Abstract
Cellular senescence (CS) is increasingly implicated in the etiology of age-related diseases. While CS can facilitate physiological processes such as tissue repair and wound healing, senescent cells also contribute to pathophysiological processes involving macromolecular damage and metabolic dysregulation that characterize multiple morbid and prevalent diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, osteoarthritis, atherosclerotic vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Preclinical studies targeting senescent cells and the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) with “senotherapeutics” have demonstrated improvement in age-related morbidity associated with these disease states. Despite promising results from these preclinical trials, few human clinical trials have been conducted. A first-in-human, open-label, pilot study of the senolytic combination of dasatinib and quercetin (DQ) in patients with IPF showed improved physical function and mobility. In this review, we will discuss our current understanding of cellular senescence, its role in age-associated diseases, with a specific focus on IPF, and potential for senotherapeutics in the treatment of fibrotic lung diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Cellular Senescence
Age-associated diseases (AADs) such as Alzheimer’s disease, osteoarthritis, diabetes mellitus, and atherosclerosis will continue to become increasingly prevalent in our aging population. One of the increasingly recognized drivers for AADs is cellular senescence (CS), defined as stress-induced, non-reversible cell cycle arrest, which depletes regenerative capability and is associated with release of pro-inflammatory mediators. Indeed, markers of CS are associated with mortality and increase with normal aging or prematurely in pathologic states [1]. The complex molecular biology of senescence has been thoroughly reviewed elsewhere [2]. Briefly, senescent cells (SC) are characterized by growth arrest, expression of anti-proliferative molecules (e.g., p16INK4a), and activation of damage sensing signaling pathways (e.g., p38MAPK and NF-kB). The growth arrest of formerly replicative cells often results from a persistent DNA damage response (DDR) or stress signaling and is effected by sustained activation of the p16INK4a-RB and/or p53 pathways [3]. While senescent cells have exited the cell cycle, they remain metabolically active and produce a heterogeneous array of signaling molecules including proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and proteases, termed the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) [4,5,6].
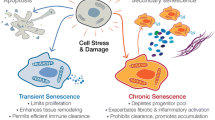
Conceptually, CS is a mechanism to counteract malignant transformation; over time, cells inevitably accumulate irreparable damage and, in response, may either undergo apoptosis or senescence to prevent the growth of damaged cells. These damaged but viable SC are required in processes including wound healing, embryogenesis, and tumor suppression by inducing immune clearance of potentially oncogenic cells [3, 7]. However, the generation and maintenance of senescent cells by activation of pro-survival pathways may outpace immune clearance, which creates self-expanding reservoirs of senescent cells and can ultimately lead to clinical disease.
The most commonly cited inducers of senescence are well established in cellular aging (e.g., DNA damage, proteotoxic stress, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction) [1, 8,9,10]. For example, telomeres are repetitive sequences of DNA that insulate the ends of chromosomes from damage. With repeated mitosis, telomeres are incompletely replicated, and thus shorten until reaching the theoretical Hayflick limit, where the loss of telomeric protective function results in p53- or p16-RB-mediated replicative senescence [11]. Shortened telomeres predispose cells to DNA damage. [12] Similarly, genotoxic agents (i.e., bleomycin) and ionizing radiation result in DNA damage. Regardless of the mechanism of activation, the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway is a major driver of cellular senescence [13]. Indeed, senescent cells have persistent evidence of DNA damage—segments with chromatin alterations reinforcing senescence (DNA-SCARs), which regulate cell cycle arrest and SASP [14].
Just as CS participates in multiple biological processes, intracellular signaling with reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a fundamental cellular function [15]. However, when ROS generation becomes excessive, oxidative stress (OS) results in a wide array of cellular damage. [16] Chronic OS plays a central role in the pathogenesis of CS through p53/p21CIP1/WAF1 activation [17]. Mitochondrial dysfunction is an important generator of ROS and has been implicated in CS generation [18]. Moreover, a positive feedback loop involving mitochondrial dysfunction and OS can accelerate intracellular metabolic derangements, such as ATP depletion and calcium dysregulation [19].
The primary upstream cell cycle regulators that cause are p21WAF1/Cip1 and p16INK4A, which act through activation of the retinoblastoma (Rb) protein family to inhibit transactivation of E2F, resulting in cell cycle arrest. CS is also characterized by activation of canonical pro-survival pathways—EFNB1/3, PI3Kδ, BCL-x, and HSP-90 [20]. SASP protein production is largely regulated by mTOR activation [21]. In models of IPF, the SASP is pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic and includes cytokines such as TGF-β, IL-6, and MMP-12. [22, 23] While none of these is specific for CS, they all have a central role in pathogenesis.
