128-7
V. Figueiredo, E. Elangovan, G. Goncalves, P. Barquinha, L. Pereira, N. Franco, ... E. Fortunato, Effect of post-annealing on the properties of copper oxide thin films obtained from the oxidation of evaporated metallic copper. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254(13), 3949–3954 (2008) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.12.019
M. Eslamian, Spray-on thin film PV solar cells: advances, potentials and challenges. Coatings 4(1), 60–84 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4010060
N. Lehraki, M.S. Aida, S. Abed, N. Attaf, A. Attaf, M. Poulain, ZnO thin films deposition by spray pyrolysis: influence of precursor solution properties. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12(5), 1283–1287 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2012.03.012
F. Zahedi, R.S. Dariani, S.M. Rozati, Effect of substrate temperature on the properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16(2), 245–249 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2012.11.005
W. Naffouti, T.B. Nasr, A. Mehdi, N. Kamoun-Turki, Effect of sprayed solution flow rate on the physical properties of anatase TiO 2 thin films. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 4033–4040 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3341-9
R.J. Deokate, A.V. Moholkar, G.L. Agawane, S.M. Pawar, J.H. Kim, K.Y. Rajpure, Studies on the effect of nozzle-to-substrate distance on the structural, electrical and optical properties of spray deposited CdIn2O4 thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(11), 3522–3530 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.12.102
V. Saravanan, P. Shankar, G.K. Mani, J.B.B. Rayappan, Growth and characterization of spray pyrolysis deposited copper oxide thin films: Influence of substrate and annealing temperatures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 111, 272–277 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2014.08.008
F.A. Akgul, G. Akgul, N. Yildirim, H.E. Unalan, R. Turan, Influence of thermal annealing on microstructural, morphological, optical properties and surface electronic structure of copper oxide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 147(3), 987–995 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.06.047
A.S. Ethiraj, D.J. Kang, Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanowires by a simple wet chemical method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 1–5 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-70
D. Zhu, L. Wang, W. Yu, H. Xie, Intriguingly high thermal conductivity increment for CuO nanowires contained nanofluids with low viscosity. Sci Rep 8(1), 5282 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23174-z
B. Jos, K.J. Saji, E.I. Anila, Effect of substrate temperature on properties of copper oxide thin films coated by spray pyrolysis. J. Mines Metals Fuels 71(1) (2023) https://doi.org/10.18311/jmmf/2023/33351
P. Vomáčka, V. Štengl, J. Henych, M. Kormunda, Shape-controlled synthesis of Sn-doped CuO nanoparticles for catalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 481, 28–38 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.07.026
G.A. Artioli, A. Mancini, V.R. Barbieri, M.C. Quattrini, E. Quartarone, M.C. Mozzati, L. Malavasi, Correlation between deposition parameters and hydrogen production in CuO nanostructured thin films. Langmuir 32(6), 1510–1520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03917
N. Jhansi, D. Balasubramanian, R. Raman, Investigation on structural, optical and electrical behaviours of Sn doped copper oxide thin films and fabrication of diode. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 34(17), 1369 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10623-3
C. Xu, Y. Liu, G. Xu, G. Wang, Preparation and characterization of CuO nanorods by thermal decomposition of CuC2O4 precursor. Mater. Res. Bull. 37(14), 2365–2372 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5408(02)00848-6
J. Chastain, R.C. King Jr., Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Perkin-Elmer Corp. 40, 221 (1992)
Z.S. Hong, Y. Cao, J.F. Deng, A convenient alcohothermal approach for low temperature synthesis of CuO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 52(1–2), 34–38 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(01)00361-5
R.A. Zarate, F. Hevia, S. Fuentes, V.M. Fuenzalida, A. Zuniga, Novel route to synthesize CuO nanoplatelets. J. Solid State Chem. 180(4), 1464–1469 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2007.01.040
G. Carraro, C. Maccato, A. Gasparotto, T. Montini, S. Turner, O.I. Lebedev, ... P. Fornasiero, Enhanced hydrogen production by photoreforming of renewable oxygenates through nanostructured Fe2O3 polymorphs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24(3), 372–378. (2014) https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201302043
D.K. Zhong, J. Sun, H. Inumaru, D.R. Gamelin, Solar water oxidation by composite catalyst/α-Fe2O3 photoanodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(17), 6086–6087 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9016478
M.P. Marder, Condensed matter physics, 2nd edition. p 992. John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
F. Parmigiani, L. Sangaletti, The Cu2p X-ray photoelectron core-lines in copper oxide based high temperature superconductors. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 66(3–4), 223–239 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0368-2048(93)01854-8
I. Platzman, R. Brener, H. Haick, R. Tannenbaum, Oxidation of polycrystalline copper thin films at ambient conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 112(4), 1101–1108 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp076981k
J.Y. Park, K.A. Lim, R.D. Ramsier, Y.C. Kang, Spectroscopic and morphological investigation of copper oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at various oxygen ratios. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 32(9), 3395–3399 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.9.3395
