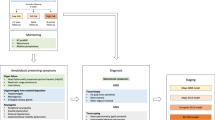
Abstract
Systemic light chain (AL) amyloidosis is caused by an usually small B cell clone that produces a toxic light chain forming amyloid deposits in tissue. The heart and kidney are the major organs affected, but all others, with the exception of the CNS, can be involved. The disease is rapidly progressive, and it is still diagnosed late. Screening programs in patients followed by hematologists for plasma cell dyscrasias should be considered. The diagnosis requires demonstration in a tissue biopsy of amyloid deposits formed by immunoglobulin light chains. The workup of patients with AL amyloidosis requires adequate technology and expertise, and patients should be referred to specialized centers whenever possible. Stagings are based on cardiac and renal biomarkers and guides the choice of treatment. The combination of daratumumab, cyclophosphamide, bortezomib and dexamethasone (dara-CyBorD) is the current standard of care. Autologous stem cell transplant is performed in eligible patients, especially those who do not attain a satisfactory response to dara-CyBorD. Passive immunotherapy targeting the amyloid deposits combined with chemo-/immune-therapy targeting the amyloid clone is currently being tested in controlled clinical trials. Response to therapy is assessed based on validated criteria. Profound hematologic response is the early goal of treatment and should be accompanied over time by deepening organ response. Many relapsed/refractory patients are also treated with daratumumab combination, but novel regimens will be needed to rescue daratumumab-exposed subjects. Immunomodulatory drugs are the current cornerstone of rescue therapy, while immunotherapy targeting B-cell maturation antigen and inhibitors of Bcl-2 are promising alternatives.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merlini G, Dispenzieri A, Sanchorawala V, Schönland SO, Palladini G, Hawkins PN, et al. Systemic immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4(1):38.
Rossi A, Voigtlaender M, Janjetovic S, Thiele B, Alawi M, März M, et al. Mutational landscape reflects the biological continuum of plasma cell dyscrasias. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7(2): e537.
Cuenca I, Alameda D, Sanchez-Vega B, Gomez-Sanchez D, Alignani D, Lasa M, et al. Immunogenetic characterization of clonal plasma cells in systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Leukemia. 2021;35(1):245–9.
Chyra Z, Sevcikova T, Vojta P, Puterova J, Brozova L, Growkova K, et al. Heterogenous mutation spectrum and deregulated cellular pathways in aberrant plasma cells underline molecular pathology of light-chain amyloidosis. Haematologica. 2021;106(2):601–4.
Huang XF, Jian S, Lu JL, Shen KN, Feng J, Zhang CL, et al. Genomic profiling in amyloid light-chain amyloidosis reveals mutation profiles associated with overall survival. Amyloid. 2020;27(1):36–44.
Bochtler T, Merz M, Hielscher T, Granzow M, Hoffmann K, Kramer A, et al. Cytogenetic intraclonal heterogeneity of plasma cell dyscrasia in AL amyloidosis as compared with multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2018;2(20):2607–18.
Comenzo R, Zhang Y, Martinez C, Osman K, Herrera G. The tropism of organ involvement in primary systemic amyloidosis: contributions of Ig V(L) germ line gene use and clonal plasma cell burden. Blood. 2001;98(3):714–20.
Perfetti V, Palladini G, Casarini S, Navazza V, Rognoni P, Obici L, et al. The repertoire of λ light chains causing predominant amyloid heart involvement and identification of a preferentially involved germline gene, IGLV1-44. Blood. 2012;119(1):144–50.
Kourelis TV, Dasari S, Theis JD, Ramirez-Alvarado M, Kurtin PJ, Gertz MA, et al. Clarifying immunoglobulin gene usage in systemic and localized immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis by mass spectrometry. Blood. 2017;129(3):299–306.
Oberti L, Rognoni P, Barbiroli A, Lavatelli F, Russo R, Maritan M, et al. Concurrent structural and biophysical traits link with immunoglobulin light chains amyloid propensity. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16809.