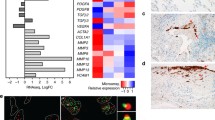
SASPs vary widely among cell types but prominently feature pro-inflammatory cytokines that initiate immune clearance. However, over time, the imbalance of pro-survival pathways outpaces immune clearance, resulting in self-expanding reservoirs of senescent cells, which can ultimately lead to clinical disease Thus, chronic inflammation and CS are closely related processes [5]. IL-6 and IL-8 are robustly associated with SASPs and established inducers of the innate immune system, which plays a critical role in both malignant and senescent cell clearances [24] (Figure 1).
Senescence in Disease
As per the foregoing, CS plays physiological roles and is needed for tissue homeostasis; however, CS also represents a stress response triggered by insults associated with aging including genomic instability, telomere attrition, and other mechanisms [6]. The seminal study by Baker et al. first demonstrated a pathogenic role of CS by utilizing a transgenic mouse model to eliminate senescent cells by ablating p16INK4A [25]. An expanding body of preclinical and ex vivo studies has demonstrated a clear pathogenic role of CS in perpetuating organ dysfunction.
As previously mentioned, CS contributes to AADs and phenotypes including development of gray hair, loss of muscle mass, increases in adiposity, reduced neurogenesis, and increased tissue fibrosis [3]. The evidence linking senescence to these diverse pathologies includes accumulation of senescence markers in tissues with advancing age supporting an increased SC burden with advancing age. Indeed, the aging cellular phenotype prominently features altered extra-cellular matrix deposition, faltering stem cells, and senescent endothelial cells [26,27,28]. The far-reaching effects of a relatively small senescent reservoir are analogous to paraneoplastic syndromes. Moreover, if the development of SC occurs in particularly important fraction of cells in a given tissue, then the loss of function of those tissue cells could have an outsized effect on tissue integrity and function.
In contrast to disease in youth, AADs occur due to dysfunction of tissues changed by aging processes, which is expedited by CS. Increased senescence burden diminishes tissue resilience through cell cycle arrest as well as through SASP-induced stem cell and parenchymal cell dysfunction. As SC burden progressively increases, an additional wave of SC is generated, increasing SC burden further and further amplify AAD development and progression. This type of positive feedback process explains why disease vulnerability and incidence increase with age. For example, increased SC burden in adipose tissue drives diabetes mellitus, and aging endothelial cells drive atherosclerosis [3].
Although the most common histologic markers of SC burden are SA-β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) and lipofuscin accumulation, assessing the SC burden in vivo is challenging because there are currently no robust clinical markers for CS [3]. A clinically useful marker of SC is clearly needed to guide future trials of senotherapeutics. Epigenetic investigations are promising [29]. Further characterization of gene expression via integration of genomic data and epigenetic markers of lung biopsies may provide a translatable assessment of CS burden [2]. In preclinical bleomycin models, growth and differentiation factor 15 (GDF15; TGF-β family member) is the most upregulated secreted protein [12]. Moreover, GDF15 levels are elevated in ILD patients prior to radiographic changes and are inversely associated with DLCO, FVC, and survival [30, 31]. Together, the foregoing suggests GDF15 or other aging biomarkers may allow for risk stratification of progressive ILDs [32, 33].
Senomorphics and Senolytics
After extensive laboratory investigations, significant progress in preclinical studies is strongly supportive of potential clinical benefits for therapeutic treatment of SC (senotherapeutics). The diversity of SASPs has necessitated the use of bioinformatic experiments to characterize the underlying molecular networks and discern possible drug targets. There are established pro-survival regulators that are central in the cellular networks of senescent preadipocytes (the most abundant SC type), including ephrins, PI3K, BCL-2, and HSP-90 [20]. These have formed the basis for numerous senotherapeutics (Table 1).
Two approaches to senotherapy have been proposed: senescent-selective apoptosis (senolytic) and SASP suppression (senomorphic). Senolytic drugs inhibit anti-apoptotic pathways and thus restore selective clearance of SC [20, 63]. Senolytics alleviate multiple chronic disease and physical dysfunction in mouse models of a wide arrange of diseases but are difficult to develop due to off-target effects on physiologic survival pathways [3]. Thus, numerous in vitro studies have been required to screen for possible off-target effects. From a clinical perspective, a benefit for senolytics is the efficacy of intermittent treatment, which reduces senescent reservoirs and mitigates adverse effects that occur with continued treatment. Senomorphic medications, such as the mTOR antagonist rapamycin, abrogate the SASP and reduce the proliferation of senescent reservoirs. Such agents are likely to be used as continuous therapy to allow for physiologic CS but attenuate pathogenic CS. Senomorphic agents are undergoing clinical trials as age-modulating agents and for some AADs including Alzheimer’s disease [64]. Combination therapy consisting of senolytic induction treatment with subsequent senomorphic maintenance treatment has been proposed by our group.
