Abstract
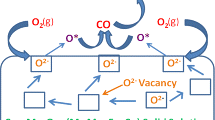
In the present study nanosized Sm3+, Eu3+, and Gd3+ doped ceria (Ce0.8M0.2O2−δ, M = Sm, Eu, and Gd) catalytic systems were synthesized by coprecipitation method. The prepared samples were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Raman spectroscopy, UV–Visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV–Vis DRS), and temperature programmed reduction (TPR) and finally evaluated for CO oxidation studies. The XRD results suggested that lattice expansion occurred with the introduction of trivalent dopants into the ceria lattice and confirms the formation of solid solutions. Raman spectra corroborated the existence of oxygen defects. TEM results indicate the presence of nanocrystalline nature of the prepared catalysts. TPR analysis revealed that trivalent dopants decreased the surface reduction temperature of the pure ceria by minimum 141 and maximum 249 K. From the activity studies, it was noticed that for pure ceria the observed T50 is 613 K, at this temperature doped ceria exhibited minimum 75 % CO conversion. The above characterization studies demonstrate that trivalent dopants successfully tuned the structural and catalytic properties of pure ceria. Among the examined samples, Ce0.8Sm0.2O2−δ material improved the CO oxidation activity much better than other samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li G-R, Qu D-L, Wang Z-L, Su C-Y, Tong Y-X, Arurault L (2009) Ceria-terbia solid solution nanobelts with high catalytic activities for CO oxidation. Chem Commun 48:7557–7559
Kašpar J, Fornasiero P, Graziani M (1999) Use of CeO2-based oxides in the three-way catalysis. Catal Today 50:285–298
Sutradhar N, Sinhamahapatra A, Pahari S, Jayachandran M, Subramanian B, Bajaj HC, Panda AB (2011) Facile low-temperature synthesis of ceria and samarium-doped ceria nanoparticles and catalytic allylic oxidation of cyclohexene. J Phys Chem C 115:7628–7637
Naga Durgasri D, Vinodkumar T, Sudarsanam P, Reddy BM (2014) Nanosized CeO2–Gd2O3 mixed oxides: study of structural characterization and catalytic CO oxidation activity. Catal Lett 144:971–979
Skorodumova NV, Simak SI, Lundqvist BI, Abrikosov IA, Johansson B (2002) Quantum origin of the oxygen storage capability of ceria. Phys Rev Lett 89:166601–166604
Singh P, Hegde MS (2008) Controlled synthesis of nanocrystalline CeO2 and Ce1−xMxO2−δ (M = Zr, Y, Ti, Pr and Fe) solid solutions by the hydrothermal method: structure and oxygen storage capacity. J Solid State Chem 181:3248–3256
Li J-G, Ikegami T, Mori T, Wada T (2001) Reactive Ce0.8RE0.2O1.9 (RE = La, Nd, Sm, Gd, Dy, Y, Ho, Er, and Yb) powders via carbonate coprecipitation. 1. Synthesis and characterization. Chem Mater 13:2913–2920
Avila-Paredes HJ, Shvareva T, Chen W, Navrotsky A, Kim S (2009) A correlation between the ionic conductivities and the formation enthalpies of trivalent-doped ceria at relatively low temperatures. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:8580–8585
Reddy BM, Thrimurthulu G, Katta L, Yamada Y, Park S-E (2009) Structural characteristics and catalytic activity of nanocrystalline ceria-praseodymia solid solutions. J Phys Chem C 113:15882–15890
Vinodkumar T, Naga Durgasri D, Reddy BM (2013) Design of transition and rare earth metal doped ceria nanocomposite oxides for CO oxidation. Int J Adv Eng Sci Appl Math 5:224–231
Thrimurthulu G, Rao KN, Devaiah D, Reddy BM (2012) Nanocrystalline ceria–praseodymia and ceria–zirconia solid solutions for soot oxidation. Res Chem Intermed 38:1847–1855
Naga Durgasri D, Vinodkumar T, Reddy BM (2014) Facile synthesis of catalytically active CeO2–Gd2O3 solid solutions for soot oxidation. J Chem Sci 126:429–435
Hernández WY, Laguna OH, Centeno MA, Odriozola JA (2011) Structural and catalytic properties of lanthanide (La, Eu, Gd) doped ceria. J Solid State Chem 184:3014–3020
Yang Z, Mao D, Guo X, Lu G (2014) CO oxidation over CuO catalysts supported on CeO2–ZrO2 prepared by microwave-assisted co-precipitation: the influence of CuO content. J Rare Earths 32:117–123
Guo M, Lu J, Wu Y, Wang Y, Luo M (2011) UV and visible Raman studies of oxygen vacancies in rare-earth-doped ceria. Langmuir 27:3872–3877
Hernández WY, Centeno MA, Romero-Sarria F, Odriozola JA (2009) Synthesis and characterization of Ce1−xEuxO2−x/2 mixed oxides and their catalytic activities for CO oxidation. J Phys Chem C 113:5629–5635
Reddy BM, Bharali P, Thrimurthulu G, Saikia P, Katta L, Park S-E (2008) Catalytic efficiency of ceria–zirconia and ceria–hafnia nanocomposite oxides for soot oxidation. Catal Lett 123:327–333
Ferreira J, Tavares P, Figueiredo JL, Faria JL (2012) Effect of Mg, Ca, and Sr on CeO2 based catalysts for the oxidative coupling of methane: investigation on the oxygen species responsible for catalytic performance. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:10535–10541
Zhan W, Zhang X, Guo Y, Wang L, Guo Y, Lu G (2014) Synthesis of mesoporous CeO2–MnOx binary oxides and their catalytic performances for CO oxidation. J Rare Earths 32:146–152
Reddy BM, Bharali P, Saikia P, Khan A, Loridant S, Muhler M, Grünert W (2007) Hafnium doped ceria nanocomposite oxide as a novel redox additive for three-way catalysts. J Phys Chem C 111:1878–1881
Valechha D, Lokhande S, Klementova M, Subrt J, Rayalu S, Labhsetwar N (2011) Study of nano-structured ceria for catalytic CO oxidation. J Mater Chem 21:3718–3725
Wang Z, Wang Q, Liao Y, Shen G, Gong X, Han N, Liu H, Chen Y (2011) Comparative study of CeO2 and doped CeO2 with tailored oxygen vacancies for CO oxidation. ChemPhysChem 12:2763–2770
Liu XW, Zhou KB, Wang L, Wang BY, Li YD (2009) Oxygen vacancy clusters promoting reducibility and activity of ceria nanorods. J Am Chem Soc 131:3140–3141
Liu Y, Wen C, Guo Y, Lu G (2010) Modulated CO oxidation activity of M-doped ceria (M = Cu, Ti, Zr, and Tb): role of the pauling electronegativity of M. J Phys Chem C 114:9889–9897
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge Prof. Dr. W Grünert, Ruhr University Bochum, Germany for providing CO oxidation results. TV, DND, and AR thank Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for the Research Fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, B.M., Vinodkumar, T., Naga Durgasri, D. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanostructured Ce0.8M0.2O2−δ (M = Sm, Eu, and Gd) Solid Solutions for Catalytic CO Oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. A Phys. Sci. 87, 155–161 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-016-0282-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-016-0282-0