Radamaker L, Lin YH, Annamalai K, Huhn S, Hegenbart U, Schönland SO, et al. Cryo-EM structure of a light chain-derived amyloid fibril from a patient with systemic AL amyloidosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1103.
Swuec P, Lavatelli F, Tasaki M, Paissoni C, Rognoni P, Maritan M, et al. Cryo-EM structure of cardiac amyloid fibrils from an immunoglobulin light chain AL amyloidosis patient. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1269.
Imperlini E, Gnecchi M, Rognoni P, Sabidò E, Ciuffreda MC, Palladini G, et al. Proteotoxicity in cardiac amyloidosis: amyloidogenic light chains affect the levels of intracellular proteins in human heart cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):15661.
Palladini G, Lavatelli F, Russo P, Perlini S, Perfetti V, Bosoni T, et al. Circulating amyloidogenic free light chains and serum N-terminal natriuretic peptide type B decrease simultaneously in association with improvement of survival in AL. Blood. 2006;107(10):3854–8.
Kourelis TV, Kumar SK, Go RS, Kapoor P, Kyle RA, Buadi FK, et al. Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis is diagnosed late in patients with preexisting plasma cell dyscrasias. Am J Hematol. 2014;89(11):1051–4.
Weiss BM, Hebreo J, Cordaro DV, Roschewski MJ, Baker TP, Abbott KC, et al. Increased serum free light chains precede the presentation of immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(25):2699–704.
Merlini G, Palladini G. Differential diagnosis of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:595–603.
Merlini G, Wechalekar AD, Palladini G. Systemic light chain amyloidosis: an update for treating physicians. Blood. 2013;121(26):5124–30.
Fernandez de Larrea C, Verga L, Morbini P, Klersy C, Lavatelli F, Foli A, et al. A practical approach to the diagnosis of systemic amyloidoses. Blood. 2015;125(14):2239–44.
Muchtar E, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Buadi FK, Kapoor P, Hayman SR, et al. Overuse of organ biopsies in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL): the consequence of failure of early recognition. Ann Med. 2017;49(7):545–51.
Foli A, Palladini G, Caporali R, Verga L, Morbini P, Obici L, et al. The role of minor salivary gland biopsy in the diagnosis of systemic amyloidosis: results of a prospective study in 62 patients. Amyloid-J Protein Fold Disord. 2011;18:80–2.
Kennel SJ, Stuckey A, McWilliams-Koeppen HP, Richey T, Wall JS. Tc-99m radiolabeled peptide p5 + 14 is an effective probe for SPECT imaging of systemic amyloidosis. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016;18(4):483–9.
Palladini G, Milani P, Merlini G. Management of AL amyloidosis in 2020. Blood. 2020;136(23):2620–7.
Quarta CC, Zheng J, Hutt D, Grigore SF, Manwani R, Sachchithanantham S, et al. 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy in immunoglobulin light chain (AL) cardiac amyloidosis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021;22(11):1304–11.
Gillmore JD, Maurer MS, Falk RH, Merlini G, Damy T, Dispenzieri A, et al. Nonbiopsy diagnosis of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis. Circulation. 2016;133(24):2404–12.
Palladini G, Merlini G. How I treat AL amyloidosis. Blood. 2022;139(19):2918–30.
Bochtler T, Hegenbart U, Heiss C, Benner A, Cremer F, Volkmann M, et al. Evaluation of the serum-free light chain test in untreated patients with AL amyloidosis. Haematologica. 2008;93(3):459–62.
Katzmann J, Kyle R, Benson J, Larson D, Snyder M, Lust J, et al. Screening panels for detection of monoclonal gammopathies. Clin Chem. 2009;55(8):1517–22.
Palladini G, Russo P, Bosoni T, Verga L, Sarais G, Lavatelli F, et al. Identification of amyloidogenic light chains requires the combination of serum-free light chain assay with immunofixation of serum and urine. Clin Chem. 2009;55(3):499–504.
