Abstract
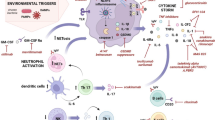
Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) is a rare inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology generally characterized by persistent high spiking fever, evanescent rash, and polyarthritis. The pathogenesis of AOSD is only partially known. The pivotal role of macrophage cell activation, which leads to T-helper 1 (Th1) cell cytokine activation, is now well-established in AOSD. Moreover, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1, -6, and -18 seem to play a key role in this disorder, giving rise to the development of new targeted therapies. For years, treatment of AOSD has been largely empirical, using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Patients with steroid- and methotrexate-refractory AOSD can now benefit from efficient and well-tolerated biologic agents such as IL-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kadavath S, Efthimiou P. Adult-onset Still’s disease-pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and new treatment options. Ann Med. 2015;47:6–14.
Sfriso P, Priori R, Valesini G, Rossi S, Montecucco CM, D’Ascanio A, et al. Adult-onset Still’s disease: an Italian multicentre retrospective observational study of manifestations and treatments in 245 patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:1683–9.
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y, Kashiwagi H, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol. 1992;19:424–30.
Maria AT, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Touitou I, Rivière S, Guilpain P. Adult onset Still’s disease (AOSD) in the era of biologic therapies: dichotomous view for cytokine and clinical expressions. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:1149–59.
Pouchot J, Fautrel B. Maladie de Still de l’adulte. In: Piette JC, Meyer O, Sibilia J, editors. Médecine/Sciences F. Maladies et syndromes systémiques, 5ème édition Paris: Médecine Sciences Flammarion; 2008; vol. 1. p. 449–68.
Fujii T, Nojima T, Yasuoka H, Satoh S, Nakamura K, Kuwana M, et al. Cytokine and immunogenetic profiles in Japanese patients with adult Still’s disease. Assoc Chron Articul Dis Rheumatol (Oxford). 2001;40:1398–404.
Magadur-Joly G, Billaud E, Barrier JH, Pennec YL, Masson C, Renou P, et al. Epidemiology of adult Still’s disease: estimate of the incidence by a retrospective study in west France. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995;54:587–90.
Wakai K, Ohta A, Tamakoshi A, Ohno Y, Kawamura T, Aoki R, et al. Estimated prevalence and incidence of adult Still’s disease: findings by a nationwide epidemiological survey in Japan. J Epidemiol. 1997;7:221–5.
Evensen KJ, Nossent HC. Epidemiology and outcome of adult-onset Still’s disease in Northern Norway. Scand J Rheumatol. 2006;35:48–51.
Jamilloux Y, Gerfaud-Valentin M, Martinon F, Belot A, Henry T, Seve P. Pathogenesis of adult-onset Still’s disease: new insights from the juvenile counterpart. Immunol Res. 2015;61:53–62.
Nirmala N, Brachat A, Feist E, Blank N, Specker C, Witt M, et al. Gene-expression analysis of adult-onset Still’s disease and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is consistent with a continuum of a single disease entity. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2015;13:50.
Sampalis JS, Esdaile JM, Medsger TA, Partridge AJ, Yeadon C, Senécal JL, et al. A controlled study of the long-term prognosis of adult Still’s disease. Am J Med. 1995;98:384–8.
Terkeltaub R, Esdaile J, Décary F, Harth M, Lister J, Lapointe N. HLA-Bw35 and prognosis in adult Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1981;12:1469–72.
Joung CI, Lee HS, Lee SW, Kim CG, Song YH, Jun JB, et al. Association between HLA-DR B1 and clinical features of adult onset Still’s disease in Korea. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21:489–92.
Sugiura T, Kawaguchi Y, Harigai M, Terajima-Ichida H, Kitamura Y, Furuya T, et al. Association between adult-onset Still’s disease and interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms. Genes Immun. 2002;3:394–9.
Wang FF, Huang XF, Shen N, Leng L, Bucala R, Chen SL, et al. A genetic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15:R65.
