Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to prove the suitability of simultaneously administered microdoses of the factor Xa inhibitors (FXaIs) rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban (100 µg in total). To evaluate drug–drug interactions, the impact of ketoconazole, a known strong inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A4 and P-glycoprotein, was studied.
Methods
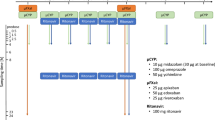
In a crossover clinical trial, 18 healthy volunteers were randomized to the two treatments using microdoses of rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban alone and when coadministered with ketoconazole. Plasma and urine concentrations of microdosed apixaban, edoxaban and rivaroxaban were quantified using a validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry assay with a lower limit of quantification of 2.5 pg/ml.
Results
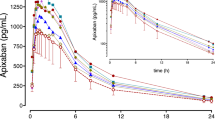
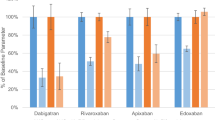
The microdosed FXaI cocktail showed similar pharmacokinetic parameters compared with published data, using normal therapeutic doses of each FXaI. Ketoconazole significantly increased exposure, with geometric mean AUC ratios of 1.90 (apixaban), 2.35 (edoxaban) and 2.27 (rivaroxaban).
Conclusion
The microdosed FXaI cocktail approach was able to precisely predict the drug interaction with ketoconazole. This is the first study that has been conducted to evaluate drug–drug interactions with a drug class, and the low administered doses also allow evaluation in vulnerable target populations.
Study Protocol
EudraCT 2016-003024-23.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heidbuchel H, Verhamme P, Alings M, Antz M, Diener HC, Hacke W, et al. Updated European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2015;17(10):1467–507.
Steffel J, Verhamme P, Potpara TS, Albaladejo P, Antz M, Desteghe L, et al. The 2018 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. European Heart Journal. 2018;39(16):1330–93.
Mueck W, Schwers S, Stampfuss J. Rivaroxaban and other novel oral anticoagulants: pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects, specific patient populations and relevance of coagulation monitoring. Thromb J. 2013;11(1):10.
Mueck W, Kubitza D, Becka M. Co-administration of rivaroxaban with drugs that share its elimination pathways: pharmacokinetic effects in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;76(3):455–66.
Raghavan N, Frost CE, Yu Z, He K, Zhang H, Humphreys WG, et al. Apixaban metabolism and pharmacokinetics after oral administration to humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37(1):74–81.
Wang L, Zhang D, Raghavan N, Yao M, Ma L, Frost CE, et al. In vitro assessment of metabolic drug-drug interaction potential of apixaban through cytochrome P450 phenotyping, inhibition, and induction studies. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(3):448–58.
Mikkaichi T, Yoshigae Y, Masumoto H, Imaoka T, Rozehnal V, Fischer T, et al. Edoxaban transport via P-glycoprotein is a key factor for the drug’s disposition. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42(4):520–8.
Bathala MS, Masumoto H, Oguma T, He L, Lowrie C, Mendell J. Pharmacokinetics, biotransformation, and mass balance of edoxaban, a selective, direct factor Xa inhibitor, in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012;40(12):2250–5.
Parasrampuria DA, Mendell J, Shi M, Matsushima N, Zahir H, Truitt K. Edoxaban drug-drug interactions with ketoconazole, erythromycin, and cyclosporine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;2(6):1591–600.
Frost CE, Byon W, Song Y, Wang J, Schuster AE, Boyd RA, et al. Effect of ketoconazole and diltiazem on the pharmacokinetics of apixaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;79(5):838–46.
Brais C, Larochelle J, Turgeon MH, Blais L, Farand P, Perreault S, et al. Predictors of direct oral anticoagulants utilization for thromboembolism prevention in atrial fibrillation. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2017;20:8–14.
European Medicines Agency. ICH Topic M 3 (R2): Non-clinical safety studies for the conduct of human clinical trials and marketing authorization for pharmaceuticals. 2008. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500002941.pdf. Accessed Jul 2018.
Hohmann N, Haefeli WE, Mikus G. Use of microdose phenotyping to individualise dosing of patients. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015;54(9):893–900.