Palladini G, Jaccard A, Milani P, Lavergne D, Foli A, Bender S, et al. Circulating free light chain measurement in the diagnosis, prognostic assessment and evaluation of response of AL amyloidosis: comparison of Freelite and N latex FLC assays. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017;55(11):1734–43.
Benson MD, Berk JL, Dispenzieri A, Damy T, Gillmore JD, Hazenberg BP, et al. Tissue biopsy for the diagnosis of amyloidosis: experience from some centres. Amyloid. 2022;29(1):8–13.
Gonzalez Suarez ML, Zhang P, Nasr SH, Sathick IJ, Kittanamongkolchai W, Kurtin PJ, et al. The sensitivity and specificity of the routine kidney biopsy immunofluorescence panel are inferior to diagnosing renal immunoglobulin-derived amyloidosis by mass spectrometry. Kidney Int. 2019;96(4):1005–9.
Satoskar AA, Efebera Y, Hasan A, Brodsky S, Nadasdy G, Dogan A, et al. Strong transthyretin immunostaining: potential pitfall in cardiac amyloid typing. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35(11):1685–90.
Satoskar A, Burdge K, Cowden D, Nadasdy G, Hebert L, Nadasdy T. Typing of amyloidosis in renal biopsies: diagnostic pitfalls. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131(6):917–22.
Schönland SO, Hegenbart U, Bochtler T, Mangatter A, Hansberg M, Ho AD, et al. Immunohistochemistry in the classification of systemic forms of amyloidosis: a systematic investigation of 117 patients. Blood. 2012;119(2):488–93.
Vrana J, Gamez J, Madden B, Theis J, Bergen H, Dogan A. Classification of amyloidosis by laser microdissection and mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis in clinical biopsy specimens. Blood. 2009;114(24):4957–9.
Brambilla F, Lavatelli F, Di Silvestre D, Valentini V, Rossi R, Palladini G, et al. Reliable typing of systemic amyloidoses through proteomic analysis of subcutaneous adipose tissue. Blood. 2012;119(8):1844–7.
Dispenzieri A, Gertz M, Kyle R, Lacy M, Burritt M, Therneau T, et al. Serum cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide: a staging system for primary systemic amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(18):3751–7.
Wechalekar AD, Schonland SO, Kastritis E, Gillmore JD, Dimopoulos MA, Lane T, et al. A European collaborative study of treatment outcomes in 346 patients with cardiac stage III AL amyloidosis. Blood. 2013;121(17):3420–7.
Palladini G, Sachchithanantham S, Milani P, Gillmore J, Foli A, Lachmann H, et al. A European collaborative study of cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in upfront treatment of systemic AL amyloidosis. Blood. 2015;126(5):612–5.
Lilleness B, Ruberg FL, Mussinelli R, Doros G, Sanchorawala V. Development and validation of a survival staging system incorporating BNP in patients with light chain amyloidosis. Blood. 2019;133(3):215–23.
Kumar S, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK, Colby C, et al. Revised prognostic staging system for light chain amyloidosis incorporating cardiac biomarkers and serum free light chain measurements. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(9):989–95.
Palladini G, Hegenbart U, Milani P, Kimmich C, Foli A, Ho AD, et al. A staging system for renal outcome and early markers of renal response to chemotherapy in AL amyloidosis. Blood. 2014;124(15):2325–32.
Visram A, Al Saleh AS, Parmar H, McDonald JS, Lieske JC, Vaxman I, et al. Correlation between urine ACR and 24-h proteinuria in a real-world cohort of systemic AL amyloidosis patients. Blood Cancer J. 2020;10(12):124.
Basset M, Milani P, Ferretti VV, Nuvolone M, Foli A, Benigna F, et al. Prospective urinary albumin/creatinine ratio for diagnosis, staging, and organ response assessment in renal AL amyloidosis: results from a large cohort of patients. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022;60(3):386–93.
