Abstract
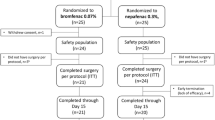
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug bromfenac has recently been reformulated with a lower pH to facilitate a reduction in the concentration of bromfenac (to 0.07 %) while ensuring an ocular bioavailability similar to that of the 0.09 % formulation. Bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07 % (hereafter referred to as bromfenac 0.07 %) [Prolensa®] is a once-daily topical ophthalmic solution available in the USA and Canada for the treatment of postoperative inflammation and the reduction of ocular pain in patients who have undergone cataract surgery. In an integrated analysis of two multicentre, phase III studies, bromfenac 0.07 % was significantly more effective than placebo in reducing ocular inflammation and pain. In these studies, bromfenac 0.07 % was well tolerated, with significantly lower incidences of adverse events, and adverse events affecting the study eye than with placebo. The most common adverse events in the study eye (eye pain, anterior chamber inflammation, foreign body sensation, photophobia, conjunctival hyperaemia and corneal oedema) occurred in numerically fewer bromfenac 0.07 % than placebo recipients. Thus, current evidence suggests once-daily bromfenac 0.07 % extends the treatment options currently available for the management of postoperative inflammation and pain following cataract surgery.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Harazi SM, Feldman RM. Control of intra-ocular inflammation associated with cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2001;12(1):4–8.
Dua HS, Attre R. Treatment of post-operative inflammation following cataract surgery: a review. European Ophthalmic Review. 2012;6(2):98–103.
Rajpal RK, Ross B, Rajpal SD, et al. Bromfenac ophthalmic solution for the treatment of postoperative ocular pain and inflammation: safety, efficacy, and patient adherence. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:925–31.
Baklayan GA, Muñoz M. The ocular distribution of 14C-labeled bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07 % in a rabbit model. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014;8:1717–24.
Ahuja M, Dhake AS, Sharma SK, et al. Topical ocular delivery of NSAIDs. AAPS J. 2008;10(2):229–41.
ISTA Pharmaceuticals Inc. Bromday (bromfenac ophthalmic solution) 0.09 %: US prescribing information. 2010. http://www.fda.gov/. Accessed 22 Jun 2015.
Bausch & Lomb Inc. PROLENSA™ (bromfenac ophthalmic solution) 0.07 %: US prescribing information. 2013. http://www.fda.gov/. Accessed 22 Jun 2015.
Schoenberger SD, Kim SJ. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for retinal disease. Int J Inflam. 2013. doi:10.1155/2013/281981
Kida T, Kozai S, Takahashi H, et al. Pharmacokinetics and efficacy of topically applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in retinochoroidal tissues in rabbits. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(5):e96481.
Ruiz J, López M, Milà J, et al. QSAR and conformational analysis of the antiinflammatory agent amfenac and analogues. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1993;7(2):183–98.
Singer DD, Kennedy J, Wittpenn JR. Topical NSAIDs effect on corneal sensitivity. Cornea. 2015;34(5):541–3.
Geneva II, Henderson BA. Prospective interventional pilot study using bromfenac 0.07 % after cataract surgery for prevention of macular thickening. In: American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery & American Society of Ophthalmic Administrators Symposium & Congress (ASCRS). Boston, MA. 2014.
Data on file, Bausch & Lomb Inc, 2015.
Walters TR, Goldberg DF, Peace JH, et al. Bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07 % dosed once daily for cataract surgery: results of 2 randomized controlled trials. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(1):25–33.
US FDA. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research application number 203168Orig1s000: summary review. 2013. http://www.fda.gov/. Accessed 22 Jun 2015.
Silverstein SM, Jackson MA, Goldberg DF, et al. The efficacy of bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07 % dosed once daily in achieving zero-to-trace anterior chamber cell severity following cataract surgery. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014;8:965–72.
Health Canada. Summary basis of decision (SBD) for Prolensa. 2015. http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/. Accessed 22 Jun 2015.
Goldkind L, Laine L. A systematic review of NSAIDs withdrawn from the market due to hepatotoxicity: lessons learned from the bromfenac experience. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2006;15(4):213–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding. During the peer review process, the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on this article. Changes resulting from comments received were made by the author on the basis of scientific and editorial merit. Sheridan Hoy is a salaried employee of Adis/Springer.
Additional information
The manuscript was reviewed by: S. J. Kim, Department of Ophthalmology, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN, USA; S. M. Silverstein, Silverstein Eye Centers, Kansas City, MO, USA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoy, S.M. Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution 0.07 %: A Review of Its Use After Cataract Surgery. Clin Drug Investig 35, 525–529 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0309-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-015-0309-3