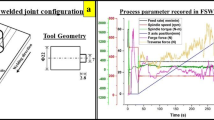
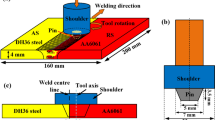
Abstract
In the present work, DH36 steel and AISI 1008 steel sheets were joined using friction stir welding (FSW) process to investigate the influence of the rotational speed, traverse speed, and tool offset on temperature distribution, z-force, microstructure, and mechanical properties of the welded specimens. At a traverse speed (v) of 50 mm/min with a rotational speed (ω) of 600 rpm and tool offset of 2 mm, the maximum impact toughness and hardness were obtained due to higher grain refinement. The transverse tensile test specimens fractured in the weaker material (i.e., AISI 1008 steel) and exhibited the ultimate tensile strength values at least on the level of the weaker material. The impact toughness and hardness were highly dependent on the grain size variation. The effect of pitch ratio (ω/v) on grain size variation was more as compared with that on tool offset. Increasing the pitch ratio reduced the grain size and improved the impact toughness and hardness. Stir zone exhibited the acicular-shaped bainitic ferrite in DH36 steel and Widmanstatten ferrite grains in AISI 1008 steel. The higher hardness values were observed in thermo-mechanically affected zone of both steels due to significant grain refinement. Increasing the rotational speed and decreasing the traverse speed result in a higher welding temperature, which reduced the z-force.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin JP, Stanhope C, Gascoyne S (2011) Novel techniques for corner joints using friction stir welding. In: TMS 2001 Annual Meeting & Exhibition. Friction Stir Welding and Processing VI, San Diego, pp 177–186
Tiwari A, Singh P, Pankaj P, Biswas P, Kore SD, Pal S (2019) Effect of tool offset and rotational speed in dissimilar friction stir welding of AISI 304 stainless steel and mild steel. J Mater Eng Perform 28(10):6365–6379
Murr LE (2010) A review of FSW research on dissimilar metal and alloy systems. J Mater Eng Perform 19(8):1071–1089
Mishra RS, Ma ZY (2005) Friction stir welding and processing. M Sci Eng R Rep 50(1–2):1–78
Tiwari A, Pankaj P, Biswas P, Kore SD, Rao AG (2019) Tool performance evaluation of friction stir welded shipbuilding grade DH36 steel butt joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103(5–8):1989–2005
Cheng CP, Lin HM, Lin JC (2010) Friction stir welding of ductile iron and low carbon steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 15(8):706–711
Lakshminarayanan AK, Balasubramanian V (2010) An assessment of microstructure, hardness, tensile and impact strength of friction stir welded ferritic stainless steel joints. Mater Des 31(10):4592–4600
Sunilkumar D, Muthukumaran S, Vasudevan M, Reddy MG (2019) Effect of friction stir and activated-GTA welding processes on the 9Cr–1Mo steel to 316LN stainless steel dissimilar weld joints. Sci Technol Weld Joi 1–9
Rai R, De A, Bhadeshia HKDH, DebRoy T (2011) Friction stir welding tools. Sci Technol Weld Joi 16(4):325–342
Rahimi S, Konkova TN, Violatos I, Baker TN (2019) Evolution of microstructure and crystallographic texture during dissimilar friction stir welding of duplex stainless steel to low carbon-manganese structural steel. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 50(2):664–687
Thomas WM, Threadgill PL, Nicholas ED (1999) Feasibility of friction stir welding steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 4(6):365–372
Miyano Y, Fujii H, Sun Y, Katada Y, Kuroda S, Kamiya O (2011) Mechanical properties of friction stir butt welds of high nitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 528(6):2917–2921
Jafarzadegan M, Feng AH, Abdollah-Zadeh A, Saeid T, Shen J, Assadi H (2012) Microstructural characterization in dissimilar friction stir welding between 304 stainless steel and st37 steel. Mater Charact 74:28–41
Lienert TJ, Stellwag WL Jr, Grimmett BB, Warke RW (2003) Friction stir welding studies on mild steel. Weld J N Y 82(1):1–S
Kucukomeroglu T, Aktarer SM, Ipekoglu G, Cam G (2018) Mechanical properties of friction stir welded St 37 and St 44 steel joints. Mater Test 60(12):1163–1170
Tang W, Yang X, Li S, Li H (2019) Microstructure and properties of CLAM/316L steel friction stir welded joints. J Mater Process Tech 271:189–201