Palladini G, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Kumar S, Wechalekar A, Hawkins PN, et al. New criteria for response to treatment in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis based on free light chain measurement and cardiac biomarkers: impact on survival outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(36):4541–9.
Palladini G, Schonland SO, Sanchorawala V, Kumar S, Wechalekar A, Hegenbart U, et al. Clarification on the definition of complete haematologic response in light-chain (AL) amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2021;7:1–2.
Lilleness B, Doros G, Ruberg FL, Sanchorawala V. Establishment of brain natriuretic peptide—based criteria for evaluating cardiac response to treatment in light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Br J Haematol. 2020;188(3):424–7.
Ravichandran S, Cohen OC, Law S, Foard D, Fontana M, Martinez-Naharro A, et al. Impact of early response on outcomes in AL amyloidosis following treatment with frontline Bortezomib. Blood Cancer J. 2021;11(6):118.
Kastritis E, Fotiou D, Theodorakakou F, Dialoupi I, Migkou M, Roussou M, et al. Timing and impact of a deep response in the outcome of patients with systemic light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2021;28(1):3–11.
Basset M, Milani P, Foli A, Nuvolone M, Benvenuti P, Nanci M, et al. Early cardiac response is possible in stage IIIb cardiac AL amyloidosis and is associated with prolonged survival. Blood. 2022;140:1964–71.
Kastritis E, Leleu X, Arnulf B, Zamagni E, Cibeira MT, Kwok F, et al. Bortezomib, melphalan, and dexamethasone for light-chain amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(28):3252–60.
Kastritis E, Palladini G, Minnema MC, Wechalekar AD, Jaccard A, Lee HC, et al. Daratumumab-based treatment for immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(1):46–58.
Jaccard A, Moreau P, Leblond V, Leleu X, Benboubker L, Hermine O, et al. High-dose melphalan versus melphalan plus dexamethasone for AL amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(11):1083–93.
Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Kumar SK, Dingli D, Leung N, et al. Refinement in patient selection to reduce treatment-related mortality from autologous stem cell transplantation in amyloidosis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(4):557–61.
Sidiqi MH, Aljama MA, Buadi FK, Warsame RM, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, et al. Stem cell transplantation for light chain amyloidosis: decreased early mortality over time. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(13):1323–9.
Sanchorawala V, Sun F, Quillen K, Sloan JM, Berk JL, Seldin DC. Long-term outcome of patients with AL amyloidosis treated with high-dose melphalan and stem cell transplantation: 20-year experience. Blood. 2015;126(20):2345–7.
Sanchorawala V, Boccadoro M, Gertz M, Hegenbart U, Kastritis E, Landau H, et al. Guidelines for high dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation for systemic AL amyloidosis: EHA-ISA working group guidelines. Amyloid. 2022;29(1):1–7.
Wechalekar AD, Cibeira MT, Gibbs SD, Jaccard A, Kumar S, Merlini G, et al. Guidelines for non-transplant chemotherapy for treatment of systemic AL amyloidosis: EHA-ISA working group. Amyloid. 2022;15:1–15.
Hwa YL, Kumar SK, Gertz MA, Lacy MQ, Buadi FK, Kourelis TV, et al. Induction therapy pre-autologous stem cell transplantation in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: a retrospective evaluation. Am J Hematol. 2016;91(10):984–8.
Manwani R, Hegenbart U, Mahmood S, Sachchithanantham S, Kyriakou C, Yong K, et al. Deferred autologous stem cell transplantation in systemic AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2018;8(11):101.
Basset M, Milani P, Nuvolone M, Benigna F, Rodigari L, Foli A, et al. Sequential response-driven bortezomib-based therapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant in AL amyloidosis. Blood Adv. 2020;4(17):4175–9.
Bochtler T, Hegenbart U, Kunz C, Granzow M, Benner A, Seckinger A, et al. Translocation t(11;14) is associated with adverse outcome in patients with newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis when treated with bortezomib-based regimens. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(12):1371–8.