Fishman D, Faulds G, Jeffery R, Mohamed-Ali V, Yudkin JS, Humphries S, et al. The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:1369–76.
Gattorno M, Piccini A, Lasiglie D, Tassi S, Brisca G, Carta S, et al. The pattern of response to anti-interleukin-1 treatment distinguishes two subsets of patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:1505–15.
Sighart R, Rech J, Hueber A, Blank N, Löhr S, Reis A, et al. Evidence for genetic overlap between adult onset Still’s disease and hereditary periodic fever syndromes. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38:111–20.
Wouters JM, van der Veen J, van de Putte LB, de Rooij DJ. Adult onset Still’s disease and viral infections. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988;47:764–7.
Balleari E, Cutolo M, Accardo S. Adult-onset Still’s disease associated to toxoplasma gondii infection. Clin Rheumatol. 1991;10:326–7.
Liozon E, Ly KH, Vidal-Cathala E, Fauchais AL. Adult-onset Still’s disease as a manifestation of malignancy: report of a patient with melanoma and literature review. Rev Med Interne. 2014;35:60–4.
Chen DY, Lin CC, Chen YM, Lan JL, Hung WT, Chen HH, et al. Involvement of TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15:R39.
Gerfaud-Valentin M, Jamilloux Y, Iwaz J, Sève P. Adult-onset Still’s disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:708–22.
Komiya A, Matsui T, Nogi S, Iwata K, Futami H, Takaoka H, et al. Neutrophil CD64 is upregulated in patients with active adult-onset Still’s disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2012;41:156–8.
Choi JH, Suh CH, Lee YM, Suh YJ, Lee SK, Kim SS, et al. Serum cytokine profiles in patients with adult onset Still’s disease. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:2422–7.
Matsui K, Tsuchida T, Hiroishi K, Tominaga K, Hayashi N, Hada T, et al. High serum level of macrophage-colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) in adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999;38:477–8.
Hoshino T, Ohta A, Yang D, Kawamoto M, Kikuchi M, Inoue Y, et al. Elevated serum interleukin 6, interferon-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in patients with adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol. 1998;25:396–8.
Zou YQ, Lu LJ, Li SJ, Zeng T, Wang XD, Bao CD, et al. The levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor as an indicator of disease activity and severity in adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Biochem. 2008;41:519–24.
Chen DY, Lan JL, Lin FJ, Hsieh TY. Association of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 with clinical manifestations and interleukin-18 in patients with active, untreated adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;53:320–7.
Lee SJ, Cho YN, Kim TJ, Park SC, Park DJ, Jin HM, et al. Natural killer T cell deficiency in active adult-onset Still’s Disease: correlation of deficiency of natural killer T cells with dysfunction of natural killer cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:2868–77.
Wulffraat NM, Rijkers GT, Elst E, Brooimans R, Kuis W. Reduced perforin expression in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is restored by autologous stem-cell transplantation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42:375–9.
Netea MG, Nold-Petry CA, Nold MF, Joosten LA, Opitz B, van der Meer JH, et al. Differential requirement for the activation of the inflammasome for processing and release of IL-1beta in monocytes and macrophages. Blood. 2009;113:2324–35.
Hsieh CW, Chen YM, Lin CC, Tang KT, Chen HH, Hung WT, et al. Elevated expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome and its correlation with disease activity in adult-onset still disease. J Rheumatol. 2017;44:1142–50.
Chen DY, Chen YM, Chen HH, Hsieh CW, Gung NR, Hung WT, et al. Human parvovirus B19 nonstructural protein NS1 activates NLRP3 inflammasome signaling in adult-onset Still’s disease. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:3364–71.
Antoniou KM, Margaritopoulos GA, Giannarakis I, Choulaki C, Fountoulakis N, Siafakas NM, et al. Adult onset Still’s disease: a case report with a rare clinical manifestation and pathophysiological correlations. Case Rep Med. 2013;2013:981232.
