Abstract
Phase separation with solvent exchange induced-in situ forming gel (ISG) is an attractive delivery system for periodontitis treatment. Eudragit® RS-PO (ERS) in N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP) was used as polymer matrix for doxycycline hyclate (DH)-loaded solvent-exchanged ISG; however, a high burst drug release was evident. The present study revealed the role of PEG 1500 on physicochemical properties and modification of a burst release for DH-loaded ISG. DH-loaded ISG system comprising PEG 1500 exhibited the Newtonian flow with acceptable injectability with PEG 1500 concentration dependence and high in vitro degradation owing to NMP and PEG 1500 liberation. Solvent exchange between NMP with PBS pH 6.8 conveyed the rapid phase separation of ERS/PEG 1500 as a matrix which the entrapped DH diffused out gradually. Both dialysis membrane and membrane-less methods proved the slower drug release of DH-loaded ERS ISG comprising PEG than PEG 1500-free ISG. SEM revealed the porous matrix topography from polymeric phase separation especially for higher PEG 1500 loading. PEG 1500 incorporation significantly decreased the inhibition diameter against S. aureus, E. coli and S. mutans (P < 0.05) indicating the retardation of drug release owing to the high viscosity of the PEG 1500. PEG 1500-incorporated DH-loaded ERS ISG exhibited the potential use for periodontitis treatment.
Graphical abstract
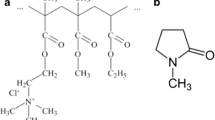
PEG loading into solvent induced ERS in situ forming gel for doxycycline hyclate periodontal pocket delivery.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abashzadeh R, Dinarvand M, Sharifzadeh G, Hassanzadeh G, Amini M, Atyabi F (2011) Formulation and evaluation of an in situ gel forming system for controlled delivery of triptorelin acetate. Eur J Pharm Sci 44:514–521
Ahmed TA, Ibrahim HM, Ibrahim F, Samy AM, Kaseem A, Nutan MTH, Hussain MD (2012) Development of biodegradable in situ implant and microparticle injectable formulations for sustained delivery of haloperidol. J Pharm Sci 10:3753–3762
Arendt-Nielsen L, Egekvist H, Bjerring P (2006) Pain following controlled cutaneous insertion of needles with different diameters. Somatosens Mot Res 23:37–43
Bodmeier R, Paeratakul O (1997) Plasticizer uptake by aqueous colloidal polymer dispersions used for the coating of solid dosage forms. Int J Pharm 52:17–26
Brodbeck KJ, DesNoyer JR, McHugh J (1999) Phase inversion dynamics of PLGA solutions related to drug delivery. Part II. The role of solution thermodynamics and bathside mass transfer. J Control Release 62:333–344
Do MP, Neut C, Metz H, Delcourt E, Mäder K, Siepmann J, Siepmann F (2015) In-situ forming composite implants for periodontitis treatment: how the formulation determines system performance. Int J Pharm 486:38–51
Engelhardt G, Fleig H (1993) Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) does not induce structural and numerical chromosomal aberrations in vivo. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol 298:149–155
Esposito E, Sebben S, Cortesi R, Menegatti E, Nastruzzi C (1999) Preparation and characterization of cationic microspheres for gene delivery. Int J Pharm 189:29–41
Hatefi A, Amsden B (2002) Biodegradable injectable in situ forming drug delivery systems. J Control Release 80:9–28
Heidari MR (2014) Reference module in biomedical sciences, Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 588–593
Irimia-Vladu M, Głowacki ED, Schwabegger G, Leonat L, Akpinar HZ, Sitter H, Bauer S, Sariciftci NS (2013) Natural resin shellac as a substrate and a dielectric layer for organic field-effect transistors. Green Chem 15:1473–1476