Hohmann N, Kocheise F, Carls A, Burhenne J, Haefeli WE, Mikus G. Midazolam microdose to determine systemic and pre-systemic metabolic CYP3A activity in humans. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;79(2):278–85.
Katzenmaier S, Markert C, Riedel KD, Burhenne J, Haefeli WE, Mikus G. Determining the time course of CYP3A inhibition by potent reversible and irreversible CYP3A inhibitors using a limited sampling strategy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;90(5):666–73.
Burhenne J, Halama B, Maurer M, Riedel KD, Hohmann N, Mikus G, et al. Quantification of femtomolar concentrations of the CYP3A substrate midazolam and its main metabolite 1’-hydroxymidazolam in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;402(7):2439–50.
Foerster KI, Huppertz A, Muller OJ, Rizos T, Tilemann L, Haefeli WE, et al. Simultaneous quantification of direct oral anticoagulants currently used in anticoagulation therapy. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal. 2018;148:238–44.
US Food and Drug Administration. Bioanalytical method validation—guidance for industry. 2018. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm070107.pdf. Accessed Sep 2018.
European Medicines Agency. Guideline on bioanalytical method validation. 2012. https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf. Accessed Sep 2018.
Hohmann N, Kreuter R, Blank A, Weiss J, Burhenne J, Haefeli WE, et al. Autoinhibitory properties of the parent but not of the N-oxide metabolite contribute to infusion rate-dependent voriconazole pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;83(9):1954–65.
Frost C, Wang J, Nepal S, Schuster A, Barrett YC, Mosqueda-Garcia R, et al. Apixaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor: single dose safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and food effect in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;75(2):476–87.
Vakkalagadda B, Frost C, Byon W, Boyd RA, Wang J, Zhang D, et al. Effect of rifampin on the pharmacokinetics of apixaban, an oral direct inhibitor of factor Xa. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2016;16(2):119–27.
Ogata K, Mendell-Harary J, Tachibana M, Masumoto H, Oguma T, Kojima M, et al. Clinical safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the novel factor Xa inhibitor edoxaban in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;50(7):743–53.
Mendell J, Zahir H, Matsushima N, Noveck R, Lee F, Chen S, et al. Drug-drug interaction studies of cardiovascular drugs involving P-glycoprotein, an efflux transporter, on the pharmacokinetics of edoxaban, an oral factor Xa inhibitor. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2013;13(5):331–42.
Matsushima N, Lee F, Sato T, Weiss D, Mendell J. Bioavailability and safety of the factor Xa inhibitor edoxaban and the effects of quinidine in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2013;2(4):358–66.
Parasrampuria DA, Truitt KE. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Edoxaban, a non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant that inhibits clotting factor Xa. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55(6):641–55.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Voith B, Zuehlsdorf M, Wensing G. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of single doses of BAY 59-7939, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78(4):412–21.
Lee CA, Jones JP 3rd, Katayama J, Kaspera R, Jiang Y, Freiwald S, et al. Identifying a selective substrate and inhibitor pair for the evaluation of CYP2J2 activity. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012;40(5):943–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Sarah Mächler and Anette Lampert for monitoring the study, Marlies Stützle-Schnetz for her excellent assistance during the study performance, and Magdalena Longo and Andrea Deschlmayr for supporting the analysis of the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported in part by PharmCompNet Baden Württemberg (Ministerium für Wissenschaft, Forschung und Kunst, Baden-Württemberg).
Conflict of Interest
Walter Haefeli has received speaker fees from Pfizer and Daiichi-Sankyo, and research funding from Bayer, BMS and Daiichi-Sankyo. Gerd Mikus, Kathrin Foerster, Marlene Schaumaeker, Marie-Louise Lehmann and Jürgen Burhenne declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest that might be relevant to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikus, G., Foerster, K.I., Schaumaeker, M. et al. Microdosed Cocktail of Three Oral Factor Xa Inhibitors to Evaluate Drug–Drug Interactions with Potential Perpetrator Drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 58, 1155–1163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-019-00749-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-019-00749-1