Chen DY, Lan JL, Lin FJ, Hsieh TY, Wen MC. Predominance of Th1 cytokine in peripheral blood and pathological tissues of patients with active untreated adult onset Still’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:1300–6.
Chen DY, Chen YM, Chen HH, Hsieh CW, Lin CC, Lan JL. The associations of circulating CD4+CD25 high regulatory T cells and TGF- b with disease activity and clinical course in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease. Connect Tissue Res. 2010;51:370–7.
Chen DY, Lan JL, Lin FJ, Hsieh TY. Proinflammatory cytokine profiles in sera and pathological tissues of patients with active untreated adult onset Still’s disease. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:2189–98.
Kastner DL, Aksentijevich I, Goldbach-Mansky R. Autoinflammatory disease reloaded: a clinical perspective. Cell. 2010;140:784–90.
Rooney T, Murphy E, Benito M, Roux-Lombard P, FitzGerald O, Dayer J-M, et al. Synovial tissue interleukin-18 expression and the response to treatment in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:1393–8.
Priori R, Barone F, Alessandri C, Colafrancesco S, McInnes IB, Pitzalis C, et al. Markedly increased IL-18 liver expression in adult-onset Still’s disease-related hepatitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50:776–80.
Kawashima M, Yamamura M, Taniai M, Yamauchi H, Tanimoto T, Kurimoto M, et al. Levels of interleukin-18 and its binding inhibitors in the blood circulation of patients with adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:550–60.
Maruyama J, Inokuma S. Cytokine profiles of macrophage activation syndrome associated with rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:967–73.
Gabay C, Fautrel B, Rech J, Spertini F, Feist E, Kötter I, et al. Open-label, multicentre, dose-escalating phase II clinical trial on the safety and efficacy of tadekinig alfa (IL-18BP) in adult-onset Still’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:840–7.
Scheinberg MA, Chapira E, Fernandes ML, Hubscher O. Interleukin 6: a possible marker of disease activity in adult onset Still’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996;14:653–5.
Chen DY, Chen YM, Lan JL, Lin CC, Chen HH, Hsieh CW. Potential role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49:2305–12.
Billiau AD, Roskams T, Van Damme-Lombaerts R, Matthys P, Wouters C. Macrophage activation syndrome: characteristic findings on liver biopsy illustrating the key role of activated, IFN-gamma-producing lymphocytes and IL-6- and TNF-alpha-producing macrophages. Blood. 2005;105:1648–51.
Canna SW. Interferon-γ: friend or foe in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult Still’s Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:1072–6.
Avau A, Mitera T, Put S, Put K, Brisse E, Filtjens J, et al. Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis-like syndrome in mice following stimulation of the immune system with Freund’s complete adjuvant: regulation by interferon-γ. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:1340–51.
Kasama T, Furuya H, Yanai R, Ohtsuka K, Takahashi R, Yajima N, et al. Correlation of serum CX3CL1 level with disease activity in adult-onset Still’s disease and significant involvement in hemophagocytic syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31:853–60.
Govoni M, Bortoluzzi A, Rossi D, Modena V. How I treat patients with adult onset Still’s disease in clinical practice. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:1016–23.
Franchini S, Dagna L, Salvo F, Aiello P, Baldissera E, Sabbadini MG. Efficacy of traditional and biologic agents in different clinical phenotypes of adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2530–5.
Wouters JM, van de Putte LB. Adult-onset Still’s disease; clinical and laboratory features, treatment and progress of 45 cases. QJM. 1986;61:1055–65.
Gerfaud-Valentin M, Maucort-Boulch D, Hot A, Iwaz J, Ninet J, Durieu I, et al. Adult-onset Still disease: manifestations, treatments, outcome, and prognostic factors in 57 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2014;93:91–9.
Kim YJ, Koo BS, Kim YG, Lee CK, Yoo B. Clinical features and prognosis in 82 patients with adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32:28–33.