The first two and best-characterized senolytics are dasatinib and quercetin (DQ). They have proven in vitro synergism and preclinical health span improvement [34, 35, 65]. Quercetin is a plant-based polyphenol flavonoid that has anti-oxidant properties and has been shown to induce autophagy through proteasome activation in vitro. In fibroblasts from mouse models, quercetin restored Fas-L- and TNF-mediated apoptosis [66]. Dasatinib is an orally available tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), originally developed to target SRC and ABL kinases [67], and is a second-line treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) [68].
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathophysiology
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a classic AAD and devastating interstitial lung disease (ILD) characterized by restricted ventilation and compromised gas exchange leading to progressive dyspnea, impaired quality of life, and ultimately death [69,70,71]. The pathophysiology of IPF is largely extrapolated from preclinical models of pulmonary fibrosis and ex vivo cell culture of lung epithelial cells. There are several hypothesized mechanisms for IPF, including chronic micro-aspiration, viral infection, and environmental exposures [72]. The most common mouse model for IPF employs intra-tracheal bleomycin to induce fibrosis and has elucidated numerous molecular mechanisms [73, 74]. There is mounting evidence that cellular senescence significantly contributes to chronic matrix remodeling and fibrosis and may be central to IPF pathophysiology [13, 22, 75, 76].
Inflammation has long been postulated to be the inciting factor in IPF patients [77]. Multiple studies have implicated inflammatory derangements. There is evidence of early alveolar macrophage activation and increased production of IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, and TNF-α [78, 79]. This inflammatory milieu transitions to a chronic fibrotic phase that is mediated by a SASP primarily of TGF-β, PDGF, and GM-CSF [22]. Despite these preliminary findings, anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids have not been effective in modifying disease progression but, in fact, harmful [80]. This is likely because chronic inflammation has multiple positive feedback loops that reinforce immune activation and induce senescence, which are accelerated based on patient risk factors.
There has been extensive investigation into the genetic risk factors. Familial interstitial pneumonia (FIP) is an inherited form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), and studies of patients with FIP have provided some insight regarding the role of genetic risk factors of pulmonary fibrosis. Surfactant-related proteins were identified by genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and account for ~30% of spontaneous IPF cases [81,82,83]. Other GWAS of IPF identified mutations of telomerase-associated genes in up to 25% of non-familial IPF cases [13]. Short telomeres are histologically associated with CS markers in IPF patients [29]. An important observation in IPF is shortening of telomeres in about 10% of IPF patients, which has implications for clinical outcomes [84,85,86]. However, defects in telomerase pathways are not specific for IPF and have also been associated with other ILDs and emphysema [87]. An association of Toll interacting protein (TOLLIP) variants with IPF susceptibility has also been described and associated with mortality [88]. TOLLIP negatively regulates Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) activity, which is a key step in immune activation. Taken together, these findings support a role for inflammatory activation during the pathogenesis of IPF but have not translated to effective risk stratification of IPF patients without a family history [89]. Genetic risk stratification has not been widely adopted, but the implicated genes are compatible with cellular senescence.
IPF Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Senescent Cell Burden
IPF presents with nonspecific symptoms of dyspnea and nonproductive cough. A thorough history and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the chest are critical for confirming the diagnosis of IPF. The radiologic hallmark of IPF is a usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern, which includes subpleural and basilar predominant reticular opacities, honeycombing, and traction bronchiectasis [90]. Histopathologic UIP pattern obtained by surgical lung biopsies includes patchy, paraseptal destructive fibrosis and fibroblastic foci without granulomas or inflammatory infiltrates [90]. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cellular analysis is usually not helpful in confirming IPF diagnosis but may be supportive of an alternative diagnosis (e.g., significant BAL lymphocytosis may suggest hypersensitivity pneumonitis) [91, 92]. Transbronchial lung biopsies (TBLB) are usually non-diagnostic due to inadequate tissue sample size. However, next-generation RNA sequencing of TBLB specimens has potential to be a less invasive approach to confirm the presence of UIP histopathology. In two recent trials, genomic classification (GC) of lung biopsies improved the ability to differentiate IPF from other ILDs [93, 94]. Thus, GC may be useful to identify patients with significant senescence burden and benefit from senotherapeutics [95]. Transbronchial cryobiopsy (TBCB) is a promising diagnostic procedure that is less invasive than a surgical lung biopsy, but is only available at a few expert ILD centers and is not yet established as standard of care. Twenty genetic variants have been associated with IPF by genome-wide association studies [30]. While genotyping is not a routine diagnostic approach, the implicated genes may provide avenues for further investigation (e.g., DEPTOR, which inhibits mTOR signaling) and develop into a risk assessment tool for possible IPF patients.
