Abstract
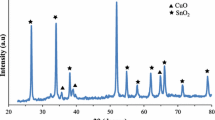
In this work, (1−x)CdO–xSnO2 nanocomposites (≤ 0.15) have been synthesized via hydrothermal route. The structural study reveals that CdO nanostructures possess crystalline phase and cubic structure. The CdO–SnO2 nanocomposites possess both cubic and orthorhombic structure with good crystallinity. The crystallite size in the nanocomposites was found to be in the range of 9.6–19.6 nm. Field emission scanning electronic microscopy and high-resolution tunnelling microscopy analysis confirm the presence of both cubic and orthorhombic structures which is also confirmed from X-ray diffraction studies. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) studies confirm that CdO–SnO2 nanocomposites possess the characteristics band of both CdO and SnO2 nanostructures. The UV–visible absorption studies confirm that the optical absorption band in CdO–SnO2 nanocomposites possesses both blue and red shift as compared to that of CdO nanostructures. Photoluminescence spectroscopy studies reveal the appearance of strong emission peak at 513, 469 and 369 nm corresponding to green, blue and violet emission spectrum, respectively, in CdO–SnO2 nanocomposites. The FTIR studies confirm the presence of hydroxyl and water functional group due to atmospheric water vapours and chemical bonding in CdO and CdO–SnO2 nanocomposites. Raman spectroscopy confirms the presence of Raman bands of both CdO and SnO2 phases in the CdO–SnO2 nanocomposites.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.H.C. Camargo, K.G. Satyanarayana, F. Wypych, Mater. Res. 12, 1 (2007)
Z.L. Wang, Mater. Today 7(6), 26 (2004)
H. Wang, A.L. Rogach, Chem. Mater. 26, 123 (2014)
T. Singh, D.K. Pandya, R. Singh, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 945 (2011)
A.C. Cakir, S. Erten-Ela, Adv. Powder Technol. 23, 655 (2012)
W.H. Zhang, W.D. Zhang, Sens. Actuators B 2, 403 (2008)
X. Jia, H. Fan, L. Qin, C. Yang, J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 31, 1405 (2010)
H. Karami, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 5, 720 (2010)
S.P. Meshram, J.D. Ambekar, I.S. Mulla, D.P. Amalnerkar, P.V. Adhyapak, J. Nanoeng. Nanomanuf. 4(2), 127 (2014)
E. Mosquera, I.D. Pozo, M. Morel, J. Solid State Chem. 206, 265 (2013)
S. Erten-Ela, Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 436831 (2013)
A. Hamrouni, N. Moussaa, F. Parrino, A.D. Paola, A. Houas, L. Palmisano, J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 390, 133 (2014)
W. Chen, Q. Li, L. Xu, W. Zeng, J. Nano Sci. Nanotechnol. 15, 1245 (2015)
C.J.D. Godines, F.J.F. Ruiz, R.C. Perez, G.T. Delgado, F.J.E. Broitman, J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 74, 114 (2015)
N.B. Hasan, G.H. Mohammed, M.A.A. Majeed, Phys. Astronaut. 59, 62 (2015)
R. Chandiramouli, B.G. Jeyaprakash, Solid State Sci. 16, 102 (2013)
F.T. Thema, P. Beukes, A.G. Fakim, M. Maaza, J. Alloys Compd. 646, 1043 (2015)
X. Fu, J. Liu, T. Han, X. Zhang, F. Meng, J. Liu, Sens. Actuators B 184, 260 (2013)
G.E. Patil, D.D. Kajale, V.B. Gaikwad, G.H. Jain, Int. Nano Lett. 2, 17 (2012)
J. Pan, H. Shen, S. Mathur, J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 1 (2011)
A. Ayeshamariam, C. Sanjeeviraja, R.P. Samy, J. Photonics Spintron. 2, 2324 (2013)
A.T. Ravichandran, A.R. Xavier, K. Pushpanathan, B.M. Nagabhushana, R. Chandramohan, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 2693 (2016)
N.C.S. Selvam, R.T. Kumar, K. Yogeenth, L.J. Kennedy, G. Sekaran, J.J. Vijaya, Powder Technol. 211, 250 (2011)
A. Tadjarodi, M. Imani, Mater. Lett. 65, 1025 (2011)
H. Seema, K.C. Kemp, V. Chandra, K.S. Kim, Nanotechnology 23, 355705 (2012)
A. Kumar, L. Rout, R.S. Dhaka, S.L. Samal, P. Dash, RSC Adv. 5, 39193 (2015)
L. Tan, L. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Nanomater. 2011, 529874 (2011)
A. Kumar, A.C. Pandey, R. Parkash, Catal. Sci. Technol. 2, 2533 (2012)
K. Anandhan, R.T. Kumar, Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 143, 476 (2015)
E.A. Davis, N.F. Mott, Philos. Mag. 22, 903 (1970)
Z.X. Yang, W. Zhong, Y.X. Yin, X. Du, Y. Deng, C. Au, Y.W. Du, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 961 (2010)
N. Rajesh, J.C. Kannanb, T.K. Kumarc, G. Neri, Acta Phys. Pol. A 125, 1229 (2014)
S. Kumar, A.K. Ojha, AIP Adv. 3, 052109 (2013)
S. Kumar, A.K. Ojha, R.K. Singh, J. Raman Spectrosc. 45, 717 (2014)
R. Cusco, J. Ibanez, N.D. Amador, L. Artus, J.Z. Perez, V.M. Sanjose, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 063519 (2010)
S. Kumar, A.K. Ojha, B. Walkenfort, J. Photochem. Photobiol. 159, 111 (2016)
T.M. Khan, T. Shahid, M. Zakria, I.R. Shakoor, Electron. Mater. Lett. 11, 366 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India (No. SB/EMEQ/190/2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirohi, K., Kumar, S., Singh, V. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of CdO–SnO2 Nanocomposites Prepared by Hydrothermal Method. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 31, 254–262 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-017-0659-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-017-0659-3