Kastritis E, Minnema M, Dimopoulos M, Merlini G, Theodorakakou F, Fotiou D, Huart A, Belhadj K, Leonidakis A, Manousou K, Sonneveld P, Palladini G. Efficacy and safety of daratumumab monotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with stage 3B light chain amyloidosis: a phase 2 study by the European myeloma network. Blood. 2021;138:2730.
Li J, Chen S, Hu Y, Cai J. Bortezomib-induced severe pulmonary complications in multiple myeloma: a case report and literature review. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(3):2255–60.
Saglam B, Kalyon H, Ozbalak M, Ornek S, Keske S, Tabak L, et al. Bortezomib induced pulmonary toxicity: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Blood Res. 2020;10(6):407–15.
Cibeira MT, Oriol A, Lahuerta JJ, Mateos MV, de la Rubia J, Hernandez MT, et al. A phase II trial of lenalidomide, dexamethasone and cyclophosphamide for newly diagnosed patients with systemic immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Br J Haematol. 2015;170(6):804–13.
Manwani R, Sachchithanantham S, Mahmood S, Foard D, Sharpley F, Rezk T, et al. Treatment of IgM-associated immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis with rituximab-bendamustine. Blood. 2018;132(7):761–4.
Palladini G, Foli A, Russo P, Milani P, Obici L, Lavatelli F, et al. Treatment of IgM-associated AL amyloidosis with the combination of rituximab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011;11(1):143–5.
Pika T, Hegenbart U, Flodrova P, Maier B, Kimmich C, Schönland SO. First report of ibrutinib in IgM-related amyloidosis: few responses, poor tolerability, and short survival. Blood. 2018;131(3):368–71.
Tam CS, Opat S, D’Sa S, Jurczak W, Lee HP, Cull G, et al. A randomized phase 3 trial of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in symptomatic Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia: the ASPEN study. Blood. 2020;136(18):2038–50.
Nuvolone M, Nevone A, Merlini G. Targeting amyloid fibrils by passive immunotherapy in systemic amyloidosis. BioDrugs. 2022;36(5):591–608.
Wechalekar A, Antoni G, Al Azzam W, Bergström M, Biswas S, Chen C, et al. Pharmacodynamic evaluation and safety assessment of treatment with antibodies to serum amyloid P component in patients with cardiac amyloidosis: an open-label Phase 2 study and an adjunctive immuno-PET imaging study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022;22(1):49.
Gertz M, Sanchorawala V, Wechalekar A, Ando Y, Koh Y, Nie N, Sheng X, Conrad A, Kastritis E. Birtamimab in patients with Mayo stage IV AL amyloidosis: rationale for confirmatory affirm-AL phase 3 study. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:TPS8076.
Edwards CV, Rao N, Bhutani D, Mapara M, Radhakrishnan J, Shames S, et al. Phase 1a/b study of monoclonal antibody CAEL-101 (11–1F4) in patients with AL amyloidosis. Blood. 2021;138(25):2632–41.
Muchtar E, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Kumar SK, Buadi FK, Leung N, et al. Treatment of AL amyloidosis: mayo stratification of myeloma and risk-adapted therapy (mSMART) consensus statement 2020 update. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(6):1546–77.
Palladini G, Paiva B, Wechalekar A, Massa M, Milani P, Lasa M, et al. Minimal residual disease negativity by next-generation flow cytometry is associated with improved organ response in AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2021;11(2):34.
Staron A, Burks EJ, Lee JC, Sarosiek S, Sloan JM, Sanchorawala V. Assessment of minimal residual disease using multiparametric flow cytometry in patients with AL amyloidosis. Blood Adv. 2020;4(5):880–4.
Kastritis E, Kostopoulos IV, Theodorakakou F, Fotiou D, Gavriatopoulou M, Migkou M, et al. Next generation flow cytometry for MRD detection in patients with AL amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2021;28(1):19–23.