The key parameters for assessing IPF severity and prognosis are age, gender, forced vital capacity (FVC), and diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO), which have been incorporated into a scoring system to predict short-term mortality [96]. A six-minute walk test (6MWT) is an objective measurement of exercise tolerance and symptom severity. Regular monitoring of pulmonary function is important to identify disease progression and acute exacerbations (AE-IPF), which are associated with acute to subacute clinical deterioration and new bilateral GGO superimposed on UIP background on HRCT. AE-IPF becomes more common with advanced disease and associated with poor prognosis. Unless a reversible trigger is present, there does not exist a proven safe and effective treatment. The unrelentingly predictable course of IPF reinforces the importance of early palliative care discussions.
Evaluating SC burden may mitigate the difficulties with diagnosis and uncertainties in prognosis. In a small study of IPF patient lung biopsies, SA-β-gal, a specific SC marker, was increased compared to patients with COPD or hypersensitivity pneumonitis [29, 97]. We hypothesized that in patients with different fibrotic lung diseases, a lung biopsy and staining for SA-β-gal may help identify subtypes that may be more responsive to senolytic treatments. Specificity may be increased with other preclinical markers such as p16 and p21, but these have not yet been investigated in IPF patients. Uncertainties that require further research include the most appropriate SC biomarker, precise measurement of SC burden, ideal SC assay compartment (e.g., BAL, lung biopsy, blood, urine, skin, etc.), and ultimately impact of clinically important patient outcomes.
Current Therapy of IPF
The majority of IPF therapy is supportive and includes supplemental oxygen if needed, pulmonary rehabilitation, and smoking cessation. Early referral for transplant evaluation is critical, as bilateral lung transplant is the only known curative treatment for IPF.
Numerous clinical trials have shown no benefit or harm in IPF. Currently, pirfenidone and nintedanib are the only FDA-approved medications for treatment of IPF. Both treatments slow the progression of fibrosis in some patients with IPF but do not halt or reverse progressive fibrosis. Early identification of IPF is important for initiation of anti-fibrotic treatment as patients with advanced IPF (FVC <50% or DLCO<35%) may demonstrate less benefit than those with mild or moderate disease [98].
Pirfenidone negatively regulates lung fibroblasts through inhibition of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and reduces extracellular matrix production. A meta-analysis of multiple randomized controlled trials evaluating pirfenidone demonstrated a benefit in progression-free survival, 6MWT, and subjective symptoms [99]. Nintedanib inhibits activation of fibrogenic growth factors through blocking receptor-associated tyrosine kinases (PDGF, FGF, and VEGF) [100]. In the INPULSIS-1 and INPULSIS-2 trials, nintedanib reduced the decline in FVC and increased time to first exacerbation [101]. In a meta-analysis, nintedanib also reduced the risk of AE-IPF [102]. Nintedanib has also shown benefits with advanced disease after the initial trials only included mild-to-moderate disease [98, 103, 104]. Dose-dependent diarrhea is a common adverse effect and can result in discontinuation of treatment.
Senotherapeutics for IPF
Senomorphics have not been studied in human clinical trials yet. However, senolytics have been successfully used in a single open-label pilot study followed by a yet unpublished small randomized controlled trial as detailed below. DQ showed significant improvement in senescent burden, physical function, and pulmonary function in bleomycin-induced fibrosis mouse models [22], as well as ex vivo senolysis of alveolar epithelial cells and lung fibroblasts [105].
Based on these preclinical data on the emerging pathogenic role of CS in IPF, we undertook a first-in-human, two-stage, prospective, clinical trial of intermittent administration of DQ (D, 100 mg/day; Q, 1250 mg/day, 3 days/week over 3 weeks) in older adults with stable IPF [106]. First, an open-label study (OL) was performed at two clinical sites followed by a single-site double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial (RCT; ongoing). The primary endpoints demonstrated excellent therapeutic feasibility (e.g., participant retention, planned assessment completion rate, DQ adherence). Secondary endpoints were safety, functional health status, and changes in SASP. Although DQ was associated with greater mild-to-moderate adverse events, it was generally well tolerated. Interestingly, IPF patients treated with intermittent DQ showed significantly improved physical function and mobility by 6MWT, 4-minute gait speed, timed chair stands, and short physical performance battery (SPPB). Functional and reported health measures were unchanged. Although DQ effects on circulating SASP factors were inconclusive, improved physical function correlated with reduced SASP-related factors (23/48 markers, r ≥ 0.50). Analysis of our small completed RCT of DQ in IPF is pending.
Although not done in IPF, Martyanov et al. tested dasatinib alone (100mg daily for 6 months) in 31 patients with scleroderma-associated ILD [107]. In scleroderma patients, dasatinib treatment (without quercetin) manifested no significant clinical efficacy. While scleroderma ILD has similarities with IPF, it also has many divergent features reflecting differences in mechanistic pathways, immune dysregulation, and fibroblast responses. As such, further prospective clinical trials of the safety and efficacy of senotherapeutics (such as senolytics DQ) are greatly needed in fibrotic lung diseases, such as scleroderma-associated ILD and IPF.
