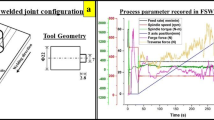
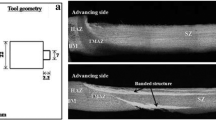
Abstract
In the present study, dissimilar friction stir welding was carried out between stainless steel (UNS S30400) and mild steel (UNS G10080) plates of 4 mm thickness using a tungsten carbide tool. The influence of tool rotational speeds (600, 875 rpm) and tool offsets (0.6, 1.2 mm) on mechanical properties, i.e., hardness, tensile strength, and impact toughness of welded joints was investigated. Maximum tensile strength of the joint was about 107.6% of the mild steel under rotational speed of 875 rpm and tool offset of 1.2 mm. The maximum hardness reached in the stir zone was about 281 HV0.5 due to the phase transformations and grain refinement. Charpy’s notch toughness of the welded joints was observed lower than the base materials. The microstructural characterizations were carried by using an optical microscope, and FESEM–EDS analysis which revealed the complex material mixing and material movement during the welding. Tungsten-rich bands were observed in the weld micrograph especially toward the advancing side. During this study, various wear mechanisms like oxidation wear, abrasive wear, and adhesion wear were responsible for the degradation of tungsten carbide tool.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Wang, K. Wang, W. Wang, L. Huang, P. Peng, and H. Yu, Materials Characterization Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Friction Stir Welded Type 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel to Q235 Low Carbon Steel, Mater. Charact., 2019, 155, p 109803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.109803
D. Kumar, G. Sahoo, R. Basu, V. Sharma, and M.A. Mohtadi-bonab, Investigation on the Microstructure—Mechanical Property Correlation in Dissimilar Steel Welds of Stainless Steel SS 304 and Medium Carbon Steel EN 8, J. Manuf. Process., 2018, 36, p 281–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.10.018
H. Vashishtha, R.V. Taiwade, S. Sharma, and A.P. Patil, Effect of Welding Processes on Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Weldments Between Conventional Austenitic and High Nitrogen Austenitic Stainless Steels, J. Manuf. Process., 2017, 25, p 49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.10.008
L.E. Murr, A Review of FSW Research on Dissimilar Metal and Alloy Systems, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2010, 19, p 1071–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9598-0
K.P. Mehta and V.J. Badheka, A Review on Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding of Copper to Aluminum: Process, Properties, and Variants, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2016, 31, p 233–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1025971
R.S. Mishra and Z.Y. Ma, Friction Stir Welding and Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep., 2005, 50, p 1–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2005.07.001
R. Rai, A. De, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, and T. DebRoy, Review: Friction Stir Welding Tools, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2011, 16, p 325–342. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171811Y.0000000023
G. Cam, Friction Stir Welded Structural Materials: Beyond Al-Alloys, Int. Mater. Rev., 2011, 56, p 1–48. https://doi.org/10.1179/095066010X12777205875750
D.-H. Choi, C.-Y. Lee, B.-W. Ahn, Y.-M. Yeon, S.-H.C. Park, Y.-S. Sato et al., Effect of Fixed Location Variation in Friction Stir Welding of Steels with Different Carbon Contents, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2010, 15, p 299–304. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217109X12577814486737
D.H. Choi, B.W. Ahn, Y.M. Yeon, S.H.C. Park, Y.S. Sato, H. Kokawa et al., Microstructural Characterizations Following Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Alloys of Low- and High-Carbon Steels, Mater. Trans., 2011, 52, p 1500–1505. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2010438
B.P. Logan, A.I. Toumpis, A.M. Galloway, N.A. McPherson, and S.J. Hambling, Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding of Duplex Stainless Steel to Low Alloy Structural Steel, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2016, 21, p 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171815Y.0000000063
W.M. Thomas, P.L. Threadgill, and E.D. Nicholas, Feasibility of Friction Stir Welding Steel, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 1999, 4, p 365–372. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217199101538012
C.P. Cheng, H.M. Lin, and J.C. Lin, Friction Stir Welding of Ductile Iron and Low Carbon Steel, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2010, 15, p 706–711. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217110X12785889549507
M. Jafarzadegan, A. Abdollah-zadeh, A.H.H. Feng, T. Saeid, J. Shen, and H. Assadi, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Dissimilar Friction Stir Weld between Austenitic Stainless Steel and Low Carbon Steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 29, p 367–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.02.008
A. Tiwari, P. Pankaj, P. Biswas, S.D. Kore, and A.G. Rao, Tool Performance Evaluation of Friction Stir Welded Shipbuilding Grade DH36 Steel Butt Joints, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03618-0
Y.D. Chung, H. Fujii, Y. Sun, and H. Tanigawa, Interface Microstructure Evolution of Dissimilar Friction Stir Butt Welded F82H Steel and SUS304, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, 528, p 5812–5821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.04.023
