Abstract
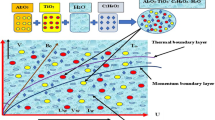
This effort aims to explain the Jeffrey-Hamel mechanism of the nanofluid flowing via a non-parallel channel under the influence of Lorentz force. The developed model evaluates the converging/diverging channel flow and heat transfer using the mass-based nanofluid method. The mathematical modelling of nanofluid flow containing molybdenum disulfide nanoparticles and water as base liquid through a converging/diverging conduit is analyzed. The Tiwari-Das nanofluid method constitutes the basis for the current strategy. Nanoparticle masses are used in place of the volume fraction in this modelling. With the similarity solution approach, the partial differential equations for the conservation of mass, momentum, and energy are transformed into a system of ordinary differential equations. By using the bvp4c approach and the shooting method, the final governing equations are solved. Graphical reports are used to assess how developing parameters affect temperature, velocity, Nusselt number, and skin friction. It has been noted that the resistance to nanofluid flow is more pronounced when non-spherical particles are present than when particles are present. This problem shows that the form of the particles affects the rheology of a nanofluid. Moreover, for high Reynolds number values, backflow regimes develop in the diverging channel. Moreover, this modelling of the nanofluid has applications in a variety of fields, including biology. The most significant accomplishment of this study is the remarkable performance of the mass-based algorithm for heat transfer and nanofluid flow.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The author confirms that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the manuscript.
References
Adun H, Wole-Osho I, Okonkwo EC, Kavaz D, Dagbasi M (2021) A critical review of specific heat capacity of hybrid nanofluids for thermal energy applications. J Mol Liquids 340:116890
Avramenko AA, Kobzar SG, Shevchuk IV, Kuznetsov AV, Iwanisov LT (2001) Symmetry of turbulent boundary-layer flows: Investigation of different eddy viscosity models. Acta Mech 151:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01272521
Awais M, Saad M, Ayaz H, Ehsan MM, Bhuiyan AA Computational assessment of nano-particulate (Al2O3/Water) utilization for enhancement of heat transfer with varying straight section lengths in a serpentine tube heat exchanger. Thermal Sci Eng Progress 20: 100521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2020.100521.
Biswal U, Chakraverty S, Ojha BK, Hussein AK (2022) Numerical investigation on nanofluid flow between two inclined stretchable walls by optimal homotopy analysis method. J Comput Sci. 63:101759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2022.101759
Boudjemline A, Ahmad I, Rehman S, Hashim, & Khedher, N. B. (2023) Jeffery-Hamel flow extension and thermal analysis of Oldroyd-B nanofluid in expanding channel. J Non-Equilib Thermodyn 48(1):75–90
Boujelbene M, Rehman S, Alqahtani S, Alshehery S, Eldin SM (2023a) Thermal transport and magnetohydrodynamics flow of generalized Newtonian nanofluid with inherent irreversibility between conduit with slip at the walls. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 17:2182364. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2023.2182364
Boujelbene M, Rehman S, Alqahtani S, Eldin SM (2023) Optimizing thermal characteristics and entropy degradation with the role of nanofluid flow configuration through an inclined channel. Alexand Eng J 69:85–10
Choi SUS, Eastman JA (2022) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States), 1995. https://www.osti.gov/biblio/196525. Accessed November 29, 2022)
Ellahi R (2013) The effects of MHD and temperature dependent viscosity on the flow of non-Newtonian nanofluid in a pipe: Analytical solutions. Appl Math Model 3:1451–1467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2012.04.004
Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Hussain F, Asadollahi A (2019a) Peristaltic blood flow of couple stress fluid suspended with nanoparticles under the influence of chemical reaction and activation energy. Symmetry 11:276. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11020276
Ellahi R, Hussain F, Ishtiaq F, Hussain A (2019b) Peristaltic transport of Jeffrey fluid in a rectangular duct through a porous medium under the effect of partial slip: an application to upgrade industrial sieves/filters. Pramana - J Phys 93:34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-019-1781-8
Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Hussain F, Abbas T (2019c) Thermally charged MHD bi-phase flow coatings with non-newtonian nanofluid and hafnium particles along slippery walls. Coatings 9:300. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050300
Esmaeilpour M, Ganji DD (2010) Solution of the Jeffery-Hamel flow problem by optimal homotopy asymptotic method. Comput Math Appl 59:3405–3411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2010.03.024
Ezzat MA (2001) Free convection effects on perfectly conducting fluid. Int J Eng Sci 39:799–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7225(00)00059-8
Ezzat MA (2008) State space approach to solids and fluids. Can J Phys 86:1241–1250. https://doi.org/10.1139/p08-069
Ezzat MA, Abd-Elaal MZ (1997) State space approach to viscoelastic fluid flow of hydromagnetic fluctuating boundary-layer through a porous medium. ZAMM J Appl Math Mech 77:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.19970770307