Logan BP, Toumpis AI, Galloway AM, McPherson NA, Hambling SJ (2016) Dissimilar friction stir welding of duplex stainless steel to low alloy structural steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 21(1):119
Singh DK, Sahoo G, Basu R, Sharma V, Mohtadi-Bonab MA (2018) Investigation on the microstructure-mechanical property correlation in dissimilar steel welds of stainless steel SS 304 and medium carbon steel EN 8. J Manuf Process 36:281–292
Takashima Y, Ito Y, Lu F, Minami F (2019) Fracture toughness evaluation for dissimilar steel joints by Charpy impact test. Weld World 2019:1–12
Choi DH, Ahn BW, Yeon YM, Park SH, Sato YS, Kokawa H, Jung SB (2011) Microstructural characterizations following friction stir welding of dissimilar alloys of low-and high-carbon steels. Mater Trans 52(7):1500–1505
Kalvala PR, Akram J, Misra M, Ramachandran D, Gabbita JR (2016) Low temperature friction stir welding of P91 steel. Def Technol 12(4):285–289
Fujii H, Cui L, Nakata K, Nogi K (2008) Mechanical properties of friction stir welded carbon steel joints-friction stir welding with and without transformation. Weld World 52(9˗10):75–81
Ipekoglu G, Kucukomeroglu T, Aktarer SM, Sekban DM, Cam G (2019) Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar St37/St52 joints. Mater Res Express 6(4):1–8
Dong J, Zhang D, Zhang W, Zhang W, Qiu C (2018) Microstructure evolution during dissimilar friction stir welding of AA7003-T4 and AA6060-T4. Materials 11(3):342
Simar A, Avettand-Fenoel MN (2017) State of the art about dissimilar metal friction stir welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 22(5):389–403
Ceschini L, Boromei I, Minak G, Morri A, Tarterini F (2007) Effect of friction stir welding on microstructure, tensile and fatigue properties of the AA7005/10 vol.% Al2O3p composite. Compos Sci Technol 67(3–4):605–615
Grujicic M, Arakere G, Yalavarthy HV, He T, Yen CF, Cheeseman BA (2010) Modeling of AA5083 material-microstructure evolution during butt friction-stir welding. J Mater Eng Perform 19(5):672–684
Crawford R, Cook GE, Strauss AM, Hartman DA, Stremler MA (2006) Experimental defect analysis and force prediction simulation of high weld pitch friction stir welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 11(6):657–665
Failla DM (2009) Friction stir welding and microstructure simulation of HSLA-65 and austenitic stainless steels, Thesis, The Ohio State University
Gan W, Li ZT, Khurana S (2007) Tool materials selection for friction stir welding of L80 steel. Sci Technol Weld Join 12(7):610–613
Thompson BT (2010) Tool degradation characterization in the friction stir welding of hard metals (Doctoral dissertation, The Ohio State University)
Mishra RS, Komarasamy M (2016) Friction stir welding of high strength 7XXX aluminum alloys. Butterworth-Heinemann
Adamowski J, Gambaro C, Lertora E, Ponte M, Szkodo M (2007) Analysis of FSW welds made of aluminium alloy AW6082-T6. Arch Mater Sci Eng 28(8):453–460
Tiwari A, Pankaj P, Bharadwaj A, Singh P, Biswas P, Kore SD (2019) Friction stir welding of shipbuilding grade DH36 steel. Manufacturing Engineering. Springer, Singapore, pp 17–34
Palanivel R, Mathews PK, Murugan N, Dinaharan I (2012) Effect of tool rotational speed and pin profile on microstructure and tensile strength of dissimilar friction stir welded AA5083-H111 and AA6351-T6 aluminum alloys. Mater Des 40:7–16
Micallef D, Camilleri D, Toumpis A, Galloway A, Arbaoui L (2016) Local heat generation and material flow in friction stir welding of mild steel assemblies. P I Mech Eng L-J Mat 230(2):586–602
Hernandez CA, Ferrer VH, Mancilla JE, Martínez LC (2017) Three-dimensional numerical modeling of the friction stir welding of dissimilar steels. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(5–8):1567–1581
Saeid T, Abdollah-Zadeh A, Assadi H, Ghaini FM (2008) Effect of friction stir welding speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 496(1–2):262–268
Jain R, Pal SK, Singh SB (2016) A study on the variation of forces and temperature in a friction stir welding process: a finite element approach. J Manuf Process 23:278–286
Krishnan KN (2002) On the formation of onion rings in friction stir welds. Mater Sci Eng A 327(2):246–251
Tingey C, Galloway A, Toumpis A, Cater S (1980-2015) Effect of tool centreline deviation on the mechanical properties of friction stir welded DH36 steel. Mater Des 65:896–906
