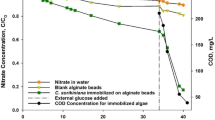
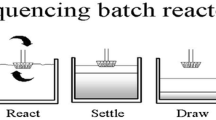
Abstract
Microalgae absorb various nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) in wastewater, providing bioproduct production and ensuring sustainability in wastewater treatment. The use of waste biomass becomes more effective with immobilized algae biomass usage. This study aims to investigate the removal of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) and phosphate (PO43−) in wastewater taken from the outlet of the primary settling unit of the domestic wastewater treatment plant using immobilized Chlorella Vulgaris pure algae culture. A batch reactor setup was used in the laboratory-scale study. The removal rates of NH4+-N and PO43− were evaluated with the effects of different environmental (luminous photoperiod:24-h (h), 16/8 h), chemical (pH: 7.5, 8.0, 8.5 and nitrogen:phosphorus (N:P): 21.4, 18.7, 16.7) and shape factors (bead diameter: 3.4, 5.3 mm) using wastewater samples taken from the presettlement outlet of a typical domestic wastewater treatment plant. pH 8.5 and 24-h luminous photoperiod conditions, the use of 5.3 mm diameter immobilized beads, and the addition of excess phosphate concentration to obtain a nutrient ratio of 16 N:P have increased the NH4+-N and PO43− removal rates and algal biomass growth rate. As a result, in the batch reactor using immobilized Chlorella vulgaris algae biomass, 83% NH4+-N and 95% PO43− removal rates were achieved in domestic wastewater in approximately 20 h.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Raouf N, Al-Homaidan AA, Ibraheem IBM (2012) Microalgae and wastewater treatment. Saudi J Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2012.04.005
Akhtar N, Iqbal J, Iqbal M (2004) Removal and recovery of nickel(II) from aqueous solution by loofa sponge-immobilized biomass of Chlorella sorokiniana: characterization studies. J Hazard Mater 108(1–2):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.01.002
Aravantinou AF, Theodorakopoulos MA, Manariotis ID (2013) Selection of microalgae for wastewater treatment and potential lipids production. Bioresour Technol 147:130–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.024
Banerjee S, Tiwade PB, Sambhav K, Banerjee C, Bhaumik SK (2019) Effect of alginate concentration in wastewater nutrient removal using alginate-immobilized microalgae beads: uptake kinetics and adsorption studies. Biochem Eng J 149:107241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107241
Barros Ó, Costa L, Costa F, Lago A, Rocha V, Vipotnik Z, Silva B, Tavares T (2019) Recovery of rare earth elements from wastewater towards a circular economy. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061005
Beal CM, Stillwell AS, King CW, Cohen SM, Berberoglu H, Bhattarai RP, Connelly RL, Webber ME, Hebner RE (2012) Energy return on investment for algal biofuel production coupled with wastewater treatment. Water Environ Res 84(9):692–710. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143012X13378023685718
Bhatnagar A, Sillanpaa M (2011) A review of emerging adsorbents for nitrate removal from water. Chem Eng J 168(2):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.103
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algal species, University of Texas
Bunce JT, Ndam E, Ofiteru ID, Moore A, Graham DW (2018) A review of phosphorus removal technologies and their applicability to small-scale domestic wastewater treatment systems. Front Environ Sci 6:8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2018.00008
Cassidy MB, Lee H, Trevors JT (1996) Environmental applications of immobilized microbial cells: a review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 16(2):79–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01570068
Cheremisinoff NP, Knovel F (2002) Handbook of water and wastewater treatment technologies. Butterworth-Heinemann, Elsevier Science, Boston
Clark T, Stephenson T, Pearce PA (1997) Phosphorus removal by chemical precipitation in a biological aerated filter. Water Res 31(10):2557–2563. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00091-2
Delgadillo-Mirquez L, Lopes F, Taidi B, Pareau D (2016) Nitrogen and phosphate removal from wastewater with a mixed microalgae and bacteria culture. Biotechnol Rep 11:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2016.04.003
El-Sheekh M, El-Dalatony MM, Thakur N, Zheng Y, Salama E-S (2022) Role of microalgae and cyanobacteria in wastewater treatment: genetic engineering and omics approaches. Int J Environ Sci Technol 19(3):2173–2194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03270-w
Eroglu E, Smith SM, Raston CL (2015) Application of various immobilization techniques for algal bioprocesses. In: Moheimani NR, McHenry MP, de Boer K, Bahri PA (eds) Biomass and Biofuels from microalgae: advances in engineering and biology. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 19–44