Future Directions
Senotherapeutics, particularly DQ, are potentially important therapeutic interventions for IPF and perhaps other fibrotic ILDs that feature an initial inflammatory, followed by fibroproliferative, phase such as viral pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Could senotherapeutics be used for pulmonary fibrosis in patients with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC)? Elderly patients who require ICU care and mechanical ventilation appear to be at the highest risk of developing PASC ILD, including pulmonary fibrosis [108]. Considering the vast prevalence of COVID-19 worldwide, even a small proportion of PASC lung fibrosis would have a tremendous deleterious impact on our health-care system. While the prevalence of PASC pulmonary fibrosis will become apparent with time, early data from such patients suggest that 25–65% of recovered patients develop fibrotic lung abnormalities at 3 months on HRCT [108, 109]. Currently, no proven options are available for their treatment though anti-fibrotic agents are in clinical trials, albeit none with DQ.
As another example, there are other pulmonary diseases that feature interstitial fibrosis following an initial inflammatory phase. Fibrotic/chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is initiated by an antigen that results in a robust TH1 predominant response, which may be visualized by GGOs on HRCT or non-necrotizing granulomas on lung biopsy. There are many clinical and pathogenetic parallels between fibroproliferative HP and IPF, including an association with advanced age, shortened telomeres, and lack of significant improvement with anti-inflammatory treatments [110,111,112,113]. Interestingly, telomere shortening has been identified and is prognostically significant in many ILDs. However, given the disparate results with scleroderma-associated ILD, use of senolytics in fibrotic HP should undergo a proof of concept trial first [114, 115]. Indeed, there are many unanswered questions in the general fields of senescence and senotherapeutics in fibrotic pulmonary diseases.
Abbreviations
- AE-IPF:
-
Acute exacerbation of IPF
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- DLCO:
-
Diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide
- FVC:
-
Forced vital capacity
- HRCT:
-
High-resolution computed tomography
- ILD:
-
Interstitial lung disease
- IPF:
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- UIP:
-
Usual interstitial pneumonia
- NSIP:
-
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia
- TBCB:
-
Transbronchial cryobiopsy
- TBLB:
-
Transbronchial lung biopsy
- SPPB:
-
Short physical performance battery
- 6MWT:
-
Six-minute walk test
References
Childs BG, Durik M, Baker DJ, et al. Cellular senescence in aging and age-related disease: from mechanisms to therapy. Nat Med. 2015;21:1424–35.
Gorgoulis V, Adams PD, Alimonti A, et al. Cellular senescence: defining a path forward. Cell. 2019;179:813–27.
He S, Sharpless NE. Senescence in health and disease. Cell. 2017;169:1000–11.
Salama R, Sadaie M, Hoare M, et al. Cellular senescence and its effector programs. Genes Dev. 2014;28:99–114.
Freund A, Orjalo AV, Desprez PY, et al. Inflammatory networks during cellular senescence: causes and consequences. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16:238–46.
McHugh D, Gil J. Senescence and aging: causes, consequences, and therapeutic avenues. J Cell Biol. 2018;217:65–77.
Lopez-Otin C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, et al. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013;153:1194–217.
Hamon MP, Ahmed EK, Baraibar MA, et al. Proteome oxidative modifications and impairment of specific metabolic pathways during cellular senescence and aging. Proteomics. 2019;20:e1800421.
d'Adda di Fagagna F. Living on a break: cellular senescence as a DNA-damage response. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:512–22.
Munoz-Espin D, Serrano M. Cellular senescence: from physiology to pathology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:482–96.
Karlseder J, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T. Senescence induced by altered telomere state, not telomere loss. Science. 2002;295:2446–9.
Zhang Y, Jiang M, Nouraie M, et al. GDF15 is an epithelial-derived biomarker of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys. 2019;317:L510–L21.
Armanios MY, Chen JJ, Cogan JD, et al. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1317–26.
Rodier F, Munoz DP, Teachenor R, et al. DNA-SCARS: distinct nuclear structures that sustain damage-induced senescence growth arrest and inflammatory cytokine secretion. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:68–81.
Sies H. Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015;4:180–3.
Rahman I, Skwarska E, Henry M, et al. Systemic and pulmonary oxidative stress in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999;27:60–8.
Luo Y, Zou P, Zou J, et al. Autophagy regulates ROS-induced cellular senescence via p21 in a p38 MAPKalpha dependent manner. Exp Gerontol. 2011;46:860–7.
Barja G. The mitochondrial free radical theory of aging. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2014;127:1–27.
