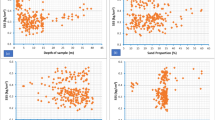
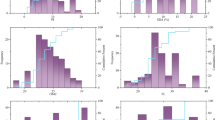
Abstract
California bearing ratio (CBR) is one of the important parameters that is used to express the strength of the pavement subgrade of railways, roadways, and airport runways. CBR is usually determined in the laboratory in soaked and unsoaked conditions, which is an exhaustive and time-consuming process. Therefore, to sidestep the operation of conducting actual laboratory tests, this study presents the development of efficient hybrid soft computing techniques, by hybridizing artificial neural network (ANN) with nature-inspired optimization algorithm, namely, gradient-based optimization (GBO), firefly algorithm (FF), cultural algorithms (CA), grey wolf optimization (GWO), genetic algorithm (GA), particle swarm optimization (PSO), Harris Hawk optimization (HHO), teaching learning-based optimization (TLBO), Whale optimization algorithm (WOA) and invasive weed optimization (IWO). For this purpose, a data set was prepared from the experimental results of soaked CBR of soil samples collected from an ongoing Nepal’s Mid-Hill Highway project. Based on the detailed comparative study one explicit model is proposed to estimate the CBR of soils in soaked conditions. The predictive accuracy of the proposed models was evaluated via several statistical and graphical parameters. Separate statistical indices were employed to evaluate the generalization capabilities of the developed models. In addition, in the end, the best predictive model was determined using a novel tool called order analysis. The results of the study reveal that the proposed artificial neural network coupled with the gradient-based optimizer (ANN–GBO) model attained the most accurate prediction (R2 = 0. 997and R2 = 0.956, during the training and testing phase) in predicting the soaked CBR. Based on the accuracies attained, the proposed ANN–GBO model has very potential to be an alternate solution to estimate the CBR value in different phases of civil engineering projects.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and supplementary material are available on request.
References
Alam SK, Mondal A, Shiuly A (2020) Prediction of CBR value of fine grained soils of Bengal Basin by genetic expression programming, artificial neural network and krigging method. J Geol Soc India 95(2):190–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1409-0
Amin MN, Iqbal M, Ashfaq M, Salami BA, Khan K, Faraz MI, Alabdullah AA, Jalal FE (2022) Prediction of strength and CBR characteristics of chemically stabilized coal gangue: ANN and random forest tree approach. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124330
Asteris PG, Skentou AD, Bardhan A, Samui P, Pilakoutas K (2021) Predicting concrete compressive strength using hybrid ensembling of surrogate machine learning models. Cem Concr Res 145:106449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2021.106449
Baghbani A, Choudhury T, Costa S, Reiner J (2022) Application of artificial intelligence in geotechnical engineering: A state-of-the-art review. Earth-Sci Rev 228:103991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103991
Bardhan A, Gokceoglu C, Burman A, Samui P, Asteris PG (2021a) Efficient computational techniques for predicting the California bearing ratio of soil in soaked conditions. Eng Geol 291:106239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106239
Bardhan A, Samui P, Ghosh K, Gandomi AH, Bhattacharyya S (2021b) ELM-based adaptive neuro swarm intelligence techniques for predicting the California bearing ratio of soils in soaked conditions. Appl Soft Comput 110:107595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107595
Bardhan A, Singh RK, Ghani S, Konstantakatos G, Asteris PG (2023) Modelling soil compaction parameters using an enhanced hybrid intelligence paradigm of ANFIS and improved grey wolf optimiser. Mathematics 11(14):3064. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11143064
Bui QAT, Al-Ansari N, Le HV, Prakash I, Pham BT (2022) Hybrid model: teaching learning-based optimization of artificial neural network (TLBO-ANN) for the prediction of soil permeability coefficient. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8938836
Ceryan N, Samui P (2020) Application of soft computing methods in predicting uniaxial compressive strength of the volcanic rocks with different weathering degree. Arab J Geosci 13(7):288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5273-4
Coello Coello CA, Becerra RL (2004) Efficient evolutionary optimization through the use of a cultural algorithm. Eng Optim 36(2):219–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150410001647966
Dababneh O, Kipouros T, Whidborne JF (2018) Application of an efficient gradient-based optimization strategy for aircraft wing structures. Aerospace. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace5010003
Erzin Y, Turkoz D (2016) Use of neural networks for the prediction of the CBR value of some Aegean sands. Neural Comput Appl 27(5):1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1943-7
Ghani S, Kumari S (2023) Plasticity-based liquefaction prediction using support vector machine and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. In: Muthukkumaran-Kasinathan KS, Ayothiraman R (eds) Soil dynamics, earthquake and computational geotechnical engineering. Springer Nature, Singapore, pp 515–527
Ghani S, Kumari S, Ahmad S (2022a) Prediction of the seismic effect on liquefaction behavior of fine-grained soils using artificial intelligence-based hybridized modeling. Arab J Sci Eng 47(4):5411–5441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06697-6
Ghani S, Kumari S, Jaiswal S, Sawant VA (2022b) Comparative and parametric study of AI-based models for risk assessment against soil liquefaction for high-intensity earthquakes. Arab J Geosci 15(14):1262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10534-3