Muchtar E, Wisniowski B, Palladini G, Milani P, Merlini G, Schönland S, Veelken K, Hegenbart U, Dispenzieri A, Kumar K, Leung N, Kastritis E, Dimopoulos M, Liedtke M, Witteles R, Sanchorawala V, Szalat R, Landau H, Petrlik E, Lentzsch S, Coltoff A, Bladé J, Cibeira M, Cohen O, Foard D, Gillmore J, Lachmann H, Wechalekar A, Gertz M. Graded renal response criteria for light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Blood. 2021;138:2721.
Muchtar E, Dispenzieri A, Wisniowski B, Palladini G, Milani P, Merlini G, Schönland S, Veelken K, Hegenbart U, Kumar S, Kastritis E, Dimopoulos M, Liedtke M, Witteles R, Sanchorawala V, Szalat R, Landau H, Petrlik E, Lentzsch S, Coltoff A, Bladé J, Cibeira M, Cohen O, Foard D, Wechalekar A, Gertz M. Graded cardiac response criteria for AL amyloidosis: the impact of depth of cardiac response on survival. Blood. 2021;138:2720.
Milani P, Gertz MA, Merlini G, Dispenzieri A. Attitudes about when and how to treat patients with AL amyloidosis: an international survey. Amyloid. 2017;24(4):213–6.
Palladini G, Merlini G. When should treatment of AL amyloidosis start at relapse? Early, to prevent organ progression. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):212–5.
Sanchorawala V. Delay treatment of AL amyloidosis at relapse until symptomatic: devil is in the details. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):216–8.
Palladini G, Milani P, Foli A, Basset M, Russo F, Perlini S, et al. Presentation and outcome with second-line treatment in AL amyloidosis previously sensitive to nontransplant therapies. Blood. 2018;131(5):525–32.
Cohen OC, Sathyanath A, Petrie A, Ravichandran S, Law S, Manwani R, et al. Prognostic importance of the 6 min walk test in light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Heart. 2022.
Cohen OC, Ismael A, Pawarova B, Manwani R, Ravichandran S, Law S, et al. Longitudinal strain is an independent predictor of survival and response to therapy in patients with systemic AL amyloidosis. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(4):333–41.
Martinez-Naharro A, Patel R, Kotecha T, Karia N, Ioannou A, Petrie A, Chacko L, Razvi Y, Ravichandran S, Brown J, Law S, Quarta C, Mahmood S, Wisniowski B, Pica S, Sachchithanantham S, Lachmannm H, Moon J, Knight D, Whelan C, Venneri L, Xue H, Kellman P, Gillmore J, Hawkins P, Wechalekar A, Fontana M. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in light-chain amyloidosis to guide treatment. Eur Heart J. 2022.
Tandon N, Sidana S, Gertz MA, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Buadi FK, et al. Treatment patterns and outcome following initial relapse or refractory disease in patients with systemic light chain amyloidosis. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(6):549–54.
Dispenzieri A, Kastritis E, Wechalekar AD, Schönland SO, Kim K, Sanchorawala V, et al. A randomized phase 3 study of ixazomib-dexamethasone versus physician’s choice in relapsed or refractory AL amyloidosis. Leukemia. 2022;36(1):225–35.
Basset M, Kimmich CR, Schreck N, Krzykalla J, Dittrich T, Veelken K, et al. Lenalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis: results from a large cohort of patients with long follow-up. Br J Haematol. 2021;195(2):230–43.
Specter R, Sanchorawala V, Seldin DC, Shelton A, Fennessey S, Finn KT, et al. Kidney dysfunction during lenalidomide treatment for AL amyloidosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(3):881–6.
Milani P, Sharpley F, Schönland SO, Basset M, Mahmood S, Nuvolone M, et al. Pomalidomide and dexamethasone grant rapid haematologic responses in patients with relapsed and refractory AL amyloidosis: a European retrospective series of 153 patients. Amyloid. 2020;27(4):231–6.
Dispenzieri A, Dingli D, Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Lacy MQ, Hayman S, et al. Discordance between serum cardiac biomarker and immunoglobulin-free light-chain response in patients with immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis treated with immune modulatory drugs. Am J Hematol. 2010;85(10):757–9.