Ziegler DV, Wiley CD, Velarde MC. Mitochondrial effectors of cellular senescence: beyond the free radical theory of aging. Aging Cell. 2015;14:1–7.
Zhu Y, Tchkonia T, Pirtskhalava T, et al. The Achilles' heel of senescent cells: from transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell. 2015;14:644–58.
Herranz N, Gallage S, Mellone M, et al. mTOR regulates MAPKAPK2 translation to control the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17:1205–17.
Schafer MJ, White TA, Iijima K, et al. Cellular senescence mediates fibrotic pulmonary disease. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14532.
Coppe JP, Patil CK, Rodier F, et al. Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008;6:2853–68.
Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence relayed by an interleukin-dependent inflammatory network. Cell. 2008;133:1019–31.
Baker DJ, Wijshake T, Tchkonia T, et al. Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature. 2011;479:232–6.
Janssens JP, Pache JC, Nicod LP. Physiological changes in respiratory function associated with ageing. Eur Respir J. 1999;13:197–205.
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Hong K, et al. Circulating fibrocytes traffic to the lungs in response to CXCL12 and mediate fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:438–46.
Katsuumi G, Shimizu I, Yoshida Y, et al. Vascular senescence in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:18.
Disayabutr S, Kim EK, Cha SI, et al. miR-34 miRNAs regulate cellular senescence in type II alveolar epithelial cells of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0158367.
Allen RJ, Guillen-Guio B, Oldham JM, et al. Genome-wide association study of susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201:564–74.
Tanaka T, Biancotto A, Moaddel R, et al. Plasma proteomic signature of age in healthy humans. Aging Cell. 2018;17:e12799.
Oldham JM. Interstitial lung abnormalities and aging biomarkers: a mediation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;203:1058–60.
Bowman WS, Echt GA, Oldham JM. Biomarkers in progressive Fibrosing interstitial lung disease: optimizing diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:680997.
Farr JN, Xu M, Weivoda MM, et al. Targeting cellular senescence prevents age-related bone loss in mice. Nat Med. 2017;23:1072–9.
Xu M, Pirtskhalava T, Farr JN, et al. Senolytics improve physical function and increase lifespan in old age. Nat Med. 2018;24:1246–56.
Roos CM, Zhang B, Palmer AK, et al. Chronic senolytic treatment alleviates established vasomotor dysfunction in aged or atherosclerotic mice. Aging Cell. 2016;15:973–7.
Ogrodnik M, Zhu Y, Langhi LGP, et al. Obesity-induced cellular senescence drives anxiety and impairs neurogenesis. Cell Metab. 2019;29:1233.
Ogrodnik M, Miwa S, Tchkonia T, et al. Cellular senescence drives age-dependent hepatic steatosis. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15691.
Zhu Y, Doornebal EJ, Pirtskhalava T, et al. New agents that target senescent cells: the flavone, fisetin, and the BCL-XL inhibitors, A1331852 and A1155463. Aging (Albany NY). 2017;9:955–63.
Yousefzadeh MJ, Zhu Y, McGowan SJ, et al. Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan. EBioMedicine. 2018;36:18–28.
Althunibat OY, Al Hroob AM, Abukhalil MH, et al. Fisetin ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Life Sci. 2019;221:83–92.
Nabavi SF, Braidy N, Habtemariam S, et al. Neuroprotective effects of fisetin in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: from chemistry to medicine. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16:1910–5.
Kwak S, Ku SK, Bae JS. Fisetin inhibits high-glucose-induced vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Inflamm Res. 2014;63:779–87.
Huang W, Li ML, Xia MY, et al. Fisetin-treatment alleviates airway inflammation through inhibition of MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42:208–18.
Harrison DE, Strong R, Sharp ZD, et al. Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature. 2009;460:392–5.
Dhanabalan KM, Gupta VK, Agarwal R. Rapamycin-PLGA microparticles prevent senescence, sustain cartilage matrix production under stress and exhibit prolonged retention in mouse joints. Biomater Sci. 2020;8:4308–21.
Jeon OH, Kim C, Laberge RM, et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23:775–81.
Zhu Y, Tchkonia T, Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, et al. Identification of a novel senolytic agent, navitoclax, targeting the Bcl-2 family of anti-apoptotic factors. Aging Cell. 2016;15:428–35.
Chang J, Wang Y, Shao L, et al. Clearance of senescent cells by ABT263 rejuvenates aged hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Nat Med. 2016;22:78–83.
Pan J, Li D, Xu Y, et al. Inhibition of Bcl-2/xl with ABT-263 selectively kills senescent type II pneumocytes and reverses persistent pulmonary fibrosis induced by ionizing radiation in mice. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;99:353–61.
Sharma AK, Roberts RL, Benson RD Jr, et al. The senolytic drug navitoclax (ABT-263) causes trabecular bone loss and impaired osteoprogenitor function in aged mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:354.