Jaiswal J, Gupta SK, Kreuter J (2004) Preparation of biodegradable cyclosporine nanoparticles by high-pressure emulsification-solvent evaporation process. J Control Release 96:69–178
Jouyban A, Fakhree MA, Shayanfar A (2010) Reivew of pharmaceutical applications of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. J Pharm Sci 13:524–535
Kempe S, Metz H, Mader K (2008) Do in situ forming PLG/NMP implants behave similar in vitro and in vivo: a non-invasive and quantitative EPR investigation on the mechanism of the implant formation process. J Control Release 130:220–225
Kogawa AC, Salgado HRN (2012) Doxycycline hyclate: a review of properties, applications and analytical methods. Int J Life Sci Pharm Res 2:11–25
Kojima H, Yoshihara K, Sawada T, Kondo H, Sako K (2008) Extended release of a large amount of highly water-soluble diltiazem hydrochloride by utilizing counter polymer in polyethylene oxides (PEO)/polyethylene glycol (PEG) matrix tablets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 70:556–562
Liu H, Venkatraman SS (2012) Cosolvent effects on the drug release and depot swelling in injectable in situ depot-forming systems. J Pharm Sci 101:1783–1793
Liu Q, Zhang H, Zhou G, Xie S, Zou H, Yu Y, Li G, Sun D, Zhang G, Lu Y, Zhong Y (2010) In vitro and in vivo study of thymosin alpha1 biodegradable in situ forming poly(lactide-co-glycolide) implants. Int J Pharm 397:122–129
Lopedota A, Trapani A, Cutrignelli A, Chiarantini L, Pantucci E, Curci R, Manuali E, Trapani G (2009) The use of ERS® RS 100/cyclodextrin nanoparticles for the transmucosal administration of glutathione. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 72:509–520
Mahadlek J, Charoenteeraboon J, Phaechamud T (2013) Benzoyl peroxide in situ forming antimicrobial gel for periodontitis treatment. Key Eng Mater 545:63–68
Martin A (1993) Physical pharmacy. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 393–476
McHugh AJ (2005) The role of polymer membrane formation in sustained release drug drlivery systems. J Control Release 109:211–221
Mohl S, Winter G (2004) Continuous release of the interferon alpha 2a from triglyceride matrices. J Control Release 97:67–78
Morcol T, Nagappan P, Nerenbaum L, Mitchell A, Bell SJD (2004) Calcium phosphate-PEG-insulin-casein (CAPIC) particles as oral delivery systems for insulin. Int J Pharm 277:91–97
Morishita M, Kamei N, Ehara J, Isowa K, Takayama K (2004) A novel approach using functional peptides for efficient intestinal absorption of insulin. J Control Release 118:177–184
Nirmal HB, Bakliwal SR, Pawar SP (2010) In-situ gel: new trends in controlled and sustained drug delivery system. Int J PharmTech Res 2:1398–1408
Okarter TU, Singla K (2000) The effects of plasticizers on the release of metoprolol tartrate from granules coated with a polymethacrylate film. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 26:323–329
Pandya Y, Sisodiya D, Dashora K (2014) Atrigel, implants and controlled released drug delivery system. Int J Biopharm 5:208–213
Parent M, Nouvel C, Koerber M, Sapin A, Maincent P, Boudier A (2013) PLGA in situ implants formed by phase inversion: critical physicochemical parameters to modulate drug release. J Control Release 172:292–304
Patel RR, Patel JK (2011) Development and evaluation of in situ novel intragastric controlled-release formulation of hydrochlorothiazide. Acta Pharm 61:73–82
Peppas NA (2004) Devices based on intelligent biopolymers for oral protein delivery. Int J Pharm 277:11–17
Phaechamud T, Mahadlek J, Charoenteeraboon J, Choopun S (2013)Characterization and antimicrobial activity of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone-loaded ethylene oxide-propylene oxide block copolymer thermosensitive gel. Indian J Pharm Sci 74:498–504.
