Abstract
Background
In the field of particle therapy, the method of pencil beam scanning is of great potential for clinical application, now and in the future.
Purpose
The authors made strong effort to develop a spot scanning system for Shanghai Proton Therapy Facility. Design parameters and basic layout of the system are introduced.
Methods
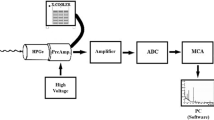
Functionalities and specifications of crucial devices are described in detail. Most of the devices in the system were designed in house by the authors themselves, including scanning nozzle, scanning magnets and their power supplies, beam monitors, irradiation control modules and safety interlock modules. During the technical commissioning stage in the fix beam room, the spot scanning system was tested and verified.
Results
Under conditions of the maximum dose rate and minimum dose rate, a) repeatability of the single spot dose is less than ± 0.1%; b) nonlinearity of the single spot dose is less than ± 0.1%; c) FWHM for spot size in air at isocenter varies from 8mm to 12mm for full energy, consistent with the design values; d) lateral dose distribution achieves a flatness of less than 2% for multiple proton energies.
Conclusion
According to the results of technical commissioning, the spot scanning system is capable of producing a prescribed 3D dose distribution for target tumor successfully.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.R. Wilson, Radiological use of fast protons. Radiology 47, 487–491 (1946). https://doi.org/10.1148/47.5.487
M.Z. Zhang, D.M. Li, K. Wang, X.C. Xie, Q.L. Zhang, Z.T. Zhao, Commissioning of Shanghai advanced proton therapy, in Proceedings of IPAC’2018. TUPAL059, (2018), pp. 1151–1154. https://doi.org/10.18429/JACoW-IPAC2018-TUPAL059
M. Engelsman, H.M. Lu, D. Herrup, Commissioning a passive-scattering proton therapy nozzle for accurate SOBP delivery. Med. Phys. 36, 2171–2180 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3121489
T. Furukawa, T. Inaniwa, S. Sato et al., Performance of the NIRS fast scanning system for heavy-ion radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 37, 5672–5682 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3501313
M.T. Gillin, N. Sahoo, M. Bues et al., Commissioning of the discrete spot scanning proton beam delivery system at the University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Proton Therapy Center, Houston. Med. Phys. 37, 154–163 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3259742
E. Pedroni, D. Meer, C. Bula et al., Pencil beam characteristics of the next-generation proton scanning gantry of PSI: design issues and initial commissioning results. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 126, 66 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2011-11066-0
S. Giordanengo, M. Donetti, F. Marchetto et al., Performances of the scanning system for the CNAO center of oncological hadron therapy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 613, 317–322 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2009.11.068
S. Giordanengo, L. Manganaro, A. Vignati, Review of technologies and procedures of clinical dosimetry for scanned ion beam radiotherapy. Physica Med 43, 79–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.10.013
S. Han, G. Cho, S.B. Lee, An assessment of the secondary neutron dose in the passive scattering proton beam facility of the National Cancer Center. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 49, 801–809 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2016.12.003
C.H. Miao, M. Liu, H. Shu et al., Design of a proton spot scanning position control system. Nucl. Tech. 41, 040201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.11889/j.0253-3219.2018.hjs.41.040201. (in Chinese)
B.Q. Zhao, M.H. Zhao, M. Liu et al., The front-end electronics design of dose monitors for beam delivery system of Shanghai Advanced Proton Therapy Facility. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 28, 83 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0230-y
C.H. Miao, M. Liu, C.X. Yin et al., Precise magnetic field control of the scanning magnets for the APTRON beam delivery system. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 28, 172 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0324-6
M. Liu, C.X. Yin, K.C. Chu et al., A scheme design of collimator for gantry in proton therapy facility. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 791, 47–53 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2015.04.045
T. Furukawa, Y. Hara, K. Mizushima et al., Development of NIRS pencil beam scanning system for carbon ion radiotherapy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 406, 361–367 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2016.10.029
M. Ciocca, A. Mirandola, S. Molinelli et al., Commissioning of the 4-D treatment delivery system for organ motion management in synchrotron-based scanning ion beams. Physica Med (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2016.11.107
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2016238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Zhang, H., Shu, H. et al. Technical commissioning of the spot scanning system in Shanghai Proton Therapy Facility. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 4, 46–55 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-019-0148-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-019-0148-5