Saleh T, Carpenter VJ, Tyutyunyk-Massey L, et al. Clearance of therapy-induced senescent tumor cells by the senolytic ABT-263 via interference with BCL-XL -BAX interaction. Mol Oncol. 2020.
Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, Ling YY, Zhao J, et al. Identification of HSP90 inhibitors as a novel class of senolytics. Nat Commun. 2017;8:422.
Ramanathan RK, Trump DL, Eiseman JL, et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study of 17-(allylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17AAG, NSC 330507), a novel inhibitor of heat shock protein 90, in patients with refractory advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3385–91.
Pacey S, Gore M, Chao D, et al. A phase II trial of 17-allylamino, 17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG, tanespimycin) in patients with metastatic melanoma. Investig New Drugs. 2012;30:341–9.
Modi S, Stopeck A, Linden H, et al. HSP90 inhibition is effective in breast cancer: a phase II trial of tanespimycin (17-AAG) plus trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer progressing on trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5132–9.
Goldman JW, Raju RN, Gordon GA, et al. A first in human, safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity phase I study of once weekly administration of the Hsp90 inhibitor ganetespib (STA-9090) in patients with solid malignancies. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:152.
Pillai RN, Fennell DA, Kovcin V, et al. Randomized phase III study of ganetespib, a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, with docetaxel versus docetaxel in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (GALAXY-2). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:613–22.
Ramalingam S, Goss G, Rosell R, et al. A randomized phase II study of ganetespib, a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, in combination with docetaxel in second-line therapy of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (GALAXY-1). Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1741–8.
Shapiro GI, Kwak E, Dezube BJ, et al. First-in-human phase I dose escalation study of a second-generation non-ansamycin HSP90 inhibitor, AT13387, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:87–97.
Seggewiss-Bernhardt R, Bargou RC, Goh YT, et al. Phase 1/1B trial of the heat shock protein 90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 as monotherapy or in combination with bortezomib in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Cancer. 2015;121:2185–92.
Saif MW, Takimoto C, Mita M, et al. A phase 1, dose-escalation, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of BIIB021 administered orally in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:445–55.
Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T. Classification of usual interstitial pneumonia in patients with interstitial lung disease: assessment of a machine learning approach using high-dimensional transcriptional data. Clinical strategies and animal models for developing senolytic agents. Exp Gerontol. 2015;68:19–25.
Hampel H, Lista S, Neri C, et al. Time for the systems-level integration of aging: resilience enhancing strategies to prevent Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2019;181:101662.
Zhang P, Kishimoto Y, Grammatikakis I, et al. Senolytic therapy alleviates Abeta-associated oligodendrocyte progenitor cell senescence and cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer's disease model. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:719–28.
Hohmann MS, Habiel DM, Coelho AL, et al. Quercetin enhances ligand-induced apoptosis in senescent idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts and reduces lung fibrosis in vivo. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019;60:28–40.
Kantarjian H, Jabbour E, Grimley J, et al. Dasatinib. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:717–8.
Talpaz M, Shah NP, Kantarjian H, et al. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2531–41.
King TE Jr, Pardo A, Selman M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2011;378:1949–61.
Ley B, Collard HR. Epidemiology of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Epidemiol. 2013;5:483–92.
Raghu G, Chen SY, Yeh WS, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older: incidence, prevalence, and survival, 2001-11. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2:566–72.
Naik PK, Moore BB. Viral infection and aging as cofactors for the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2010;4:759–71.
Liu T, De Los Santos FG, Phan SH. The bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis. Methods Mol Biol. 1627;2017:27–42.
Peng R, Sridhar S, Tyagi G, et al. Bleomycin induces molecular changes directly relevant to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a model for "active" disease. PLoS One. 2013;8:e59348.
Faner R, Rojas M, Macnee W, et al. Abnormal lung aging in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:306–13.
Hashimoto M, Asai A, Kawagishi H, et al. Elimination of p19(ARF)-expressing cells enhances pulmonary function in mice. JCI Insight. 2016;1:e87732.
Heukels P, Moor CC, von der Thusen JH, et al. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir Med. 2019;147:79–91.
Gauldie J, Jordana M, Cox G. Cytokines and pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 1993;48:931–5.
Brieland JK, Jones ML, Clarke SJ, et al. Effect of acute inflammatory lung injury on the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in rat pulmonary alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992;7:134–9.
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research N, Raghu G, Anstrom KJ, et al. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1968–77.
Lawson WE, Grant SW, Ambrosini V, et al. Genetic mutations in surfactant protein C are a rare cause of sporadic cases of IPF. Thorax. 2004;59:977–80.
Stock CJ, Sato H, Fonseca C, et al. Mucin 5B promoter polymorphism is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis but not with development of lung fibrosis in systemic sclerosis or sarcoidosis. Thorax. 2013;68:436–41.