N. Kumar, S.S. Parui, S. Limbu, D.K. Mahato, N. Tiwari, R.N. Chauhan, Structural and optical properties of sol–gel derived CuO and Cu2O nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. 41, 237–241 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.800
B. Balamurugan, B.R. Mehta, D.K. Avasthi, F. Singh, A.K. Arora, M. Rajalakshmi, G. Raghavan, S. Tyagi, S.M. Shivaprasad, Modifying the nanocrystalline characteristics—structure, size, and surface states of copper oxide thin films by high-energy heavy-ion irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 92(6), 3304–3310 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1499752
K. Draou, N. Bellakhal, B.G. Cheron, J.L. Brisset, Heat transfer to metals In low pressure oxygen plasma: application to oxidation of the 90Cu–10Zn alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 58(3), 212–220 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(98)00268-5
M.R. Johan, M.S.M. Suan, N.L. Hawari, H.A. Ching, Annealing effects on the properties of copper oxide thin films prepared by chemical deposition. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci, 6(12), 6094–6104. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6, 6094 – 6104. (2011) http://www.electrochemsci.org/papers/vol6/6126094.pdf
J.F. Xu, W. Ji, Z.X. Shen, W.S. Li, S.H. Tang, X.R. Ye, et al., J. Raman Spectrosc. 30 43.(1999) https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4555(199905)30:5%3C413::AIDJRS387%3E3.0.CO;2-N
O. Diachenko, J. Kováč Jr., O. Dobrozhan, P. Novák, J. Kováč, J. Skriniarova, A. Opanasyuk, Structural and optical properties of CuO thin films synthesized using spray pyrolysis method. Coatings 11(11), 1392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111392
B. Balamurugan, B.R. Mehta, D.K. Avasthi, F. Singh, A.K. Arora, M. Rajalakshmi, S.M. Shivaprasad, Modifying the nanocrystalline characteristics—structure, size, and surface states of copper oxide thin films by high-energy heavy-ion irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 92(6), 3304–3310 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1499752
V. Muralikrishnan, H. Liu, L. Yang, B. Conry, C.J. Marvel, M.P. Harmer, ... R. Krause, Observations of unexpected grain boundary migration in SrTiO3. Scripta Mater. 222, 115055 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2022.115055
R. Aydın, A. Akkaya, O. Kahveci, B. Şahin, Nanostructured CuO thin-film-based conductometric sensors for real-time tracking of sweat loss. ACS Omega (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c02232
M.A. Baba, A. Gasim, A.M. Awadelgied, N.A. Almuslet, A.M. Salih, Influence of the annealing temperature on the thickness and roughness of La2Ti2O7 thin films. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 10(08), 189–198 (2020). https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2020.108014
L. Cui, G.G. Wang, H.Y. Zhang, R. Sun, X.P. Kuang, J.C. Han, Effect of film thickness and annealing temperature on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films deposited on sapphire (0001) substrates by sol–gel. Ceram. Int. 39(3), 3261–3268 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.10.014
D. Mahana, A.K. Mauraya, P. Singh, S.K. Muthusamy, Evolution of CuO thin films through thermal oxidation of Cu films prepared by physical vapour deposition techniques. Solid State Commun. 366, 115152 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2023.115152
M.H. Kabir, M. Hafiz, S. Rahman, M. Saifur Rahman, H. Rahman, M.M. Rashid, ... M.S. Rahman, Effect of Ga doping on structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties of CuO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 34(16), 1258 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10711-4
D.N. Oosthuizen, D.E. Motaung, A.M. Strydom, H.C. Swart, Underpinning the interaction between NO2 and CuO nanoplatelets at room temperature by tailoring synthesis reaction base and time. ACS Omega 4(19), 18035–18048 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b01882
N. Wang, W. Tao, X. Gong, L. Zhao, T. Wang, L. Zhao, ... G. Lu, Highly sensitive and selective NO2 gas sensor fabricated from Cu2O-CuO microflowers. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 362, 131803 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131803
Y. Tan, J. Zhang, Highly sensitive ethanol gas sensors based on Co-doped SnO2 nanobelts and pure SnO2 nanobelts. Physica E 147, 115604 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2022.115604
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge “INUP, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore” for providing characterization and device testing facilities and “The Central Research Facilities, Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences, Bengaluru” for providing characterization facilities.
The authors also thank the Principals of J S S Academy of Technical Education, Bangalore, Government College for Women (Autonomous), Mandya, and Global Academy of Technology, Bangalore for their kind support and encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
“All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Mr. Madhukeswara R S, Dr. Shashidhar R, Dr. Raghu A and Mr. Prakasha G S. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mr. Madhukeswara R S. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.”
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Madhukeswara, R.S., Shashidhar, R., Raghu, A. et al. Influence of air annealing on the microstructural, morphological, compositional, optical and electrical properties of spray deposited CuO thin films and their utility as MOM gas sensors. emergent mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-024-00738-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-024-00738-6