Pouchot J, Sampalis JS, Beaudet F, Carette S, Decary F, Salusinsky-Sternbach M, et al. Adult Still’s disease: manifestations, disease course, and outcome in 62 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991;70:118–36.
Colafrancesco S, Priori R, Valesini G, Argolini L, Baldissera E, Bartoloni E, et al. Response to interleukin-1 inhibitors in 140 italian patients with adult-onset still’s disease: a multicentre retrospective observational study. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:369.
Al-Homood IA. Biologic treatments for adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53:32–8.
Cavagna L, Caporali R, Epis O, Bobbio-Pallavicini F, Montecucco C. Infliximab in the treatment of adult Still’s disease refractory to conventional therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001;19:329–32.
Husni ME, Maier AL, Mease PJ, Overman SS, Fraser P, Gravallese EM, et al. Etanercept in the treatment of adult patients with Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1171–6.
Fautrel B, Sibilia J, Mariette X, Combe B. Tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents in refractory adult Still’s disease: an observational study of 20 cases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:262–6.
Benucci M, Li GF, Del Rosso A, Manfredi M. Adalimumab (anti-TNF-alpha) therapy to improve the clinical course of adult-onset Still’s disease: the first case report. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23:733.
Rech J, Ronneberger M, Englbrecht M, Finzel S, Katzenbeisser J, Manger K, et al. Successful treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease refractory to TNF and IL-1 blockade by IL-6 receptor blockade. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:390–2.
Aikawa NE, Ribeiro AC, Saad CG, Pereira RM, Levy M, Silva CA, et al. Is anti-TNF switching in refractory Still’s disease safe and effective? Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30:1129–34.
Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood. 2011;117(14):3720–32.
Ortiz-Sanjan F, Blanco R, Riancho-Zarrabeitia L, Castañeda S, Olivé A, Riveros A, et al. Efficacy of anakinra in refractory adult-onset Still’s disease: multicenter study of 41 patients and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e1554.
Kone-Paut I, Piram M. Targeting interleukin-1 b in CAPS (cryopyrin-associated periodic) syndromes: what did we learn? Autoimmun Rev 2012;12:77e80.
Giampietro C, Fautrel B. Anti-interleukin-1 agents in adult onset still’s disease. Int J Inflam. 2012;2012:317820.
Lequerré T, Quartier P, Rosellini D, Alaoui F, De Bandt M, Mejjad O, et al. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) treatment in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis or adult onset Still disease: preliminary experience in France. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:302–8.
Nigrovic PA, Mannion M, Prince FH, Zeft A, Rabinovich CE, van Rossum MA, et al. Anakinra as first-line disease-modifying therapy in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: report of forty-six patients from an international multicenter series. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:545–55.
Laskari K, Tzioufas AG, Moutsopoulos HM. Efficacy and long-term follow-up of IL-1R inhibitor anakinra in adults with Still’s disease: a case-series study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R91.
Kalliolias GD, Georgiou PE, Antonopoulos IA, Andonopoulos AP, Liossis SN. Anakinra treatment in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease is fast, effective, safe and steroid sparing: experience from an uncontrolled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:842–3.
Guignard S, Dien G, Dougados M. Severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome in a patient with adult onset Still’s disease treated with the anti-IL1 drug anakinra: a case report. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25:758–9.
Ruperto N, Quartier P, Wulffraat N, Woo P, Ravelli A, Mouy R, et al. A phase II, multicenter, open-label study evaluating dosing and preliminary safety and efficacy of canakinumab in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis with active systemic features. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:557–67.
Kontzias A, Efthimiou P. The use of Canakinumab, a novel IL-1 b long-acting inhibitor, in refractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;42:201–5.
Feist E, Quartier P, Fautrel B, Schneider R, Sfriso P, Efthimiou P, et al. Efficacy and safety of canakinumab in patients with Still’s disease: exposure-response analysis of pooled systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis data by age groups. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018. (Epub ahead of print).