Ezzat M, Zakaria M, Shaker O, Barakat F (1996) State space formulation to viscoelastic fluid flow of magnetohydrodynamic free convection through a porous medium. Acta Mech 119:147–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01274245
Farhan M, Shahid MI, Jamil F, Usman M, Mujtaba MA, Saleem MW, El-Shafay AS (2022) Performance evaluation of compound parabolic solar collector using different nanofluids: an experimental study. Front Energy Res. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2022.951233
Habiyaremye F, Wainaina M, Kimathi M (2022) The effect of heat and mass transfer on unsteady MHD nanofluid flow through convergent-divergent channel. Int J Fluid Mech Thermal Sci 8(1):10–22
Hamel G (1917) Spiralförmige Bewegungen zäher Flüssigkeiten. Jahresber Deutsch Math-Verein 25:34–60
Hamrelaine S, Kezzar M, Sari MR, Eid MR (2022) Analytical investigation of hydromagnetic ferro-nanofluid flowing via rotating convergent/divergent channels. Eur Phys J plus 137:1291. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03480-2
Ishtiaq F, Ellahi R, Bhatti MM, Alamri SZ (2022) Insight in thermally radiative cilia-driven flow of electrically conducting non-newtonian jeffrey fluid under the influence of induced magnetic field. Mathematics 10:2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10122007
Jeffery GB (1915) The two-dimensional steady motion of a viscous fluid. Lond, Edinb, Dublin Philos Maga J Sci. 29:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440408635327
Kalpana G, Madhura KR, Kudenatti RB (2022) Numerical study on the combined effects of Brownian motion and thermophoresis on an unsteady magnetohydrodynamics nanofluid boundary layer flow. Math Comput Simul 200:78–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2022.04.010
Khan U, Ahmed N, Mohyud-Din ST (2016) Thermo-diffusion, diffusion-thermo and chemical reaction effects on MHD flow of viscous fluid in divergent and convergent channels. Chem Eng Sci 141:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2015.10.032
Khan U, Adnan Ahmed, N., Mohyud-Din, S. T., Baleanu, D., Khan, I., & Nisar, K. S. (2020) A novel hybrid model for Cu–Al2O3/H2O nanofluid flow and heat transfer in convergent/divergent channels. Energies 13(7):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071686
Meher R, Patel ND (2019) Analytical Investigation of MHD Jeffery-Hamel flow problem with heat transfer by differential transform method. SN Appl Sci 1:656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0632-z
Menbari A, Alemrajabi AA, Rezaei A (2016) Heat transfer analysis and the effect of CuO/Water nanofluid on direct absorption concentrating solar collector. Appl Therm Eng 104:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.05.064
Mohammadiun H, Amerian V, Mohammadiun M, Rahimi AB (2017) Similarity solution of axisymmetric stagnation-point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid on a stationary cylinder with constant wall temperature. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 41:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-016-0022-8
Moradi A, Alsaedi A, Hayat T (2013) Investigation of nanoparticles effect on the Jeffery-Hamel flow. Arab J Sci Eng 38:2845–2853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0472-2
Qadeer M, Khan U, Ahmad S, Ullah B, Mousa M, Khan I (2022) Irreversibility analysis for flow of nanofluids with aggregation in converging and diverging channel. Sci Rep 12:10214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-14529-8
Rana P, Shukla N, Gupta Y, Pop I (2019) Homotopy analysis method for predicting multiple solutions in the channel flow with stability analysis. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 66:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2018.06.012
Rehman S, Hashim, & Ali Shah, S. I. (2022) Numerical simulation for heat and mass transport of non-Newtonian Carreau rheological nanofluids through convergent/divergent channels. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 236(11):6025–6039
Rehman S, Eldin EMT, Bafakeeh OT (2022) & Guedri, K, Coupled energy and mass transport for non-Newtonian nanofluid flow through non-parallel vertical enclosure. Ain Shams Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2022.102023
Rehman S, Alqahtani S, Alshehery S (2023) Modeling a non-Newtonian nanofluid flow between intersecting planes with slip mechanism. Continuum Mech Thermodyn 35(1):61–80
Shampine LF, Thompson S (2001) Solving DDEs in Matlab. Appl Numer Math 37:441–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9274(00)00055-6
Sushila J, Singh YS (2014) Shishodia, A modified analytical technique for Jeffery-Hamel flow using sumudu transform. J Assoc Arab Univ Basic Appl Sci 16:11–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaubas.2013.10.001
Yekani Motlagh S, Deyhim S (2023) Numerical study of magnetic drug targeting inside the bifurcated channel as a simplified model of right common iliac artery using Fe3O4–blood magnetic nanofluid. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 47(1):51–65
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University, Abha, KSA, for funding this work through Research Group under number (RGP2/97/44)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hashim, Rehman, S., Afef, K. et al. Heat Transport Analysis for MHD Jeffery-Hamel Flow with Molybdenum Disulfide Nanoparticles: Dual Solution. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-023-00675-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-023-00675-5