Schwartz DA. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a genetic disease involving mucus and the peripheral airways. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018;15:S192–S7.
Cronkhite JT, Xing C, Raghu G, et al. Telomere shortening in familial and sporadic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:729–37.
Newton CA, Oldham JM, Ley B, et al. Telomere length and genetic variant associations with interstitial lung disease progression and survival. Eur Respir J. 2019;53.
Courtwright AM, El-Chemaly S. Telomeres in interstitial lung disease: the short and the long of it. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16:175–81.
Alder JK, Guo N, Kembou F, et al. Telomere length is a determinant of emphysema susceptibility. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184:904–12.
Noth I, Zhang Y, Ma SF, et al. Genetic variants associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility and mortality: a genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir Med. 2013;1:309–17.
Kropski JA, Young LR, Cogan JD, et al. Genetic evaluation and testing of patients and families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:1423–8.
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:e44–68.
Snider GL. Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 1986;89:115S–21S.
Reynolds HY, Fulmer JD, Kazmierowski JA, et al. Analysis of cellular and protein content of broncho-alveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1977;59:165–75.
Raghu G, Flaherty KR, Lederer DJ, et al. Use of a molecular classifier to identify usual interstitial pneumonia in conventional transbronchial lung biopsy samples: a prospective validation study. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7:487–96.
Richeldi L, Scholand MB, Lynch DA, et al. Utility of a molecular classifier as a complement to high-resolution computed tomography to identify usual interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;203:211–20.
Kim SY, Diggans J, Pankratz D, et al. Classification of usual interstitial pneumonia in patients with interstitial lung disease: assessment of a machine learning approach using high-dimensional transcriptional data. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3:473–82.
Ley B, Ryerson CJ, Vittinghoff E, et al. A multidimensional index and staging system for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156:684–91.
Minagawa S, Araya J, Numata T, et al. Accelerated epithelial cell senescence in IPF and the inhibitory role of SIRT6 in TGF-beta-induced senescence of human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys. 2011;300:L391–401.
Harari S, Caminati A, Poletti V, et al. A real-life multicenter national study on nintedanib in severe idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respiration. 2018;95:433–40.
Noble PW, Albera C, Bradford WZ, et al. Pirfenidone for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: analysis of pooled data from three multinational phase 3 trials. Eur Respir J. 2016;47:243–53.
Wollin L, Wex E, Pautsch A, et al. Mode of action of nintedanib in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2015;45:1434–45.
Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2071–82.
Richeldi L, Cottin V, du Bois RM, et al. Nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Combined evidence from the TOMORROW and INPULSIS((R)) trials. Respir Med. 2016;113:74–9.
Richeldi L, Kolb M, Jouneau S, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in patients with advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm Med. 2020;20:3.
Yoon HY, Park S, Kim DS, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 2018;19:203.
Lehmann M, Korfei M, Mutze K, et al. Senolytic drugs target alveolar epithelial cell function and attenuate experimental lung fibrosis ex vivo. Eur Respir J. 2017;50:1602367.
Justice JN, Nambiar AM, Tchkonia T, et al. Senolytics in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: results from a first-in-human, open-label, pilot study. EBioMedicine. 2019;40:554–63.
Martyanov V, Kim GJ, Hayes W, et al. Novel lung imaging biomarkers and skin gene expression subsetting in dasatinib treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0187580.
Zhao YM, Shang YM, Song WB, et al. Follow-up study of the pulmonary function and related physiological characteristics of COVID-19 survivors three months after recovery. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;25:100463.
Tale S, Ghosh S, Meitei SP, et al. Post-COVID-19 pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis. QJM. 2020;113:837–8.
Selman M, Lopez-Otin C, Pardo A. Age-driven developmental drift in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2016;48:538–52.
Newton CA, Batra K, Torrealba J, et al. Telomere-related lung fibrosis is diagnostically heterogeneous but uniformly progressive. Eur Respir J. 2016;48:1710–20.
Bouros D, Tzouvelekis A. Telomeropathy in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200:1086–7.
Salisbury ML, Myers JL, Belloli EA, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonia. Where We Stand and Where We Need to Go. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196:690–9.
Snetselaar R, van Moorsel CHM, Kazemier KM, et al. Telomere length in interstitial lung diseases. Chest. 2015;148:1011–8.
George G, Rosas IO, Cui Y, et al. Short telomeres, telomeropathy, and subclinical extrapulmonary organ damage in patients with interstitial lung disease. Chest. 2015;147:1549–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Molecular Biology of Cell Death and Aging
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kellogg, D.L., Kellogg, D.L., Musi, N. et al. Cellular Senescence in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Curr Mol Bio Rep 7, 31–40 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40610-021-00145-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40610-021-00145-4