Phaechamud T, Jantadee T, Mahadlek J, Charoensuksai P, Pichayakorn W (2016) Characterization of antimicrobial agent loaded ERS solvent exchange-induced in situ forming gels of periodontitis treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 18:494–508
Phaechamud T, Mahadlek J, Tuntarawongsa S (2017) Peppermint oil/doxycycline hyclate-loaded ERS in situ forming gel for periodontitis treatment. J Pharm Investig 48:451–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-017-0340-x
Popa L, Ghica MV, Dinu-Pirvu C (2013) Periodontal chitosan-gels designed for improved local intra-pocket drug delivery. Farmacia 61:240–249
Qiaoa M, Luo Y, Zhang L, Ma Y, Stephenson TS, Zhu J (2010) Sustained release coating of tablets with ERS® RS/RL using a novel electrostatic dry powder coating process. Int J Pharm 399:37–43
Rachakonda VK, Terramsetty KM, Madihally SV, Robinson RL, Gasem KA (2008) Screening of chemical penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery using electrical resistance of skin. Pharm Res 25:2697–2704
Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ, Quinn EM (2009) Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients, 6th edn. Pharmaceutical Press and American Pharmaceutical Association, Washington, DC
Sanghvi R, Narazaki R, Machatha SG, Yalkowsky SH (2008) Solubility improvement of drugs using N-methyl pyrrolidone. AAPS PharmSciTech 9:366–376
Sangster J (1997) Octanol-water partition coefficients: fundamentals and physical chemistry. Wiley, New York
Schwach AK, Vivien CN, Gurny R (2000) Local delivery of antimicrobial agents for the treatment of periodontal diseases. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:83–99
Seymour RA, Heasman PA (1995) Tetracyclines in the management of periodontal diseases. A review. J Clin Periodontal 22:22–35
Siepmann J, Siepmann F (2008) Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. Int J Pharm 364:328–343
Solouk A, Mirzadeh H, Amanpour S (2014) Injectable scaffold as minimally invasive technique for cartilage tissue engineering: in vitro and in vivo preliminary study. Prog Biomat 3:143–151
Srichan T, Phaechamud T (2017) Designing solvent exchange-induced in situ forming gel from aqueous insoluble polymers as matrix base for periodontitis treatment. AAPS PharmSciTech 18:195–201
Stickley RG (2004) Solubilizing excipients in oral and injectable formulations. Pharm Res 21:201–230
Tan LP, Venkatraman SS, Sung PF, Wang XT (2004) Effect of plasticization on heparin release from biodegradable matrices. Int J Pharm 283:89–96
Tang Y, Singh J (2008) Controlled delivery of aspirin: effect of aspirin on polymer degradation and in vitro release from PLGA based phase sensitive systems. Int J Pharm 357:119–125
Trapani G, Franco M, Latrofa A, Pantaleo MR, Provenzano MR, Sanna E, Maciocco E, Liso G(1999)Physicochemical characterization and in vivo properties of zolpidem in solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol 4000 and 6000. Int J Pharm 184:121–130.
Velasco-De-Paola MVR, Santoro MIRM, Gai MN (1999) Dissolution kinetics evaluation of controlled-release tablets containing propranolol hydrochloride. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 25:535–541
Wang J, Li D, Li T, Ding J, Liu J, Li B, Chen X (2015) Gelatin tight-coated poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffold incorporating rhBMP-2 for bone tissue engineering. Materials 8:1009–1026
Xiong W, Gao X, Zhao Y, Xu H, Yang X (2011) The dual temperature/pH-sensitive multiphase behavior of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) microgels for potential application in in situ gelling system. Colloids Surf B Bointerfaces 84:103–110
Acknowledgements
This research work was supported by the Research and Development Institute, Silpakorn University (Grant no. SURDI 57/01/42). This research work was also facilitated by the Faculty of Pharmacy, Silpakorn University, Thailand. We also would like to thank Anthony Phonpituck for valuable comments and help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lwin, W.W., Puyathorn, N., Senarat, S. et al. Emerging role of polyethylene glycol on doxycycline hyclate-incorporated Eudragit RS in situ forming gel for periodontitis treatment. J. Pharm. Investig. 50, 81–94 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-019-00430-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-019-00430-6