L. Zhou, R.X. Zhang, G.H. Li, W.L. Zhou, Y.X. Huang, and X.G. Song, Effect of Pin Profile on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Spot Welded Al-Cu Dissimilar Metals, J. Manuf. Process., 2018, 36, p 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.09.017
C. Tingey, A. Galloway, A. Toumpis, and S. Cater, Effect of Tool Centreline Deviation on the Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded DH36 Steel, Mater. Des., 2015, 65, p 896–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.017
Y. Mao, L. Ke, F. Liu, Q. Liu, C. Huang, and L. Xing, Effect of Tool Pin Eccentricity on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Friction Stir Welded 7075 Aluminum Alloy Thick Plate, Mater. Des., 2014, 62, p 334–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.05.038
D.K. Yaduwanshi, S. Bag, and S. Pal, On the Effect of Tool Offset in Hybrid-FSW of Copper-Aluminium Alloy, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2018, 33, p 277–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1279309
S. Zandsalimi, A. Heidarzadeh, and T. Saeid, Dissimilar Friction-Stir Welding of 430 Stainless Steel and 6061 Aluminum Alloy: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Joints, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl., 2018, https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420718789447
G. Guo and Y. Shen, Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Stainless Steels: Evaluation of Flow Pattern, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(5), art. no. 056510
R. Nandan, G.G. Roy, T.J. Lienert, and T. Debroy, Three-Dimensional Heat and Material Flow During Friction Stir Welding of Mild Steel, Acta Mater., 2007, 55, p 883–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.09.009
M. Al-Moussawi and A.J. Smith, Defects in Friction Stir Welding of Steel, Metallog.r Microstruct. Anal., 2018, 7, p 194–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-018-0438-1
R. Stevenson, A. Toumpis, and A. Galloway, Defect Tolerance of Friction Stir Welds in DH36 Steel, Mater. Des., 2015, 87, p 701–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.08.064
C. Cheng, H. Lin, J. Lin, C. Cheng, H. Lin, and J. Lin, Friction Stir Welding of Ductile Iron and Low Carbon Steel Friction Stir Welding of Ductile Iron and Low Carbon Steel, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2013, 15, p 706–711. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217110X12785889549507
G. İpekoğlu, T. Küçükömeroğlu, S.M. Aktarer, D. Murat Sekban, and G. Çam, Investigation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Dissimilar St37/St52 Joints, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(4), art. no. 046537.
S. Rahimi, T.N. Konkova, I. Violatos, and T.N. Baker, Evolution of Microstructure and Crystallographic Texture During Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding of Duplex Stainless Steel to Low Carbon-Manganese Structural Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2019, 50, p 664–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-5023-3
T. Saeid, A. Abdollah-zadeh, H. Assadi, and Ghaini F. Malek, Effect of Friction Stir Welding Speed on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Duplex Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, 496, p 262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.05.025
D.M. Sekban, S.M. Aktarer, P. Xue, Z.Y. Ma, and G. Purcek, Impact Toughness of Friction Stir Processed Low Carbon Steel Used in Shipbuilding, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, 672, p 40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.06.063
A.K. Lakshminarayanan, V. Balasubramanian, and M. Salahuddin, Microstructure, Tensile and Impact Toughness Properties of Friction Stir Welded Mild Steel, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2010, 17, p 68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60186-0
A. Tiwari, P. Singh, P. Biswas, and S.D. Kore, Friction Stir Welding of Low-Carbon Steel, Advanced Materials, Mechanical and Structural Engineering, P. Sahoo and J.P. Davim, Ed., Springer, Cham, 2019, p 209–226 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96968-8_10
D.H. Choi, C.Y. Lee, B.W. Ahn, J.H. Choi, Y.M. Yeon, K. Song et al., Frictional Wear Evaluation of WC-Co Alloy Tool in Friction Stir Spot Welding of Low Carbon Steel Plates, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2009, 27, p 931–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2009.05.002
A. Warren, A. Nylund, and I. Olefjord, Oxidation of Tungsten and Tungsten Carbide in Dry and Humid Atmospheres, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard. Mater., 1996, 14, p 345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-4368(96)00027-3
W. Gan, Z.T. Li, and S. Khurana, Tool Materials Selection for Friction Stir Welding of L80 Steel, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2007, 12, p 610–613. https://doi.org/10.1179/174329307X213792
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by Naval Research Board (NRB), Govt. of India. The authors are also thankful to the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Central Instruments Facility and Department of Physics of IIT Guwahati, for providing the required research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, A., Singh, P., Pankaj, P. et al. Effect of Tool Offset and Rotational Speed in Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding of AISI 304 Stainless Steel and Mild Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 6365–6379 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04362-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04362-y