Ge H, Batstone DJ, Keller J (2013) Operating aerobic wastewater treatment at very short sludge ages enables treatment and energy recovery through anaerobic sludge digestion. Water Res 47(17):6546–6557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.08.017
Hoffman JP (1998) Wastewater treatment with suspended and nonsuspended algae. J Phycol 34:757–763. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1529-8817.1998.340757.x
Huang H, Wang Z, Xia F, Shang X, Liu Y, Zhang M, Dahlgren RA, Mei K (2017) Water quality trend and change-point analyses using integration of locally weighted polynomial regression and segmented regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(18):15827–15837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9188-x
Jayaseelan M, Usman M, Somanathan A, Palani S, Muniappan G, Jeyakumar RB (2021) Microalgal production of biofuels integrated with wastewater treatment. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13168797
Jelali N, Moez S, Dhifi W, Mnif W, Abdelly C, Gharsalli M (2012) Secondary metabolism responses in two Pisum sativum L. cultivars cultivated under Fe deficiency conditions. Afr J Biotechnol 11(82):14828–14836
Jensen VB, Darby JL, Seidel C, Gorman C (2012) Drinking water treatment for nitrate. Retrieved from Center for Watershed Sciences, University of California, Davis. https://groundwaternitrate.ucdavis.edu/files/139107.pdf
Kim T-H, Lee Y, Han S-H, Hwang S-J (2013) The effects of wavelength and wavelength mixing ratios on microalgae growth and nitrogen, phosphorus removal using Scenedesmus sp. for wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 130:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.134
Kube M, Jefferson B, Fan LH, Roddick F (2018) The impact of wastewater characteristics, algal species selection and immobilisation on simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Algal Res Biomass Biofuels Bioprod 31:478–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.01.009
Lebeau T, Robert J-M, Subba Rao D (2006) Biotechnology of immobilized micro algae: a culture technique for the future. In: Subba Rao DV (ed) Algal cultures, analogues of blooms and applications. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 801–837
Lee K, Lee CG (2002) Nitrogen removal from wastewaters by microalgae without consuming organic carbon sources. J Microbiol Biotechnol 12(6):979–985
Liu Y, Li L, Jia R (2011) The optimum resource ratio (N:P) for the growth of microcystis aeruginosa with abundant nutrients. Procedia Environ Sci 10:2134–2140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2011.09.334
Mallick N (2002) Biotechnological potential of immobilized algae for wastewater N, P and metal removal: a review. Biometals 15(4):377–390. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020238520948
Mao Y, Xiong R, Gao X, Jiang L, Peng Y, Xue Y (2021) Analysis of the status and improvement of microalgal phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater. Processes. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9091486
Matei A, Racoviteanu G (2021) Review of the technologies for nitrates removal from water intended for human consumption. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, vol 664, no 1, p 012024. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/664/1/012024
Mohammadi R, Tang W, Sillanpää M (2021) A systematic review and statistical analysis of nutrient recovery from municipal wastewater by electrodialysis. Desalination 498:114626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114626
Mohsenpour SF, Hennige S, Willoughby N, Adeloye A, Gutierrez T (2021) Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 752:142168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142168
Molazadeh M, Ahmadzadeh H, Pourianfar HR, Lyon S, Rampelotto PH (2019a) The use of microalgae for coupling wastewater treatment with CO2 biofixation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00042
Molazadeh M, Danesh S, Ahmadzadeh H, Pourianfar HR (2019b) Influence of CO2 concentration and N:P ratio on Chlorella vulgaris-assisted nutrient bioremediation, CO2 biofixation and biomass production in a lagoon treatment plant. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 96:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.01.005
Moreno-Garrido I (2008) Microalgae immobilization: current techniques and uses. Bioresour Technol 99(10):3949–3964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.05.040
Morse GK, Brett SW, Guy JA, Lester JN (1998) Review: phosphorus removal and recovery technologies. Sci Total Environ 212(1):69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00332-X
Murujew O, Whitton R, Kube M, Fan L, Roddick F, Jefferson B, Pidou M (2021) Recovery and reuse of alginate in an immobilized algae reactor. Environ Technol 42(10):1521–1530. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1673827
Padri M, Boontian N, Piasai C, Phorndon T (2020) Coupling wastewater treatment with microalgae biomass production: focusing on biomass generation and treatment efficiency. Eng J 24(6):11–29. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/623/1/012025