Sirong Y, Xianjun C, Huang Z, Yaohui L (2010) Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welding of AZ31B magnesium alloy added with cerium. J Rare Earth 28(2):316–320
McPherson NA, Galloway AM, Cater SR, Hambling SJ (2013) Friction stir welding of thin DH36 steel plate. Sci Technol Weld Joi 18(5):441–450
Toumpis A, Galloway A, Cater S, McPherson N (2014) Development of a process envelope for friction stir welding of DH36 steel–a step change. Mater Des 62:64–75
Qian J, Li J, Sun F, Xiong J, Zhang F, Lin X (2013) An analytical model to optimize rotation speed and travel speed of friction stir welding for defect-free joints. Scr Mater 68(3–4):175–178
Arora A, Zhang Z, De A, DebRoy T (2009) Strains and strain rates during friction stir welding. Scr Mater 61(9):863–866
Fonda RW, Knipling KE, Bingert JF (2008) Microstructural evolution ahead of the tool in aluminum friction stir welds. Scr Mater 58(5):343–348
Sahu PK, Pal S (2017) Mechanical properties of dissimilar thickness aluminium alloy weld by single/double pass FSW. J Mater Process Technol 243:442–455
Buffa G, Hua J, Shivpuri R, Fratini L (2006) A continuum based fem model for friction stir welding-model development. Mater Sci Eng A 419(1–2):389–396
Kadian AK (2018) Material flow analysis of similar and dissimilar friction stir welding (Doctoral dissertation)
Al-Moussawi M, Smith AJ, Young A, Cater S, Faraji M (2017) Modelling of friction stir welding of DH36 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92(1–4):341–360
Azimzadegan T, Serajzadeh S (2010) An investigation into microstructures and mechanical properties of AA7075-T6 during friction stir welding at relatively high rotational speeds. J Mater Eng Perform 19(9):1256–1263
Sahu PK, Pal S (2018) Effect of FSW parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of AM20 welds. Mater Manuf Process 33(3):288–298
Sahu PK, Pal S, Pal SK, Jain R (2016) Influence of plate position, tool offset and tool rotational speed on mechanical properties and microstructures of dissimilar Al/Cu friction stir welding joints. J Mater Process Tech 235:55–67
Booth DP, Starink MJ, Sinclair I (2007) Analysis of local microstructure and hardness of 13 mm gauge 2024-T351 AA friction stir welds. Mater Sci Technol 23(3):276–284
Cho HH, Kang SH, Kim SH, Oh KH, Kim HJ, Chang WS, Han HN (2012) Microstructural evolution in friction stir welding of high-strength line pipe steel. Mater Des 34:258–267
Khan NZ, Siddiquee AN, Khan ZA, Mukhopadhyay AK (2017) Mechanical and microstructural behavior of friction stir welded similar and dissimilar sheets of AA2219 and AA7475 aluminium alloys. J Alloys Compd 695:2902–2908
Liu H, Hu Y, Dou C, Sekulic DP (2017) An effect of the rotation speed on microstructure and mechanical properties of the friction stir welded 2060-T8 Al-Li alloy. Mater Charact 123:9–19
Ghosh M, Kumar K, Mishra RS (2012) Process optimization for friction-stir-welded martensitic steel. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 43(6):1966–1975
Aoki S, Kishimoto K, Yoshida T, Sakata M (1987) A finite element study of the near crack tip deformation of a ductile material under mixed mode loading. J Mech Phys Solids 35(4):431–455
Motalleb-Nejad P, Saeid T, Heidarzadeh A, Darzi K, Ashjari M (2014) Effect of tool pin profile on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AZ31B magnesium alloy. Mater Des 59:221–226
Tiwari A, Singh P, Pankaj P, Biswas P, Kore SD (2019) FSW of low carbon steel using tungsten carbide (WC-10wt.% Co) based tool material. J Mech Sci Technol 33(10):4931–4938
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Central Instruments Facility of IIT Guwahati for providing the required research facilities.
Funding
The authors received financial support from the Naval Research Board (NRB), Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Commission III - Resistance Welding, Solid State Welding, and Allied Joining Process
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pankaj, P., Tiwari, A., Biswas, P. et al. Experimental studies on controlling of process parameters in dissimilar friction stir welding of DH36 shipbuilding steel–AISI 1008 steel. Weld World 64, 963–986 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-00886-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-00886-3