Petryna O, Cush JJ, Efthimiou P. IL-1 trap rilonacept in refractory adult onset Still’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:2056–7.
Henderson C, Wilson M, Pham TH, Dolan G, Gobbo A, Snyder C, et al. Safety and efficacy of IL-1 trap in resistant adult onset Still’s disease: 24 month follow-up of open label treatment and biomarkers of response. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1831.
Ortiz-Sanjuan F, Blanco R, Calvo-Rio V, Narvaez J, Rubio Romero E, Olive A, et al. Efficacy of tocilizumab in conventional treatment-refractory adult-onset Still’s disease: multicenter retrospective open-label study of thirty-four patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(6):1659–65.
Cipriani P, Ruscitti P, Carubbi F, Pantano I, Liakouli V, Berardicurti O, et al. Tocilizumab for the treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease: results from a case series. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:49–55.
Elkayam O, Jiries N, Dranitzki Z, Kivity S, Lidar M, Levy O, et al. Tocilizumab in adult-onset Still’s disease: the Israeli experience. J Rheumatol. 2014;41:244–7.
Puéchal X, DeBandt M, Berthelot JM, Breban M, Dubost JJ, Fain O, et al. Tocilizumab in refractory adult Still’s disease. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63:155–9.
De Benedetti F, Brunner HI, Ruperto N, Kenwright A, Wright S, Calvo I, et al. Randomized trial of tocilizumab in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2385–95.
Ma Y, Wu M, Zhang X, Xia Q, Yang J, Xu S, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab with inhibition of interleukin-6 in adult-onset Still’s disease: a meta-analysis. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;8:1–9.
Watanabe E, Sugawara H, Yamashita T, Ishii A, Oda A, Terai C. Successful tocilizumab therapy for macrophage activation syndrome associated with adult-onset Still’s disease: a case-based review. Case Rep Med. 2016;2016:5656320.
Masui-Ito A, Okamoto R, Ikejiri K, Fujimoto M, Tanimura M, Nakamori S, et al. Tocilizumab for uncontrollable systemic inflammatory response syndrome complicating adult-onset Still disease: case report and review of literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e7596.
Tsuchida Y, Sumitomo S, Shoda H, Kubo K, Fujio K, Yamamoto K. Macrophage activation syndrome associated with tocilizumab treatment in adult-onset Still’s disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2017;27:556–7.
Permal S, Wechsler B, Cabane J, Perrot S, Blum L, Imbert JC. Treatment of Still disease in adults with intravenous immunoglobulins. Rev Med Interne. 1995;16:250–4.
Vignes S, Wechsler B, Amoura Z, Papo T, Francès C, Huong DL, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin in adult Still’s disease refractory to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998;16:295–8.
Prieur AM. Intravenous immunoglobulins in Still’s disease: still controversial, still unproven. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:797–800.
Ostrowski RA, Tehrani R, Kadanoff R. Refractory adult-onset still disease successfully treated with abatacept. J Clin Rheumatol. 2011;17:315–7.
Quartuccio L, Maset M, De Vita S. Efficacy of abatacept in a refractory case of adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010;28:265–7.
Ahmadi-Simab K, Lamprecht P, Jankowiak C, Gross WL. Successful treatment of refractory adult onset Still’s disease with rituximab. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1117–8.
Bartoloni E, Alunno A, Luccioli F, Santoboni G, Gerli R. Successful treatment of refractory adult-onset Still’s disease with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27:888–9.
Giampietro C, Ridene M, Lequerre T, Costedoat Chalumeau N, Amoura Z, Sellam J, et al. Anakinra in adult-onset Still’s disease: long-term treatment in patients resistant to conventional therapy. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65:822–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No sources of funding were used to conduct this study or prepare this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Paolo Sfriso, Sara Bindoli, and Paola Galozzi have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sfriso, P., Bindoli, S. & Galozzi, P. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Molecular Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Advances. Drugs 78, 1187–1195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-0956-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-0956-9