Kimmich CR, Terzer T, Benner A, Dittrich T, Veelken K, Carpinteiro A, et al. Daratumumab for systemic AL amyloidosis: prognostic factors and adverse outcome with nephrotic-range albuminuria. Blood. 2020;135(18):1517–30.
Kimmich CR, Terzer T, Benner A, Hansen T, Carpinteiro A, Dittrich T, et al. Daratumumab, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone in systemic light-chain amyloidosis: high efficacy, relevant toxicity and main adverse effect of gain 1q21. Am J Hematol. 2021;96(7):E253–7.
Szalat RE, Gustine J, Sloan JM, Edwards CV, Sanchorawala V. Predictive factors of outcomes in patients with AL amyloidosis treated with daratumumab. Am J Hematol. 2022;97(1):79–89.
Sanchorawala V, Sarosiek S, Schulman A, Mistark M, Migre ME, Cruz R, et al. Safety, tolerability, and response rates of daratumumab in relapsed AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 2 study. Blood. 2020;135(18):1541–7.
Roussel M, Merlini G, Chevret S, Arnulf B, Stoppa AM, Perrot A, et al. A prospective phase 2 trial of daratumumab in patients with previously treated systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Blood. 2020;135(18):1531–40.
Premkumar VJ, Lentzsch S, Pan S, Bhutani D, Richter J, Jagannath S, et al. Venetoclax induces deep hematologic remissions in t(11;14) relapsed/refractory AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2021;11(1):10.
Parker T, Rosenthal A, Sanchorawala V, Landau H, Campagnaro E, Kapoor P, Neparidze N, Hagen P, Sarosiek S, Scott E, Hoering A, Durie B, Usmani S, Orlowski R. A Phase II Study of Isatuximab (SAR650984) NSC-795145) for Patients with Previously Treated AL Amyloidosis (SWOGS1702; NCT#03499808). Blood. 2020;ASH2020 abstract 728.
Khwaja J, Bomsztyk J, Mahmood S, Wisniowski B, Shah R, Tailor A, et al. High response rates with single-agent belantamab mafodotin in relapsed systemic AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2022;12(9):128.
Zhang Y, Godara A, Pan S, Toskic D, Mann H, Sborov D, et al. Belantamab mafodotin in patients with relapsed/refractory AL amyloidosis with myeloma. Ann Hematol. 2022;101(9):2119–21.
Oliver-Caldes A, Jiménez R, Español-Rego M, Cibeira MT, Ortiz-Maldonado V, Quintana LF, et al. First report of CART treatment in AL amyloidosis and relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(12).
Kfir-Erenfeld S, Asherie N, Grisariu S, Avni B, Zimran E, Assayag M, et al. Feasibility of a novel academic BCMA-CART (HBI0101) for the treatment of relapsed and refractory AL amyloidosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2022.
Yan S, Zhu H, Zhu A, Golabek A, Du H, Roher A, et al. Receptor-dependent cell stress and amyloid accumulation in systemic amyloidosis. Nat Med. 2000;6(6):643–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No external funding was used in the preparation of this manuscript.
Competing interests
Giovanni Palladini: Alexion (Advisory board, honoraria), Argobio (Advisory board, honoraria), Janssen (Advisory board, honoraria), Protego (Advisory board, honoraria), Gate bioscience (Research funding), The Binding Site (Research funding, honoraria), Pfizer (Honoraria), Prothena (Honoraria), Sebia (Honoraria), Siemens (Honoraria). Paolo Milani: Janssen (Advisory board, honoraria), Pfizer (honoraria).
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
Data are available on request due to privacy or other restrictions.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Author contributions
GP and PM wrote the manuscript and gave final approval. No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Palladini, G., Milani, P. Diagnosis and Treatment of AL Amyloidosis. Drugs 83, 203–216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-022-01830-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-022-01830-z