Abstract
This study investigated the decomposition of π-AlMgFeSi into β-Al5FeSi phase needles during extended periods of solution heat treatment and its effects on the mechanical properties of Al–7Si–0.55Mg–0.1Fe alloys. An analysis of the results obtained from the Charpy impact test using unnotched samples shows that the highest initiation and propagation energies are obtained for the as-cast and heat-treated alloys when these alloys are solidified at a high cooling rate and modified with strontium. An increase in the solution treatment time improves the impact properties of the alloys compared to the as-cast condition. In accordance with this finding, the recommended solution treatment time at which the maximum initiation and propagation energy values can be obtained is 20 h for all alloys studied. The results also show that the impact properties are more sensitive to the changes occurring in the microstructure which result from solution heat treatment and Sr modification, namely, the eutectic Si and π-phase morphologies, rather than those related to the tensile properties, i.e., to the Mg content in the matrix. Fracture analysis was carried out using a scanning electron microscope equipped with an EDX system for element analysis. The results obtained show that the tensile and impact fracture behavior of the Al–7Si–0.55Mg–0.1Fe alloys is controlled mainly by the morphology of the eutectic silicon. The π-phase iron intermetallics act as crack initiation sites and provide an easy path for crack propagation in both non-modified and Sr-modified alloys. The fracture analysis of the 80-h solution-treated sample shows the presence of newly formed β-phase needles which provide an additional source for crack initiation, and thus all the 80-h solution-treated alloys show the lowest energy values.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.Z. Yi, Y.X. Gao, P.D. Lee, T.C. Lindley, Effect of Fe Content on Fatigue Crack Initiation and Propagation in a Cast Aluminum–Silicon Alloy (A356–T6). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 386, 396–407 (2004)
W.A. Bailey, Beryllium Effect on Strength and Mechanical Properties of 356 Variant–T 6 Aluminum Alloys. AFS Trans. 72, 443–454 (1964)
S. Musmar, F. Mucciardi, J. Gruzleski, A Novwel In-Situ Thermal Analysis Technique for Aluminum alloys 356, 319, Al-X Si, Al–Si–Cu X Mg, and 6063-Experimental Study. AFS Trans. 115, 1–15 (2007)
Q.G. Wang, Plastic Deformation Behavior of Aluminum Casting Alloys A356/357. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 35A, 2707–2718 (2004)
J. Barresi, M.J. Kerr, H. Wang, M.J. Couper, Effect of Magnesium, Iron and Cooling Rate on Mechanical Properties of Al–7Si–Mg Foundry Alloys. AFS Trans. 108, 563–570 (2000)
Q.G. Wang, Microstructural Effects on the Tensile and Fracture Behavior of Aluminum Casting Alloys A356/357. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34A, 2887 (2003)
O. Vorren, J.E. Evensen, T.B. Pedersen, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Si–Mg Casting Alloys. AFS Trans. 92, 459–466 (1984)
M.M. Tuttle, D.L. McLellan, Silicon Particle Characteristics in Al–Si–Mg Castings. AFS Trans. 90, 13–32 (1982)
M. Tsukuda, M. Harada, T. Suzuki, S. Koike, Interaction of Mg and Fe Content and Aging Temperature on mechanical Properties of Al–7%Si–Mg Alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 29(4), 131–138 (1979)
Y. Kaneko, H. Murakami, K. Kuroda, S. Nakazaki, Squeeze Casting of Aluminum. Die Cast. Eng. 23(3), 26 (1979)
G.E. Nagel, J.P. Mouret, A357 Type Alloy with Improved Properties. AFS Trans. 91, 157–160 (1983)
J.A. Taylor, D.H. St John, L. Zheng, G.A. Edwards, J. Barresi, M.J. Couper, Solution Treatment Effect of Al–Si–Mg Casting Alloy: Part 1: Intermetallic Phase. Alum. Tran. 4(5), 95–110 (2001)
M. Tsukuda, S. Koike, M. Harada, The Heat Treatment of Al–7%Si–0.3Mg Alloy. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 28(1), 8–14 (1978)