Paul E, Laval ML, Sperandio M (2001) Excess sludge production and costs due to phosphorus removal. Environ Technol 22(11):1363–1371. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332208618195
Phanwilai S, Noophan P, Li C-W, Choo K-H (2020) Effect of COD: N ratio on biological nitrogen removal using full-scale step-feed in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sustain Environ Res 30(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42834-020-00064-6
Quijano G, Arcila JS, Buitrón G (2017) Microalgal-bacterial aggregates: applications and perspectives for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Adv 35(6):772–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.07.003
Rahimi S, Modin O, Mijakovic I (2020) Technologies for biological removal and recovery of nitrogen from wastewater. Biotechnol Adv 43:107570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107570
Rasmussen LA, Iordachescu L, Tumlin S, Vollertsen J (2021) A complete mass balance for plastics in a wastewater treatment plant—Macroplastics contributes more than microplastics. Water Res 201:117307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117307
Rasoul-Amini S, Montazeri-Najafabady N, Shaker S, Safari A, Kazemi A, Mousavi P, Mobasher MA, Ghasemi Y (2014) Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater using microalgae free cells in bath culture system. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3(2):126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2013.09.003
Rezaei R, Akbulut A, Sanin SL (2019) Effect of algae acclimation to the wastewater medium on the growth kinetics and nutrient removal capacity. Environ Monit Assess 191(11):679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7856-7
Rezvani F, Sarrafzadeh M-H, Ebrahimi S, Oh H-M (2019) Nitrate removal from drinking water with a focus on biological methods: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(2):1124–1141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9185-0
Sharma S, Bhattacharya A (2017) Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl Water Sci 7(3):1043–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0455-7
Shelknanloymilan L, Atici T, Obal O (2012) Removal of nitrogen and phosphate by using Choleralla vulgaris on synthetic and organic materials waste water. Biol Divers Conserv 5(2):89–94
Siciliano A, Curcio GM, Limonti C (2020) Chemical denitrification with Mg0 particles in column systems. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072984
Valigore JM, Gostomski PA, Wareham DG, O’Sullivan AD (2012) Effects of hydraulic and solids retention times on productivity and settleability of microbial (microalgal-bacterial) biomass grown on primary treated wastewater as a biofuel feedstock. Water Res 46(9):2957–2964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.023
Van Loosdrecht MCM, Jetten MSM (1998) Microbiological conversions in nitrogen removal. Water Sci Technol 38(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00383-7
Wang J-H, Zhang T-Y, Dao G-H, Xu X-Q, Wang X-X, Hu HY (2017) Microalgae-based advanced municipal wastewater treatment for reuse in water bodies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(7):2659–2675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8184-x
Whitton R, Le Mével A, Pidou M, Ometto F, Villa R, Jefferson B (2016) Influence of microalgal N and P composition on wastewater nutrient remediation. Water Res 91:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.054
Yamaguchi K (1996) Recent advances in microalgal bioscience in Japan, with special reference to utilization of biomass and metabolites: a review. J Appl Phycol 8(6):487–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02186327
Zhang ED, Wang B, Wang QH, Zhang SB, Zhao BD (2008) Ammonia-nitrogen and orthophosphate removal by immobilized Scenedesmus sp isolated from municipal wastewater for potential use in tertiary treatment. Bioresour Technol 99(9):3787–3793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.07.011
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the personnel of the Eskisehir Technical University Faculty of Science, Biology Department, assistant Eda Tuna Öztürk, for assisting laboratory studies and Professor Erdem Ahmet Albek for his suggestions.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The laboratory setup was carried out by SG. The laboratory measurements were conducted by YÖ. The paper was written by SG.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The manuscript was not submitted to another journal simultaneously. The submitted work is original and has not been published elsewhere in any form or language. Results were presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Özgür, Y., Göncü, S. The effect of process parameters on use of immobilized algae culture for nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 6015–6026 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04590-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04590-1