Ghani S, Kumari S, Choudhary AK (2023) Geocell mattress reinforcement for bottom ash: a comprehensive study of load-settlement characteristics. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01205-8
Huang M, Ma Y, Wan J, Chen X (2015) A sensor-software based on a genetic algorithm-based neural fuzzy system for modeling and simulating a wastewater treatment process. Appl Soft Comput 27:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.10.034
Kassa SM, Wubineh BZ (2023) Use of machine learning to predict california bearing ratio of soils. Adv Civ Eng 2023:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/8198648
Katte VY, Mfoyet SM, Manefouet B, Wouatong ASL, Bezeng LA (2019) Correlation of California bearing ratio (CBR) value with soil properties of road subgrade soil. Geotech Geol Eng 37(1):217–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0604-x
Khatti J, Grover KS (2023a) CBR prediction of pavement materials in unsoaked condition using LSSVM, LSTM-RNN, and ANN approaches. Int J Pavement Res Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42947-022-00268-6
Khatti J, Grover KS (2023b) Prediction of soaked CBR of fine-grained soils using soft computing techniques. Multiscale Multidiscip Model Exp Des 6(1):97–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-022-00131-y
Khatti J, Grover KS (2023c) Relationship between index properties and CBR of soil and prediction of CBR. Springer Nature, Singapore, pp 171–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6774-0_16
Kim M, Ordu S, Arslan O, Ko J (2023) Prediction of California bearing ratio (CBR) for coarse- and fine-grained soils using the GMDH-model. Geomech Eng 33(2):183–194
Koti Marg K, Puram R (2012) IRC: 37-2012 iii guidelines for the design of flexible pavements Indian roads congress
Koti Marg K, Puram R (2019) Guidelines for the design of flexible pavements Indian roads congress
Kumar D, Gandhi BGR, Bhattacharjya RK (2020) Introduction to invasive weed optimization method. Springer, Cham, pp 203–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26458-1_12
Kurnaz TF, Kaya Y (2020) The performance comparison of the soft computing methods on the prediction of soil compaction parameters. Arab J Geosci 13(4):159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5171-9
Nagaraju TV, Bahrami A, Prasad ChD, Mantena S, Biswal M, Islam MdR (2023) Predicting California bearing ratio of lateritic soils using hybrid machine learning technique. Buildings 13(1):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13010255
Prakash S, Kumar S, Rai B (2023) A new technique based on the gorilla troop optimization coupled with artificial neural network for predicting the compressive strength of ultrahigh performance concrete. Asian J Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00822-y
Raj Kiran N, Ravi V (2008) Software reliability prediction by soft computing techniques. J Syst Softw 81(4):576–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2007.05.005
Soltanali H, Rohani A, Abbaspour-Fard MH, Farinha JT (2021) A comparative study of statistical and soft computing techniques for reliability prediction of automotive manufacturing. Appl Soft Comput 98:106738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106738
Taha S, Gabr A, El-Badawy S (2019) Regression and neural network models for california bearing ratio prediction of typical granular materials in Egypt. Arab J Sci Eng 44(10):8691–8705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03803-z
Taskiran T (2010) Prediction of California bearing ratio (CBR) of fine grained soils by AI methods. Adv Eng Softw 41(6):886–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2010.01.003
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D7):7183–7192. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JD900719
Tenpe AR, Patel A (2020) Utilization of support vector models and gene expression programming for soil strength modeling. Arab J Sci Eng 45(5):4301–4319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04441-6
Vamsi Krishna SH, Sai Santosh B, Sai Prasanth BHS (2023) Prediction of UCS and CBR of a stabilized Black-cotton soil using artificial intelligence approach: ANN. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.05.097
Varghese VK, Babu SS, Bijukumar R, Cyrus S, Abraham BM (2013) Artificial neural networks: a solution to the ambiguity in prediction of engineering properties of fine-grained soils. Geotech Geol Eng 31(4):1187–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-013-9643-5
Verma G, Kumar B, Kumar C, Ray A, Khandelwal M (2023) Application of KRR, K-NN and GPR algorithms for predicting the soaked CBR of fine-grained plastic soils. Arab J Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07962-y
Yildirim B, Gunaydin O (2011) Estimation of California bearing ratio by using soft computing systems. Expert Syst Appl 38(5):6381–6391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.12.054
Zhou J, Zhu S, Qiu Y, Armaghani DJ, Zhou A, Yong W (2022) Predicting tunnel squeezing using support vector machine optimized by whale optimization algorithm. Acta Geotech 17(4):1343–1366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01450-7
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IT data collection, processing, results compilation, and writing the first draft. SG machine learning application and interpretation of ML results, finalizing the draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Young Kwon.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix
Appendix
Following are the steps provided for the supplementary code: See Table 8

Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thapa, I., Ghani, S. Estimation of California bearing ratio for hill highways using advanced hybrid artificial neural network algorithms. Multiscale and Multidiscip. Model. Exp. and Des. 7, 1119–1144 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-023-00269-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-023-00269-3