M.M. Haque, M.A. Maleque, Effect of Process Variable on Structure and Properties of Aluminum–Silicon Piston Alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 77, 122–128 (1998)
M. Hafiz, T. Kobayashi, Mechanical Properties of Modified and Non-modified Eutectic Al–Si Alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 44(1), 28–34 (1994)
M. Hafiz, T. Kobayashi, Metallurgical Factors Affecting Impact Toughness of Eutectic Al–Si Casting Alloy. Z. Met. 89(6), 445–449 (1998)
A. Thirugnanam, K. Sukumaran, K. Raghukandan, U.T.S. Pillai, B.C. Pai, Microstructural Aspects and Fracture Behavior of A356/357 Alloys-an-Overview. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 58(5), 777–787 (2005)
S. Murali, K.S. Raman, K.S.S. Murthy, Effect of Magnesium, Iron (Impurity) and Solidification Rates on the Fracture Toughness of Al–7Si–0.3Mg Casting Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 151, 1–10 (1992)
C.W. Meyers, J.S. Lyons, Fracture Toughness—Second Particle Interactions in A357 Alloys (Technology for Premium Quality Casting, Denver, 1988), pp. 151–178
S. Shivkumar, L. Wang, C. Keller, Impact Properties of A356–T6 Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 3, 83–90 (1994)
J.A. Taylor, D.H. St John, J. Barresi, M.J. Couper, Influence of Mg Content on The Microstructure and Solid Solution Chemistry of Al–7Si–Mg Casting Alloys During Solution Treatment. Mater. Sci. Forum 331–337, 277–282 (2000)
S. Hotta, K. Saruki, M. Nakamura, Effects of T6 Heat Treatment on the Impact Strength of AC4C and AC2B Aluminum Alloy Castings Solidified for a Long Time. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 37(7), 478–482 (1987)
S. Shivkumar, The Interactive Effect of Sr Modification and Heat Treatment on The Mechanical Properties of Cast Aluminum Alloys, in 17th ASM Heat Treating Society Conference Proceedings, vol. 15–18 (1998), pp. 265–269
N. Fat-Halla, Structural Modification of Al–Si Eutectic Alloy by Sr and its Effect on Tensile and Fracture Characteristics. J. Mater. Sci. 24, 2488–2492 (1989)
Q.G. Wang, C.H. Câceres, The Fracture Mode in Al–Si–Mg Casting Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A A 241, 72–82 (1998)
R.C. Voigt, D.R. Bye, Microstructural Aspects of Fracture in A356. AFS Trans. 99, 33–50 (1991)
B. Zhang, M. Garro, C. Tagliano, Dendrite Arm Spacing in Aluminum Alloy Cylinder Heads Produced by Gravity Semi-Permanent Mold. Metall. Sci. Technol. 21(1), 3–9 (2003)
C. Triveno Rios, C. Bolfarini, W.J. Botta, C.S. Kiminami, Rapidly Solidified Al–Si–Mg Alloy. J. Metastable Nanocryst. Mater. 20–21, 594–598 (2004)
M K. Surappa, E.W. Blank, J.C. Jaquet, Microstructural Approach to Deformation and Fracture of Cast Al–7Si–0.3Mg, in 3rd International Conference on Solidification Processing (Sheffield, UK, 1987), pp. 424–427
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Amal Samuel for enhancing the quality of the images used in the present article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
See Figure 14.
(a) Temperature–time curve and first derivative of the A356 base alloy showing: (1) precipitation of α-Al dendrite network, (2) Al–Si eutectic reaction, (3) transformation of β-Fe to π-Fe phase, (4) precipitation of Mg2Si, (5) end of solidification. (b) Temperature–time curve and its first derivative obtained from the A356 alloy modified with about 100 ppm Sr.
Appendix 2
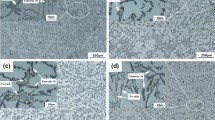
Morphology of the eutectic Si particles: effect of solutionizing time at 540 °C (see Figures 15, 16).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsharkawi, E.A., Abdelaziz, M.H., Doty, H.W. et al. Effect of β-Al5FeSi and π-Al8Mg3FeSi6 Phases on the Impact Toughness and Fractography of Al–Si–Mg-Based Alloys. Inter Metalcast 12, 148–163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0153-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-017-0153-8